Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogawa, Masuro*
JAEA-Technology 2019-010, 22 Pages, 2019/07
Transition phenomena from laminar to turbulent flow are roughly classified into three categories. Circular pipe flow of the third category is linearly stable against any small disturbance, despite that flow actually transitions and transitional flow exhibits intermittency. These are among major challenges that are yet to be resolved in fluid dynamics. Thus, author proposes hypothesis as follows; "Flow in a circular pipe transitions from laminar flow because of vortices released from separation bubble forming in vicinity of inlet of pipe, and transitional flow becomes intermittent because vortex-shedding is intermittent." Present hypothesis can easily explain why linear stability theory has not been able to predict transition in circular pipe flow, why circular pipe flow actually transitions, why transitional flow actually exhibits intermittency even due to small disturbance, and why numerical analysis has not been able to predict intermittency of transitional flow in circular pipe.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 238(1-4), p.154 - 159, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)It is well know that many substances have different structures in the crystalline state and they exhibit first-order structural phase transitions by a change in pressure. On the other hand, pressure-induced structural changes in the liquid and glassy states were supposed to be monotonous. The recent development of synchrotron radiation sources enables us to perform structural studies on liquids and glasses under high pressure and high temperature conditions. These studies revealed that the changes in the liquid and glassy states are not necessarily monotonous. We will present recent results on liquid phosphorus and silica glass.
 Si investigated by ac calorimetry
Si investigated by ac calorimetryTateiwa, Naoyuki; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Ikeda, Shugo; Yasuda, Takashi*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(7), p.1903 - 1906, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:88.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The pressure dependences of the antiferromagnetic and superconducting transition temperatures have been investigated by ac heat capacity measurement under high pressures for the heavy-fermion superconductor CePt Si without inversion symmetry in the tetragonal structure. The N
Si without inversion symmetry in the tetragonal structure. The N el temperature
el temperature  = 2.2 K decreases with increasing pressure and becomes zero at the critical pressure
= 2.2 K decreases with increasing pressure and becomes zero at the critical pressure 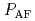
 0.6 GPa. On the other hand, the superconducting phase exists in a wider pressure region from ambient pressure to about 1.5 GPa. The pressure phase diagram of CePt
0.6 GPa. On the other hand, the superconducting phase exists in a wider pressure region from ambient pressure to about 1.5 GPa. The pressure phase diagram of CePt Si is thus very unique and has never been reported before for other heavy fermion superconductors.
Si is thus very unique and has never been reported before for other heavy fermion superconductors.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro*; Mizutani, Takeshi*; Yamakata, Masaaki*; Utsumi, Wataru; Shimomura, Osamu*
Science, 306(5697), p.848 - 851, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:157 Percentile:96.83(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Structural transformation between two liquid structures of phosphorus that occurred at about 1 GPa and 1000 C was investigated by in-situ X-ray radiography. When the low-pressure liquid was compressed, dark and round objects appeared in the radiograph. X-ray diffraction measurements confirmed that these objects were the high-pressure liquid. The drops grew and eventually filled the sample space. Decompressing caused the reverse process. The macroscopic phase separation supported the view that it was a first-order liquid-liquid phase transition. X-ray absorption measurements revealed that the change in density at the transition is about 40 % of the density of the high-pressure liquid.
C was investigated by in-situ X-ray radiography. When the low-pressure liquid was compressed, dark and round objects appeared in the radiograph. X-ray diffraction measurements confirmed that these objects were the high-pressure liquid. The drops grew and eventually filled the sample space. Decompressing caused the reverse process. The macroscopic phase separation supported the view that it was a first-order liquid-liquid phase transition. X-ray absorption measurements revealed that the change in density at the transition is about 40 % of the density of the high-pressure liquid.
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.479 - 485, 2004/07
In the structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessel, fracture toughness values are estimated by assuming that the radiation effect on fracture toughness is equivalent to that on Charpy properties. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the correlation between both properties especially on irradiation embrittlement. In this paper, we present the fracture toughness data obtained by applying the master curve approach that was adopted recently in the ASTM test method. Materials used in this study are five ASTM A533B class 1 steels and one weld metal. Neutron irradiation for Charpy-size specimens as well as standard Charpy-v specimens was carried out at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor. The shifts of the reference temperature on fracture toughness due to neutron irradiation are evaluated. Correlation between the fracture toughness reference temperature and Charpy transition temperature is established. Based on the correlation, the optimum test temperature for fracture toughness testing and the method to determine a lower bound fracture toughness curve are discussed.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(36), p.6085 - 6103, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:92.19(Physics, Condensed Matter)X-ray structural studies on several elemental liquids under high pressure are reviewed. Combination of synchrotron radiation sources and large volume presses enables us to carry out in-situ structural measurements on liquids at high pressures up to several GPa. The measurements have revealed that compressions of liquid alkali metals are almost uniform, whereas those of liquids that have covalent components in bonding are mostly anisotropic. In some elements, different types of volume dependence of the nearest neighbour distances are observed in different pressure ranges. This behaviour suggests that the liquid phase can be divided in regions. Although most of the observed structural changes are continuous, a discovery of an abrupt structural change in liquid phosphorus, which is completed over a pressure range of less than 0.05 GPa around 1GPa and 1050  C, supports existence of a first-order liquid-liquid phase transition.
