Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kudo, Tamotsu; Hidaka, Akihide*; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Proceedings of 2005 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting (CD-ROM), p.883 - 889, 2005/10
The VEGA program have been performed at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The program was comprised of series of experiments on radionuclides release from fuel under severe accident conditions and post-test evaluation with numerical calculations. Effects on the release of ambient pressure, fuel temperature, inert or steam environment and MOX-effect were studied in the program. These effects had been hardly investigated in previous studies due to difficulties in experiments with high temperature and pressure conditions. Release of cesium was mitigated at elevated pressure in comparison with atmospheric pressure. Cesium release was enhanced in the temperature region where fuel foaming occurred below the melting point of UO . Release of cesium and ruthenium under steam condition was greater than that under the inert helium condition. Released mass of plutonium above 2800 K was higher by nearly three orders of magnitude than that in lower temperature than 2800 K.
. Release of cesium and ruthenium under steam condition was greater than that under the inert helium condition. Released mass of plutonium above 2800 K was higher by nearly three orders of magnitude than that in lower temperature than 2800 K.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Ishikawa, Jun; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(5), p.451 - 461, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)The radionuclide release from MOX under severe accident conditions was investigated in VEGA program to contribute to the technical bases for safety evaluation including PSA for LWR using MOX. The MOX specimens irradiated at ATR Fugen were heated up to 3123K in helium at 0.1 and 1.0MPa. The release of volatile FP was slightly enhanced below 2200K compared with that of UO . The volatile FP release at elevated pressure was decreased as in the case with UO
. The volatile FP release at elevated pressure was decreased as in the case with UO . The total fractional release of Cs reached almost 100% while almost no release of low-volatile FP even after the fuel melting. The release rate of plutonium above 2800K increased rapidly although the amount was small. Since the existing models cannot predict this increase, an empirical model was prepared based on the data. There is no large difference in FP inventories between UO
. The total fractional release of Cs reached almost 100% while almost no release of low-volatile FP even after the fuel melting. The release rate of plutonium above 2800K increased rapidly although the amount was small. Since the existing models cannot predict this increase, an empirical model was prepared based on the data. There is no large difference in FP inventories between UO and MOX, and the fractional releases from MOX can be mostly predicted by the model for UO
and MOX, and the fractional releases from MOX can be mostly predicted by the model for UO . This suggests that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO
. This suggests that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO from a view point of risks.
from a view point of risks.
Hidaka, Akihide*; Kudo, Tamotsu; Kida, Mitsuko; Fuketa, Toyoshi
JAERI-Research 2005-001, 67 Pages, 2005/02
In the VEGA program to investigate radionuclides release from irradiated fuel during severe accidents, the analyses are being performed with VICTORIA2.0 code for comprehensive understanding of radionuclides release and transport phenomena. The VEGA-1 and -3 tests were analyzed in the present study. The correlation for Cs diffusion coefficient in fuel grain obtained from VEGA-1 was applied to the release analysis of VEGA-3. The calculated release of Cs agreed well with the measurement. The correlation was applied to subsequent Cs transport and deposition analyses. The calculation underpredicted the total mass of Cs deposited onto the test apparatuses because nucleation of aerosol and its growth were underestimated due to the consideration of aerosol nucleation originated only from released FP in VICTORIA2.0. A sensitivity analysis with aerosol seeds for heterogeneous nucleation showed a reasonable agreement with the measured Cs distribution. It turned out that additional aerosol seeds besides the released FP be considered when the VICTORIA2.0 code is applied to the VEGA test analyses.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Ishigami, Tsutomu; Ishikawa, Jun; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1192 - 1203, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)An experimental program VEGA is being performed at JAERI to understand mechanisms of radionuclides release from fuel during severe accidents and to improve source term predictability. The VEGA tests showed that the Cs release rate at 1.0MPa decreased by about 30% compared with that at 0.1MPa. To explain this pressure effect, a numerical release model on 2-stage diffusion that considers the lattice diffusion in grains followed by gaseous diffusion in open pores was newly developed and a simplified model 1/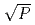 CORSOR-M was derived from the numerical model. The effect of pressure on source term was also estimated for a transient sequence at BWR with JAERI's THALES-2 code in which the simplified model was incorporated. Since the adequacy and applicability of 1/
CORSOR-M was derived from the numerical model. The effect of pressure on source term was also estimated for a transient sequence at BWR with JAERI's THALES-2 code in which the simplified model was incorporated. Since the adequacy and applicability of 1/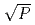 CORSOR-M model were confirmed for the pressures up to 16 MPa through comparison with the VEGA tests and mechanistic models, it is proposed that the model be used for source term analyses.
