Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wilson, J.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Tachi, Yukio; Kawama, Daisuke*
Applied Clay Science, 275, p.107862_1 - 107862_15, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0High-Level Radioactive Waste (HLW) repositories include iron or steel-based containers/overpack and bentonite buffers. Over the last 25 years or so, research efforts have attempted to elucidate the nature of iron-bentonite interactions, especially the potential for the deleterious alteration of the swelling clay component (smectite), to iron-rich layer silicates, some of which lack the capacity for intracrystalline swelling. This could result in a reduction or loss in swelling pressure in the bentonite buffer which is designed to protect waste containers from shear forces and also acts to restrict water and solute transport, as part of an engineered barrier system. Most data on iron-bentonite interactions come from experimental and geochemical modelling studies, as natural analogue data are lacking. The data suggests that there is the potential for the development of an iron-rich bentonite alteration zone with smectite (generally present as the aluminous montmorillonite type) undergoing alteration to iron-rich solids, including layer silicates and steel corrosion products such as green rust or magnetite. The evidence available is complex, arguably incomplete, with many potential complex couplings. Many uncertainties remain despite efforts taken over the last 25 years, but plausible scenarios for iron-bentonite interactions have been identified and possible implications for buffer properties have been suggested.
Ono, Hirokazu; Takayama, Yusuke*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 41, p.100636_1 - 100636_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Sugita, Yutaka; Kim, J.-S.*; Jeon, M.-K.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 41, p.100628_1 - 100628_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)This study investigates the impact of primary variables selection on the modeling of non-isothermal two-phase flow, by using the numerical work on the full-scale Engineered Barrier System (EBS) experiment conducted at Horonobe URL as part of the DECOVALEX-2023 project. A validated numerical model is employed to simulate the coupled thermo-hydrological behavior of heterogeneous porous media within the EBS. Two different primary variable schemes are compared in discretizing the governing equations, revealing significant difference in results.
Ito, Shinji*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Shintaro*; Takayama, Yusuke
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 80(8), p.24-00030_1 - 24-00030_18, 2024/08
In the design consideration of a geological disposal facility for radioactive waste, it is essential to perform a mechanical evaluation that takes into account phenomena that may occur from construction and operation to post-closure. With this background, we have developed the long-term mechanical analysis system MACBECE. In this research, we have built an analysis system that can consistently evaluate the mechanical behavior considering the thermal and hydraulic evolution after the closure of the repository by incorporating the constitutive model for unsaturated soils and coupling with the thermal-hydraulic analysis. As a validation, a mechanical analysis was conducted for the in-situ experiment for full-scale engineered barrier system performance experiment at Horonobe URL. Despite some discrepancies due to constraints in two-dimensional analysis, the extended functionality of the analysis code was confirmed to effectively repro-duce the measured data.
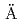 sp
sp HRL
HRLSawada, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Kazuhiko*; Watahiki, Takanori*; Imai, Hisashi*
SKB P-17-06, 154 Pages, 2023/08
Takubo, Yusaku*; Takayama, Yusuke; Idiart, A.*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*
Proceedings of 2022 International High Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2022) (Internet), p.906 - 915, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-017, 58 Pages, 2022/03
Sorption behavior of radionuclides (RNs) in buffer materials (bentonites), rocks and cementitious materials is one of the key processes in a safe geological disposal of radioactive waste because RNs migration in these materials is expected to be retarded by the sorption process. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the sorption process and develop a database compiling reliable data and mechanistic/predictive models so that reliable parameters can be set under a variety of geochemical conditions relevant to a performance assessment (PA). For this purpose, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed the database of sorption parameters in bentonites, rocks and cementitious materials. This sorption database (SDB) was firstly developed as an important basis for the H12 PA of a high-level radioactive waste disposal, and have been provided through the Web. JAEA has continued to improve and update the SDB in the view of potential future needs of data focusing on assuring the desired quality level and testing the usefulness of the databases for possible applications to the PA-related parameter setting. This report focuses on updating of the sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as a basis of integrated approach for the PA-related distribution coefficient (Kd) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. This report also includes an overview of the database structure and contents. Kd data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated from literature collected with wider ranges. As a result, 8,503 Kd data from 70 references related to the above-mentioned systems were added and the total number of Kd values in JAEA-SDB reached 79,072. The QA/classified Kd data reached about 75.4% for all Kd data in JAEA-SDB. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to give a basis for the next-step PA-related Kd setting.
