Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinohara, Masanori; Motegi, Toshihiro; Saito, Kenji; Haga, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Takada, Kiyoshi*; Higashimura, Keisuke*; Fujii, Junichi*; Ukai, Takayuki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-032, 29 Pages, 2012/11
An event, in which one of WRMs were disabled to detect the neutron flux in the reactor core, occurred during the period of reactor shut down of HTTR in March, 2010. The actual life time of WRM was unexpectedly shorter than the past developed life time. Investigation of the cause of the outage of WRM toward the recovery of the life time up to the past developed life is one of the issues to develop the technology basis of HTGR. Then, two experimental investigations were carried out to reveal the cause of the malfunction by specifying the damaged part causing the event in the WRM. One is an experiment using a mock-up sample test which strength degradation on assembly accuracy and heat cycle to specify the damaged part in the WRM. The other is a destructive test in FMF to specify the damaged part in the WRM. This report summarized the results of the destructive test and the experimental investigation using the mock-up to reveal the cause of malfunction of WRM.
Saeki, Morihisa; Esaka, Fumitaka; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Oba, Hironori
JAEA-Research 2012-030, 16 Pages, 2012/11
We proposed separation technique of platinum-group metals (PGMs) from a solution of high-level radioactive waste by using laser-induced particle formation, and performed its proof-of-principle experiment. The simulated solution of high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) was prepared by dissolving palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru) and neodymium (Nd) into distilled water. The Nd metal was added as representative of lanthanide and minor actinide. After 40-min irradiation of a mixture of the simulated solution of HLLW and ethanol (v/v = 1/1) with a UV laser (266 nm, 20 mJ), the Pd, Rh and Ru metals were separated from the Nd ion as particle with sub-micron size. The PGM particles were recovered by filtration and centrifugation. Analysis of ion concentration in the sample solution by ICP-AES suggested that the Pd, Rh and Ru metals were recovered with efficiency of 100%, 94-99%, 65-69%, while the Nd ion was completely kept in the sample solution.
Advanced Science Research Center
JAEA-Evaluation 2012-002, 153 Pages, 2012/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) consulted the "Evaluation Committee of Research Activities for Advanced Science Research" for interim assessment of "Advanced Science Research", in accordance with "General Guideline for the Evaluation of Government Research and Development (R&D) Activities" by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation of R&D Activities" by JAEA. In response to the JAEA's request, the Committee assessed the research programs and activities of the Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC) for the period of two years from April 2010. The Committee evaluated the management and the research programs of the ASRC based on the explanatory documents prepared by the ASRC and the oral presentations with questions-and-answers by the Director and the research group leaders. This report summarizes the result of the assessment by the Committee with the Committee report attached from page 7.
Ishigami, Tsutomu; Mukai, Masayuki; Sukegawa, Takenori; Matsubara, Takeshi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-023, 83 Pages, 2012/11
Verification for site release is one of procedures to confirm termination of decommissioning of nuclear installations. The verification procedure would need to confirm that the radioactive concentration at the site is lower than the criterion value by measurement. Then to efficiently perform the measurement and verification it is one of important issues how to efficiently estimate and evaluate overall spatial radioactivity distribution using a sampling method. For the efficient estimation and evaluation we have applied a Kriging technique which in the geostatistics, and have developed a computer program ESRAD (Estimation of Spatial RadioActivity Distribution). The ESRAD program is designed to support sample selection, calculate a variogram, and estimate a radioactivity distribution for the area concerned. This report describes the Kriging technique, structure and functions of ESRAD, input file format, output examples, execution procedure of ERSAR, and sample run with ESRAD.
Nagame, Yuichiro
JAEA-Review 2012-036, 27 Pages, 2012/10
The summaries of the 5 research projects conducted through the Reimei Research Program are published for the growth and development of the new researches.
Yamagishi, Hideshi*; To, Kentaro
JAEA-Research 2011-050, 16 Pages, 2012/10
For development of two-dimensional position sensitive (2-D) neutron detectors with fast response and high spatial resolution, an ASIC with fast response and low noise performances is required. The MP8 and MP16, consisting of p-MOSFETs, with high g and low noise have been proposed (1) to develop the ASIC. In this paper a simple low noise amplifier (LNA) was designed and the noise power and the noise figure were analytically calculated. The results were also applied to LNAs using MP8 or MP16 configuration. The results showed that the MP8 and MP16 had enough performances for the ASIC.
and low noise have been proposed (1) to develop the ASIC. In this paper a simple low noise amplifier (LNA) was designed and the noise power and the noise figure were analytically calculated. The results were also applied to LNAs using MP8 or MP16 configuration. The results showed that the MP8 and MP16 had enough performances for the ASIC.
Kawahara, Hirotaka; Yamamoto, Masaya; Tomita, Etsuo; Takamatsu, Misao
JAEA-Technology 2012-030, 50 Pages, 2012/09
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, in-vessel observation results showed that 6 pins which were connected between the handling head and the wrapper tube joint of the instrumented test subassembly (MARICO-2) were disconnected. Therefore, in order to confirm whether the disconnected 6 pins will influence reactor's safety or not, loose parts behavior in the reactor vessel was evaluated.
Kanazawa, Yusaku; Abiko, Shosuke; Terada, Hideyuki; Kawasaki, Ichio; Isozaki, Norio; Matsumoto, Takenari
JAEA-Technology 2012-029, 82 Pages, 2012/09
Water Supply Facility (WSF) is the facility that products and feed water for Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), Plutonium Fuel Production Facility (PFPF), etc. The kinds of feeding water are drinking water and industrial water that are used for life and operation of TRP, etc. WSF had been constructed in 1958, then it has been operated to 2008. It was received the water from AKOGI pond, then the water was conditioned and fed for many facilities. But it needed high cost for trouble and maintenance because of long-term use. Then new WSF was designed and constructed. The new design is that WSF accepts drinking water and industrial water from local governments; each receiving tank is constructed for new. And operating system and remote monitoring system are installed in WSF that is able to monitor from TUC. This report describes about various activities of the backgrounds, the design, the construction and a future action.
Nakayama, Masashi; Amano, Kenji; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Oyama, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Inagaki, Daisuke; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Kondo, Keiji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-035, 63 Pages, 2012/09
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project is planned to extend over a period 20 years. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction Phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase"(research in the underground facilities). This report summarizes the results of the investigations for the 2011 fiscal year (2011/2012). The investigations, which are composed of "Geoscientific research" and "R&D on geological disposal technology", were carried out according to "Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project Investigation Program for the 2011 Fiscal year". The results of these investigations, along with the results which were obtained in other departments of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), are properly offered to the implementations and the safety regulations. For the sake of this, JAEA has proceeded with the project in collaboration with experts from domestic and overseas research organisations.
Engineering Services Department
JAEA-Review 2012-034, 120 Pages, 2012/09
The Engineering Services Department is in charge of operation and maintenance of utility facilities (water distribution systems, electricity supply systems, steam generation systems and drain water systems etc.) in whole of the institute. And also is in charge of operation and maintenance of specific systems (a receive transmitted electricity system, an emergency electric power supply system, an air/liquid waste treatment system, a compressed air supply system) in nuclear reactor facilities, nuclear fuel treatment facilities and usual facilities or buildings. In addition, the department is in charge of maintenance of buildings, design and repair of electrical/mechanical/glass made experimental equipments and operation of the large scale experiment facilities. This annual report describes summary of activities, operation and maintenance data and technical developments of the department carried out in JFY 2010. In addition the activities of measure of the East Japan Great Earthquake Disaster that occurred on March 11 has been written. We hope that this report may help to future work.
Saito, Kosuke; Nogami, Yoshitaka; Kodato, Kazuo; Matsuyama, Kazutomi; Endo, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2012-027, 118 Pages, 2012/09
This report is compilation of 4 years tests and experiments of simulated alpha-ray irradiation on diverse materials for glove box application at Plutonium Fuel Development Center, Tokai, JAEA. Specimens prepared from the materials are irradiated with  He
He ion beam whose kinetic energy was 5 MeV and sent to exterior observation, optical microscopy and tensile tests. Experiments revealed ion-irradiation generally makes tens of micrometers of deteriorated layer which is hardened and discolored on the surface of the specimens. According to dose, tensile properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break decrease generally. Tensile strength decrease is expected to ascribe to stress concentration on cracks of irradiation-damaged surface and rupture. Lead-contained glove, which is ordinarily used on highly
ion beam whose kinetic energy was 5 MeV and sent to exterior observation, optical microscopy and tensile tests. Experiments revealed ion-irradiation generally makes tens of micrometers of deteriorated layer which is hardened and discolored on the surface of the specimens. According to dose, tensile properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break decrease generally. Tensile strength decrease is expected to ascribe to stress concentration on cracks of irradiation-damaged surface and rupture. Lead-contained glove, which is ordinarily used on highly  -radiative environments, saturates the decrease of its tensile strength around fluence of 1.4e+14 cm
-radiative environments, saturates the decrease of its tensile strength around fluence of 1.4e+14 cm . In addition, deterioration was accelerated for tension-loaded material and the saturation is around 4.6e+13 cm
. In addition, deterioration was accelerated for tension-loaded material and the saturation is around 4.6e+13 cm for 100%-extended specimens. The candidates of alternative new materials are two kinds of developed chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) and conductive rubber, which were experimented and tested in like manner. From the results and inherent properties of these materials, one kind of CSM and conductive rubber are relatively promising. Gloves used at low-dose environments and vinyl chloride applied for glove ports were also experimented and tested, and quantitative data were which are useful for life-elongation measure obtained. The irradiation tests on this report are unprecedented ones with low-energy ion, and the obtained quantitative data of material properties and deterioration are scientifically rare and important.
