Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Suyama, Kenya; Tada, Kenichi; Ferrer, R. M.*; Hykes, J.*; Wemple, C. A.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 10 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new nuclear data library for the advanced lattice physics code CASMO5 has been prepared based on JENDL-5. In JENDL-5, many essential nuclides for conventional LWR analysis have also been modified based on state-of-the-art evaluations. The new JENDL-5-based CASMO5 library was prepared by replacing as much of the nuclear data of the current CASMO5 ENDF/B-VII.1-based library as possible with JENDL-5. This study verified and validated the new library. Verifications were performed based on the OECD/NEA burnup credit criticality safety benchmark phase III-C, and the calculated k and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1372 - 1385, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1386 - 1396, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:92.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)The burnup calculations for estimating the nuclide composition of the spent fuel are highly dependent on nuclear data. Many nuclides in the latest version of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 were modified from JENDL-4.0 and the modification affects the burnup calculations. This study confirmed the validity of JENDL-5 in the burnup calculations. The PIE data of Takahama-3 was used for the validation. The effect of modifications of the parameters, e.g., cross sections and fission yields, from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5 on the nuclide compositions was quantitatively investigated. The calculation results showed that JENDL-5 has a similar performance to JENDL-4.0. The calculation results also revealed that the modifications of the cross sections of actinide nuclides, fission yields, and thermal scattering low data of hydrogen in H O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Tsukiyama, Toshihisa*
Shahei Kaiseki No V&V Gaidorain Sakutei Ni Mukete, p.4 - 8, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Ohgama, Kazuya; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Katagiri, Hiroki; Hazama, Taira
Nuclear Technology, 208(10), p.1619 - 1633, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:74.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Hideo; Bentaib, A.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Ruyer, P.*; Mascari, F.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Adorni, M.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Topical Issues in Nuclear Installation Safety; Strengthening Safety of Evolutionary and Innovative Reactor Designs (TIC 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/10
Gupta, S.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Lebel, L. S.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Marchetto, C.*; Maruyama, Yu; Dehbi, A.*; Suckow, D.*; K rkel
rkel , T.*
, T.*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 16 Pages, 2022/03
Ohgama, Kazuya; Katagiri, Hiroki; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Hazama, Taira
Nuclear Technology, 207(12), p.1810 - 1820, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Okagaki, Yuria; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Ishigaki, Masahiro; Hirose, Yoshiyasu
Fluids (Internet), 6(2), p.80_1 - 80_17, 2021/02
Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1276 - 1286, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of materials of mineral-insulated (MI) cables on their electrical characteristics upon exposure to high-temperature conditions was examined via a transmission test, in the objective of achieving the stability of the potential distribution along the cable length. Occurrence of a voltage drop along the cable was confirmed for aluminum oxide (Al O
O ) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al
) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al O
O and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires (
and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires ( ) and the distance between them (
) and the distance between them ( ) were varied. Considering the variation of
) were varied. Considering the variation of  , the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio
, the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio 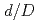 of 0.35, obtained by dividing
of 0.35, obtained by dividing  with that of the insulating material (
with that of the insulating material ( ). In case of varying
). In case of varying  , a minimum voltage drop was l/
, a minimum voltage drop was l/ of 0.5.
of 0.5.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Nakada, Kotaro*; Kudo, Yoshiro*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai-Shi, 123(1222), p.26 - 29, 2020/09
In the nuclear engineering, simulations are used in radiation, thermal hydraulic, chemical reaction, and structural fields, and the integrated fields thereof, to be applied to the design, construction and operation of nuclear facilities. This article describes brief history of discussion in the AESJ to the publication and introductory explanation of the procedures in the five major elements described in the "Guideline for Credibility Assessment of Nuclear Simulations (AESJ-SC-A008: 2015)". And also, a practical experience of the V&V activity according to the fundamental concept indicated in the Guideline is introduced.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Kudo, Yoshiro*; Nakada, Kotaro*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.1473 - 1484, 2019/08
Verification and validation (V&V) including uncertainty quantification on modeling and simulation activities has been very much focused on. Due to increase of requirement for standardization of the procedures on the V&V and prediction process to enhance the simulation credibility, "Guideline for Credibility Assessment of Nuclear Simulations (AESJ-SC-A008: 2015)" was published on July 2016 from the AESJ through ten-year discussion. The paper describes brief history of discussion in the AESJ to the publication and introductory explanation of the procedures in the five major elements and one scheme described in the Guideline. And also, a practical experience of the V&V activity according to the fundamental concept indicated in the Guideline is introduced.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Takegoshi, Atsushi; Katagiri, Hiroki*; Hazama, Taira
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
Chai, P.; Yamashita, Susumu; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
Proceedings of 9th Conference on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2019) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2019/03
In order to obtain a precise understanding of molten material behavior inside RPV and to improve the accuracy of the SA code, a new computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code with multi-phase, multi-physics models, which is called JUPITER, was developed. It optimized the algorithms of the multi-phase calculation. Besides, the chemical reactions are also modeled carefully in the code so that the melting process could be treated precisely. A series of verification and validation studies are conducted, which show good agreement with analytical solutions and previous experiments. The capabilities of the multi-physics models in JUPITER code provide us another useful tool to investigate the molten material behaviors in the relevant severe accident scenario.
Shen, X.*; Schlegel, J. P.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 333, p.87 - 98, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakada, Kotaro*; Kudo, Yoshiro*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 60(3), p.173 - 177, 2018/03
, 60(3), p.173 - 177, 2018/03
The Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) published "Guideline for Credibility Assessment of Nuclear Simulations 2015" in June, 2016 which specifies the concepts on methodology for the prediction with uncertainty quantification and the quality management based on the concept of verification and validation (V&V) of modeling and simulation. In this report, the outlines of activities in AESJ for publication of the guideline and the expectation for effective implementation of the guideline are described including that of the lectures with major respondents of the questionnaires.
Hotta, Akitoshi*; Morita, Akinobu*; Kajimoto, Mitsuhiro*; Maruyama, Yu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(3), p.139 - 152, 2017/09
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ikeda, Kazumi*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kan, Taro*; Maruyama, Shuhei; Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Oki, Shigeo
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/04
Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Keisan Kagaku Gijutsu Bukai Nyusu Reta (Internet), (27), p.9 - 15, 2017/03
In this report, the outline of the contents in the lecture course for "Guideline for Credibility Assessment of Nuclear Simulations 2015" published in June, 2016 from the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) and the result of the lectures held in Tokyo and Osaka are introduced with the results of the questionnaires from the audience.
Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Keisan Kagaku Gijutsu Bukai Nyusu Reta (Internet), (24), p.16 - 28, 2015/09
In order to enhance the simulation credibility, it is necessary to establish the procedure on verification and validation including the estimation of the modeling uncertainty. Lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi NPP Accident have indicated that it was important to recognize the credibility of the simulation. By putting forward to standardize the procedure on verification and validation including the estimation of the modeling uncertainty, it is expected to establish the basis of the simulation technology to realize the world highest level of nuclear safety and continuous improvement. The recent activity in the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) for the guideline establishment is introduced.