CORSOR-M model were confirmed for the pressures up to 16 MPa through comparison with the VEGA tests and mechanistic models, it is proposed that the model be used for source term analyses.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 91, p.499 - 500, 2004/12
The radionuclides release from MOX under severe accident conditions was investigated in the VEGA program to prepare the technical bases for safety evaluation including PSA for LWR using MOX. The MOX specimen irradiated at ATR Fugen was heated up to 3123K in He at 0.1MPa. The Cs release started at about 1000K and was enhanced below 2200K compared with that of UO . The possible reason is due to the formation of cracks connected to the high burn-up Pu spots. The total fractional releases were evaluated by alpha-ray, gamma-ray and ICP-AES and compared with the ORNL-Booth model. Although the model was prepared based on the tests with UO
. The possible reason is due to the formation of cracks connected to the high burn-up Pu spots. The total fractional releases were evaluated by alpha-ray, gamma-ray and ICP-AES and compared with the ORNL-Booth model. Although the model was prepared based on the tests with UO , the predictions are in reasonable agreement with the measurements. The VEGA test showed that the total releases from MOX are almost the same as those from UO
, the predictions are in reasonable agreement with the measurements. The VEGA test showed that the total releases from MOX are almost the same as those from UO under extremely severe accident conditions. This indicates that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO
under extremely severe accident conditions. This indicates that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO . The effect of difference between MOX and UO
. The effect of difference between MOX and UO on the consequences will be systematically investigated using the JAERI's source term code, THALES-2.
on the consequences will be systematically investigated using the JAERI's source term code, THALES-2.
Kanazawa, Toru*; Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Nakamura, Takehiko*; Fuketa, Toyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2004-050, 53 Pages, 2004/06
As a part of release evaluation in VEGA program, the mass balances of released and deposited FP onto the test apparatus are estimated from gamma ray measurement for acid solution leached from the apparatus, but short-life or radionuclides without emitting  rays and very small quantity of elements cannot be quantified. Therefore, a microanalysis by ICP-AES is planed for acid solution leached from apparatuses. Since Cs have strong
rays and very small quantity of elements cannot be quantified. Therefore, a microanalysis by ICP-AES is planed for acid solution leached from apparatuses. Since Cs have strong  ray spectrum, they have to be removed from solution in advance to avoid contamination of ICP system and to decrease exposure to
ray spectrum, they have to be removed from solution in advance to avoid contamination of ICP system and to decrease exposure to  ray. The method for Cs separation using inorganic ion exchanger, AMP was applied to the test solutions. The results showed that more than 99.9% of Cs could be removed from test solution, and once removed Sb by AMP was recovered by using a complexing agent such as citric acid. The ICP-AES analysis showed that amount of U, Sr and Zr were successfully quantified. The release and deposition will be quantified through ICP-AES analysis for acid solutions from which Cs is separated by AMP or other precipitation method.
ray. The method for Cs separation using inorganic ion exchanger, AMP was applied to the test solutions. The results showed that more than 99.9% of Cs could be removed from test solution, and once removed Sb by AMP was recovered by using a complexing agent such as citric acid. The ICP-AES analysis showed that amount of U, Sr and Zr were successfully quantified. The release and deposition will be quantified through ICP-AES analysis for acid solutions from which Cs is separated by AMP or other precipitation method.
Hidaka, Akihide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 45(8), p.493 - 496, 2003/08
In order to investigate the radionuclides release from irradiated fuel under severe accident conditions of LWR, VEGA experimental facility that realizes the highest temperature and pressure conditions was designed and constructed at JAERI. The effect of ambient pressure on radionuclides release was uniquely quantified by using this facility. A model that explains the observed pressure effect was also proposed based on the experimental results. For this effort, the atomic energy society of Japan gave us the preeminent monograph award in FY 2002. This paper describes my encounter with the research awarded this time, fascination of this research, hard-worked points, future plans and so on.