Endo, Takashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Terashima, Motoki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(1), p.9 - 22, 2021/03
Evaluation method of colloid diffusion and filtration in compacted bentonites was developed using dendrimers. Diffusion and filtration behavior of PAMAM dendrimers with the size of 5.7 7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m
7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m and saturated with 0.005
and saturated with 0.005 0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
Sugita, Yutaka; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Hoshino, Emiko*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-017, 39 Pages, 2021/01
In Japan, high-level radioactive waste (HLW) will be buried in a purpose built repository in deep underground. In the vertical disposal concept of HLW, nuclear waste canisters will be emplaced in excavated vertical disposal holes, surrounded by bentonite/sand mixture. And the galleries will be backfilled with bentonite/excavated rock mixture, which will be isolated with a concrete plug. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has performed swelling test, permeability test, thermal property measurement, uniaxial compression test, water potential measurement and infiltration tests to identify coupled thermal-hydraulic-mechanical-chemical behavior that will operate in the backfill material using excavated rock in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL). The obtained data will be used to support an ongoing full scale, in-situ experiment being conducted in the Horonobe URL.
Savage, D.*; Wilson, J.*; Benbow, S.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Oda, Chie; Walker, C.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 195, p.105741_1 - 105741_11, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:11.75(Chemistry, Physical)Safety functions for the clay buffer in a repository for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) are fulfilled if the presence of montmorillonite with high swelling capacity and low permeability is maintained in the long-term. The transformation of montmorillonite to the non-swelling mineral likely illite is addressed in most safety assessments by using simple semi-empirical kinetic models, but this approach contrasts with more complex reactive-transport simulations. In the present study, reactive-transport simulations are compared with simple semi-empirical kinetic models. Results suggest that reactive-transport simulations err on the side of conservatism, but may produce unrealistic estimates of illitization. This comparison demonstrates that reactive-transport models may be carefully applied to simulate the long-term evolution of near field environment for HLW disposal.
Savage, D.*; Wilson, J.*; Benbow, S.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Oda, Chie; Walker, C.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 179, p.105146_1 - 105146_10, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:52.80(Chemistry, Physical)Natural systems evidence for the effects of temperature and the activity of aqueous silica upon montmorillonite stability was evaluated. Thermodynamic modeling using three different TDBs shows that stability fields for montmorillonite exist from 0 to 140 C, but at low values of silica activity, a stability field for illite replaces that for montmorillonite. Pore fluid chemical and mineralogical data for sediments from ODP sites from offshore Japan show a trend from montmorillonite + amorphous silica stability at temperatures up to 60
C, but at low values of silica activity, a stability field for illite replaces that for montmorillonite. Pore fluid chemical and mineralogical data for sediments from ODP sites from offshore Japan show a trend from montmorillonite + amorphous silica stability at temperatures up to 60 C to that for illite + quartz at higher temperatures. However, even over very long timescales (
C to that for illite + quartz at higher temperatures. However, even over very long timescales (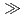 1 Ma), smectite does not transform to illite under thermodynamically-favourable conditions at temperatures less than 80
1 Ma), smectite does not transform to illite under thermodynamically-favourable conditions at temperatures less than 80 C.
C.