C, supports existence of a first-order liquid-liquid phase transition.
Iguchi, Tadashi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2003/04
Authors investigated the cooling limit under flow instability, by conducting THYNC experiments using a 2 2 bundle test section of electrical rod heaters、whose heated lengths and diameters were 3.71m and 12.3mm. The experimental result indicated periodic rise and rapid drop of the rod temperature under flow oscillation, indicating periodic film boiling. When the heating power increased further, the rod temperature indicated continuous film boiling. The power at the onset of continuous film boiling (cooling limit) under flow oscillation was about 50%-80% of the cooling limit under steady flow condition in THYNC. The ratio of both cooling limits almost agreed with the Umekawa model prediction in cases of P
2 bundle test section of electrical rod heaters、whose heated lengths and diameters were 3.71m and 12.3mm. The experimental result indicated periodic rise and rapid drop of the rod temperature under flow oscillation, indicating periodic film boiling. When the heating power increased further, the rod temperature indicated continuous film boiling. The power at the onset of continuous film boiling (cooling limit) under flow oscillation was about 50%-80% of the cooling limit under steady flow condition in THYNC. The ratio of both cooling limits almost agreed with the Umekawa model prediction in cases of P 2MPa and G
2MPa and G 400kg/m2s. For high pressure and high mass flux conditions, the ratio almost agreed with the empirical model based on the heat balance during one cycle of flow oscillation. TRAC-BF1 code simulated periodic film boiling qualitatively, but the cooling limit under the flow oscillation was not predicted well probably due to inaccurate rewetting prediction.
400kg/m2s. For high pressure and high mass flux conditions, the ratio almost agreed with the empirical model based on the heat balance during one cycle of flow oscillation. TRAC-BF1 code simulated periodic film boiling qualitatively, but the cooling limit under the flow oscillation was not predicted well probably due to inaccurate rewetting prediction.
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
Proceedings of Asian Pacific Conference on Fracture and Strength '01(APCFS '01) and International Conference on Advanced Technology in Experimental Mechanics '01 (ATEM '01), p.140 - 145, 2001/00
In the structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessel, fracture toughness values are estimated by assuming that the radiation effect on fracture toughness is equivalent to that on Charpy properties. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the correlation between both properties especially on irradiation embrittlement. In this paper, we present the fracture toughness data obtained by applying the master curve approach that was adopted recently in the ASTM test method. Materials used in this study are five ASTM A533B class 1 steels and one weld metal. Neutron irradiation for Charpy-size specimens as well as standard Charpy-v specimens was carried out at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor. The shifts of the reference temperature on fracture toughness due to neutron irradiation are evaluated. Correlation between the fracture toughness reference temperature and Charpy transition temperature is established. Based on the correlation, the optimum test temperature for fracture toughness testing and the method to determine a lower bound fracture toughness curve are discussed.
Mori, Yuki*; Kato, Sayuri*; Mori, Hiroko*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Review of High Pressure Science and Technology, 7, p.353 - 355, 1998/03
The temperature dependence of phase transitions in GaSb, AlSb, GaAs, GaP, InAs, ZnSe, and CdTe are studied by X-ray diffraction measurements under pressure upto 30 GPa at temperatures of 90-300K. The phase transitions depend on paths in a pressure-temperature phase diagram. The structure of the recovered phase after decompression depends on the ionicity in bonding: amorphous for small ionicity, the stable zincblende structure for large ionicity, and microcrystalline or moderate ionicity. These results are discussed by using a configuration-coordinate model.
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
ISIJ International, 37(8), p.821 - 828, 1997/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.15(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Tabata, Yoneho*; ; ; Seguchi, Tadao
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 48(5), p.563 - 568, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Bains, R.S.*; Sugimoto, Jun
Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 14, p.267 - 275, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:76.17(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Onizawa, Kunio; Fukaya, Kiyoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Suzuki, Masahide; Kaihara, Shoichiro*; Nakamura, Terumi*
IWG-LMNPP-94/9, 0, 12 Pages, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Hoshiya, Taiji; Takamura, Saburo; ;
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 29(8), p.L1443 - L1445, 1990/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.59(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Takamura, Saburo; Hoshiya, Taiji; ;
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 28(8), p.L1395 - L1397, 1989/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.52(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
; ; ;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 27(8), p.722 - 724, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 H(SeO
H(SeO )
) and Rb
and Rb D(SeO
D(SeO )
) at low temperature
at low temperatureJournal of the Physical Society of Japan, 50(10), p.3185 - 3186, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:91.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 in low temperature region
in low temperature regionJournal of the Physical Society of Japan, 48(4), p.1206 - 1208, 1980/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sasuga, Tsuneo; Takehisa, Masaaki
J.Macromol.Sci.,Part B, 13(2), p.215 - 229, 1977/02
no abstracts in English
; ; Anzai, Shuichiro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 18(5), p.744 - 744, 1963/00
Times Cited Count:7no abstracts in English