Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Saito, Takumi*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 258, p.107476_1 - 107476_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:48.99(Chemistry, Physical)Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*
Nuclear Technology, 210(8), p.1427 - 1443, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The retention of hydrogen (H ) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H
) bubbles generated by water radiolysis was quantitatively studied in a high-viscous suspension of carbonate slurry consisting of a mixture of suspended solid (SS) of magnesium and calcium precipitates under strongly alkaline conditions, like the radioactive wastes discharged from the coagulation sedimentation (co-precipitation) process at the multinuclide removal equipment in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The H retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H
retention properties were evaluated in two types of carbonate slurry with different hydrophilicity: the hydrophilic "current type" and the hydrophobic "return type". Then, their properties were compared with those in another suspension of clay suspension of bentonite. From the comparison between the amounts of chemical adsorption and H O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H
O in the slurry, it was confirmed that H O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H
O molecules must be shared among the SS particles, and this sharing formed the structural viscosity in the slurry, different from that in the clay suspension where electrostatic bonding between the fine clay minerals forms the viscosity. The retention of H bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H
bubbles in (by) the slurry was evaluated from the difference in the amount of H observed with and without stirring the slurry after
observed with and without stirring the slurry after  Co
Co  -irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H
-irradiation. From the comparison of the retention properties of the hydrophilic slurry, the hydrophobic slurry, the clay suspension, and treated water, it was suggested that H bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.
bubbles were retained not only by the structural viscosity but also by the steric hindrance in the hydrophilic slurry.

McGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kimuro, Shingo; Ishidera, Takamitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1586 - 1594, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.10(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kato, Tomoaki; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Technology 2023-018, 53 Pages, 2023/11
In the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, radioactive carbonate slurry waste was generated using the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS) pretreatment and temporarily stored in a high integrity container (HIC). In 2015, overflow of supernatant from HIC estimate as bubble retention in the carbonate slurry was discovered, increasing the need for a safety assessment of the carbonate slurry stored the HIC (HIC slurry). In this study, a carbonate slurry (simulated slurry) was prepared according to the Mg/Ca mass ratio in the ALPS inlet water of the HIC slurry which overflew the HIC. The effects of reaction time during the pretreatment process, suspended solids concentration (SS concentration), and settling time on the particle composition, morphology and rheological properties of the slurry were investigated. Evaluating the effect of reaction time and concentration process on chemical properties in slurry production, the effect of the reaction time was not confirmed in the simulated slurry that had undergone the concentration process, and slurry prepared at SS concentration of 150 g/L was composed of formless particles have a particle diameter of 0.4  m or less. We also investigate the effect of SS concentration on sedimentability, decrease in SS concentration by dilution with processing solution contributed to an increase in the initial slurry settling velocity. Furthermore, two different flow characteristics were observed depending on the settling time, suggesting that the slurry at the initial settling time has non-Bingham flow properties, whereas it changes to Bingham flow properties as the settling time becomes longer. In addition, yield stress was increased with settling time, and this yield stress was found to be exponentially proportional to the density of the slurry. These results provide knowledge to estimate the current state of HIC slurry and are expected to contribute to the safety assessment.
m or less. We also investigate the effect of SS concentration on sedimentability, decrease in SS concentration by dilution with processing solution contributed to an increase in the initial slurry settling velocity. Furthermore, two different flow characteristics were observed depending on the settling time, suggesting that the slurry at the initial settling time has non-Bingham flow properties, whereas it changes to Bingham flow properties as the settling time becomes longer. In addition, yield stress was increased with settling time, and this yield stress was found to be exponentially proportional to the density of the slurry. These results provide knowledge to estimate the current state of HIC slurry and are expected to contribute to the safety assessment.
Saito, Tatsuo; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Mochizuki, Akihito
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.107035_1 - 107035_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The seasonal variation of dissolved U (DU) in Lake Biwa was reproduced by the following model and parameter research. The introduced models are the water-DU mass balance, and the ion exchange between UO
 and H
and H on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
Horita, Takuma; Yamagishi, Isao; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kashiwaya, Ryunosuke*
JAEA-Technology 2021-012, 34 Pages, 2021/07
Waste mainly consisting of carbonate precipitates (carbonate slurry) from the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS) and the improved ALPS at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Holdings, Inc. have been storing in the High Integrity Container (HIC). The supernatant solution of carbonate slurry contained in some of HICs were overflowed in April of 2015. The all of level of liquid in the HICs were investigated; however, almost of the HICs were under the level of overflow. The mechanism of overflow suggested to be depending on the difference of the properties of the carbonate slurry such as the retention/release characteristics of the bubbles. Therefore, in order to clarify the mechanism of leakage, the repeatability experiment was carried out by using simulated carbonate slurry. The simulated carbonate slurry was perpetrated by using the same cross-flow filter system of the actual ALPS. Moreover, the preparative conditions for the simulated carbonate slurry were the same as Mg/Ca concentration ratio in inlet water of the ALPS (raw water) and the ALPS operating conditions. The chemical characteristics of simulated carbonate slurries were revealed by ICP-AES, pH meter, etc. The density of the settled slurry layer tended to increase depending on the calcium concentration in the raw water. The bubble injection test was conducted in order to investigate the bubble retention/release behavior in the simulated carbonate slurry layer. The simulated carbonate slurry with high settling density, which was generated by high calcium concentration solution was revealed to retain the injected bubbles. Since the ratio of concentration calcium and magnesium during the carbonate slurry generation is assumed to affect the retention of bubbles in the slurry layer, the information on the composition of raw water is one of important factor for overflow of HICs.