Jo, Mayumi*; Ono, Makoto*; Nakayama, Masashi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Ishii, Tomoko*
Geological Society Special Publications, 482, 16 Pages, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.09(Geology) sp
sp Laboratory, Sweden
Laboratory, SwedenSasamoto, Hiroshi; Isogai, Takeshi*; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Sato, Hisao*; Svensson, D.*
Clay Minerals, 52(1), p.127 - 141, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:8.71(Chemistry, Physical)Compacted bentonite has been considered as a candidate of engineering barrier material in many countries for the safe disposal of high-level radioactive waste. SKB set up an in situ experiment (named ABM project) to compare the stability of different bentonites under the conditions exposed to an iron source and elevated temperature (up to 130 C as maximum) at the
C as maximum) at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory, Sweden. Results for the Japanese bentonite (Kunigel V1) are summarized in the present paper. Mineralogical investigation using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) suggested that no indication of smectite transformation or newly formed clay phases were observed. However, a distinct change of exchangeable cations of smectite was indicated (i.e., from Na type to Fe type) in the bentonite at the vicinity of the steel heater. Physical investigation by measurements of hydraulic conductivity and swelling property suggested that no significant change occur in the bentonite even at the vicinity of the steel heater. Such results might be considered due to the limited portion affected by the iron-bentonite interactions and partially occurred ion exchange reactions. Chemical investigation based on the measurements of methylane blue (MB), cation exchange capacity (CEC) and exchangeable cations showed that the lateral distribution for these parameters were basically constant without the significant gradient.
Hard Rock Laboratory, Sweden. Results for the Japanese bentonite (Kunigel V1) are summarized in the present paper. Mineralogical investigation using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) suggested that no indication of smectite transformation or newly formed clay phases were observed. However, a distinct change of exchangeable cations of smectite was indicated (i.e., from Na type to Fe type) in the bentonite at the vicinity of the steel heater. Physical investigation by measurements of hydraulic conductivity and swelling property suggested that no significant change occur in the bentonite even at the vicinity of the steel heater. Such results might be considered due to the limited portion affected by the iron-bentonite interactions and partially occurred ion exchange reactions. Chemical investigation based on the measurements of methylane blue (MB), cation exchange capacity (CEC) and exchangeable cations showed that the lateral distribution for these parameters were basically constant without the significant gradient.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Okubo, Takahiro*
CMS Workshop Lectures, Vol.21, p.251 - 257, 2016/06
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. The ISD model gives consistent consideration to porewater chemistry, sorption and diffusion processes in compacted bentonite. The diffusion component based on the electric double layer theory and the homogeneous pore model in the ISD model accounts consistently for cation De overestimation and anion exclusion in narrow pores. The current ISD model can quantitatively account for diffusion of monovalent cations and anions, however, the model predictions disagree with diffusion data for multivalent cation and complex species. To improve the applicability of the model, it is necessary to consider the atomic level interactions between solute, solvent or clay mineral, and try that we apply the current ISD model to heterogeneous pore structure. In this study we try the application of the current ISD model to multiple pore structure. As results of numerical analysis of these models, the salinity dependence of effective diffusivity for the multi-pore model is comparatively smaller than that for the homogeneous pore model and the current diffusion model is improved.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Hoshino, Seiichi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.279 - 287, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:21.55(Chemistry, Physical)Alteration of bentonite-cement interfaces and accompanying changes in diffusivity of tritiated water was experimentally investigated using intact hardened cement specimens. The alteration by carbonate solution was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 70% of the initial value after 180-day period. Another alteration under silicate system contacting hardened cement and compacted bentonite was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 71% of the initial value after 600-day period. The changes in the diffusivity were much less than those observed for mixed specimens of granulated hardened cement and bentonite where the diffusivity decreased down to 20% of the initial value over 180 days. The results were extrapolated to 15 years under simple assumptions and showed good agreement with those observed in the cement-argillite interface at Tournemire URL. Such an explanation enhances our confidence in our assessment of alteration of cement-bentonite systems and can be a base for using our data and models in long term assessment of radioactive waste disposal.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sakamoto, Yoshifumi; Akai, Masanobu; Takazawa, Mayumi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 32(1-7), p.298 - 310, 2007/00
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:72.77(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Dissolution rate of montmorillonite, diffusivity of hydroxide ion and permeability coefficient in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures were experimentally determined and formulated. A coupled mass-transport/chemical-reaction code was developed to predict variation in permeability of engineered bentonite barrier with alkaline fluid by using the formulae.
