Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -contamination visualization (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-contamination visualization (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2024-006, 54 Pages, 2024/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of elemental technologies of hand-foot-cloth monitors for  -contamination visualization" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop hand-foot-monitors for
-contamination visualization" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop hand-foot-monitors for  -contamination visualization and cloth monitors for
-contamination visualization and cloth monitors for  /
/ -contamination visualization consisting of a portable phoswich detector for measuring
-contamination visualization consisting of a portable phoswich detector for measuring  /
/ -contamination distribution and energy to ensure the safety and security of workers involved in the decommissioning project of the 1F. The possibility of practical application of new scintillator materials and devices was examined with the goal of developing such new instruments.
-contamination distribution and energy to ensure the safety and security of workers involved in the decommissioning project of the 1F. The possibility of practical application of new scintillator materials and devices was examined with the goal of developing such new instruments.
Kinoshita, Ryoma; Sasaki, Yuji; Kaneko, Masashi; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Shinoku, Kota*; Shiroishi, Hidenobu*
Hydrometallurgy, 222, p.106159_1 - 106159_12, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.52(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Solvent extraction is conducted using a total of 20 metals revealing high stability constants with Cl and hexahexyl-nitrilotriacetamide (NTAamide(C6)) extractant. The metals used here may behave as anions at high Cl concentrations, and NTAamide(C6), which contains a tertiary N atom, is protonated under acidic conditions. Most of the metal ions in this study display higher distribution ratios (D(M)) from HCl than those from HNO , and exhibit 1:1 stoichiometries with NTAamide. Following the experimental results, the association constants and distribution coefficients of the group 12 elements are calculated via ion-pair extraction modeling using density functional theory calculations, and the simulations of D yield calculated values with the same trend as that of the measured values.
, and exhibit 1:1 stoichiometries with NTAamide. Following the experimental results, the association constants and distribution coefficients of the group 12 elements are calculated via ion-pair extraction modeling using density functional theory calculations, and the simulations of D yield calculated values with the same trend as that of the measured values.
Terashima, Motoki; Endo, Takashi*; Kimuro, Shingo; Beppu, Hikari*; Nemoto, Kazuaki*; Amano, Yuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.374 - 384, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamagata, Kazuhito*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Marumo, Kazuki*; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Haraga, Tomoko; Saito, Shingo*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(2), p.730 - 738, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.57(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The inert NpO
 complex with a fluorescein-modified phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid was found by kinetic selection using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) from a small chemical library. The small spontaneous dissociation rate constant of 8
complex with a fluorescein-modified phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid was found by kinetic selection using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) from a small chemical library. The small spontaneous dissociation rate constant of 8 10
10 s
s (the half-life of 23 hours) was determined. This is the singly-charged NpO
(the half-life of 23 hours) was determined. This is the singly-charged NpO
 complex exhibiting unusual kinetic inertness in aqueous solution, one million times slower than widely accepted fast kinetics of neptunyl complexes. Selective fluorescence detection of NpO
complex exhibiting unusual kinetic inertness in aqueous solution, one million times slower than widely accepted fast kinetics of neptunyl complexes. Selective fluorescence detection of NpO
 was achieved in PAGE with a detection limit of 68 pmol dm
was achieved in PAGE with a detection limit of 68 pmol dm (17 fg). This system was successfully applied to simulated spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste samples.
(17 fg). This system was successfully applied to simulated spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste samples.
