Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray beam measurements
-ray beam measurementsOmer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Zen, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 240, p.113467_1 - 113467_8, 2026/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Kozawa, Tatsuya*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Wu, H.-C.*; Sato, Taku*; Yano, Shinichiro*
Physical Review B, 112(18), p.184115_1 - 184115_8, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)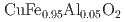
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchihara, Takeru*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Ishii, Yuta*; Nakao, Hironori*; Takehana, Kanji*; Imanaka, Yasutaka*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ding, H.*; Ito, Keita*; Endo, Yasushi*; Takanashi, Koki; Seki, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 57(38), p.385002_1 - 385002_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.37(Physics, Applied) -FeNi films with island structures on LaAlO
-FeNi films with island structures on LaAlO (110) substrates by nitrogen insertion and topotactic extraction
(110) substrates by nitrogen insertion and topotactic extractionNishio, Takahiro*; Ito, Keita*; Kura, Hiroaki*; Takanashi, Koki; Yanagihara, Hideto*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 976, p.172992_1 - 172992_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.95(Chemistry, Physical)Matsuno, Takashi*; Fujita, Taiki*; Matsuda, Tomoko*; Shibayama, Yuki; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Watanabe, Ikumu*
Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 322, p.118174_1 - 118174_16, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:68.60(Engineering, Industrial)The impact of high stress triaxiality on work hardening in transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel has been widely acknowledged, particularly through measurements of the austenite fraction. Understanding this TRIP behavior is crucial for predicting material fracture in press-forming processes. However, the actual flow stresses under high-stress-triaxiality conditions remain largely undetermined. To address this gap, we developed a new tensile testing method using tiny notched round bars to investigate stress-triaxiality-induced work hardening in TRIP steels. The specimens were analyzed using two-dimensional micrometry to allow finite element analyses to identify the flow stress. Additionally, we conducted in situ tensile tests in which their crystal lattice stresses were monitored using synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD) to realize mechanism analyses of the unexpected work-hardening behavior identified by the developed tensile testing method. Our combined approach revealed a mutual, unstable increase in the flow stress and stress triaxiality in the TRIP-aided bainitic ferrite steel, which reduced the hardening exponent coefficients and thus induced a higher stress triaxiality. In contrast, the TRIP-aided martensitic steel exhibited a weakening behavior, characterized by a significant decrease in the hardening exponent coefficients in the case of the sharpest notch. XRD analyses showed that microstructural heterogeneity led to an extraordinarily high hydrostatic stress in the austenite phase, accounting for these contrasting behaviors. This finding challenges the established consensus on TRIP steels and suggests the need for a revised framework for their application in press-forming, taking into account stress-triaxiality conditions.
Yamazaki, Takumi*; Seki, Takeshi*; Kubota, Takahide*; Takanashi, Koki
Applied Physics Express, 16(8), p.083003_1 - 083003_4, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.28(Physics, Applied)Ogawa, Fumio*; Nakayama, Yuta*; Hiyoshi, Noritake*; Hashidate, Ryuta; Wakai, Takashi; Ito, Takamoto*
Transactions of the Indian National Academy of Engineering (Internet), 7(2), p.549 - 564, 2022/06
The strain energy-based life evaluation method of Mod. 9Cr-1Mo steel under non-proportional multiaxial creep-fatigue loading is proposed. Inelastic strain energy densities were calculated as the areas inside the hysteresis loops. The effect of mean-stress has been experimentally considered and the relationship between inelastic strain energy densities and creep-fatigue lives was investigated. It was found from the investigation of hysteresis loops, the decrease in maximum stress leads to prolonged failure life, while stress relaxation during strain holding causes strength reduction. The correction method of inelastic strain energy density was proposed considering the effect of maximum stress in hysteresis loop and minimum stress during strain holding, and strain energy densities for uniaxial and non-proportional multiaxial loading were obtained. Based on these results, the mechanisms governing creep-fatigue lives under non-proportional multiaxial loading have been discussed.
Li, F.; Mihara, Takeshi; Udagawa, Yutaka; Amaya, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.633 - 645, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 129, 2015/03
no abstracts in English
Shinozaki, Takashi; Mihara, Takeshi; Udagawa, Yutaka; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Amaya, Masaki
JAEA-Research 2014-025, 34 Pages, 2014/12
EDC test is a test method on the mechanical property of fuel cladding tube, and it focuses on the stress condition generated by PCMI under a RIA. We conducted EDC tests which simulate the mechanical conditions during a RIA by using the unirradiated cladding tubes which simulate hydride rim. Circumferential residual strains observed in post-test specimens tended to decrease with increasing the hydrogen concentration in the test cladding tubes and the thickness of the hydride rim. We also prepared RAG tube and performed EDC tests on it. It was observed that circumferential total strains at failure tended to decrease with increasing pre-crack depth on the outer surface of RAG tube specimen. We conducted biaxial stress tests by applying longitudinal tensile load onto RAG tube specimens. It was observed that circumferential total strains at failure under biaxial stress conditions tended to decrease compared to the results under uniaxial tensile condition.
