Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Imai, Yasutomo*; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Sakai, Takaaki*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113785_1 - 113785_16, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Establishing an evaluation method for the gas entrainment (GE) of argon cover gas due to surface vortices is required in terms of safety design of sodium-cooled fast reactors. To modify the evaluation model in an in-house evaluation tool for GE, StreamViewer, a modified evaluation model on the pressure distribution along the vortex center line (PVL model) was proposed to identify the vortex center lines by connecting continuous vortex center points from the suction port to the surface and evaluate gas core length based on the balance between the hydrostatic pressure and the pressure decrease distribution along the vortex center line. PVL model was applied the three-dimensional numerical analysis results for the experiments where a plate induced unsteady traveling vortices in the open channel flow. Consequently, the GE evaluation using StreamViewer with PVL model could reproduce the relation between the inlet flow velocity and the gas core length in the unsteady vortex flow experiments.
Song, K.*; Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Gas entrainment (GE) phenomena caused by a free surface vortex may cause the disturbance in core power of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). For this reason, the entrained gas flow rate by the GE should be evaluated accurately for the practical safety design of SFRs. In this study, for the purpose of examining the applicability of CFD for the accurate evaluation of GE phenomena, a CFD is applied to the simulation of the free surface vortex and accompanied GE phenomena in a cylindrical vessel with a suction pipe, and the CFD results and the experimental data of the GE are compared. As a result, the CFD and experiments show similar two-phase flow pattern inside the suction pipe, and the shape of the gas core at the free surface is also very similar. Therefore, it is confirmed that the CFD can predict the GE phenomena triggered by a free surface vortex properly and accurately within the acceptable error range.
Alzahrani, H.*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Sakai, Takaaki*; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2022/10
Development of evaluation method for cover gas entrainment (GE) by vortices generated at free surface in upper plenum of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) is required. An evaluation method by predicting vortices from flow velocity distribution obtained by 3D CFD analysis is developed, and Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method is examined to improve efficiency of CFD analysis is examined. In this study, mesh refinement with two conditions were examined. The first one is to use negative second invariant of velocity gradient tensor, Q, and the second one is to use pressure gradient condition with Q 0. As a result of applying AMR method to unsteady vortices system with a flat plate, the mesh near stagnation area around flat plate was refined in the latter condition compared with the former. Transient analyses were performed with refined mesh by AMR method, the result of mesh using the latter condition was closer to the result of all refined mesh with pressure distribution near flat plate.
0. As a result of applying AMR method to unsteady vortices system with a flat plate, the mesh near stagnation area around flat plate was refined in the latter condition compared with the former. Transient analyses were performed with refined mesh by AMR method, the result of mesh using the latter condition was closer to the result of all refined mesh with pressure distribution near flat plate.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Yamagata, Yoji*; Miyakoshi, Ken*; Mashii, Tatsuya*; Miura, Yoshiaki*; Takahashi, Kazunori*
JAEA-Research 2022-007, 28 Pages, 2022/09
To enhance energy separation in a counter-current Ranque-Hilsch vortex tube, a newly designed hollow helical fin was inserted into the hot tube of the vortex tube. In this study, the effect of the fin on the energy separation was investigated using three types of the vortex tube, and then computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation has been conducted to understand the experimental results and discuss the flow structure in the vortex tube with the hollow helical fin. As a result, it was found from the experimental data that the fin effectively enhanced energy separation, and that the tube length could be shorten. When the inlet air pressure was 0.5 MPa, the maximum temperature difference from the inlet to the cold exit was 62.2 C. The CFD code employing the Reynolds Stress Model (RSM) turbulence model was used to analyze the fluid dynamics in the vortex tube. As a result, it was confirmed that the temperature, velocity, and pressure distributions changed significantly at the stagnation point, and that the distributions in the tube with the fin were completely different from those without the fin. It was thought that a strong reversing helical vortex flow with small recirculating vortex structure formed between the fin end and the stagnation point on the cold exit side would enhance energy separation in the vortex tube with the hollow helical fin.