Saito, Tatsuo; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Mochizuki, Akihito
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.107035_1 - 107035_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The seasonal variation of dissolved U (DU) in Lake Biwa was reproduced by the following model and parameter research. The introduced models are the water-DU mass balance, and the ion exchange between UO
 and H
and H on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-028, 54 Pages, 2022/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Tailor-made Adsorbents for Uranium Recovery from Seawater on the Basis of Uranyl Coordination Chemistry" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a new ligand class for efficient and selective capture of uranium from seawater. On the basis of deep understanding on uranyl coordination chemistry, we design molecular structures of pentadentate ligands as functional moieties for uranium adsorption from seawater and study fundamental coordination chemistry of uranyl ion with those ligands in order to resolve current problems in uranium recovery technology …
 and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
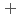 U
U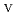
 Fe
Fe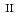
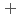 U
U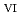 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
Omasa, Yoshinori*; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Toshima, Kento*; Yokoyama, Kaito*; Endo, Wataru*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033215_1 - 033215_9, 2022/09
Matsuda, Shohei; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Kaneta, Yui; Simonnet, M.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimojo, Kojiro; Doi, Reisuke; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 8(20), p.eabn1991_1 - eabn1991_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:41.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 and Eu
and Eu ions onto sedimentary rock in the presence of gamma-irradiated humic acid
ions onto sedimentary rock in the presence of gamma-irradiated humic acidZhao, Q.*; Saito, Takeshi*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, p.128211_1 - 128211_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.72(Engineering, Environmental)The influence of humic acid and its radiological degradation on the sorption of Cs and Eu
and Eu by sedimentary rock was investigated to understand the sorption process of metal ions and humic substances. Aldrich humic acid (HA) solution was irradiated with different doses of gamma irradiation using a Co-60 gamma-ray source prior to the contact between the metal ions and the solid sorbent. The HA molecule decomposed to smaller molecules with a lower complexation affinity. Batch sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effect of gamma-irradiated HA on the sorption of Cs
by sedimentary rock was investigated to understand the sorption process of metal ions and humic substances. Aldrich humic acid (HA) solution was irradiated with different doses of gamma irradiation using a Co-60 gamma-ray source prior to the contact between the metal ions and the solid sorbent. The HA molecule decomposed to smaller molecules with a lower complexation affinity. Batch sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effect of gamma-irradiated HA on the sorption of Cs and Eu
and Eu ions. The addition of non-irradiated HA weakened the sorption of Eu because of the lower sorption of the neutral or negatively charged Eu-HA complexes compared with free Eu ions. The sorption of monovalent Cs ions was barely affected by the presence of HA and its gamma irradiation. The concentration ratio of HA complexed species and non-complexed species in the solid and liquid phases was evaluated by sequential filtration and chemical equilibrium calculations. The ratios supported the minimal contribution of HA to Cs sorption. However, the concentration ratio for Eu
ions. The addition of non-irradiated HA weakened the sorption of Eu because of the lower sorption of the neutral or negatively charged Eu-HA complexes compared with free Eu ions. The sorption of monovalent Cs ions was barely affected by the presence of HA and its gamma irradiation. The concentration ratio of HA complexed species and non-complexed species in the solid and liquid phases was evaluated by sequential filtration and chemical equilibrium calculations. The ratios supported the minimal contribution of HA to Cs sorption. However, the concentration ratio for Eu in the liquid phase was high, indicating that the complexing ability of HA to Eu
in the liquid phase was high, indicating that the complexing ability of HA to Eu was higher than that of HA to Cs
was higher than that of HA to Cs ions. Therefore, the sorption of free Eu
ions. Therefore, the sorption of free Eu would predominate with the gamma irradiation dose applied to the HA solution under a radiation field near the HLW package.
would predominate with the gamma irradiation dose applied to the HA solution under a radiation field near the HLW package.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-041, 42 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of tailor-made adsorbents for uranium recovery from seawater on the basis of uranyl coordination chemistry" conducted in FY2020. On the basis of deep understanding on uranyl coordination chemistry, we design molecular structures of pentadentate ligands as functional moieties for uranium adsorption from seawater and study coordination chemistry of uranyl ion with those ligands in order to resolve current problems in uranium recovery technology from seawater and to develop novel selective and efficient adsorbents for this purpose.
 and Tb
and Tb measured by gel electrophoresis techniques
measured by gel electrophoresis techniquesNakano, Sumika*; Marumo, Kazuki*; Kazami, Rintaro*; Saito, Takumi*; Haraga, Tomoko; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Saito, Shingo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 55(22), p.15172 - 15180, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.63(Engineering, Environmental)Humic acid (HA) can strongly complex with metal ions to form a supramolecular assembly via coordination binding. However, determining the supramolecular size distribution and stoichiometry between small HA unit molecules constituting HA supramolecule and metal ions has proven to be challenging. Here, we investigated the changes in the size distributions of HAs induced by Cu and Tb
and Tb ions using a unique polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the separation and quantification of HA complexes and metal ions bound, followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and EEM-PARAFAC. It was found that the supramolecular behaviors of Cu
ions using a unique polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the separation and quantification of HA complexes and metal ions bound, followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and EEM-PARAFAC. It was found that the supramolecular behaviors of Cu and Tb
and Tb complexes with HA collected from peat and deep groundwater (HHA) differed. Our results suggest that this supramolecular stoichiometry is related to the abundance of sulfur atoms in the elemental composition of HHA. Our results provide new insights into HA supramolecules formed via metal complexation.