for 100%-extended specimens. The candidates of alternative new materials are two kinds of developed chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) and conductive rubber, which were experimented and tested in like manner. From the results and inherent properties of these materials, one kind of CSM and conductive rubber are relatively promising. Gloves used at low-dose environments and vinyl chloride applied for glove ports were also experimented and tested, and quantitative data were which are useful for life-elongation measure obtained. The irradiation tests on this report are unprecedented ones with low-energy ion, and the obtained quantitative data of material properties and deterioration are scientifically rare and important.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
JAEA-Research 2012-026, 25 Pages, 2012/09
Boiling events of reprocessed liquid wastes are postulated to be occurred caused by the loss of cooling function persisting over a long period of time at a fuel reprocessing plant. Some amounts of radioactive materials could be released from facilities caused by vapor flow from a boiling liquid waste storage tank. Thermal-hydraulic behaviors in compartments of facility building are essential to be analyzed for assessing amount of released radioactive materials. MELCOR, which has been developed for severe accident analysis of nuclear reactors, has been applied in this study. Functional features of Control Functions and Time-Specified Volumes in MELCOR have been used to model key phenomena such as, boiling at higher temperature than water boiling point, vaporization of nitric acid and generation of non-condensable gases due to denitrating reaction. Results of analysis demonstrate applicability of MELCOR to those events.
Sanada, Masanori; Kishi, Hirokazu*; Sugita, Yutaka; Hayashi, Katsuhiko*; Takebe, Atsuji*; Okubo, Seisuke*
JAEA-Research 2012-025, 130 Pages, 2012/09
In this study, strength recovery, generalized stress relaxation and two tensile strength tests were carried out using shale sampled in the Wakkanai-formation. As the results, by using the value of a suitable constant with the constitutive equation showing strength recovery, it was showed that change of the axial stress in a compacting test could be expressed. About the generalized relaxation, it examined by the air dried and the saturated condition. Visco-elastic behavior was more remarkable in saturated condition than the air dried. Moreover, when the loading rate up to the starting point of the generalized relaxation test was large, the influence on visco-elastic behavior was remarkable. About tensile characteristics, a splitting tensile strength test and a uniaxial tensile strength test were carried out. About splitting tensile strength, it turned out that the influence of the loading direction on a bedding plane is great.
Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yamada, Kunimi; Kusano, Tomohiro; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Takatori, Ryoichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-024, 132 Pages, 2012/09
This annual report documents the progress of R&D in the 2nd fiscal year during the JAEA 2nd Midterm Plan (FY 2010 - 2014) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planed framework is structured into the following categories: (1) development and systematization of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application and verification of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Komatsu, Mitsuru*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Seno, Shoji*; Hirata, Yoichi*; Takenobu, Kazuyoshi*; Tagishi, Hirotaka*; Kunimaru, Takanori; Maekawa, Keisuke; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Toida, Masaru*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-001, 77 Pages, 2012/09
This research focused on methods of estimating the amounts of groundwater recharge, which are normally required as upper boundary conditions in groundwater flow analyses, based on measurements of infiltrating water in the ground, to systematize the methods and establish systems which are stable and measurable on site over a long time. Regarding developing measurement systems, fiber-optic strain measurement methods that enable multiple-point and long-distance measurement were used for measuring three quantities: suction pressure, soil moisture and volumetric water content rate obtained by applying water absorption swelling material, and each measurement was discussed. The results showed that the fiber-optic soil aquameter has two types of practical application: one for measuring suction pressure (Type I), and the other for measuring volumetric water content rate obtained by applying water absorption swelling material (Type III). Furthermore, by using measurement instruments in actual fields, the validity of the two methods for estimating the rainfall infiltration capacities of shallow-layer soils, that is, estimating the capacities either directly by measurements of soil water or from unsaturated hydraulic conductivities, was confirmed.
Yano, Yasuhide; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Tanno, Takashi; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Koyama, Shinichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-022, 51 Pages, 2012/09
It is necessary to develop core materials for fast reactors in order to achieve high-burnup. Ferritic steels are expected to be good candidate core materials to achieve this objective because of their excellent void swelling resistance. Therefore, oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel and 11Cr-ferritic/martensitic steel (PNC-FMS) have been respectively developed for cladding and wrapper tube materials in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In this study, various physical properties of PNC-FMS wrapper materials were measured and equations and future standard measurement technique of physical properties for the design and evaluation were conducted.
Takeyasu, Masanori; Onuma, Toshimitsu; Sumiya, Shuichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-021, 29 Pages, 2012/09
A computer code, ORION-WIN, has been developed to estimate environmental concentration and radiation dose to public due to airborne discharge of radioactive materials from multiple sources of nuclear fuel cycle facilities. The modified Gaussian plume model is applied to calculate atmospheric dispersion of the discharged radioactive material. The plume depletion processes such as gravitational settling, dry deposition, precipitation scavenging and radioactive decay are considered. Inhalation and oral intake are considered as internal pathways, and submersion in the radioactive cloud and external exposure to contaminated ground surface are considered as external pathways, respectively. Radiation dose to an individual is calculated. ORION-WIN is an updated version of ORION-II and runs on PC mounting Windows OS, and has a graphical user interface for inputting the parameters and referring output files.
Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Onoe, Hironori; Saegusa, Hiromitsu
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-020, 44 Pages, 2012/09
This report summarize the results of the single borehole hydraulic tests of 79 sections conducted as part of the Construction phase (Phase 2) in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project. The details of each test (test interval depth, geology, etc.) as well as the interpreted hydraulic parameters and analytical method used are presented in this report.
Inagaki, Daisuke; Sawada, Sumiyuki; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Amano, Yuki; Niinuma, Hiroaki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-019, 137 Pages, 2012/09
In the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project, construction of the ventilation shaft, the east shaft and the drifts has been conducted as a phase 2 research. In the research, observation of the lithofacies and fracture, and in-situ tests, simple elastic wave exploration, schmidt hammer test, equotip test, point load test are conducted in each face, and measuring instruments such as extensometer, rock-bolt axial force meter, shotcrete stress meter and tunnel lining concrete stress meter are installed in particular face. In addition, for the purpose of the validation of the results of predictive analysis, conducted in phase 1, about the amount of spring water during construction of underground facilities, data on the changes of amount of spring water and water quality is obtained. This report summarizes the measurements data acquired at the east shaft (GL-210 m - 250 m) and the 250 m Gallery.
Nishihara, Kenji; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Suyama, Kenya
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-018, 190 Pages, 2012/09
This document describes the analytical results of the amount of the radioactive nuclides in the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on March 31, 2011 and the following period with the use of the ORIGEN2 code. The results are given for the irradiated uranium pellet and the cladding tube of zirconium alloy in the core and the spent fuel storage pools of the respective reactors. The evaluated values are weight, radioactivity, heat generation, photon generation and neutron generation rate.
Kusano, Tomohiro; Asamori, Koichi; Umeda, Koji
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-017, 19 Pages, 2012/09
We constructed "Helium Isotopic Database in Japan", which includes isotope ratios of noble gases and chemical compositions of gas samples collected from hot springs and water wells. The helium isotopes are excellent natural tracers for indicating the presence of mantle derived volatiles, because they are chemically inert and thus conserved in crustal rock-water systems. It is common knowledge that mantle degassing does not occur homogeneously over the Earth's surface. The  He/
He/ He ratios higher than the typical crustal values are interpreted to indicate that transfer of mantle volatiles into the crust by processes or mechanisms such as magmatic intrusion, faulting. In particular the spatial variation of helium isotope ratios could provide a valuable information to identify volcanic regions and tectonically active areas. The database was compiled geochemical data of groundwater from 108 published papers. As a result of the data compiling, the database has 1728 Helium isotopic data.
He ratios higher than the typical crustal values are interpreted to indicate that transfer of mantle volatiles into the crust by processes or mechanisms such as magmatic intrusion, faulting. In particular the spatial variation of helium isotope ratios could provide a valuable information to identify volcanic regions and tectonically active areas. The database was compiled geochemical data of groundwater from 108 published papers. As a result of the data compiling, the database has 1728 Helium isotopic data.
Takeda, Masaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-016, 39 Pages, 2012/09
At the Tono Geoscientific Research Unit, the subsurface water balance observation has been carried out in order to estimate groundwater recharge rate for setting the upper boundary conditions on groundwater flow simulation and to obtain data for the calibration of the hydrogeological model. In the subsurface water balance observations, meteorological data, river flow rate, groundwater level and soil moisture to estimate precipitation and evapotranspiration have been observed in the Shoba river area, the Shoba river model area and MIU Construction Site. After missed data and data error in the monitoring data from the fiscal year 2009 were complemented or corrected, the data was compiled in data set. Both of the observation data and compiled data are included in the data set, and the data set is recorded on DVD-ROM.
