Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chanyshev, A. D.*; Litasov, K. D.*; Rashchenko, S.*; Sano, Asami; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Shatskiy, A. F.*; Dymshits, A. M.*; Sharygin, I. S.*; Higo, Yuji*
Crystal Growth & Design, 18(5), p.3016 - 3026, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The high-temperature structural properties of solid benzene were studied at 1.5-8.2 GPa up to melting or decomposition using multi-anvil apparatus and in situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure of deuterated benzene phase II (P2 /c unit cell) was refined at 3.6-8.2 GPa and 473-873 K. Our data show a minor temperature effect on the change in the unit cell parameters of deuterated benzene at 7.8-8.2 GPa. At 3.6-4.0 GPa, we observed the deviation of deuterium atoms from the benzene ring plane and minor zigzag deformation of the benzene ring, enhancing with the temperature increase caused by the displacement of benzene molecules and decrease of van der Waals bond length between the
/c unit cell) was refined at 3.6-8.2 GPa and 473-873 K. Our data show a minor temperature effect on the change in the unit cell parameters of deuterated benzene at 7.8-8.2 GPa. At 3.6-4.0 GPa, we observed the deviation of deuterium atoms from the benzene ring plane and minor zigzag deformation of the benzene ring, enhancing with the temperature increase caused by the displacement of benzene molecules and decrease of van der Waals bond length between the  -conjuncted carbon skeleton and the deuterium atom of adjacent molecule. Deformation of benzene molecule at 723-773 K and 3.9-4.0 GPa could be related to the benzene oligomerization at the same conditions. In the pressure range of 1.5-8.2 GPa, benzene decomposition was defined between 773-923 K. Melting was identified at 2.2 GPa and 573 K. Quenched products analyzed by Raman spectroscopy consist of carbonaceous material. The defined benzene phase diagram appears to be consistent with those of naphthalene, pyrene, and coronene at 1.5-8 GPa.
-conjuncted carbon skeleton and the deuterium atom of adjacent molecule. Deformation of benzene molecule at 723-773 K and 3.9-4.0 GPa could be related to the benzene oligomerization at the same conditions. In the pressure range of 1.5-8.2 GPa, benzene decomposition was defined between 773-923 K. Melting was identified at 2.2 GPa and 573 K. Quenched products analyzed by Raman spectroscopy consist of carbonaceous material. The defined benzene phase diagram appears to be consistent with those of naphthalene, pyrene, and coronene at 1.5-8 GPa.
 1
1 -type AlNi
-type AlNi alloy at high pressure and temperature
alloy at high pressure and temperatureEndo, Naruki*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 645(Suppl.1), p.S61 - S63, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Endo, Naruki*; Saita, Itoko*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40(8), p.3283 - 3287, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:38.81(Chemistry, Physical)Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Matsuoka, Takehiro*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Solid State Communications, 205, p.24 - 27, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.42(Physics, Condensed Matter) FeH
FeH ; Iron-containing complex hydride with high gravimetric hydrogen density
; Iron-containing complex hydride with high gravimetric hydrogen densitySaito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Iijima, Yuki*; Endo, Naruki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Orimo, Shinichi*
APL Materials (Internet), 2(7), p.076103_1 - 076103_7, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:67.98(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Saito, Hiroyuki; Utsumi, Wataru; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Kiriyama, Koji*; Aoki, Katsutoshi
State-of-the-Art Program on Compound Semiconductors XLI and Nitride and Wide Bandgap Semiconductors for Sensors, Photonics, and Electronics V, p.587 - 592, 2004/10
Single crystals of GaN were successfully synthesized by slowly cooling its stoichiometric melt under high pressure. Applying high pressures above 6.0 GPa prevented decomposition and allowed the congruent melt of GaN at 2220 C, which was confirmed by an in situ X-ray diffraction study. Using a cubic-anvil-type, large volume, high-pressure apparatus and a GaN powder as a starting material, single crystal growth was achieved by reducing the temperature from 2400
C, which was confirmed by an in situ X-ray diffraction study. Using a cubic-anvil-type, large volume, high-pressure apparatus and a GaN powder as a starting material, single crystal growth was achieved by reducing the temperature from 2400 C at 6.5 GPa. The X-ray rocking curve of the recovered sample showed a very narrow line width, less than 30 arcsec, suggesting a low dislocation density. Bulk specimens of Al
C at 6.5 GPa. The X-ray rocking curve of the recovered sample showed a very narrow line width, less than 30 arcsec, suggesting a low dislocation density. Bulk specimens of Al Ga
Ga N alloys, which covered a composition range of 0
N alloys, which covered a composition range of 0 x
x 1 were also synthesized under high pressures.
