Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ochs, M.*; Dolder, F.*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 136, p.105161_1 - 105161_11, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:67.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Various types of radioactive wastes and environments contain organic substances that can stabilize the aqueous complexes with radionuclides and therefore lead to a decrease of sorption. The present study focuses on testing a methodology to quantify sorption reduction factors (SRFs) in the presence of organic ligands for cement systems. Three approaches for the estimation of SRFs; (1) analogy with solubility enhancement factors, (2) radionuclide speciation based on the thermodynamic calculations, and (3) experimental sorption data in ternary systems, were coupled and tested for the representative organic ligands (ISA and EDTA) and selected key radionuclides (actinides). Our approach allows to critically evaluate the dependence of SRFs for various systems on the chosen method of quantification, in accordance with the data availability for a given systems. The reliable SRFs can only be derived from the sorption measurements in ternary systems. SRF often need to be derived in the absence of such direct evidence, and estimations need to be made based on analogies and speciation information. However, such estimates may be subject to substantial uncertainties.
Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-020, 164 Pages, 2021/03
Part of JAEA's Thermodynamic Database (JAEA-TDB) for solubility and speciation of radionuclides (JAEA-TDB-RN) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes has been updated with subsuming the database for geochemical calculations (JAEA-TDB-GC). This report has focused to update JAEA-TDB-RN after selecting change in standard Gibbs free energy of formation (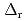
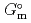 ), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (
), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (


 ), standard molar entropy (
), standard molar entropy (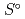
 ) and, heat capacity (
) and, heat capacity (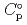 ), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (
), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (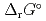
 ), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
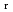


 ) and standard entropy change of reaction (
) and standard entropy change of reaction (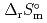 ) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
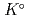 ) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
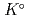 have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Yano, Kimihiko; Washiya, Tadahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.704 - 718, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)To suggest efficient process of the fuel debris treatment after the retrieval from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), thorough investigation is indispensable on potential source of U in the fuel debris. Estimation on the fuel debris accumulated in the reactor pressure vessel is specifically important due to its limited accessibility. The present study aims to estimate the chemical forms of U in the in-vessel fuel debris, especially in the minor phases such as metallic phases, by performing the thermodynamic calculation considering the material relocation and changing environment during the accident progression in the 1F Unit 2. Input conditions for the thermodynamic calculation such as composition, temperature, and oxygen amount were assumed mainly based on the results of severe accident analysis. The chemical form of U varied depending on the local amount of Fe and O. In regions of low steel content, the U-containing metallic phase was dominated by  -(Zr,U)(O), while regions of high steel content were dominated by Fe
-(Zr,U)(O), while regions of high steel content were dominated by Fe (Zr,U) (Laves phase). A few percent of U was transferred to the metallic phases under reducing conditions, raising challenging issues on the chemical removal of nuclear material from fuel debris.
(Zr,U) (Laves phase). A few percent of U was transferred to the metallic phases under reducing conditions, raising challenging issues on the chemical removal of nuclear material from fuel debris.
 -UO
-UO
 -CO
-CO
 system and integration with JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculations
system and integration with JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculationsKitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-018, 103 Pages, 2019/03
The latest available thermodynamic data were critically reviewed and the selected values were included into the JAEA-TDB for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. This critical review specifically addressed thermodynamic data for (1) a zirconium-hydroxide system through comparison of thermodynamic data selected by the Nuclear Energy Agency within the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA), (2) complexation of metal ions with isosaccharinic acid based on the latest review papers. Furthermore, the author performed (3) tentative selection of thermodynamic data on ternary complexes among alkaline-earth metal, uranyl and carbonate ions, and (4) integration with the latest version of JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculations. The internal consistency of the selected data was checked by the author. Text files of the updated and integrated thermodynamic database have been prepared for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Piluso, P.*; Fouquart, P.*; Excoffier, E.*; David, C.*; Brackx, E.*
Proceedings of 8th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2017) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2017/05
no abstracts in English
Kato, Chiaki
JAERI-Research 2003-013, 143 Pages, 2003/08
This study is investigation about stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of zirconium in nuclear fuel reprocessing. Chapter 1 is described background. Chapter 2 is explained experimental apparates. Chapter 3 is described the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface and suggested the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface. Chapter 4 is described that the SCC susceptibility increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature on notched specimen by SSRT. In addition, the SCC susceptibility effected by the crystal anisotropy by the hot rolling direction and increased on a parallel face to the rolling direction. Chapter 5 is described that the SCC susceptibility increased in HAZ/base metal boundary in order to the preferential orientation of cleavage plane (0002). Chapter 6 is described that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles.
Nakano, Junichi; Yamada, Reiji
JAERI-Research 95-045, 26 Pages, 1995/06
no abstracts in English
 CN molecule; An Experimental and ab initio study
CN molecule; An Experimental and ab initio studyKudo, Hiroshi; Hashimoto, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Wu, C. H.*; A.E.Dorigo*; F.M.Bickelhaupt*; P.von-R.Schleyer*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 99(17), p.6477 - 6482, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Noguchi, Yoshihiro*; Kondo, Yoshikazu*; Yano, Kimihiko; Kaji, Naoya; Washiya, Tadahiro
no journal, ,