Wilson, J.*; Cressey, G.*; Cressey, B.*; Cuadros, J.*; Ragnarsdottir, K. V.*; Savage, D.*; Shibata, Masahiro
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(2), p.323 - 336, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:85.70(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This work investigates montmorillonite stability in the presence of metal iron, magnetite under hydrothermal conditions. Two series of experiments were conducted. In the first, mixtures of Na-montmorillonite, native Fe, (magnetite, calcite,) and NaCl solutions were reacted at 250 C for about 100 days. In the second, mixtures of Na-montmorillonite, native Fe and FeCl
C for about 100 days. In the second, mixtures of Na-montmorillonite, native Fe and FeCl solutions were reacted at 80
solutions were reacted at 80 250
250 C for about 90 days. In the first series, the starting montmorillonite was transformed to Fe(II)-rich smectite only when the Fe metal was predominantly added. The reaction product was oxidised to Fe(III)-rich form on exposure to air. The expansion of this material on ethylene glycol solvation was much reduced compared to the starting montmorillonite. TEM imaging shows that partial loss of tetrahedral sheets, resulting in adjacent layers becoming H-bonded with a 7 angstrom repeat. Solute activities corresponded to the approximate stability field for Fe(II)-saponite. In the second series, significant smectite alteration was only observed at 250
C for about 90 days. In the first series, the starting montmorillonite was transformed to Fe(II)-rich smectite only when the Fe metal was predominantly added. The reaction product was oxidised to Fe(III)-rich form on exposure to air. The expansion of this material on ethylene glycol solvation was much reduced compared to the starting montmorillonite. TEM imaging shows that partial loss of tetrahedral sheets, resulting in adjacent layers becoming H-bonded with a 7 angstrom repeat. Solute activities corresponded to the approximate stability field for Fe(II)-saponite. In the second series, significant smectite alteration was only observed at 250 C and the product contained a small proportion of a 7
C and the product contained a small proportion of a 7 repeat structure, observable by XRD. In these experiments, solute activities coincide with berthierine.
repeat structure, observable by XRD. In these experiments, solute activities coincide with berthierine.
Wilson, J.*; Savage, D.*; Cuadros, J.*; Shibata, Masahiro; Ragnarsdottir, K. V.*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(2), p.306 - 322, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:58.40(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In some geological repository designs, steel canister and bentonite backfill are placed in contact. Some previous studies indicate that the montmorillonite component of the backfill could react with steel corrosion products to produce non-swelling Fe-rich phyllosilicates (e.g. chamosite, berthierine) or Fe-rich smectite. If montmorillonite were altered to non-swelling minerals, the expected swelling capacity of the bentonite backfill could be reduced. This paper discuss Fe-rich phyllosilicate mineral stability at the canister-backfill interface using thermodynamic modelling. Estimates of thermodynamic properties were made for Fe-rich clay minerals in order to construct approximate phase-relations for end-member/simplified mineral compositions in activity space. The diagrams (for the system Al O
O -FeO-Fe
-FeO-Fe O
O -MgO-Na
-MgO-Na O-SiO
O-SiO -H
-H O) suggest that if pore waters are supersaturated with magnetite, Fe(II)-rich saponite is the most likely alteration product (if fo
O) suggest that if pore waters are supersaturated with magnetite, Fe(II)-rich saponite is the most likely alteration product (if fo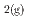 values are significantly lower than magnetite-hematite equilibrium). Therefore, the alteration of montmorillonite may not be detrimental to HLW repositories that include Fe, as long as the swelling behaviour of the Fe-rich smectite produced is maintained. If fo
values are significantly lower than magnetite-hematite equilibrium). Therefore, the alteration of montmorillonite may not be detrimental to HLW repositories that include Fe, as long as the swelling behaviour of the Fe-rich smectite produced is maintained. If fo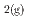 exceeds magnetite-hematite equilibrium, and solutions are saturated with magnetite, berthierine is likely to be more stable than smectite minerals. The alteration of montmorillonite to berthierine could be detrimental to the performance of the repositories.