C. The CFD code employing the Reynolds Stress Model (RSM) turbulence model was used to analyze the fluid dynamics in the vortex tube. As a result, it was confirmed that the temperature, velocity, and pressure distributions changed significantly at the stagnation point, and that the distributions in the tube with the fin were completely different from those without the fin. It was thought that a strong reversing helical vortex flow with small recirculating vortex structure formed between the fin end and the stagnation point on the cold exit side would enhance energy separation in the vortex tube with the hollow helical fin.
Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Imai, Yasutomo*; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/08
Development of evaluation method for cover gas entrainment (GE) by vortices generated at free surface in upper plenum of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) is required. GE evaluation tool, named StreamViewer, based on method using numerical results of three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics analysis for loop-type SFRs has been developed. In this study, modification of evaluation method of StreamViewer to rationalize conservativeness in evaluation results was examined by identifying vortex center lines and calculating three-dimensional distribution of pressure decrease along vortex center lines. The applicability of modified method was checked using water experimental result in rectangular open channel where unsteady vortices are generated. As the result, it was indicated that evaluation results on gas core depth which were excessive in current method were improved in modified method, and it is confirmed that modified method may discriminate onset of GE with appropriate criteria.
Torikawa, Tomoaki*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Konsoryu, 36(1), p.63 - 69, 2022/03
On free surface of a sodium cooled fast reactor, gas entrainment can be caused by free surface vortices, which may result in disturbance in core power. It is important to develop an evaluation model to predict accurately entrained gas flow rate. In this study, entrained gas flow rate a simple gas entrainment experiment is conducted with focusing on effect of pressure difference between upper and lower tanks. Pressure difference between upper and lower tanks are controlled by changing gas pressure in lower tank. As a result, it is confirmed that the entrained gas flow rate increases with increasing pressure difference between upper and lower tanks. By visualization of swirling annular flow in suction pipe, it is also observed that pressure drop in suction pipe increases with increase in entrained gas flow rate, which implies that entrained gas flow rate can be predicted by evaluation model based on pressure drop in swirling annular flow region.
Taya, Hidetoshi*; Park, A.*; Cho, S.*; Gubler, P.; Hattori, Koichi*; Hong, J.*; Huang, X.-G.*; Lee, S. H.*; Monnai, Akihiko*; Onishi, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.021901_1 - 021901_6, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.84(Physics, Nuclear)Ogawa, Masuro*
JAEA-Technology 2019-010, 22 Pages, 2019/07
Transition phenomena from laminar to turbulent flow are roughly classified into three categories. Circular pipe flow of the third category is linearly stable against any small disturbance, despite that flow actually transitions and transitional flow exhibits intermittency. These are among major challenges that are yet to be resolved in fluid dynamics. Thus, author proposes hypothesis as follows; "Flow in a circular pipe transitions from laminar flow because of vortices released from separation bubble forming in vicinity of inlet of pipe, and transitional flow becomes intermittent because vortex-shedding is intermittent." Present hypothesis can easily explain why linear stability theory has not been able to predict transition in circular pipe flow, why circular pipe flow actually transitions, why transitional flow actually exhibits intermittency even due to small disturbance, and why numerical analysis has not been able to predict intermittency of transitional flow in circular pipe.
Ito, Kei; Ohno, Shuji; Koizumi, Yasuo*; Kawamura, Takumi*
Proceedings of 10th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2014/12
Ito, Kei; Ezure, Toshiki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kawamura, Takumi*; Nakamine, Yoshiaki*
Proceedings of 9th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-9) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/11
The authors have been studied the vortex cavitation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this paper, the authors present a modified evaluation method for vortex cavitation, in which a surface tension is modeled mechanistically. Namely, the cavity radius is calculated in consideration of radial pressure distribution, saturated vapor pressure and the pressure jump condition at an interface. As the basic validation of the developed surface tension model, numerical analyses of a simple experiment under various velocity conditions are performed. The evaluation results give qualitatively appropriate tendency, that is, the cavity radius becomes larger with the higher liquid velocity and/or lower reference pressure which cause the larger pressure drop at the vortex. In addition, the authors evaluate the influence of the kinematic viscosity which plays an important role in the vortex cavitation occurrences in the experiments.