1 were also synthesized under high pressures.
 Ga
Ga N alloy by solid-phase reaction under high pressure
N alloy by solid-phase reaction under high pressureSaito, Hiroyuki; Utsumi, Wataru; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2, 43(7B), p.L981 - L983, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.53(Physics, Applied)Bulk specimens of Al Ga
Ga N alloys covering a composition range of 0
N alloys covering a composition range of 0
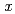
 1 were synthesized by a solid-phase reaction under high pressure.
1 were synthesized by a solid-phase reaction under high pressure.  X-ray diffraction profiles were measured to observe the alloying process, which began at around 800
X-ray diffraction profiles were measured to observe the alloying process, which began at around 800 C under 6.0 GPa. SEM observation and X-ray analysis of the recovered specimen indicated a uniform distribution of Al and Ga and continuous variations of the lattice constants against the composition, which implies that a solid solution of AlN and GaN is formed regardless of atomic composition.
C under 6.0 GPa. SEM observation and X-ray analysis of the recovered specimen indicated a uniform distribution of Al and Ga and continuous variations of the lattice constants against the composition, which implies that a solid solution of AlN and GaN is formed regardless of atomic composition.
Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Yamakata, Masaaki*; Shimomura, Osamu
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 29(7), p.439 - 445, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:54.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An experimental technique to make real-time observations at high pressure and temperature of the diamond forming process in candidate material of mantle fluids as a catalyst has been established for the first time. In situ X-ray diffraction experiments using synchrotron radiation have been performed upon a mixture of brucite (Mg(OH) ) and graphite as starting material. Brucite decomposes into periclase (MgO) and H
) and graphite as starting material. Brucite decomposes into periclase (MgO) and H O at 3.6 GPa and 1050
O at 3.6 GPa and 1050 C while no periclase is formed after the decomposition of brucite at 6.2 GPa and 1150
C while no periclase is formed after the decomposition of brucite at 6.2 GPa and 1150 C, indicating that the solubility of the MgO component in H
C, indicating that the solubility of the MgO component in H O greatly increases with increasing pressure. The conversion of graphite to diamond in aqueous fluid has been observed at 7.7 GPa and 1835
O greatly increases with increasing pressure. The conversion of graphite to diamond in aqueous fluid has been observed at 7.7 GPa and 1835 C. Time-dependent X-ray diffraction profiles for this transformation have been successfully obtained.
C. Time-dependent X-ray diffraction profiles for this transformation have been successfully obtained.
Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Ioka, Ikuo; Tachibana, Katsumi; Suzuki, Tomio; Fukaya, Kiyoshi*; Inohara, Yasuto*; Kambara, Shozo; Kuroda, Yuji*; Miyamoto, Satoshi*; Ogura, Kazutomo*
JAERI-Research 2002-008, 63 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
 C
CKondo, Tatsuo; ; Kawasaki, Masayuki
Trans.Jpn.Inst.Met., 3(2), p.110 - 118, 1962/00
no abstracts in English
 CuH
CuH
Saito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Endo, Naruki*; Machida, Akihiko; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,