Hemmi, Ko; Walker, A.*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Radiochimica Acta, 109(7), p.539 - 546, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.59(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Plutonium(IV) sorption onto quartz in carbonate solutions was systematically investigated under anaerobic conditions to analyze the sorption behaviors of Pu(IV) with a non-electrostatic model (NEM). Pu(IV) sorption data was obtained from batch sorption experiments as a function of pH and carbonate concentration. The Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz showed similar tendencies to Th(IV), which is considered to be chemically analogous as a tetravalent actinoid. The distribution coefficient,  d, of Pu(IV) onto quartz showed inverse proportionality to the square of the total carbonate concentration under the investigated pH conditions of 8 to 11. The modeling study, however, revealed a Th(IV) sorption model, which is
d, of Pu(IV) onto quartz showed inverse proportionality to the square of the total carbonate concentration under the investigated pH conditions of 8 to 11. The modeling study, however, revealed a Th(IV) sorption model, which is  SOTh(OH)
SOTh(OH)
 and
and  SOThOH(CO
SOThOH(CO )
)
 , could not be applied to simulate the Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz. It was inferred that the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged ligands limited the formation of
, could not be applied to simulate the Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz. It was inferred that the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged ligands limited the formation of  SOM(OH)
SOM(OH)
 and
and  SOMOH(CO
SOMOH(CO )
)
 for Pu(IV) with smaller ionic radii than Th(IV). The Pu(IV) sorption model was developed as
for Pu(IV) with smaller ionic radii than Th(IV). The Pu(IV) sorption model was developed as  SOPu(OH)
SOPu(OH) and
and  SOPu(OH)
SOPu(OH)
 . In addition, data of Pu(IV) sorption onto muscovite was obtained in order to be compared with data for quartz.
. In addition, data of Pu(IV) sorption onto muscovite was obtained in order to be compared with data for quartz.
Miyajima, Yusuke*; Saito, Ayaka*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Hirata, Takafumi*
Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 45(1), p.189 - 205, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.22(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Uncertainty for elemental and isotopic analyses of calcite by LA-ICP-MS is largely controlled by the homogeneity of the reference materials (RMs) used for normalization and validation. In order to produce calcite RMs with homogeneous elemental and isotopic compositions, we incorporated elements including U, Pb, and rare earth elements into calcite through heat- and pressure-induced crystallization from amorphous calcium carbonate that was precipitated from element-doped reagent solution. X-ray absorption spectra showed that U was present as U(VI) in the synthesized calcite, probably with a different local structure from that of aqueous uranyl ions. The uptake rate of U by our calcite was higher in comparison to synthetic calcite of previous studies. Variations of element mass fractions in the calcite were better than 12% 2RSD, mostly within 7%. The  Pb/
Pb/ Pb ratio in the calcite showed
Pb ratio in the calcite showed  1% variations, while the
1% variations, while the  U/
U/ Pb ratio showed 3-24% variations depending on element mass fractions. Using the synthetic calcite as primary RMs, we could date a natural calcite RM, WC-1, with analytical uncertainty as low as
Pb ratio showed 3-24% variations depending on element mass fractions. Using the synthetic calcite as primary RMs, we could date a natural calcite RM, WC-1, with analytical uncertainty as low as  3%. The method presented can be useful to produce calcite with controlled and homogeneous element mass fractions, and is a promising alternative to natural calcite RMs for U-Pb geochronology.
3%. The method presented can be useful to produce calcite with controlled and homogeneous element mass fractions, and is a promising alternative to natural calcite RMs for U-Pb geochronology.
 (am) in the aqueous K
(am) in the aqueous K - HCO
- HCO
 - CO
- CO
 - OH
- OH - H
- H O system
O systemRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K.*
Radiochimica Acta, 105(8), p.637 - 647, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.60(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility of HfO (am) was determined as a function of KHCO
(am) was determined as a function of KHCO concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg
concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg to 0.1 mol.kg
to 0.1 mol.kg . The solubility of HfO
. The solubility of HfO (am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO
(am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO
concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-)
concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-) (CO
(CO )
)
 and Hf(CO
and Hf(CO )
)
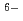 . The log
. The log K
K values for the reactions [Hf
values for the reactions [Hf + 2 CO
+ 2 CO
 +2 OH
+2 OH
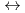 Hf(OH)
Hf(OH) (CO
(CO )
)
 ] and [Hf
] and [Hf + 5 CO
+ 5 CO

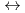 Hf(CO
Hf(CO )
)
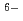 ], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53
], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53  0.46 and 41.53
0.46 and 41.53  0.46, respectively.
