Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ono, Masato; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.235 - 242, 2025/05
Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Oi, Motoki; Klinkby, E.*; Zanini, L.*; Batkov, K.*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 903, p.38 - 45, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:75.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kai, Tetsuya; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Hiraga, Fujio*; Oi, Motoki; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.283 - 289, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takada, Hiroshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 13(Sp.1), p.2505013_1 - 2505013_8, 2018/03
The pulsed spallation neutron source of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has been supplying users with high intensity and sharp pulse cold neutrons using the moderators with following distinctive features; (1) 100% para-hydrogen for increasing pulse peak intensity with decreasing pulse tail, (2) cylindrical shape with 14 cm diam. 12 cm long for providing high intensity neutrons to wide neutron extraction angles of 50.8
12 cm long for providing high intensity neutrons to wide neutron extraction angles of 50.8 , (3) neutron absorber made from Ag-In-Cd alloy to make pulse width narrower and pulse tails lower. Actually, it was measured at a low power operation that high neutron intensity of 4.5
, (3) neutron absorber made from Ag-In-Cd alloy to make pulse width narrower and pulse tails lower. Actually, it was measured at a low power operation that high neutron intensity of 4.5 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /s/sr could be emitted from the coupled moderator surface for 1-MW operation, and a superior resolution of
/s/sr could be emitted from the coupled moderator surface for 1-MW operation, and a superior resolution of  d/d = 0.035% was achieved at a beamline (BL8) with a poisoned moderator, where d is the d-spacing of reflection. Towards the goal to achieve the target operation at 1-MW for 5000 h in a year, technical developments to mitigate cavitation damages on the target vessel with injecting gas micro-bubbles into mercury target and design improvement of target vessel structure to reducing welds and bolt connections as much as possible are under way.
d/d = 0.035% was achieved at a beamline (BL8) with a poisoned moderator, where d is the d-spacing of reflection. Towards the goal to achieve the target operation at 1-MW for 5000 h in a year, technical developments to mitigate cavitation damages on the target vessel with injecting gas micro-bubbles into mercury target and design improvement of target vessel structure to reducing welds and bolt connections as much as possible are under way.
Takada, Hiroshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Teshigawara, Makoto; Aso, Tomokazu; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Oi, Motoki; Harada, Masahide; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.8_1 - 8_26, 2017/09
At the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), a pulsed spallation neutron source provides neutrons with high intensity and narrow pulse width to promote researches on a variety of science in the Materials and life science experimental facility. It was designed to be driven by the proton beam with an energy of 3 GeV, a power of 1 MW at a repetition rate of 25 Hz, that is world's highest power level. A mercury target and three types of liquid para-hydrogen moderators are core components of the spallation neutron source. It is still on the way towards the goal to accomplish the operation with a 1 MW proton beam. In this paper, distinctive features of the target-moderator-reflector system of the pulsed spallation neutron source are reviewed.
Harada, Masahide; Watanabe, Noboru; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 539(1-2), p.345 - 362, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutronic studies of decoupled hydrogen moderators were performed by calculations taking into account para hydrogen content, decoupling energy, moderator dimensions/shapes and reflector material. Low-energy parts of calculated spectral intensities with different para hydrogen contents were analyzed by a modified Maxwell function to characterize neutron spectra. The result shows that a 100% para hydrogen moderator gives the highest pulse peak intensity together with the narrowest pulse width and the shortest decay times. Pulse broadening with a reflector was explained by time distributions of source neutrons entering into the moderator through a decoupler. Material dependence of time distribution was studied. A decoupling energy higher than 1 eV does not bring about a large improvement in pulse widths and decay times, even at a large penalty in the peak intensity. The optimal moderator thickness was also discussed for a rectangular parallelepiped shape and a canteen shape moderators.
Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Watanabe, Noboru; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 523(3), p.398 - 414, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:89.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutronic performance of a coupled hydrogen moderator was studied as a function of para hydrogen concentration, moderator thickness, height and premoderator thickness. It was found that a thick (120 140mm) moderator with 100% para hydrogen was optimal to provide the highest time- and energy- integrated neutron intensity below 15 meV together with the highetst possible pulse-peak intensity. Low-energy neutron distribution on the moderator viewed surface was found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. The rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use.
140mm) moderator with 100% para hydrogen was optimal to provide the highest time- and energy- integrated neutron intensity below 15 meV together with the highetst possible pulse-peak intensity. Low-energy neutron distribution on the moderator viewed surface was found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. The rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use.
Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Watanabe, Noboru; Kai, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 2, p.697 - 706, 2003/07
For two decoupled moderators in JSNS, optimization studies were performed by model calculations using NMTC/JAM and MCNP-4C codes. The model was based on a realistic Target-Moderator-Reflector Assembly. We assumed a para-hydrogen ratio of 100%. The shape of poisoned and unpoisoned moderators is a canteen type with dimensions of 13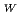
 12
12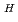
 6.2
6.2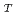 cm
cm . A decoupling energy of about 1 eV was adopted to meet the user's requests. As a decoupler material we selected silver-indium-cadmium alloy. It was found that for the decoupled moderators, especially the poisoned moderator, pulse broadening due to a finite beam-extraction angle (
. A decoupling energy of about 1 eV was adopted to meet the user's requests. As a decoupler material we selected silver-indium-cadmium alloy. It was found that for the decoupled moderators, especially the poisoned moderator, pulse broadening due to a finite beam-extraction angle ( ) was very serious. Therefore,
) was very serious. Therefore,  for the poisoned and the unpoisoned moderators were limited to be 7.5
for the poisoned and the unpoisoned moderators were limited to be 7.5 and 17.5
and 17.5 , respectively. Cadmium (Cd) was selected as a poison material due to higher cut-off energy than gadolinium and higher peak intensity with narrower pulse width. The poison plate will be placed at 25 mm from the viewed surface which meets the user's requirements.
, respectively. Cadmium (Cd) was selected as a poison material due to higher cut-off energy than gadolinium and higher peak intensity with narrower pulse width. The poison plate will be placed at 25 mm from the viewed surface which meets the user's requirements.
Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Watanabe, Noboru; Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.657 - 666, 2003/07
Neutronic design studies were carried out on the J-PARC coupled H moderator. The highest time- and energy- integrated intensity below 15 meV, pulse peak intensity at 2 meV and 10 meV, were given by 100% para-H
moderator. The highest time- and energy- integrated intensity below 15 meV, pulse peak intensity at 2 meV and 10 meV, were given by 100% para-H moderators, but the optimal moderator thickness was different for each: more than 220 mm, about 120 mm and 80 mm, respectively. Finally, we concluded 140 mm was the optimal thickness for the 100% para-H
moderators, but the optimal moderator thickness was different for each: more than 220 mm, about 120 mm and 80 mm, respectively. Finally, we concluded 140 mm was the optimal thickness for the 100% para-H coupled moderator. Cold neutron distributions on the moderator viewed surface were found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. This rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use. The intensity decreases along with beam-extraction angle to the normal direction down to about 70% at 25.4
coupled moderator. Cold neutron distributions on the moderator viewed surface were found to exhibit an intensity-enhanced region at a picture frame part near premoderator. This rather peculiar distribution suggested that the moderator and the viewed surface must be designed so as to take the brighter region near premoderator in use. The intensity decreases along with beam-extraction angle to the normal direction down to about 70% at 25.4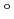 . Then, we propose a cylindrical shape coupled moderator which brings about a slight intensity decrease for 0
. Then, we propose a cylindrical shape coupled moderator which brings about a slight intensity decrease for 0 but a increase in the averaged intensity over the angles of interest.
but a increase in the averaged intensity over the angles of interest.
 - and
- and  -alumina tube as the support tube in the Hi-H
-alumina tube as the support tube in the Hi-H O gaseous mixture
O gaseous mixtureHwang, G.*; Kim, J.*; Choi, H.*; Onuki, Kaoru
Journal of Membrane Science, 215(1-2), p.293 - 302, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:55.53(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English
 O+SO
O+SO atmosphere
atmosphereKurata, Yuji; Suzuki, Tomio; Shimizu, Saburo
JAERI-Research 2000-011, p.56 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
 -H
-H O-HI gaseous mixture using the silica membrance prepared by chemical vapor deposition
O-HI gaseous mixture using the silica membrance prepared by chemical vapor depositionHwang, G.*; Onuki, Kaoru; Shimizu, Saburo;
J. Membr. Sci., 162(1-2), p.83 - 90, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:90.38(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English
 -alumina tube
-alumina tubeHwang, G.*; Onuki, Kaoru; Shimizu, Saburo
JAERI-Research 98-002, 8 Pages, 1998/01
no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; ; Sekita, Kenji; ; Hino, Ryutaro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 40(1), p.59 - 64, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; ; Sekita, Kenji; Haga, Katsuhiro; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Research 97-076, 33 Pages, 1997/10
no abstracts in English
 solution by electrodialysis
solution by electrodialysisOnuki, Kaoru; Nakajima, Hayato; Shimizu, Saburo
Kagaku Kogaku Rombunshu, 23(2), p.289 - 291, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.22(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English
Onuki, Kaoru; Nakajima, Hayato; Ioka, Ikuo; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Shimizu, Saburo
JAERI-Review 94-006, 53 Pages, 1994/11
no abstracts in English
Fusion Technology, 9, p.492 - 498, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
; ;
Fusion Technology, 10, p.462 - 473, 1986/00
no abstracts in English