Takeda, Masaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-015, 19 Pages, 2012/09
At the Tono Geoscientific Research Unit, the subsurface water balance observation has been carried out in order to estimate groundwater recharge rate for setting the upper boundary conditions on groundwater flow simulation and to obtain data for the calibration of the hydrogeological model. In the subsurface water balance observations, rainfall data and river flow rate have been observed in the Garaishi river area and the Hiyoshi river area. The missed data and data error in the monitoring data from the fiscal year 2009 were complemented or corrected, and these data were compiled in data set. Both of the observation data and compiled data are included in the data set, and the data set is recorded on DVD-ROM.
Imaizumi, Kazuyuki; Saito, Takakazu; Tobita, Shigeharu; Nagai, Akinori; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Okazaki, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2012-027, 49 Pages, 2012/08
In-Vessel Observations (IVO) techniques for Sodium cooled Fast Reactors (SFRs) are important in confirming its safety and integrity. In order to secure the reliability of IVO techniques, it was necessary to demonstrate the performance under the actual reactor environment with high temperature, high radiation dose and remained sodium. During the investigation of an incident occurred in Joyo, the following observation systems were specifically developed for Joyo. And the following two observations were conducted. (1) Simple overhead observation using a standard video camera for the top of the sub-assemblies and the in-vessel storage rack (2) Narrow space observation using remote handling device equipped with radiation-resistant fiberscope for the bottom face of the upper core structure. As a result, the observations under the actual reactor environment were successfully made even in the narrow space in the reactor vessel and the results provided useful information on incident investigations and planning of restoration work.
Shinohara, Masanori; Motegi, Toshihiro; Saito, Kenji; Takada, Shoji; Ishimi, Akihiro; Katsuyama, Kozo
JAEA-Technology 2012-026, 21 Pages, 2012/08
An event, in which one of WRMs were disabled to detect the neutron flux in the reactor core, occurred during the period of reactor shut down of HTTR in March, 2010. The actual life time of WRM was unexpectedly shorter than the past developed life time. Investigation of the cause of the outage of WRM toward the recovery of the life time up to the past developed life is one of the issues to develop the technology basis of HTGR. Then, two experimental investigations were carried out to reveal the cause of the outage by specifying the damaged part causing the event in the WRM. The one is a post irradiation examination using the X-ray computed tomography scanner in Fuels Monitoring Facility (FMF) to specify the damaged part in the WRM. The other is an experiment using a mock-up simulating the WRM fabricated by the fabricator. This report summarized the results of the PIE and the experimental investigation using the mock-up to reveal the cause of outage of WRM.
Shinohara, Masanori; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Kawamoto, Taiki; Motegi, Toshihiro; Saito, Kenji; Takada, Shoji; Yoshida, Naoaki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Katsuyama, Kozo
JAEA-Technology 2012-025, 31 Pages, 2012/08
An event, in which one of WRMs were disabled to detect the neutron flux in the reactor core, occurred during the period of reactor shut down of HTTR in March, 2010. The actual life time of WRM was unexpectedly shorter than the past developed life time. Investigation of the cause of the outage of WRM toward the recovery of the life time up to the developed life is one of the issues to develop the technology basis of High Temperature Gas cooled Reactor (HTGR). Then, a post irradiation examination was planned to specify the damaged part causing the event in the WRM was also planned. For the investigation, the X-ray computed tomography scanner in Fuels Monitoring Facility (FMF). This report describes the preliminary investigation on the cause of outage of the WRM. The results of study for transportation method of the irradiated WRM from HTTR to FMF is also reported with the record to complete the transport operation.
Zaima, Naoki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Kado, Kazumi
JAEA-Technology 2012-023, 36 Pages, 2012/08
We developed uranium mass assay systems for 200-litter wastes drums applied neutron and  measurements by NDA method. In this report we will describe measurement experiences followed by the previous report. The systems are composed of the 16 pieces of helium-3 (
measurements by NDA method. In this report we will describe measurement experiences followed by the previous report. The systems are composed of the 16 pieces of helium-3 ( He) proportional counters for neutron detection. The neutron measurement methodology is consist of
He) proportional counters for neutron detection. The neutron measurement methodology is consist of  U (
U ( ,n)F reaction and spontaneous fission of
,n)F reaction and spontaneous fission of  U. The extensive test trials using the known amount of uranium with different enrichment and some kinds of matrices in drums were performed. By using this NWAS we tried to determine uranium mass in the actual uranium wastes drums stored in the URCP at Ningyo-toge. The actual uranium wastes drums are of great variety, in the point of matrix, bulk density, packing condition and total uranium mass. Therefore we have tried some challenging methods which eliminate problems, and established the applicability to almost all kinds of wastes drums.
U. The extensive test trials using the known amount of uranium with different enrichment and some kinds of matrices in drums were performed. By using this NWAS we tried to determine uranium mass in the actual uranium wastes drums stored in the URCP at Ningyo-toge. The actual uranium wastes drums are of great variety, in the point of matrix, bulk density, packing condition and total uranium mass. Therefore we have tried some challenging methods which eliminate problems, and established the applicability to almost all kinds of wastes drums.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Okamoto, Akiko; Ikeda, Takeshi; Tamura, Kenichi; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Abe, Minako; Sato, Sohei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-033, 70 Pages, 2012/08
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, etc., by the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. NEAT of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies with the National Government and local governments emergency equipment and materials. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for emergency response organizations at normal time. Concerning the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its the utmost effort. This annual report summarized these activities of NEAT in the fiscal year 2011.
Fast Breeder Reactor Research and Development Center, Tsuruga Head Office
JAEA-Review 2012-032, 187 Pages, 2012/08
FBR Monju has been accumulated technological achievements, for our country of FBR cycle technology, through the experience of daily operation, maintenance, etc.
Research Cooperation Section
JAEA-Review 2012-031, 139 Pages, 2012/08
This report includes a summary of the results of the research carried out in fiscal year 2011 on 27 research collaboration subjects for preceding basic engineering research related to fast breeder reactors, the nuclear fuel cycle, radiation safety and geological disposal/geoscience.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Kodama, Katsuaki
JAEA-Review 2012-029, 264 Pages, 2012/08
Characteristic technologies, instruments, and distinguished researches of each institute about "Superconductivity, Magnetism and Phonon" are introduced and discussed on the basis of "Joint Research Agreement for the Pioneering R&D with Quantum Beam Technology" concluded by NIMS, RIKEN and JAEA in addition to research outcomes of this Joint Research Agreement including a future prospect of this research area. This report includes abstracts and materials of the presentations in the workshop.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kuboshima, Koji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Mizuno, Takashi; Sato, Toshinori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-028, 31 Pages, 2012/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase and the Operation Phase. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2012 fiscal year based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010, construction plan and research collaboration plan, etc.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Oshima, Takeshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2012-027, 46 Pages, 2012/08
The research on cable degradation mechanisms was conducted for 5 years in 2006 - 2010 as the project research of plant life management for nuclear power plant by NISA (Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency) of METI (Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry). At the finish of above research, the degradation mechanisms were reviewed on the analysis of many reports on cable degradation. The reports published after 1970 were mainly surveyed and the facts or data containing the experimental accuracy were selected. The verified facts, the reasonable interpretation of the facts, unresolved aspects were checked on the view points of recent techniques or analysis, and proposed the new model of degradation mechanisms was proposed.
Geoscience Facility Construction Section, Tono Geoscience Center
JAEA-Review 2012-026, 252 Pages, 2012/08
This progress report presents an outline compilation of construction activities, primary tasks performed, construction progress and problems reported from fiscal year 2002 to fiscal year 2005 (including a part fiscal year 2006). The outline of construction activities is a summary based on the scope of work planned. The main activities are based on the Tono Geoscience Center weekly reports. The construction progress is based on the planned and actual schedules and the Tono Geoscience Center weekly reports. The problems reported are based on accident reports, natural disasters, nonconformance and defects recorded by the Geoscience Facility Construction Section. Plan and actual performance of the MIU construction project No.1 (completion on June 30, 2006) are described in this report.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sawada, Sumiyuki; Sato, Haruo; Sugita, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2012-023, 65 Pages, 2012/08
In Japan, any high-level radioactive waste repository is to be constructed at over 300m depth below surface. Tunnel support is used for safety during the construction and operation, and shotcrete and concrete lining are used as the tunnel support. Concrete is a composite material comprised of aggregate, cement and various additives. Low alkaline cement has been developed for the long term stability of the barrier systems whose performance could be negatively affected by highly alkaline conditions arising due to cement used in a repository. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC (Highly fly-ash contained silicafume cement), containing over 60wt% of silica-fume (SF) and coal ash (FA). JAEA is presently constructing an underground research laboratory (URL) at Horonobe for research and development in the geosciences and repository engineering technology. HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete material in construction of part of the 140m deep gallery in Horonobe URL in 2010. The objective of this experiment was to assess the performance of HFSC shotcrete in terms of mechanics, workability, durability, and so on. HFSC used in this experiment is composed of 40wt% OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement), 20wt% SF, and 40wt% FA. This composition was determined based on mechanical testing of various mixes of the above components. Because of the low OPC content, the strength of HFSC tends to be lower than that of OPC in normal concrete. The total length of tunnel constructed using HFSC shotcrete is about 53m. The workability of HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by this experimental construction. In this report, we present detailed results of the  construction test.
construction test.