Ito, Kei; Ezure, Toshiki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 80(818), p.FE0299_1 - FE0299_9, 2014/10
A vortex is considered as one of significant phenomena which may cause gas entrainment (GE) and/or vortex cavitation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, a new vortex model with realistic axial velocity distribution is proposed. As the verification, the new vortex model is applied to the evaluation of a simple vortex experiment, and shows good agreements with the experimental data in terms of the circumferential velocity distribution and the free surface shape. In addition, it is confirmed that the Burgers vortex model fails to calculate accurate velocity distribution with the assumption of uniform axial velocity. However, the calculation accuracy of the Burgers vortex model can be enhanced close to that of the new vortex model in consideration of the effective axial velocity which is calculated as the average value only in the vicinity of the vortex center.
Takeyama, Akinori; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ito, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 232(1-4), p.333 - 337, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Cu precipitates were formed on Si(100) by 200 keV Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing at 773 K. The shape of the Cu precipitates evolved from a large rectangle to a small elongated pyramid with increasing annealing time. This shape evolution seemed to result from the epitaxial formation of Cu precipitates to minimize the interfacial energy between the precipitate and the Cu implanted substrate. The average density of Cu precipitates monotonously increased and the average diameter of Cu precipitates decreased with increasing annealing time up to 1 h. These indicate that the morphology, size and average density of Cu precipitates can be controlled by varying annealing time, and that Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing were effective in producing a substrate dispersed with catalytic particles for oxide nanorods growth.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Ishihara, Masahiro; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*
Zairyo, 54(2), p.201 - 206, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(1), p.40 - 49, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this research, critical power correlation for tight-lattice rod bundles is newly proposed using 7-rod axially uniform-heated data, 7-rod and 37-rod axially double-humped-heated data at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). For low mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region (
s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m
s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
Nagase, Fumihisa; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(1), p.58 - 65, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:94.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tube burst tests have been performed with artificially hydrided Zircaloy-4 specimens at room temperature and at 620 K. Pressurization rate was increased to a maximum of 3.4 GPa/s in order to simulate rapid PCMI that occurs in high burnup fuel rods during a pulse-irradiation in the NSRR. Hydrogen content in the specimens ranged from 150 to 1050 ppm. Hydrides were accumulated in the cladding periphery and formed "hydride rim" as observed in high burnup PWR fuel claddings. The hydrided cladding tubes failed with an axial crack at the room temperature tests. Brittle fracture appeared in the hydride rim, and failure morphology was similar to that observed in the NSRR experiments. The hydrides rim obviously reduced burst pressure and residual hoop strain at the tests. The residual hoop strain was very small even at 620 K when thickness of the hydride rim exceeded 18% of cladding thickness. The present result accordingly indicates an important role of the hydrides layer in high burnup fuel rod failure under RIA conditions.
Takeda, Masayasu; Mibu, Ko*; Shinjo, Teruya*; Endo, Yasuo*; Suzuki, Junichi
Physical Review B, 70(10), p.104408_1 - 104408_9, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:39.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Detailed magnetic structure of spin-density waves (SDWs) in epitaxial Cr(001)/Sn multilayer was investigated by neutron scattering combined with M ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
Shelley, A.; Kugo, Teruhiko; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Research 2004-002, 47 Pages, 2004/03
Neutronic study has been done for a PWR-type reduced-moderation water reactor with seed-blanket fuel assemblies to achieve a high conversion ratio, a negative void coefficient and a high burnup by using a MOX fuel. The results of the precise assembly burnup calculations show that the recommended numbers of seed and blanket layers are 15(S15) and 5(B5), respectively. By the optimization of axial configuration, the S15B5 assembly with the seed of 1000 2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400
2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400 2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500
2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500 2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO
2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO +ThO
+ThO ) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
 Zn
ZnKoizumi, Mitsuo; Seki, Akiyuki*; Toh, Yosuke; Osa, Akihiko; Utsuno, Yutaka; Kimura, Atsushi; Oshima, Masumi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Katakura, Junichi; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 730(1-2), p.46 - 58, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:72.82(Physics, Nuclear)Coulomb excitation experiment was carried out with a  Zn beam bombarding a
Zn beam bombarding a  Pb target. Two
Pb target. Two 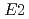 matrix elements and the quadrupole moment of the 2
matrix elements and the quadrupole moment of the 2
 state were newly derived with the least-squares search code GOSIA. The potential energy surface (PES) was calculated with the Nilsson-Strutinsky model, showing two shallow minima: the first minimum does not contain the
state were newly derived with the least-squares search code GOSIA. The potential energy surface (PES) was calculated with the Nilsson-Strutinsky model, showing two shallow minima: the first minimum does not contain the 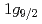 orbit below the Fermi surface, while the second minimum does. The ground state band and the intruder band seem to be constructed on the first and the second minimum, respectively. As for the ground state band, the asymmetric rotor model and the IBM in O(6) limit reproduced the experimental values rather well. The shallow PES may suggest unstability of the shape. The ground state band structure may be explained assuming a soft triaxial deformation.
orbit below the Fermi surface, while the second minimum does. The ground state band and the intruder band seem to be constructed on the first and the second minimum, respectively. As for the ground state band, the asymmetric rotor model and the IBM in O(6) limit reproduced the experimental values rather well. The shallow PES may suggest unstability of the shape. The ground state band structure may be explained assuming a soft triaxial deformation.
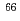 Zn
ZnKoizumi, Mitsuo; Seki, Akiyuki*; Toh, Yosuke; Oshima, Masumi; Osa, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Matsuda, Makoto; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 18(1), p.87 - 92, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:67.57(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English