complexes with HA collected from peat and deep groundwater (HHA) differed. Our results suggest that this supramolecular stoichiometry is related to the abundance of sulfur atoms in the elemental composition of HHA. Our results provide new insights into HA supramolecules formed via metal complexation.
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 200, p.105910_1 - 105910_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:74.70(Chemistry, Physical)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-026, 41 Pages, 2020/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Tailor-Made Adsorbents for Uranium Recovery from Seawater on the Basis of Uranyl Coordination Chemistry". On the basis of deep understanding on uranyl coordination chemistry, we design molecular structures of pentadentate ligands as functional moieties for uranium adsorption from seawater and study coordination chemistry of uranyl ion with those ligands in order to resolve current problems in uranium recovery technology from seawater and to develop novel selective and efficient adsorbents for this purpose.
 for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protons
for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protonsMatsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 483, p.33 - 40, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)A thick target neutron yield for a mercury target at an angle of 180 from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Ohira, Saki; Hemmi, Ko; Barr, L.; Shimada, Asako; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Iida, Yoshihisa
Radiochimica Acta, 108(11), p.873 - 877, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:54.81(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) -isosaccharinic acid
-isosaccharinic acidKobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 138, p.151 - 158, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:23.66(Thermodynamics)The effect of  -isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH
-isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) range of 6
) range of 6 13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]
13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]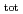 ) = 10
) = 10
 10
10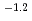 mol/dm
mol/dm . The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH
. The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH and [ISA]
and [ISA]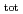 suggested the existence of U(OH)
suggested the existence of U(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 as a dominant species within the investigated pH
as a dominant species within the investigated pH range of 6
range of 6 12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO
12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO (OH)
(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 was suggested as a dominant species at pH
was suggested as a dominant species at pH 7
7 13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
Otaka, Toshiki*; Sato, Tatsumi*; Ono, Shimpei; Nagoshi, Kohei; Abe, Ryoji*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Analytical Sciences, 35(10), p.1129 - 1133, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.12(Chemistry, Analytical)Rai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 114, p.135 - 143, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:20.39(Thermodynamics)Isosaccharinic acid is a cellulose degradation product that can form in low-level nuclear waste repositories and is known to form strong complexes with many elements, including actinides, disposed of in these repositories. We (1) reviewed the available data for deprotonation and lactonisation constants of isosaccharinic acid, and the isosaccharinate binding constants for Ca, Fe(III), Th, U(IV), U(VI), Np(IV), Pu(IV), and Am(III), (2) summarized complexation constant values for predicting actinide behavior in geologic repositories in the presence of isosaccharinate, and (3) outlined additional studies to acquire reliable thermodynamic data where the available data are inadequate.
 (am) in the aqueous K
(am) in the aqueous K - HCO
- HCO
 - CO
- CO
 - OH
- OH - H
- H O system
O systemRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K.*
Radiochimica Acta, 105(8), p.637 - 647, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.58(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility of HfO (am) was determined as a function of KHCO
(am) was determined as a function of KHCO concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg
concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg to 0.1 mol.kg
to 0.1 mol.kg . The solubility of HfO
. The solubility of HfO (am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO
(am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO
concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-)
concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-) (CO
(CO )
)
 and Hf(CO
and Hf(CO )
)
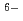 . The log
. The log K
K values for the reactions [Hf
values for the reactions [Hf + 2 CO
+ 2 CO
 +2 OH
+2 OH
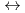 Hf(OH)
Hf(OH) (CO
(CO )
)
 ] and [Hf
] and [Hf + 5 CO
+ 5 CO

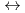 Hf(CO
Hf(CO )
)
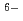 ], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53
], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53  0.46 and 41.53
0.46 and 41.53  0.46, respectively.
0.46, respectively.