Ando, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Onoe, Hironori
JAEA-Research 2012-022, 60 Pages, 2012/08
In this study, water conducting features in Toki granite were defined by the interpretation and integration of geological and hydrogeological data obtained from the borehole investigation in the Phase I of the MIU Project and Regional Hydrogeological Study. Then, the hydrogeological model of Block scale was constructed using hydraulic discrete fracture networks, and equivalent hydraulic conductivities in Block scale were calculated. And, adequacy of equivalent hydraulic conductivities in Block scale was confirmed using result of hydraulic packer tests.
Morihira, Masayuki
JAEA-Research 2012-021, 25 Pages, 2012/08
Cladding inner corrosion is one of the life control factors of FBR MOX fuels. Because excess oxygen during fission brings the corrosion, oxygen getter option was proposed and a feasibility study has been conducted. In the previous study, an option was proposed to locate getter titanium in the lower end of the upper axial blanket region of a fuel element. Also the titanium roll pellet method was proposed to reduce the smear density of the getter titanium to absorb the swelling during the oxidation. In this study, producibility of titanium roll pellets and their oxidation behavior were evaluated.
Satoh, Daiki; Kojima, Kensuke; Oizumi, Akito; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kugo, Teruhiko; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Endo, Akira; Okajima, Shigeaki
JAEA-Research 2012-020, 97 Pages, 2012/08
A computer software, named CDE (Calculation system for Decontamination Effect), has been developed to support planning the decontamination. CDE calculates the dose rates before the decontamination by using a database of dose contributions by radioactive cesium. The decontamination factor is utilized in the prediction of the dose rates after the decontamination, and dose rate reduction factor is evaluated to express the decontamination effect. The results are visualized on the image of a target zone with color map. In this paper, the overview of the software and the dose calculation method are reported. The comparison with the calculation results by a three-dimensional radiation transport code PHITS is also presented. In addition, the source code of the dose calculation program and user's manual of CDE are attached as appendices.
Fukushima Environmental Safety Center, Headquarters of Fukushima Partnership Operations; Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center; Fuel Cycle Safety Research Unit, Nuclear Safety Research Center; Geological Isolation Research Unit, Geological Isolation Research and Development Directorate; Nuclear Cycle Backend Directorate
JAEA-Research 2012-019, 125 Pages, 2012/08
Measures against environmental contamination by radioactive materials originated from the Fukushima nuclear accident (May, 2011), are being conducted in Fukushima and surrounding prefectures. Regarding to the measures, a phytoremediation experiment with several types of lawn grasses in a field scale have been carried out. Lawn grasses are generally characterized by shallow rizosphere, high density and root mat formation. Decontamination effectiveness of radioactive cesium by plant uptake and by sod removing was investigated. As a result, the range of decontamination factors by plant uptake was below than 1% because of low transfer rate form soil to plant. On the other hand, maximum decontamination factor by sod removing reached about 100%. Decontamination activities with various methods will be implemented according to the national decontamination policy and related plans in each municipality. The phytoremediation method with lawn grass would be applicable in limited circumstances.
Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki
JAEA-Research 2011-053, 41 Pages, 2012/08
To understand the migration phenomenon of radionuclide, actual migration data are experimentally acquired by a batch test, a column test and field trial. In the present study, experimental models about the interactions of radionuclide between the solid phase and the liquid phase were discussed systematically to interpret the migration data acquired by the various techniques and conditions. Equilibrium, reversibility, linearity, mechanism and chemistry in the interactions were considered in discussion of the experimental models. A calculation program, which can analyze migration data obtained under various conditions by applying the selected 9 types of experimental models, was maintained. The calculation program makes it be able to predict the migration behavior of radionuclide under various conditions and to decide the important parameter by a fitting analysis of the migration data.
Namekawa, Masakazu; Fukahori, Tokio
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-014, 206 Pages, 2012/08
Several numerical data (mass, level energy, spin and parity, abundance, mass excess, beta-decay energy, and half-life) of nuclides were collected with each element into the "Tables of Nuclear Data (JENDL/TND-2012)." These tables are related to the "Chart of the Nuclides" published by Japanese Nuclear Data Committee and Nuclear Data Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), and data of the nuclides synthesized in the chart. Moreover, new determinations are adopted instead of the values in ENSDF for half-lives of ground state of Se-79 and Sn-126.
Ichikawa, Shoichi; Haga, Hiroyuki; Katsuyama, Kozo; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Maeda, Koji; Nishinoiri, Kenji
JAEA-Testing 2012-001, 36 Pages, 2012/07
The life of FBR (Fast Breeder Reactor) fuel assembly is restricted by BDI (Bundle-Duct Interaction). Therefore, it is very important to carry out the out pile bundle compressive tests which can imitate BDI, in order to evaluate BDI behavior. The target of the conventional BDI behavior was thin pins ( 6.5 mm) for fuel pellets which were used with the assembly of Monju (the Monju prototype fast breeder reactor) etc. Furthermore by an upgraded Monju core and a demonstration core, adoption of thick pins for the holler annular pellets is planned. Therefore, it was necessary to carry out BDI evaluation of a thick pin. Then, the plans for out of pile bundle compressive test for large diameter pins were are reported this time.
6.5 mm) for fuel pellets which were used with the assembly of Monju (the Monju prototype fast breeder reactor) etc. Furthermore by an upgraded Monju core and a demonstration core, adoption of thick pins for the holler annular pellets is planned. Therefore, it was necessary to carry out BDI evaluation of a thick pin. Then, the plans for out of pile bundle compressive test for large diameter pins were are reported this time.
Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Yasuda, Ryo; Takano, Takao; Seko, Noriaki; Naganawa, Hirochika; Kuroki, Ryota; Saegusa, Jun
JAEA-Testing 2011-007, 189 Pages, 2012/07
Because of TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, a huge amount of radioactive materials was widely dispersed and precipitated into the environment. Swimming pools in Fukushima prefectures were contaminated with the radioactives. We JAEA carried out several demonstration tests to decontaminate the radioactives and discharge the pool water safely. We concluded the results obtained from the tests as "Guide for decontaminating swimming pool at school" and released it quickly. Following this, we also released the guide in English. This manuscript, as an experimental report of the swimming pool water decontamination, is consisted from the guide in Japanese and English prepared.
Policy Planning and Administration Department; Nuclear Cycle Backend Directorate
JAEA-Technology 2012-028, 71 Pages, 2012/07
In the second medium term (2010-2015) plans of JAEA, effective and reasonable medium and long term plan for decommissioning of nuclear facility and treatment and disposal of low level radioactive waste in JAEA, based on the premise of safety assurance, is to be formulated by the end of March, 2012. This medium and long term plan is the plan targeting the period over next ten years based on the prospect of the long term waste management from waste generation to waste disposal, and is mainly referred to decommissioning, clearance, waste treatment, waste storage and R&D works. JAEA will be carried out practical work for treatment and disposal of the radioactive waste based on this plan, and also the updating of this plan will be made flexibly according to consideration situation of new framework for nuclear energy policy by the Atomic Energy Commission, technology advance and progress situation of laws and regulations.
 reflector and proton beam window
reflector and proton beam windowTeshigawara, Makoto; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakui, Takashi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Seki, Masakazu; Harada, Masahide; Ito, Manabu; Suzuki, Toru; Ikezaki, Kiyomi; Maekawa, Fujio; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-024, 303 Pages, 2012/07
3 GeV Protons with 1 MW beam power are irradiated to mercury target of spallation neutron source in Materials and Life science Facility (MLF), which is one of facilities of J-PARC. Irradiated components, such as target container, moderator, reflector and proton beam window, are needed to replace periodically due to irradiation damage of high energy protons and neutrons. These used components are replaced remotely because of highly activated. Maintenance scenario was settled so as to handle these components. Required remote handling machines were designed and installed in hot cell and other room of the MLF. We performed remote handling tests by using actual components to confirm the design. We report results, such as replacement procedure, trouble and its solution, etc., for moderator, reflector and proton beam window in order to provide the handling of actual used components.
Honda, Junichi; Matsui, Hiroki; Harada, Akio; Obata, Hiroki; Tomita, Takeshi
JAEA-Technology 2012-022, 35 Pages, 2012/07
The advanced utilization of Light Water Reactor (LWR) fuel is progressed in Japan to save the power generating cost and the volume of nuclear wastes. The electric power companies have been continued the approach to extend the burnup and to rise up the thermal power of the commercial fuel. The government should be accumulating the detailed information of the newest technologies to make the regulations and guidelines for the safety of the advanced nuclear fuels. The remote controlled Electron Prove Micro Analyzer attached with crystal orientation analyzer (EPMA) has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to evaluate the fuel behavior effected by the cladding microstructure under the accident condition. The device was modified to the airtight and earthquake resistant structure for the examination of high radioactive elements. This paper describes the specification of EPMA and the test results of the cold mock-up to confirm their performances and reliabilities.
Honda, Junichi; Matsui, Hiroki; Harada, Akio; Obata, Hiroki; Tomita, Takeshi
JAEA-Technology 2012-021, 17 Pages, 2012/07
The advanced utilization of Light Water Reactor (LWR) fuel is progressed in Japan to save the power generating cost and the volume of nuclear wastes. The electric power companies have been continued the approach to extend the burnup and to rise up the thermal power of the commercial fuel. The government should be accumulating the detailed information of the newest technologies to make the regulations and guidelines for the safety of the advanced nuclear fuels. The ion milling for post irradiation examination has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to investigate cladding microstructure. This device has been modified to operate the high radioactive elements remotely and have the performance of earthquake resistant. This paper describes the specification of the device which were specialized for post irradiation examination and the test results of the cold mock-up to confirm their performances and reliabilities.
