Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S379 - S385, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:73.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The JAERI MeV accelerator has been designed extrapolating vacuum insulation design guidelines (the clump theory and Paschen law) to Mega Volt and long vacuum gap. Reduction of electric field concentration at triple junction by a large stress ring was effective to prevent flashover along insulator surface. By the vacuum insulation technology above, the accelerator sustained 1 MV for 8,500 s continuously. Strong enhancement of negative ion surface production has been attained by stopping vacuum leaks due to SF permeation through Viton O rings and a damage of port by backstream ions, followed by increase of the H
permeation through Viton O rings and a damage of port by backstream ions, followed by increase of the H ion current density without saturation. Operating the KAMABOKO source with high power arc discharge (
ion current density without saturation. Operating the KAMABOKO source with high power arc discharge ( 40 kW), H
40 kW), H ion beams of 146 A/m
ion beams of 146 A/m (total ion current: 0.2 A) have been obtained stably at the beam energy of 836 keV (pulse length:
(total ion current: 0.2 A) have been obtained stably at the beam energy of 836 keV (pulse length:  0.2 s). Bremsstrahlung generation in the accelerator is also estimated from EGS4 analysis, and then discussion on the breakdown possibility follows.
0.2 s). Bremsstrahlung generation in the accelerator is also estimated from EGS4 analysis, and then discussion on the breakdown possibility follows.
Sumita, Taishi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Matsuda, Sumio*; Oshima, Takeshi; Oi, Akihiko; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Proceedings of 3rd World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion (WCPEC-3) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2004/01
While high beginning-of-life efficiencies are important for space solar cells, the end-of-life performance is also critical factor. Two different prediction methods, "relative damage dose" and "displacement damage dose" methods, based on analysis of ground radiation test have been produced. We report proton radiation response for triple-junction space solar cells and analyze prediction methodology for the cell radiation response using the two methods. The results show that V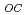 degradation behavior can be predicted by taking into account a cell structure and proton penetration depth. Accurate prediction of power degradation, however, is required to determine the current-limiting sub cell after proton irradiations.
degradation behavior can be predicted by taking into account a cell structure and proton penetration depth. Accurate prediction of power degradation, however, is required to determine the current-limiting sub cell after proton irradiations.