Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion, 79(11), p.1277 - 1286, 2023/11
Hirato, Misaki*; Yokoya, Akinari*; Baba, Yuji*; Mori, Seiji*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Wada, Shinichi*; Izumi, Yudai*; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 25(21), p.14836 - 14847, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.29(Chemistry, Physical)Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Irisawa, Keita; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153170_1 - 153170_7, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
Hirao, Norie; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Izumi, Toshinori; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi
Bunseki Kagaku, 65(5), p.259 - 266, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.71(Chemistry, Analytical)After the Fukushima nuclear plant accident, radiocesium was strongly fixed to clay minerals in the soil. Some dry methods with heating are being developed to remove radiocesium from the soil. In this work, we propose a new dry method that combines heat treatment in vacuum and molten salts to reduce the processing temperature in dry methods. Vermiculite saturated with non-radioactive Cs was heated in vacuum, and Cs contents in the vermiculite were compared before and after heating using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Approximately 40% of cesium were removed by heating at 800 C for three minutes when only vermiculite was heated. Approximately 70% of cesium were removed by heating at 450
C for three minutes when only vermiculite was heated. Approximately 70% of cesium were removed by heating at 450 C for three minutes when vermiculite was heated with NaCl/CaCl
C for three minutes when vermiculite was heated with NaCl/CaCl mixed salts. Based on these results, this method is expected to reduce temperature and increase efficiency on dry methods for cesium removal from clay minerals.
mixed salts. Based on these results, this method is expected to reduce temperature and increase efficiency on dry methods for cesium removal from clay minerals.
Uddin, M. N.; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Nath, K. G.; Nagano, Masamitsu*
Applied Surface Science, 241(1-2), p.246 - 249, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:36.09(Chemistry, Physical)Recently, much attention has been given on the synthesis and characterization of graphite-like B-C-N hybrid. Since graphite-like B-C-N hybrid may have semiconducting property, this material is interesting for applications to electronic and luminescent devices. In order to synthesize this material, borazine ion plasma was implanted in graphite at room temperature (RT) and 600  C. An ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) chamber with base pressure
C. An ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) chamber with base pressure  10
10 Pa was used for the experiment. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study suggested that B atoms in the deposited films are in a wide variety of atomic environment such as BC3, BN3 and B-C-N hybrid. The ratios of these coordinations strongly depend on the temperature during the ion implantation. It was found that the B-C-N hybrid is predominantly synthesized by the implantation at 600
Pa was used for the experiment. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study suggested that B atoms in the deposited films are in a wide variety of atomic environment such as BC3, BN3 and B-C-N hybrid. The ratios of these coordinations strongly depend on the temperature during the ion implantation. It was found that the B-C-N hybrid is predominantly synthesized by the implantation at 600  C where the surface [B]/([B]+[C]+[N]) ratio ranges from 0.1 to 0.35. The results imply that it is possible to control the composition of B-C-N hybrid by changing the fluence of the ion plasma and the temperature of graphite during ion implantation.
C where the surface [B]/([B]+[C]+[N]) ratio ranges from 0.1 to 0.35. The results imply that it is possible to control the composition of B-C-N hybrid by changing the fluence of the ion plasma and the temperature of graphite during ion implantation.
 100
100 systems
systemsFujieda, Shinji*; Miura, Yoshinao*; Saito, Motofumi*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Microelectronics Reliability, 45(1), p.57 - 64, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.73(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To characterize the interface defects that are responsible for the negative-bias temperature instability (NBTI) of a thin plasma-nitrided SiON/Si system, we carried out inerface trap density measurements, electron-spin resonance spectroscopy and synchrotron radiation XPS. The NBTI was shown to occur mainly through the dehydrogenation of the interfacial Si dangling bonds (P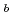 defects). Although we suggest that non- P
defects). Although we suggest that non- P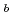 defects are also generated by the negative-bias temperature stress, nitrogen dangling bonds do not seem to be included. The plasma-nitridation process was confirmed to generate sub-oxides at the interface and thus increase the interface trap density. Furthermore, it was found that the nitridation induces another type of P
defects are also generated by the negative-bias temperature stress, nitrogen dangling bonds do not seem to be included. The plasma-nitridation process was confirmed to generate sub-oxides at the interface and thus increase the interface trap density. Furthermore, it was found that the nitridation induces another type of P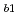 defect than that at pure-SiO
defect than that at pure-SiO /Si interfacec. Such an increase and structural change of the interfacial defects are likely the causes of the nitridation-enhanced NBTI.
/Si interfacec. Such an increase and structural change of the interfacial defects are likely the causes of the nitridation-enhanced NBTI.
Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Nath, K. G.
Applied Surface Science, 237(1-4), p.176 - 180, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.13(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.899 - 903, 2004/08
A CVD diamond has been the reference material of a torus widow for a rf heating system in a fusion reactor. Since the window is in the circumstance of tritium, helium and radio activated dust, it is important to elucidate the effect of ions on chemical structure of the diamond, existing states of tritium and tritium inventory. Polycrystalline CVD diamond disks( =10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar
=10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
 ) or helium ions (He
) or helium ions (He ) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D
) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D and 0.45 keV He
and 0.45 keV He , respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
, respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.899 - 903, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Nath, K. G.