Takamatsu, Misao; Kobayashi, Tetsuhiko; Nagai, Akinori
JAEA-Technology 2012-020, 60 Pages, 2012/07
With the incident as an opportunity, repair techniques for upper core structure (UCS) replacement was developed in Joyo. Since UCS of Joyo was designed as an eternal structure and it has high radioactivity due to the irradiation for over 30 years, (1) Prevention of deformation during UCS jack-up and retrieval, (2) Reducing UCS cask weight were mainly discussed in this study as critical tasks. UCS replacement is scheduled in 2014. Achievement of UCS replacement and accumulated experience will be able to provide valuable insights for further improving and verifying repair techniques in SFRs.
Ijiri, Yuji*; Noda, Masaru*; Sasakura, Takeshi*; Nobuto, Jun*; Matsui, Hiroya; Mikake, Shinichiro; Hashizume, Shigeru
JAEA-Technology 2012-018, 288 Pages, 2012/07
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory plan consists of (1) research on engineering technology at a deep underground, and (2) research on engineering technology as a basis of geological disposal. The former research mainly aimed in this study are categorized in (a) development of design and construction planning technologies, (b) development of construction technology, (c) development of countermeasure technology, (d) development of technology for security. In this study, the researches on engineering technology are proceeded in these four categories by using data measured down to GL-300m during construction as a part of the second phase of the MIU plan.
 ) Method; March 9-10, 2012, Yurakucho Asahi Hall, Tokyo, Japan
) Method; March 9-10, 2012, Yurakucho Asahi Hall, Tokyo, JapanIshitsuka, Etsuo; Ishihara, Masahiro; Suzuki, Masahide
JAEA-Review 2012-030, 247 Pages, 2012/07
This report summarizes the documents presented in the Specialist Meeting on  Mo Production by (n,
Mo Production by (n, ) Method, which was held on March 9 to 10, 2012, at the Yurakucho Asahi Hall in Tokyo, hosted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The objective of the meeting is to exchange the information of current status, future plan for the
) Method, which was held on March 9 to 10, 2012, at the Yurakucho Asahi Hall in Tokyo, hosted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The objective of the meeting is to exchange the information of current status, future plan for the  Mo production, and to make a discussion of "How to cooperate" in each research and test reactors. There were 27 participants from Poland, Kazakhstan, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Netherlands, Korea and Japan. As a result of this meeting, it was recognized that to push forward the development of
Mo production, and to make a discussion of "How to cooperate" in each research and test reactors. There were 27 participants from Poland, Kazakhstan, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Netherlands, Korea and Japan. As a result of this meeting, it was recognized that to push forward the development of  Mo production by (n,
Mo production by (n, ) method is necessary for the future steady supply of
) method is necessary for the future steady supply of  Mo. Moreover, an irradiation test using the high density MoO
Mo. Moreover, an irradiation test using the high density MoO pellet developed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency was proposed from a viewpoint of a merit for the common irradiation target in each research and test reactors.
pellet developed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency was proposed from a viewpoint of a merit for the common irradiation target in each research and test reactors.
Kutsuna, Hideki; Otani, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Yasuyuki
JAEA-Review 2012-025, 30 Pages, 2012/07
Fugen Nuclear Power Plant was reorganized to Fugen Decommissioning Engineering Center and started dismantling removal work of the facilities on February 12, 2008. In planning and carrying out our decommissioning technical development, "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning", which consists of the members well-informed, is established, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened inside and outside the country, as the central point in the energy research and development base making project of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report compiles presentation materials "Current Situation of Fugen Decommissioning", "Basic Test for Making Waste Body for Spent Resin disposal", "Current Status and Future Plan on Laser Cutting Method", presented in the 25th Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning which was held on March 16, 2012.
Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yamada, Kunimi; Kusano, Tomohiro; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Takatori, Ryoichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji
JAEA-Review 2012-024, 44 Pages, 2012/07
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2012. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2012 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planed framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2012-022, 208 Pages, 2012/07
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Coordination Office and seven departments such as Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities, Department of Criticality and Fuel Cycle Research Facilities, Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and Engineering Services Department. This annual report of JFY 2009 & JFY 2010 summarizes the activities of NSRI, the R&D activities of the Research and Development Directorates and human resources development at site, and is expected to be referred to and utilized by R&D departments and project promotion sectors at NSRI site for the enhancement of their own research and management activities to attain their goals according to "Middle-term Plan" successfully and effectively.
 Y extracted from high radioactive liquid waste in spent-fuel reprocessing
Y extracted from high radioactive liquid waste in spent-fuel reprocessingHosoma, Takashi
JAEA-Review 2012-008, 83 Pages, 2012/07
Pharmaceuticals and medical devices containing radioactive  Y are realized, approved and placed on the international market where three products are available in Europe and the United States, and one product in Japan. These products are used not for diagnosis but for treatment by internal irradiation. It was estimated from the deliberative report of the approval in Japan that
Y are realized, approved and placed on the international market where three products are available in Europe and the United States, and one product in Japan. These products are used not for diagnosis but for treatment by internal irradiation. It was estimated from the deliberative report of the approval in Japan that  Y was extracted in Europe from high radioactive liquid waste (HALW) yielded in spent fuel reprocessing. In this report, products placed on the market and physical properties were reviewed, reasons of the realization and conditions to realize succeeding products were estimated, extraction method was compared with other methods, technical subjects, and relevant regulations were investigated. Although a medical device containing radioactive
Y was extracted in Europe from high radioactive liquid waste (HALW) yielded in spent fuel reprocessing. In this report, products placed on the market and physical properties were reviewed, reasons of the realization and conditions to realize succeeding products were estimated, extraction method was compared with other methods, technical subjects, and relevant regulations were investigated. Although a medical device containing radioactive  Y has been studied in Japan and one pharmaceutical product was approved, a breakthrough would be necessary to put
Y has been studied in Japan and one pharmaceutical product was approved, a breakthrough would be necessary to put  Y utilization beyond alternative treatments. The breakthrough would become be promising; for example, if conventional treatments could be supported by technical development to deliver
Y utilization beyond alternative treatments. The breakthrough would become be promising; for example, if conventional treatments could be supported by technical development to deliver  Y more sharply to the target with shorter serum half-life. Extraction of
Y more sharply to the target with shorter serum half-life. Extraction of  Y nuclide from HALW has advantages over thermal neutron irradiation of natural nuclide, a system is envisioned where
Y nuclide from HALW has advantages over thermal neutron irradiation of natural nuclide, a system is envisioned where  Sr as a parent nuclide is separated in the reprocessing then transported to and stored in a factory of radiopharmaceuticals followed by
Sr as a parent nuclide is separated in the reprocessing then transported to and stored in a factory of radiopharmaceuticals followed by  Y extraction on demand.
Y extraction on demand.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kurihara, Arata*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji
JAEA-Research 2012-018, 48 Pages, 2012/07
This document presents about updating of geological models at the Phase 2 in the Mizunami underground research laboratory project. In the phase 2, the geological models has been updated four times (Shaft180 geological model, Pilot500 geological model, Sustage200 geological model, Stage300 geological model) based on geological mapping date and/or some borehole investigation data at the shafts and research galleries. These geological models represent distributions of lithofacies and/or geological structures based on each geological investigation. In order to evaluate relationship between understanding of geological environments and progress of investigations, to organize the history of geological models updating is important.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Emonot, P.*
JAEA-Research 2012-017, 97 Pages, 2012/07
A quantitative evaluation on thermal striping is of importance for reactor safety. In this study, sodium and water experiments of parallel triple jets configuration were performed. For these experiments, numerical simulations were carried out to evaluate the transfer characteristics of temperature fluctuation from fluid to structure. The analysis code, called Trio-U, used in the study has been developed at the CEA in France. In the simulations, the calculated time-averaged temperature distributions in fluid and structure were close to the experimental results in sodium and water. The power spectrum densities of temperature fluctuation in fluid and structure were also in good agreements between the experiments and calculations. Furthermore the calculated decay characteristics of temperature fluctuation from fluid to structure were in good agreements with the experimental results.
Tanaka, Masaru*; Gofuku, Akio*; Ishizaka, Kaoru*; Sato, Kazuhiko; Nagahama, Yoji
JAEA-Research 2012-016, 23 Pages, 2012/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Okayama University, Tottori University of Environmental Studies and Research Institute of Solid Waste Management Engineering had been conducting a research on risk perception and confidence-building among stakeholders regarding environmental remediation of Uranium mine site and disposal of industrial waste. Cognitive structure of public on safety for wide area disposal of disaster waste which had been generated from Iwate and Miyagi prefectures after the Great East Japan Earthquake would be important from a view of our research. Therefore, a questionnaire survey on public risk perception of the disposal of disaster waste for residents in Okayama prefecture has been carried out. The results are; (1) 93% of respondents support the local government cooperation for the disposal, (2) 87% of respondents support the acceptance and the disposal in their home town, and (3) 70% of respondents were concerned about radioactive contamination caused by the disposal.