 -ray measurements of VEGA-5 test
-ray measurements of VEGA-5 testHidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Nakamura, Takehiko; Kanazawa, Toru; Kiuchi, Toshio; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-009, 30 Pages, 2003/03
The VEGA (Verification Experiments of radionuclides Gas/Aerosol release) program is being performed at JAERI to clarify mechanisms of radionuclides release from irradiated fuel during severe accidents and to improve source term predictability. The fifth VEGA-5 test was conducted in January 2002 to confirm the reproducibility of decrease in cesium release under elevated pressure that was observed in the VEGA-2 test and to investigate the release behavior of short-life radionuclides. The PWR fuel of 47GWd/tU after 8.2 years of cooling was re-irradiated at Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) for 8 hours before the heat-up test. After that, the two pellets of 10.9g without cladding were heated up to about 2,900K at 1.0MPa under the inert He condition. The experiment reconfirmed the decrease in cesium release under elevated pressure. The release data on short-life radionuclides such as Ru-103 and Ba-140 that has never been observed in the previous VEGA tests without re-irradiation was obtained using the gamma ray measurement.
Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2002-027, 147 Pages, 2002/11
The Fuel Safety Research Laboratory is in charge of research activity which covers almost research items related to fuel safety of water reactor in JAERI. Various types of experimental and analytical researches are being conducted by using some unique facilities such as the NSRR, the JMTR, the JRR-3 and the Reactor Fuel Examination Facility of JAERI. The research to confirm the safety of high burn-up fuel and MOX fuel under accident conditions is the most important item among them. The research conducted in the year 2001 produced many important data and information. They are, for example, the fuel behavior data under BWR power oscillation conditions in the NSRR, the data on failure-bearing capability of hydrided cladding under LOCA conditions and the FP release data at very high temperature in steam which simulate the reactor core condition during severe accidents.This report summarizes the outline of research activities and major outcomes of the research executed in 2001 in the Fuel Safety Research Laboratory.
 fuel in helium atmosphere under elevated pressure of 1.0MPa at temperature up to 2,773K
fuel in helium atmosphere under elevated pressure of 1.0MPa at temperature up to 2,773KHidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Nakamura, Takehiko; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(7), p.759 - 770, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Nakamura, Takehiko; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(3), p.273 - 275, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide; Nakamura, Takehiko; Kudo, Tamotsu; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Research 2001-055, 48 Pages, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Tamotsu; Hidaka, Akihide; Nakamura, Takehiko; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(10), p.910 - 911, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)This article describes the effects of system pressure on the cesium release obtained in the first two tests of radionuclides release from irradiated fuel, VEGA-1 and VEGA-2, which were conducted at the same maximum temperature of 2773K and different system pressures. The fractional releases of Cs in VEGA-2 test at 1.0MPa were smaller than those in VEGA-1 test at atmospheric pressure. In order to quantify the difference of the release rate in the two tests due to the pressure, the release rate coefficients of Cs were evaluated. The Cs release rate coefficient in VEGA-2 was smaller by a factor of about 2.8 than that in VEGA-1 at temperature above about 1900K.
Hayashida, Retsu*; Hidaka, Akihide; Nakamura, Takehiko; Kudo, Tamotsu; Otomo, Takashi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Tech 2001-029, 161 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2001-013, 140 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide; Nakamura, Takehiko; Kudo, Tamotsu; Hayashida, Retsu*; Nakamura, Jinichi; Otomo, Takashi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Conf 2000-015, p.193 - 200, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Takehiko; Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Hayashida, Retsu*; Otomo, Takashi; Nakamura, Jinichi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Conf 2000-015, p.201 - 209, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Kaminaga, Masanori
Nihon Kikai Gakkai-Shi, 103(981), p.42 - 43, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
Uetsuka, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2000-010, 113 Pages, 2000/07
no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide; Nakamura, Takehiko; Kudo, Tamotsu
Genshiryoku eye, 46(3), p.79 - 83, 2000/03
no abstracts in English