Ito, Kei; Ezure, Toshiki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 80(818), p.FE0299_1 - FE0299_9, 2014/10
A vortex is considered as one of significant phenomena which may cause gas entrainment (GE) and/or vortex cavitation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, a new vortex model with realistic axial velocity distribution is proposed. As the verification, the new vortex model is applied to the evaluation of a simple vortex experiment, and shows good agreements with the experimental data in terms of the circumferential velocity distribution and the free surface shape. In addition, it is confirmed that the Burgers vortex model fails to calculate accurate velocity distribution with the assumption of uniform axial velocity. However, the calculation accuracy of the Burgers vortex model can be enhanced close to that of the new vortex model in consideration of the effective axial velocity which is calculated as the average value only in the vicinity of the vortex center.
Koizumi, Yasuo*; Ote, Naosuke*; Kamide, Hideki; Ohno, Shuji; Ito, Kei
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
Okayasu, Satoru; Nishio, Taichiro; Ono, Masao; Mashimo, Tsutomu; Tanaka, Yasutomo*; Iyo, Akira*
Physica C, 445-448, p.245 - 248, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.16(Physics, Applied)Vortex imagings of Tl-2223 thin film are achieved below Tc with a scanning SQUID microscope. Vortex arrangements are almost the same just below Tc, indicating the existence of strong pinning centers in the sample. The origin of the strong pinning centers comes from the morphological inhomogeneity on the surface.
Nishio, Taichiro; Okayasu, Satoru; Suzuki, Junichi; Kadowaki, Kazuo
Physica C, 412-414(Part1), p.379 - 384, 2004/10
We have studied the vortex states in a meoscopic superconductor with geometrical constraints such as disks, triangles, squares, etc. with dimensions between 30-50 m using a scanning SQUID microscope (SQM2000,Seiko Instruments Inc.). The sample was fabricated by electron lithography and Focused Ion Beam (FIB) techniques. Quantized vortices enter into a mesoscopic superconductor discretely as a function of magnetic field accompanied by the sequential step-wise jump of magnetization of the superconductor. Quantitative as well as qualitative analyses of spatial vortex arrangement as a function of the number of vortices will be shown in comparison with the recent theoretical predictions.
m using a scanning SQUID microscope (SQM2000,Seiko Instruments Inc.). The sample was fabricated by electron lithography and Focused Ion Beam (FIB) techniques. Quantized vortices enter into a mesoscopic superconductor discretely as a function of magnetic field accompanied by the sequential step-wise jump of magnetization of the superconductor. Quantitative as well as qualitative analyses of spatial vortex arrangement as a function of the number of vortices will be shown in comparison with the recent theoretical predictions.
Machida, Masahiko; Koyama, Tomio*
Physical Review Letters, 90(7), p.077003_1 - 077003_4, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:80.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 B
B C by scanning SQUID microscopy
C by scanning SQUID microscopyHata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Junichi; Kakeya, Itsuhiro*; Kadowaki, Kazuo*; Nakayama, Satoshi*; Nagata, Atsushi*; Odawara, Akikazu*; Chinone, Kazuo*
Physica C, 378-381(Part1), p.420 - 423, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Masaya; Anoda, Yoshinari
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 68(665), p.86 - 93, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Masaya; Anoda, Yoshinari
JSME International Journal, Series B, 44(4), p.688 - 694, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Ayumi
Physical Review B, 64(6), p.064504_1 - 064504_6, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study parametric level statistics of the discretized excitation spectra inside a moving vortex core in layered superconductors with impurities. The universal conductivity is evaluated numerically for the various values of rescaled vortex velocities  from the clean case to the dirty limit case. The random matrix theoretical prediction is verified numerically in the large
from the clean case to the dirty limit case. The random matrix theoretical prediction is verified numerically in the large  regime. On the contrary in the low velocity regime, we observe
regime. On the contrary in the low velocity regime, we observe 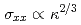 which is consistent with the theoretical result for the super-clean case, where the energy dissipation is due to the Landau-Zener transition which takes place at the points called ``avoided crossing''.
which is consistent with the theoretical result for the super-clean case, where the energy dissipation is due to the Landau-Zener transition which takes place at the points called ``avoided crossing''.
Kondo, Masaya; Anoda, Yoshinari
Emerging Technologies for Fluids, Structures and Fluid-Structure Interaction, 2001 (PVP-Vol.431), p.111 - 117, 2001/07
no abstracts in English