Yamada, Satoshi*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu
JAEA-Research 2012-015, 32 Pages, 2012/07
Tottori University and Japan Atomic Energy Agency started a joint study to develop an environmental remediation technique for agricultural soil. Nine plants were water-cultured and examined for screening. A few were selected as candidates for demonstrations in fields. Preselected plants were mainly halophytes. Easily cultivated and harvested plants without harmful effect on new agriculture were also considered. Seedings prepared were first grown for a certain term. Additive-free,  Cs and
Cs and  Sr groups, which are both stable isotopes, were then made. Stems, leaves and roots were harvested, in principle, two weeks after the addition, to measure K, Ca, Mg, Sr and Cs concentrations in them. It was concluded that New Zealand spinach and ice plant were most adequate for removing contaminants from surface soil. The two accumulate Cs and Sr mostly in the shoots, are prostrate, and spread the roots shallowly. For valid application, growth-phase dependences of absorption and distribution, growth property and root distribution should be elucidated. Finally, the application study plan was developed based on screening test results.
Sr groups, which are both stable isotopes, were then made. Stems, leaves and roots were harvested, in principle, two weeks after the addition, to measure K, Ca, Mg, Sr and Cs concentrations in them. It was concluded that New Zealand spinach and ice plant were most adequate for removing contaminants from surface soil. The two accumulate Cs and Sr mostly in the shoots, are prostrate, and spread the roots shallowly. For valid application, growth-phase dependences of absorption and distribution, growth property and root distribution should be elucidated. Finally, the application study plan was developed based on screening test results.
Kobayashi, Jun; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Tobita, Akira; Kamide, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2012-014, 40 Pages, 2012/07
As the temperatures difference between the control rod channels and the core fuel subassemblies is around 100  C centigrade, temperature fluctuation due to the fluid mixing at the core outlet may cause high cycle thermal fatigue at the bottom of upper internal structure (UIS) in JSFR. Then, a water experiment was conducted using an 1/3 scale 60
C centigrade, temperature fluctuation due to the fluid mixing at the core outlet may cause high cycle thermal fatigue at the bottom of upper internal structure (UIS) in JSFR. Then, a water experiment was conducted using an 1/3 scale 60  sector model. As a result, thermal striping phenomena in the region between the fuel subassembly outlet and the bottom of the UIS were grasped. The modified geometry of the UIS bottom and the handling head of the primary CR channel was created so as to suppress the cold jets from the CR channels. The comparison of measured temperature fluctuations around the CR channels revealed that the modified geometry was effective to decrease the temperature fluctuation intensity and amplitude in the sensitive frequency band to the stress conversion.
sector model. As a result, thermal striping phenomena in the region between the fuel subassembly outlet and the bottom of the UIS were grasped. The modified geometry of the UIS bottom and the handling head of the primary CR channel was created so as to suppress the cold jets from the CR channels. The comparison of measured temperature fluctuations around the CR channels revealed that the modified geometry was effective to decrease the temperature fluctuation intensity and amplitude in the sensitive frequency band to the stress conversion.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Ishikawa, Makoto; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Iwai, Takehiko*; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Hazama, Taira; Chiba, Go*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Kugo, Teruhiko
JAEA-Research 2012-013, 411 Pages, 2012/07
Aiming at evaluating the core design prediction accuracy of fast reactors, various kinds of fast reactor core experiments/tests have been analyzed with the Japan's latest evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. Totally 643 characteristics of reactor physics experiments/tests and irradiation tests performed using the critical facilities: ZPPR, FCA, ZEBRA, BFS, MASURCA, ultra-small cores of LANL and power plants: SEFOR, Joyo, Monju were dealt. In analyses, a standard scheme/method for fast reactor cores was applied including detailed or precise calculations for best estimation. In addition, results of analyses were investigated from the viewpoints of uncertainties caused by experiment/test, analytical modeling and cross-section data in order to synthetically evaluate the consistency among different cores and characteristics. Further, by utilizing these evaluations, prediction accuracy of core characteristics were evaluated for fast power reactor cores that are under designing in the fast reactor cycle technology development (FaCT) project.
Kosaka, Hiroshi; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Kurihara, Arata*; Onoe, Hironori
JAEA-Research 2012-012, 100 Pages, 2012/07
In this study, groundwater flow and particle tracking simulations using hydrogeological models have been carried out in order to evaluate the relationship between understanding of groundwater flow characteristics and the amount of information that is increased by the progress of investigations. The influences of difference of the method for interpretation of hydrogeology have been also evaluated. As a result, uncertainties of the groundwater flow characteristics were decreased by increasing the amount of information. It was also found that the distribution of large-scale discrete features and the heterogeneity of groundwater flow characteristics affect the groundwater flow characteristics. Furthermore, the method to identify the target of further investigation and to make plan for the investigation were proposed.
Sasao, Eiji
JAEA-Research 2012-011, 147 Pages, 2012/07
Dose assessment associated with closure activity of the Tono Mine has been performed. Localities for dose evaluation are selected at the Higashihoragawa and Hiyoshigawa. Evaluation scenarios are classified into the base and alternative scenarios. Parameters are set-up based on the existing data. But the range and uncertainty of parameters are considered in the alternative cases. Maximum exposure doses of the base and alternative scenarios are 0.08 mSv/year, and 0.09 mSv/year including direct and skyshine  rays and exposure of exhalated radon at the Higashihoragawa. On the alternative cases, exposure doses are calculated as 0.05-0.14 mSv/year in the base and alternative scenarios. At the Hiyoshigawa, maximum exposure dose is less than 0.001 mSv/year for the base scenario, and 0.001 mSv/year for the alternative scenario. On the alternative cases, maximum exposure doses are less than 0.001 mSv/year for the base scenario and 0.0006-0.002 mSv/year for the alternative scenario.
rays and exposure of exhalated radon at the Higashihoragawa. On the alternative cases, exposure doses are calculated as 0.05-0.14 mSv/year in the base and alternative scenarios. At the Hiyoshigawa, maximum exposure dose is less than 0.001 mSv/year for the base scenario, and 0.001 mSv/year for the alternative scenario. On the alternative cases, maximum exposure doses are less than 0.001 mSv/year for the base scenario and 0.0006-0.002 mSv/year for the alternative scenario.
Hasegawa, Ken; Kunitomo, Takahiro; Hashizume, Shigeru; Horiuchi, Yasuharu; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Evaluation 2012-001, 117 Pages, 2012/07
ACROSS has been developed to acquire the detailed information on the tectonically active zone. The technology developed here, the transmission and reception technique, the data analysis and the interpretation technique of the ACROSS signal for example, is able to use in seismology but also in other fields. We considered the ACROSS technology may apply to the engineering technology of the MIU project, for example, to the geological environment monitoring around the shafts and the strength assessment of the shaft concrete lining. Its examination was made in the three years period from fiscal year 2007 to 2009. However, it was concluded that we required another two years of observation to evaluate the applicability of the ACROSS as a technology to monitor the geological environment around the shafts and research galleries. In this report, we describe the evaluation result of the ACROSS based on the data observed by the end of 2011.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Morikawa, Keita; Tachi, Yukio; Kuno, Yoshio*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Shimoda, Satoko*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ikuse, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Masako*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-013, 96 Pages, 2012/07
For the purpose to understand the relationship between characteristic of mass transport and characteristic of fracture, the following experiments were carried out using core sample, which was sampled from the -300 m Stage. This paper compiled the results of these experiment. (1) Diffusion experiments of Cs, Sr, I and uranin in granite samples (2) Sorption experiments of Cs and Sr on crushed granite (3) Measurement of pore physicality by Mercury Intrusion and water saturation
Suzuki, Motoe; Saito, Hiroaki*; Udagawa, Yutaka; Nagase, Fumihisa
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-012, 374 Pages, 2012/07
A light water reactor fuel analysis code FEMAXI-7 has been developed for the purpose of analyzing the fuel behavior in normal conditions and in anticipated transient conditions. Numerous functional improvements and extensions have been incorporated in FEMAXI-7, which has been fully disclosed in the code model description published recently as JAEA-Data/Code 2010-035. The present manual, which is the counterpart of this description, gives detailed explanations of operation method of FEMAXI-7 code and its related codes, methods of input/output, methods of source code modification, features of subroutine modules, and internal variables in a specific manner in order to facilitate users to perform a fuel analysis with FEMAXI-7.
Takeyasu, Masanori; Onuma, Toshimitsu; Sumiya, Shuichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-011, 28 Pages, 2012/07
A computer code, ORION-WIN, has been developed to estimate environmental concentration and radiation dose to the public due to the airborne release of radioactive materials from multiple sources of nuclear fuel cycle facilities. The modified Gaussian plume model is applied to calculate atmospheric dispersion of the released radioactive material. The plume depletion processes such as gravitational settling, dry deposition, precipitation scavenging and radioactive decay are considered, and re-suspension from the ground and the produce of progeny from the parent radionuclides are also considered. Inhalation and oral intake are considered as internal pathways, and submersion in the radioactive cloud and external exposure to contaminated ground surface are considered as external pathways, respectively. Radiation dose to an individual is calculated.
Kawamoto, Koji; Kuboshima, Koji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Sasao, Eiji; Ikeda, Koki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Hara, Ikuo; Yamamoto, Masaru
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-009, 47 Pages, 2012/07
This document presents the data of geological investigations in the shafts and research galleries to the depth of 300 m of the MIU from the 2004 fiscal year to the 2008 fiscal year. In the shafts and research galleries of the MIU, the Cretaceous Toki granite is unconformably overlain by the generally flat lying Miocene Mizunami Group (younging upwards from the Toki Lignite-bearing Formation to the Hongo and Akeyo Formations) with a depth of about 166 m to 168 m.
Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Kawamoto, Koji; Kuboshima, Koji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Sasao, Eiji; Ikeda, Koki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Hara, Ikuo; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-008, 136 Pages, 2012/07
This report compiles data of results from borehole investigations which has been carried out research gallery of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) in the fiscal year from 2005 to 2011. These data include results of core observation, geophysical logging, and so on.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-006, 65 Pages, 2012/07
We additionally selected thermodynamic data for solid and gaseous phases of nickel, selenium, zirconium, technetium, thorium, uranium, neptunium, plutonium and americium to our thermodynamic database JAEA-TDB for geological disposal of radioactive waste of high-level and TRU wastes. We thermodynamically obtained equilibrium constant from addition and subtraction of Gibbs free energy of formation, which were selected in the thermochemical database project by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Furthermore, we collected and updated thermodynamic data on iodine, changed master species of technetium(IV), and added thermodynamic data on selenium due to improving reliability of the thermodynamic database. We prepared text files of the updated thermodynamic database (JAEA-TDB) for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC, EQ3/6 and Geochemist's Workbench. These text files are contained in the attached CD-ROM and will be available on our Website.
Karino, Tomoyuki; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-002, 110 Pages, 2012/07
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III), with a total duration of 20 years. The main goals of the MIU Project from Phase I through to Phase III are: to establish techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment, and to develop a range of engineering for deep underground application. Currently, the project is being carried out under the Phase II. One of the Phase II goals is set to develop and revise models of the geological environment using the investigation results obtained during excavation, and determine and assess the changes in the geological environment in response to excavation. The long term hydro-pressure monitoring has been continued to achieve the Phase II goals. This paper describes the results of the long term hydro-pressure monitoring from April, 2010 to March, 2011.
Karino, Tomoyuki; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-001, 54 Pages, 2012/07
Tono Regional Hydrogeological Study (RHS) Project is a one of the geoscientific research programme at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC). This project started since April, 1992 and main investigations were finished to March 2004. Since 2005, hydrogeological and hydrochemical monitoring are continued by the existing monitoring system. This paper describes the results of the long term hydro-pressure monitoring from April, 2010 to March, 2011.
Harada, Hideo; Yokoyama, Kenji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Shoji; Koura, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Conf 2012-001, 200 Pages, 2012/07
The 2011 data symposium on nuclear data, organized by the Nuclear Data Division of Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) was held at Ricotti, Tokai, on Nov.16 and 17, 2011 in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate of JAEA and North-Kanto Branch of AESJ. The symposium was devoted for discussions and presentations of current topics in the field of nuclear data such as nuclear accident and accident analysis code, innovative methods on nuclear data theory and measurements, and nuclear data applications, including 2 tutorial talks, NJOY99 and PHITS. Talks as well as posters presented at the symposium aroused lively discussions among 97 participants. This report contains 34 papers submitted from the oral and poster presenters.
Hirayama, Takashi; Kannari, Masaaki; Sato, Tomohiko
JAEA-Testing 2012-002, 29 Pages, 2012/06
In pursuance of "The Optimization Plan on the network of JAEA", which aims to ensure network reliability and information security and to improve convenience in using the network, we are engaged in the optimization of inter-institute/center network bandwidth. This is a record of an introduction of WAN accelerator into the network to Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center which bandwidth is limited due to a geographically constraint.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Sato, Hiroyuki; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Technology 2012-019, 142 Pages, 2012/06
JAEA has started the conceptual designs of small-sized HTGR systems, aiming for the deployment in developing countries. The small-sized HTGR systems can provide power generation by steam turbine, high temperature steam for industry process and/or low temperature steam for district heating. As one of the conceptual designs in the first stage, the core thermal and hydraulic design of a power generation and steam supply small-sized HTGR with a thermal power of 50 MW (HTR50S) was carried out. HTR50S in the first stage has the same coated particle fuel as HTTR. The purpose of the design is to make sure that the maximum fuel temperature in normal operation doesn't exceed the design target. Following the design, safety analysis assuming a depressurization accident was carried out. The fuel temperature in the normal operation and the fuel and reactor pressure vessel temperatures in the depressurization accident were evaluated. As a result, it was cleared that the thermal integrity of the fuel and the reactor coolant pressure boundary is not damaged.
Goto, Minoru; Seki, Yasuyoshi; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Fukaya, Yuji; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Technology 2012-017, 29 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has started a conceptual design of a small-sized HTGR with 50 MW thermal power (HTR50S), which is a first-of-a-kind commercial or demonstration plant of a small-sized HTGR to be deployed in developing countries in the 2020s. The nuclear of the HTR50S was performed by upgrading the proven technology of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to reduce cost for the construction. In the nuclear design, reduce the number of fuel enrichment comparing with the HTTR is one of the important subject to be upgraded. The optimization of the power distribution in the core, which is required to suppress the maximum fuel temperature below the limitation, was completed successfully by using only three fuel enrichment and the number of fuel enrichment was reduced significantly compared with the HTTR.
Imamoto, Nobuo; Koiso, Keiichi
JAEA-Technology 2012-016, 27 Pages, 2012/06
The shaking table tests have been employed to evaluate the seismic fragilities of the machine-electric equipments. Through the shaking table test, in ordinarily it is depending on resonance frequency, repetitive adjustments are needed to search a normal/malfunction boundary. However, a small relay used for the electric panel and the control system, can not be measured the resonance frequency because the acceleration sensor installation affects the vibration characteristic of the test body. And more, the moving parts leading to a relay malfunction is settled in the case, it can not be carried out direct measurement of the vibration. To improve the shaking table test methods, magnetization current perturbation method was invented and developed. Instead the mechanical shaking force, magnetization current perturbation method employs vibrating electromagnet force. Moreover, obtained impedance characteristic curve, the resonance frequency can be obtained by fitting to a theoretical curve. This paper deals with the principle of the magnetization current perturbation method, theoretical derivation of impedance, measurement electronics circuit, and system design and test results.
Uesaka, Takahiro; Kozawa, Masachiyo; Matsumoto, Junko; Endo, Masayuki; Kinoshita, Junichi; Suzuki, Takeshi; Suzuki, Hisao; Morishita, Satoru; Sakamoto, Yu
JAEA-Technology 2012-015, 29 Pages, 2012/06
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Nuclear Science Research Institute waste treatment building No.2 treat intermediate-level solid waste. Solid wastes are reduced in volume by compaction. They are then canned in stainless can, which are subsequently put in 200-liter concrete-lined drums or 1-m concrete containers, filled with concrete. To prepare for disposal in future, be able to make fit with the technical standard of waste package, we were asked to change the lid type shielded container. Therefore due to the change of lid type shielded container, we confirmed integrity of it with evaluation of close volt by drop analysis, evaluation of shielding, and drop test with a prototype model.
concrete containers, filled with concrete. To prepare for disposal in future, be able to make fit with the technical standard of waste package, we were asked to change the lid type shielded container. Therefore due to the change of lid type shielded container, we confirmed integrity of it with evaluation of close volt by drop analysis, evaluation of shielding, and drop test with a prototype model.
Hara, Hironori; Amazawa, Hiroya; Sakai, Akihiro; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2012-014, 49 Pages, 2012/06
Low level radioactive waste which is included high concentrated nitrate are planned to be disposed into concrete pit facility. From the point of view of environmental effect by easily soluble nitrate ion into groundwater, the safety assessment will be needed for the concrete pit type disposal facilities. In this study, the nitrate ion concentration in groundwater, lake and stream nearby the concrete pit type disposal facilities was simulated by advective-diffusion analysis. From the results of analysis, the limitation of amount of nitrate in the waste package was estimated from the environmental standard determined by Basic Environment Law.
Mizukoshi, Yasutaka; Yasu, Tetsunori
JAEA-Technology 2012-013, 26 Pages, 2012/06
The Materials Monitoring Facility is equipped with an exhaust stack to emit air from a controlled area (the hot laboratory) into the atmosphere. Cracks and exfoliation have been observed for the surface of the exhaust stack, which is made of reinforced concrete and was constructed on the seacoast about 25 years ago, so exposed to a salt-corrosive condition. In order to get details of the present condition of the exhaust stack, an inspection was carried out using an electromagnetic wave radar method and chloride content method. Cracks and exfoliation were observed for the whole stack surface, especially for high positions. Moreover, salt damage was observed for the outer surface of the exhaust stack, and it was estimated that the infiltration of the chloride content was about 17 mm. Based on this detailed inspection of the exhaust stack, maintenance and repair work were carried out.
