Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Motomu*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.177 - 191, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)With the release of the latest Japanese evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5, the prediction accuracy of JENDL-5 for neutronics parameters of the BEAVRS benchmark for the hot zero power condition was evaluated in this study. The criticality, control rod bank worth (CRW), isothermal temperature coefficient (ITC), and in-core detector signals were calculated and compared with the measured data for evaluation. For the criticality, the calculation-to-experimental (C/E) values varied between 1.0001 and 1.0045. Sensitivity analysis by replacing cross section data from the JENDL-4.0u1 with JENDL-5 revealed that 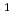 H,
H,  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  O significantly affected the criticality. The individual CRW agreed within 50 pcm, and total CRW also agreed within 100 pcm from the measured values. The ITC results calculated with a temperature deviation of 5.56 K case were negatively overestimated comparing with the measured values; whereas those of with 2.78 K were improved and agree with the measured values within a standard deviation. The axial detector signals indicated a maximum relative error of 4.46% and the root mean squared error (RMSE) of 2.13%. The differences between the previous version of JENDL-4.0u1 and JENDL-5 were also investigated.
O significantly affected the criticality. The individual CRW agreed within 50 pcm, and total CRW also agreed within 100 pcm from the measured values. The ITC results calculated with a temperature deviation of 5.56 K case were negatively overestimated comparing with the measured values; whereas those of with 2.78 K were improved and agree with the measured values within a standard deviation. The axial detector signals indicated a maximum relative error of 4.46% and the root mean squared error (RMSE) of 2.13%. The differences between the previous version of JENDL-4.0u1 and JENDL-5 were also investigated.
Mori, Takamasa; Okumura, Keisuke; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Nakagawa, Masayuki
Mathematics and Computation, Reactor Physics and Environmental Analysis in Nuclear Applications, 2, p.987 - 996, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Masayuki; Mori, Takamasa
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 30(7), p.692 - 701, 1993/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:92.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Miwa, Junichi*; Hino, Tetsushi*; Mitsuyasu, Takeshi*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
no journal, ,
We performed whole-core Monte Carlo calculations for core design verification of an innovative BWR concept, resource-renewable boiling water reactor (RBWR). The calculations include a coupled neutronics/thermal-hydraulics calculation with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP and an inhouse thermal-hydraulics code, and a burnup calculation with the MVP-BURN code. Such calculations for the RBWR is challenging because it requires a large memory size and a large amount of calculation time. The typical memory size required for the RBWR calculations was an order of 10 GBytes per CPU in parallel computing using a desktop PC cluster. The total calculation time for calculating the characteristics of the equilibrium core of RBWR with the whole-core Monte Carlo burnup calculation using the desktop PC cluster was about 20 days. We demonstrated that the design calculations for the RBWR were possible with such a desktop PC cluster.
Murakami, Yohei*; Mitsuyasu, Takeshi*; Miwa, Junichi*; Hino, Tetsushi*; Suyama, Kenya; Nagaya, Yasunobu
no journal, ,
A Monte Carlo code system has been developed to design an innovative water-cooled reactor, Resource-renewable Boiling Water Reactor (RBWR), which enables to burn transuranium elements (TRUs) efficiently. The system can perform multiphysics calculations of whole-core Monte Carlo neutronics, thermal-hydraulics and burnup; thus uncertainty induced by group-constant generation can be excluded. It has been confirmed that the pseudo material construct method can reduce memory requirement significantly and thus the reactor core design with whole core Monte Carlo calculations can be performed even with current computational resource.