Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Inoue, Rintaro*; Oda, Takashi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Tominaga, Taiki*; Ikegami, Takahisa*; Konuma, Tsuyoshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Sato, Mamoru*; Sugiyama, Masaaki*
Biophysical Journal, 124(3), p.540 - 548, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biophysics)Kumar, S.*; Saha, D.*; Takata, Shinichi; Aswal, V. K.*; Seto, Hideki
Applied Physics Letters, 118(15), p.153701_1 - 153701_7, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.19(Physics, Applied) -synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formationFujiwara, Satoru*; Kono, Fumiaki*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Sugimoto, Yasunobu*; Matsumoto, Tomoharu*; Narita, Tetsuhiro*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Molecular Biology, 431(17), p.3229 - 3245, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:49.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) -synuclein (
-synuclein ( Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.
Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.  Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of
Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of  Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of
Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of  Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of
Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of  Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Niimura, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Bau, R.*
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 63(3), p.285 - 300, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:36.83(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Neutron diffraction provides an experimental method of directly locating hydrogen atoms in proteins and DNA oligomers. Three different types of high resolution neutron diffractometers for biological macromolecules have been constructed in Japan, France and the U.S.A., and they have all been actively used in recent years to determine the crystal structures of numerous proteins. Examples include the detailed geometries of hydrogen bonds, information on H/D exchange in proteins, the unambiguous location of protons, the role of key hydrogen atoms in enzymatic activity and thermostability, and the dynamical behavior of hydration structures, all of which have been extracted from these structural results and reviewed in this article. Other important techniques, such as the optimization of growth of large single crystals using phase diagrams, the preparation of fully deuterated proteins, the introduction of cryogenic techniques to neutron protein crystallography, and the establishment of a "hydrogen and hydration in proteins" database, will also be described in this paper.
Metsugi. Shoichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(6), p.1865 - 1870, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We study the problem of convergence of sampling in protein simulation originating in the multidimensionality of protein's conformational space. Since several important physical quantities are given by second moments of dynamical variables, we attempt to obtain the time of simulation necessary for their sufficient convergence. We perform a molecular dynamics simulation of a protein and the subsequent principal component (PC) analysis as a function of simulation time T. As T increases, PC vectors with smaller amplitude of variations are identified and their amplitudes are equilibrated before identifying and equilibrating vectors with larger amplitude of variations. This sequential identification and equilibration mechanism makes protein simulation a useful method although it has an intrinsic multidimensional nature.
Schyman, P.*; Danielsson, J.*; Pinak, M.; Laaksonen, A.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 109(8), p.1713 - 1719, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:77.11(Chemistry, Physical)We have examined the role of the catalytic lysine (Lys 249) in breaking the glycosidic bond of 8-oxoguanine in the enzyme human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase. It has been assumed that this lysine acts as a nucleophile in a S 2 type of reaction after being activated through a donation of a proton to a strictly conserved aspartate. We use hybrid density functional theory to characterize both associative and dissociative pathways. We find that the smallest energetical barrier involves a S
2 type of reaction after being activated through a donation of a proton to a strictly conserved aspartate. We use hybrid density functional theory to characterize both associative and dissociative pathways. We find that the smallest energetical barrier involves a S 1 type of mechanism where the lysine electrostatically stabilizes the dissociating base and then donates a proton with a very small barrier and then finally attacks the sugar ring to create the covalently bounded protein-DNA intermediate complex. Reported findings give further support to the assumption that a dissociative mechanism may be the preferred mode of action for this type of enzymes.
1 type of mechanism where the lysine electrostatically stabilizes the dissociating base and then donates a proton with a very small barrier and then finally attacks the sugar ring to create the covalently bounded protein-DNA intermediate complex. Reported findings give further support to the assumption that a dissociative mechanism may be the preferred mode of action for this type of enzymes.
Niimura, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Bau, R.*
Hydrogen- and Hydration-Sensitive Structural Biology, p.17 - 35, 2005/00
At the JAERI, we have constructed several high-resolution neutron diffractometers dedicated to biological macromolecules (called BIX-type diffractometers), which use a monochromatized neutron beam and a neutron imaging plate detector. In this paper, we review several interesting results regarding hydrogen positions and hydration in proteins, obtained using the two BIX-type diffractometers in JAERI. The general subject of neutron protein crystallography has been reviewed by several authors, and several selected topics have been discussed.
