Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.957 - 962, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:96.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of blistering on deuterium retention in W was investigated using the newly established plasma generator with controllable incident energies ranging from 100 eV down to around 10 eV and incident flux of 1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5
/s. The retention in the irradiated samples was measured using a thermal desorption spectrometer (TDS) at a ramping rate of 5  C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850
C/s. The results indicate that only one peak appears in each spectrum, with the peak temperatures ranging from 500 until 850  C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
C, much higher than those from the trapping sites like vacancies, grain boundaries, dislocation loops, or impurities, implying probably a direct origin from the molecules existing inside blisters, voids/bubbles. Significant decrease in the retention at a certain incident fluence after blister appearance was observed and attributed to rupturing of the blisters, consistent with the limited size and increasing number of the blisters with increasing the incident fluence, as observed by means of SEM.
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 347(1-2), p.111 - 117, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:98.10(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Polycrystalline tungsten samples have been irradiated at room temperature by high flux (1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7
/s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7  98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering
98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering 
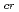 was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies
was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies  20 eV/D,
20 eV/D, 
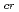 increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of
increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of 
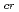 may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2
may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2 m.
m.