exceeds magnetite-hematite equilibrium, and solutions are saturated with magnetite, berthierine is likely to be more stable than smectite minerals. The alteration of montmorillonite to berthierine could be detrimental to the performance of the repositories.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Yoshifumi; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Akai, Masanobu; Tanaka, Tadao; Sato, Tsutomu*; Iida, Yoshihisa
Applied Clay Science, 27(1-2), p.53 - 65, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:87 Percentile:89.73(Chemistry, Physical)Alkaline environments induced by cement in radioactive waste repositories are likely to alter montmorillonite, the main constituent of bentonite buffer materials. Over long time periods, the alteration may cause the physical and/or chemical properties of the buffer to deteriorate. For the purpose of acquiring numerical data to quantify the effect of alteration on permeability of bentonite buffer, dissolution rates of montmorillonite and diffusivity of hydroxide ions in compacted sand-bentonite mixture specimens have been measured under highly alkaline, simulated groundwater conditions. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite was given by the linear dependence on time under the employed experimental conditions of pH 13 to 14 and temperatures of 90 to 170 C. The diffusivity of hydroxide ions was obtained in through-diffusion experiments combined with a pore diffusion model. The experiments were performed under relatively low temperatures of 10 to 50
C. The diffusivity of hydroxide ions was obtained in through-diffusion experiments combined with a pore diffusion model. The experiments were performed under relatively low temperatures of 10 to 50 C to minimize the effect of alteration of bentonite. The effective diffusivity was on the order of 10
C to minimize the effect of alteration of bentonite. The effective diffusivity was on the order of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s.
/s.
Ochs, M.*; Lothenbach, B.*; Shibata, Masahiro; Yui, Mikazu
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 29(1), p.129 - 136, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:49.66(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Compacted bentonite is foreseen as the buffer material in the engineered barrier system of the geological disposal system. To derive  d values and diffusion coefficients of radionuclides for performance assessment, it is critical to be able to describe the chemistry of the pore solution and to understand how it is influenced by different factors. This paper presents a sensitivity analysis on the influence of important parameters on porewater chemistry in compacted bentonite. The principal parameters varied were the fractions of calcite, gypsum, and NaCl dissolving from bentonite, and pCO
d values and diffusion coefficients of radionuclides for performance assessment, it is critical to be able to describe the chemistry of the pore solution and to understand how it is influenced by different factors. This paper presents a sensitivity analysis on the influence of important parameters on porewater chemistry in compacted bentonite. The principal parameters varied were the fractions of calcite, gypsum, and NaCl dissolving from bentonite, and pCO . Model calculations treated ion exchange reactions of smectite and protonation/deprotonation at the edge of smectite using the diffuse layer model. Some calculations consider electric double layer effects in the porespace. The model results show that two powerful pH buffer systems are operative in compacted bentonite: Amphoteric edge SOH sites and the carbonate buffer system. If pCO
. Model calculations treated ion exchange reactions of smectite and protonation/deprotonation at the edge of smectite using the diffuse layer model. Some calculations consider electric double layer effects in the porespace. The model results show that two powerful pH buffer systems are operative in compacted bentonite: Amphoteric edge SOH sites and the carbonate buffer system. If pCO is imposed externally, the resulting porewater pH is mainly controlled by the carbonate buffer. If bentonite is treated as a closed system, the buffering action of the SOH sites becomes more important. In both cases, the dissolution of calcite and gypsum from the bentonite is important. If the development of an electric double layer in the bentonite pores is considered, entire porespace may be occupied with diffuse layers, leaving no space for free porewater, at higher dry densities (1200 kg/m
is imposed externally, the resulting porewater pH is mainly controlled by the carbonate buffer. If bentonite is treated as a closed system, the buffering action of the SOH sites becomes more important. In both cases, the dissolution of calcite and gypsum from the bentonite is important. If the development of an electric double layer in the bentonite pores is considered, entire porespace may be occupied with diffuse layers, leaving no space for free porewater, at higher dry densities (1200 kg/m ).
).