Kimura, Hideo; Sakai, Tomo*
JAERI-Data/Code 2004-008, 41 Pages, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro
Kagaku, 59(2), p.46 - 47, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Slovic, A. M.*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Lear, J. D.*; Saven, J. G.*; DeGrado, W. F.*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(7), p.1828 - 1833, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:88 Percentile:79.48(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Kaoru; Tamura, Itaru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Middendorf, H. D.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.351 - 354, 2003/07
In this research report we describe the design of DYANA, a new neutron spectrometer dedicated for biology, biomaterials, and related soft-matter studies, which will be installed in the material and life science experimental facility project at the JAERI Tokai establishment. The DYANA spectrometer is an indirect-geometry crystal-analyzer instrument and its energy and momentum transfer range are from several 10 eV to several meV and from 0.1
eV to several meV and from 0.1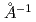 to several
to several 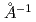 , respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
, respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
Shibata, Kaoru; Tamura, Itaru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Niimura, Nobuo
JAERI-Research 2002-036, 30 Pages, 2003/03
In this research report we describe the design of DYANA, a new neutron spectrometer dedicated for biology, biomaterials, and related soft-matter studies, which will be installed in the material and life science experimental facility project at the JAERI Tokai establishment. The DYANA spectrometer is an indirect-geometry crystal-analyzer instrument and it's energy and momentum transfer range are from several 10 eV to several meV and from 0.1
eV to several meV and from 0.1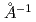 to several
to several 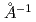 , respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
, respectively. These specifications will become possible to do the study of protein dynamics analysis.
Functional Materials Laboratory I
JAERI-Conf 2002-003, 225 Pages, 2002/03
This Takasaki symposium was held annually for radiation processing of natural polymers through research cooperation among Asian countries. The symposium includes the presentations of research outcomes on radiation processing of starches, silk proteins and marine carbohydrates. In starch and cellulose researches, radiation crosslinking of biodegradable polysaccharides was achieved by modifying it to be water-soluble paste. In silk protein researches, pulverization and water-solubilization of the irradiated silk proteins were reported. In marine carbohydrate researches, it was reported that radiation-degraded chitosan and alginate showed promotion effects for plant growth and enhancement of antibacterial properties. In addition, estimation of economic scale of radiation application in Japan and U.S. were introduced. Outcomes of this symposium should contribute the progress in radiation applications in south Asian and Japan. We had the 63 participants consisted of 16 foreign researchers and 60 from domestic organizations. This proceeding compiles the invited and contributed papers.
Tanaka, Ichiro; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki; Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 35(Part1), p.34 - 40, 2002/02
A high performance neutron diffractometer for biological crystallography (BIX-3) has been constructed at JRR-3M in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) in order to determine the hydrogen positions in biological macromolecules. It uses several recent technical innovations, such as a neutron imaging plate and an elastically bent silicon monochromator developed by the authors. These have made it possible to realize a compact vertical arrangement of the diffractometer. Diffraction data have been collected from the proteins rubredoxin and myoglobin in about one month, to a resolution of 1.5 , good enough to identify the hydrogen atoms with high accuracy. By adopting a crystal-step scan method for measuring Bragg diffraction intensities, the signal to noise ratio was much better than that of the Laue method. This shows that BIX-3 is one of the best-performing machines for neutron protein crystallography in the world currently.
, good enough to identify the hydrogen atoms with high accuracy. By adopting a crystal-step scan method for measuring Bragg diffraction intensities, the signal to noise ratio was much better than that of the Laue method. This shows that BIX-3 is one of the best-performing machines for neutron protein crystallography in the world currently.
 SOS-regulated UmuD
SOS-regulated UmuD protein
proteinSutton, M. D.*; Guzzo, A.*; Narumi, Issei; Costanzo, M.*; Altenbach, C.*; Ferentz, A. E.*; Hubbell, W. L.*; Walker, G. C.*
DNA Repair, 1(1), p.77 - 93, 2002/01
UmuD protein is a regulatory subunit of
protein is a regulatory subunit of  DNA polymerase V. This protein forms a complex with UmuC protein, a catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase V, and plays a important role in error-prone translesion DNA synthesis, which serves as the mechanistic basis for most DNA-damaging agent and UV light mutagenesis. In this paper, based on the results of a combination of experimental studies, we have developed a refined model for the structure of the UmuD
DNA polymerase V. This protein forms a complex with UmuC protein, a catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase V, and plays a important role in error-prone translesion DNA synthesis, which serves as the mechanistic basis for most DNA-damaging agent and UV light mutagenesis. In this paper, based on the results of a combination of experimental studies, we have developed a refined model for the structure of the UmuD homodimer. Implications of the structural change of UmuD
homodimer. Implications of the structural change of UmuD protein with respect to its roles in managing the action of DNA polymease V are discussed.
protein with respect to its roles in managing the action of DNA polymease V are discussed.
Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 70(Suppl.A), p.396 - 399, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Functional Materials Laboratory I
JAERI-Conf 2001-005, 273 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Nagao, Seiya; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Tanaka, Tadao; Ogawa, Hiromichi
Proceedings of OECD/NEA Workshop on Evaluation of Speciation Technology, p.181 - 188, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 -irradiation
-irradiation; ; ; ; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 35, p.95 - 99, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:72.96(Biology)no abstracts in English
; Watanabe, Hiroshi; ; Tano, Shigemitsu*
Dai-2-Kai Genken, Daigaku Purojekuto Kyodo Kenkyu Seika Happyokai Hobunshu, 0, p.100 - 103, 1992/00
no abstracts in English