0.46, respectively.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationMotooka, Takafumi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamagishi, Isao
QST-M-2; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2015, P. 95, 2017/03
We conducted  ray irradiation test using simulated carbonate slurry to investigate the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container (HIC). This test was performed at Co-60 irradiation facility in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute. We observed a rise in water level, air bubbles in the slurry, a supernatant when the carbonate slurry with 95 g/L density was irradiated by
ray irradiation test using simulated carbonate slurry to investigate the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container (HIC). This test was performed at Co-60 irradiation facility in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute. We observed a rise in water level, air bubbles in the slurry, a supernatant when the carbonate slurry with 95 g/L density was irradiated by  ray at a dose rate of 8.5 kGy/h. The cause of the rise in water level was regarded as the volume expansion by the gas retention of the carbonate slurry. It was suggested that the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container might be the volume expansion by the gas retention.
ray at a dose rate of 8.5 kGy/h. The cause of the rise in water level was regarded as the volume expansion by the gas retention of the carbonate slurry. It was suggested that the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container might be the volume expansion by the gas retention.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ishii, Eiichi; Hirota, Akinari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Ikeya, Kosuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*
Applied Geochemistry, 76, p.218 - 231, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.60(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Tanaka, Tadao; Hemmi, Ko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(10), p.1573 - 1584, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:76.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The sorption behavior of thorium (Th) onto granitic rock and its major constituent were investigated by batch sorption experiments. Experiments were carried out under variable pH and carbonate concentrations. Distribution coefficients decreased with increased carbonate concentrations and showed the minimal value at pH 9-10. This sorption tendency was likely due to forming the hydroxide-carbonate complexes of Th in the solutions. The order of sorbability for Th was mica  feldspar
feldspar  quartz = granite. The sorption behaviors of Th onto these minerals were analyzed by the triple-layer surface complexation model with the Visual Minteq computer program. The model calculations assuming the inner-sphere surface complexation of Th were able to explain the experimental results reasonably well. It was shown that the sorption behavior of Th onto granite can be explained primarily by the complexation with the surface sites of feldspar.
quartz = granite. The sorption behaviors of Th onto these minerals were analyzed by the triple-layer surface complexation model with the Visual Minteq computer program. The model calculations assuming the inner-sphere surface complexation of Th were able to explain the experimental results reasonably well. It was shown that the sorption behavior of Th onto granite can be explained primarily by the complexation with the surface sites of feldspar.
Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 92, p.286 - 297, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)Diffusion and adsorption behavior of uranyl (UO ) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO
) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO , K
, K , CO
, CO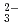 and Cl
and Cl and H
and H O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO
O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H
is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO
O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO CO
CO and UO
and UO (CO
(CO )
) can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO
can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO and K
and K were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO
were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO might be smaller than that of K
might be smaller than that of K . Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
. Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
Lee, C. G.; Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(2), p.440 - 444, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.42(Instruments & Instrumentation)The etching rates of fission track detectors made of polycarbonate containing uranium particles were measured after thermal neutron irradiation with fluence of 8 10
10 n/cm
n/cm , in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E
, in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E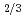 rather than E
rather than E , which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
, which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Konomi; Lee, C. G.; Inagawa, Jun; Esaka, Fumitaka; Onodera, Takashi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Suzuki, Daisuke; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.363 - 366, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)In particle analysis for safeguards environmental samples, the fission track technique is very important to detect sub-micrometer particles containing uranium. In the technique the authors developed, the particles were recovered onto the polycarbonate membrane filter. The filter was dissolved in solvent and dried to form a thin film of detector, in which the particles were confined. After thermal neutron irradiation and etching, the particles of interest in the detector were easily identified with fission tracks, and were picked up for isotope ratio analysis. It was found, however, that the particles in the vicinity of the detector surface may fall off during the etching process. Therefore, optimization of the etching condition is required. In this work, the effects of etching time and enrichment of uranium in particles were investigated. Preliminary results suggest that etching time should be shorter with the increase in the enrichment.
Watanabe, Masayuki; Tatsugae, Ryozo*; Morita, Yasuji; Kubota, Masumitsu*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 252(1), p.53 - 57, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.11(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Masayuki; Tatsugae, Ryozo*; Shirahashi, Koichi; Morita, Yasuji; Kubota, Masumitsu*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 250(2), p.377 - 379, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.74(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Uchiyama, Gunzo; Fujine, Sachio; Maeda, Mitsuru
Nuclear Technology, 120(1), p.41 - 47, 1997/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Verzilov, Y.*; Maekawa, Fujio; Oyama, Yukio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(5), p.390 - 395, 1996/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:78.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
G.Meinrath*; ; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko
Radiochimica Acta, 75(3), p.159 - 167, 1996/00
no abstracts in English