Applied Surface Science, 234(1-4), p.246 - 250, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.89(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Nath, K. G.; Shimoyama, Iwao; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Applied Surface Science, 234(1-4), p.234 - 239, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.82(Chemistry, Physical)Here we report oxidization properties of Si nanostructures grown on graphite. Si 1s X-ray photoemission spectra using synchrotron radiation are used in order to understand the oxidization pathways. Several Si films, such as 0.4, 2, 5.5 & Aring; were grown on highly oriented pyrolitic graphite (HOPG). In the case of a 0.4 & Aring; Si on HOPG, where different types of Si nanostructures in the form of nanoclusters are present, oxygen reactivity is nearly zero. In contrast, the thick film (5.5 & Aring;), where a bulk-type phase is present, shows a higher degree of reactivity. The results are discussed on the basis of nanostructure geometry, number of constituting Si atoms and cluster size.
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Yagyu, Junichi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Okuno, Kenji*; Miya, Naoyuki; et al.
Physica Scripta, T108, p.57 - 62, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Nath, K. G.; Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 21(6), p.1843 - 1848, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.75(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Ion implantation method is applied to synthesize B-C-N hybrids and their electronic structures are characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. A boron nitride film is deposited on a graphite target by borazine plasma implantation. At the interface between the BN film and the graphite, variety of bonding combinations including B-N, B-C, and C-N are observed. This proved that B-C-N hybrids is formed by this method.
Nath, K. G.; Shimoyama, Iwao; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Journal of Applied Physics, 94(7), p.4583 - 4588, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.31(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 66-68, p.651 - 656, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 -Al
-Al O
O surface at high pH conditions
surface at high pH conditionsYoshida, Takahiro; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Nakayama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(9), p.672 - 678, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:92.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pb(II) adsorption on  -Al
-Al O
O at high pH condition (11
at high pH condition (11  pH
pH  13) was studied in NaNO
13) was studied in NaNO solutions. With increasing pH from 11, Pb(II) uptake by
solutions. With increasing pH from 11, Pb(II) uptake by  -Al
-Al O
O was decreased regardless to sodium concentration (0.1 and 1.0 M). XPS spectra showed binding energy of adsorbed Pb (4f) had no dependence on pH and adsorption density and was higher than that of orthorhombic yellow PbO and Pb(NO
was decreased regardless to sodium concentration (0.1 and 1.0 M). XPS spectra showed binding energy of adsorbed Pb (4f) had no dependence on pH and adsorption density and was higher than that of orthorhombic yellow PbO and Pb(NO )
) . Molecular orbital (MO) calculation revealed lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy of Pb(OH)
. Molecular orbital (MO) calculation revealed lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy of Pb(OH)
 was about 6 eV higher than that of Pb(OH)
was about 6 eV higher than that of Pb(OH) , and suggested chemical reactivity of Pb(OH)
, and suggested chemical reactivity of Pb(OH)
 with deprotonated surface hydroxyl ligand [
with deprotonated surface hydroxyl ligand [ AlO
AlO ] was expected to be less than that of Pb(OH)
] was expected to be less than that of Pb(OH) . Although Pb(II) is adsorbed on
. Although Pb(II) is adsorbed on  -Al
-Al O
O as inner-sphere surface complex, bonding between Pb(II) and
as inner-sphere surface complex, bonding between Pb(II) and  -Al
-Al O
O shows less covalent nature.
shows less covalent nature.
 -FeSi
-FeSi fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition method
fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition methodSaito, Takeru; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Hojo, Kiichi; Haraguchi, Masaharu*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Tanaka, Tomoaki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.321 - 325, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Goto, Yoshitaka*; Yagyu, Junichi; Masaki, Kei; Kizu, Kaname; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kodama, Kozo; Arai, Takashi; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Miya, Naoyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316, p.370 - 376, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:92.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Erosion and re-deposition were studied for graphite tiles from W-shaped divertor region of JT-60U in Jun. 1997 - Oct. 1998 periods in which more than 3000 D-D discharges were made with all-carbon wall with boronizations and inner-private flux pumping. On the outer divertor targets, erosion was dominant: maximum erosion depth of around 20 micrometers was measured, while on the inner targets, re-deposition was dominant: columnar structure layers and laminar/columnar-layered structures of maximum thickness around 60 micrometers were found. Through XPS analysis, compositions of the re-deposition layers at a around mid point on the inner target were 94 - 95 at% C, 3 - 4 at% B, and less than 0.6 at% O, Fe, Cr, and Ni. Boron is mainly bound to Carbon. No continuous deposition layers on the dome top/outer wing, while deposition layers were found on the inner wing. Observed in/out asymmetry is attributable to in/out asymmetry of plasma particle conditions in the divertor region.
 -edges
-edgesBaba, Yuji
Low Temperature Physics, 29(3), p.228 - 242, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:52.06(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English