Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Tomota, Yo*; Harjo, S.; Xu, P. G.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.*
Metals, 15(6), p.610_1 - 610_19, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobatesAso, Seiyu*; Matsuo, Hiroki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Morikawa, Daisuke*; Tsuda, Kenji*; Oyama, Kenji*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Noguchi, Yuji*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
We investigate the crystal structures, phase transitions, and phase stability of undoped and Ca-modified NaNbO through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)-
through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)- phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO
phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO
is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 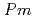
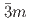 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 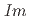
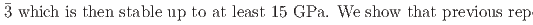 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
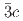 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 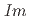
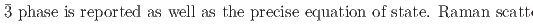 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
Hizukuri, Kyoko*; Fujibuchi, Toshio*; Han, D.*; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; Furuta, Takuya
Radiological Physics and Technology, 18(1), p.196 - 208, 2025/03
One of the radiation protection measures for medical personnel engaged in X-ray fluoroscopy is the use of radiation-protective plates and a simulation tool to evaluate effect of the plates is desired. Monte Carlo simulation has an advantage of being able to accurately calculate the interaction between radiations and various objects present in the X-ray room. However, Monte Carlo simulation has a disadvantage of being computationally time-consuming. Therefore, we developed a new simplified method to calculate the dose distribution in a short time with the presence of protective plates using pre-computed directional vectors (SCV). Using the Monte Carlo code PHITS, we simulated the ambient dose equivalent distribution the X-ray fluoroscopy room without the presence of protective plates. Assuming the dose at each voxel was all contributed from radiations in the direction indicated by the directional vector, the shielding effect of the protective plates for the dose at the voxel was determined whether the line toward backtrace of the directional vector has a intersect with the protective plate or not. With SCV, the computational time for the whole dose distribution with the presence of a protective plate was reduced approximately 1/6000 of the full PHITS simulation keeping the good accuracy to evaluate the effect of the plate.
Suzuki, Seiya; Katsube, Daiki*; Yano, Masahiro; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Terasawa, Tomoo; Ozawa, Takahiro*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Kim, Y.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yuhara, Junji*; et al.
Small Methods, 9(3), p.2400863_1 - 2400863_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Yamada, Masako*; Moussaoui, S. A.*; Makombe, E.*; Meyer, D.*; Berthon, L.*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 401, p.124372_1 - 124372_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:60.60(Chemistry, Physical) -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Physics, Applied) Pt
Pt Al
Al
Ota, Kyugo*; Watabe, Yuki*; Haga, Yoshinori; Iesari, F.*; Okajima, Toshihiko*; Matsumoto, Yuji*
Symmetry (Internet), 15(8), p.1488_1 - 1488_13, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.80(Multidisciplinary Sciences) X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.81(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Tsai, T.-H.; Sasaki, Shinji; Maeda, Koji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.715 - 723, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamazaki, Yasuhiro*; Shinomiya, Keisuke*; Okumura, Tadaharu*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakamura, Yuiga*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
Yoshida, Yukihiko
IL Nuovo Cimento, 46(2), p.33_1 - 33_8, 2023/03
Suzuki, Tomoya*; Otsubo, Ukyo*; Ogata, Takeshi*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Matsuoka, Mitsuaki*; Murayama, Norihiro*; Narita, Hirokazu*
Separation and Purification Technology, 308, p.122943_1 - 122943_7, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.39(Engineering, Chemical)HNO leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO
solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,
solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,  90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO
90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
 with [Pd(NO
with [Pd(NO )
) ]
] . The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
. The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
 synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation test
synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation testIm, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Lim, S.*; et al.
Construction and Building Materials, 365, p.130034_1 - 130034_18, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.68(Construction & Building Technology)Wang, Q.*; Hu, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, T.*; Ilavsky, J.*; Kuzmenko, I.*; Ma, B.*; Tachi, Yukio
International Journal of Coal Geology, 261, p.104093_1 - 104093_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.82(Energy & Fuels) and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
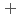 U
U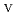
 Fe
Fe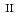
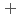 U
U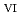 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
Kowatari, Munehiko*; Nagamoto, Keisuke*; Nakagami, Koichi*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Moritake, Takashi*; Kunugita, Naoki*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.39 - 49, 2022/03
Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Bae, S.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 104(9), p.4803 - 4818, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:83.08(Materials Science, Ceramics)Grazzi, F.*; Cialdai, C.*; Manetti, M.*; Massi, M.*; Morigi, M. P.*; Bettuzzi, M.*; Brancaccio, R.*; Albertin, F.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; et al.
Rendiconti Lincei. Scienze Fisiche e Naturali, 32(3), p.463 - 477, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)