Kimura, Nobuaki; Imaizumi, Tomomi; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Tanimoto, Masataka; Saito, Takashi; Hori, Naohiko; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Romanova, N. K.*; Gizatulin, S.*; Martyushov, A.*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-012, 34 Pages, 2012/06
Si semiconductor production by Neutron Transmutation Doping (NTD) method using the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has been investigated in Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in order to expand industry use. As a part of investigations, irradiation test of silicon ingot for development of NTD-Si with high quality was planned using WWR-K in Institute of Nuclear Physics (INP), National Nuclear Center of Republic of Kazakhstan (NNC-RK) based on one of specific topics of cooperation (STC), Irradiation Technology for NTD-Si (STC No.II-4), on the implementing arrangement between NNC-RK and the JAEA for "Nuclear Technology on Testing/Research Reactors" in cooperation in research and development in nuclear energy and technology. As for the irradiation test, Si rotating device was fabricated in JAEA, and the fabricated device was transported with irradiation specimens from JAEA to INP-NNC-RK. This report described the design, the fabrication, the performance test of the Si rotating device and transportation procedures.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sawada, Sumiyuki
JAEA-Review 2012-023, 24 Pages, 2012/06
As part of the research and development program on geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW), the Horonobe Underground Research Center, a division of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), is implementing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Horonobe URL Project) with the aim at investigating sedimentary rock formations. According to the research plan described in the 2nd Midterm Plan of JAEA, geological investigations are to be carried out during the drilling of a shaft down to around 350 m depth, while research and development in the areas of engineering technology and safety assessment are to be promoted by collaboration with other research organizations. The results of the R&D activities will be systematized as a "knowledge base" that supports a wide range of arguments related to the safety of geological disposal. The Horonobe URL Project is planned to extend over a period of about 20 years. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). This report summarizes the investigation program for the 2012 fiscal year (2012/2013). In the 2012 fiscal year, investigations in "geoscientific research", including "development of techniques for investigating the geological environment", "development of engineering techniques for use in the deep underground environment" and "studies on the long-term stability of the geological environment", are continuously carried out. Investigations in "research and development on geological disposal technology", including "improving the reliability of disposal technologies" and "enhancement of safety assessment methodologies", are also continuously carried out.
Tazaki, Makiko; Suda, Kazunori; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Kuno, Yusuke; Mochiji, Toshiro
JAEA-Review 2012-021, 83 Pages, 2012/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) held "2011 International Forum on the Peaceful Use of Nuclear Energy and Nuclear Security; Taking the lessons learned from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident to the 2012 Seoul Nuclear Security Summit" on 8 and 9 December, 2011. It intended to articulate effective strategies and measures for strengthening nuclear security using lessons learned from the Fukushima nuclear accident. Moreover, it was expected to explore comprehensive approaches which could contribute to enhancing both nuclear safety and security in order to support sustainable and appropriate development of the peaceful use of nuclear energy. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summary of panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-020, 178 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II. And Phase III started in 2010 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2010, as a part of the Phase II based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002.
Hanakawa, Hiroki
JAEA-Review 2012-018, 51 Pages, 2012/06
Halden Boiling Water Reactor (HBWR) in Norway, which is operated by IFE, is the one of the best research reactor for nuclear fuel and material testing in the world. The irradiation test in nuclear fuel and materials has been carried out since the first criticality in 1959. Recent joint program tests are summarized based on open literatures.
Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Review 2012-017, 61 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency at Tono Geoscience Center is carrying out geoscientific research in the crystalline rock environment at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, in order to establish the scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. The geoscientific research at the MIU is being carried out in three overlapping phases; the Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), the Construction Phase (Phase II) and the Operation Phase (Phase III). This report presents the following FY2010 activities. (1)  Stress Measurements using Core-based Methods on the -300 m Stage, (2) Determining the rock properties using waste rock from exacavation of the ventilation shaft, (3) Development of rock mechanical model (4) Study on the modeling based on equivalent continuum model, (5) Phenomenological study on long-term behavior, (6) Theoretical study for estimating long-term behavior, (7) Example overseas research for planning of
Stress Measurements using Core-based Methods on the -300 m Stage, (2) Determining the rock properties using waste rock from exacavation of the ventilation shaft, (3) Development of rock mechanical model (4) Study on the modeling based on equivalent continuum model, (5) Phenomenological study on long-term behavior, (6) Theoretical study for estimating long-term behavior, (7) Example overseas research for planning of  experiments in Phase III, (8) Application of specific energy for evaluation of
experiments in Phase III, (8) Application of specific energy for evaluation of  rock mass properties, (9) Study on estimation of
rock mass properties, (9) Study on estimation of  rock stress with results of various measurements
rock stress with results of various measurements
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Oda, Chie; Hirano, Fumio; Ichige, Satoru; Kurimoto, Yoshitaka; Hoshino, Seiichi; Akagi, Yosuke; Sato, Nobuyuki; Takahashi, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-010, 80 Pages, 2012/06
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H22 (2010) Japanese fiscal year and their products during the last 5 years. These include (1) evaluation of long-term mechanical stability in the near-field including development of a creep mode of rock and analyses of mechanical behavior of TRU waste repository, (2) performance assessment of the disposal system including cementitious material alteration, bentonite and hostrock alteration with alkaline solution and nitrate effect, and (3) alternative technology development including decomposition of nitrate.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Kaji, Naoya; Nomura, Kazunori
JAEA-Research 2012-009, 15 Pages, 2012/06
In terms of preventing the formation of Pu and Cs compound, Cs in the feed solution should decrease in the U crystallization process. In order to separate Cs contained within irradiated nuclear fuel, the immersion experiments were carried out with the pure water and diluted HNO solution. The elusion ratio of Cs within the powdered fuel in the pure water and 0.1 mol/dm
solution. The elusion ratio of Cs within the powdered fuel in the pure water and 0.1 mol/dm HNO
HNO solution after 67 h was 33.8 and 38.3%, respectively. The experimental results suggest a possible beneficial effect of Cs elusion by immersion of the powdered fuel in the pure water and diluted HNO
solution after 67 h was 33.8 and 38.3%, respectively. The experimental results suggest a possible beneficial effect of Cs elusion by immersion of the powdered fuel in the pure water and diluted HNO solution before the fuel dissolution process.
solution before the fuel dissolution process.
Daimaru, Shuji; Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Research 2012-008, 70 Pages, 2012/06
JAEA is performing the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project. Currently, the project is under Phase II and Phase III. As part of Phase II, the borehole investigation (10MI22, 10MI23) was conducted at 100m Measurement Niche in -300m Access/Research Gallery in 2010. As a result of long-term pumping test, completely different pressures due to the pumping test were observed in monitoring boreholes on opposite sides of the Main-shaft fault. This observation indicates that the normal direction of the Main-shaft fault is low permeable. And, the Main-shaft fault acts as a flow barrier normal to the fault plane. As a result of hydraulic test, permeability of fracture zone with accompanying host rock zone was from 9.4E-7m/s to 3.8E-11m/s. And, this zone was classified as two sections, permeability of the section is same as the upper highly fractured domain (UHFD :1.0E-7m/s) and the section of its permeability is 4 order lower than UHFD.
Tokuyasu, Shingo; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hodotsuka, Yasuyuki*
JAEA-Research 2012-007, 55 Pages, 2012/06
During drilling the pilot boring in October 2008 before construction of -300 m Access/Research Gallery, groundwater inflow more than 1,000 L/min is induced, and original signals of SP monitoring are observed. First of all in this study, we thus assess the method of data processing to extract the applicable signal from SP monitoring, and the hydrogeological structure is estimated using the treated data. Secondly, the signals of SP monitoring observed between March and April in 2006 when pumping of groundwater from the shafts are applied to the same method of data processing mentioned above. In addition, the treated data is used to estimate the hydrogeological structures more in detail. Considering all results together, the applicability of SP monitoring for estimating the distributions of major water-conducting features and faults with low permeability is discussed. As the result of this study, we conclude that it is likely that the hydrogeological structures would be estimated using the SP monitoring.
Hagiwara, Hiroki; Shingu, Shinya; Kurita, Kazuaki*; Eguchi, Keita*; Horita, Masakuni*; Mizuno, Takashi
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-005, 67 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been carried out investigations to understand the fluctuation of groundwater chemistry related to the shafts excavation at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in Mizunami City, Gifu prefecture, Japan. The data for pore water pressure, water temperature and groundwater chemistry have been provided from two surface-based boreholes, MSB-2 and MSB-4 boreholes, installed a modular multilevel groundwater monitoring system (MP system). The monitoring has been conducted once in a month since April 2003. According to the results, the shaft excavation has caused drawdown of the hydraulic head and change in the groundwater chemistry in the MIU construction site. In this report, the data of monitoring at the MSB-2 and the MSB-4 boreholes from April 2010 to March 2011 were compiled. In addition, the monitoring results at the DH-2 borehole as part of Regional Hydrogeological Study project, are summarized as an appendix.
Mizuno, Takashi; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Amano, Yuki; Hama, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-004, 30 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been carried out investigations to understand the fluctuation of groundwater chemistry related to the shafts excavation at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) in Mizunami City, Gifu prefecture, Japan. We compiled data of pore water pressure, water temperature and groundwater chemistry obtained from two surface-based boreholes, MSB-2 and MSB-4 boreholes, installed a MP system (Westbay Instruments Inc.) from April 2003. Groundwater sampling and measurements of pore water pressure and water temperature have been conducted once in a month. In this report, the data of groundwater chemistry and pore water pressure obtained from these two boreholes are summarized for sharing and for avoiding the scattering the data.
Shingu, Shinya; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Masuda, Kaoru*; Iizuka, Masatoshi*; Inui, Michiharu*; Mizuno, Takashi
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-003, 50 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigated the groundwater chemistry on excavating the underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project at Mizunami City, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. This report compiles data set of the groundwater chemistry obtained at MIU in the fiscal year 2010. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling date, sampling method, analytical method) and methodology for quality control is described.
Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Ono, Masato; Yanagi, Shunki; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2012-010, 24 Pages, 2012/05
It is necessary to confirm that the temperature of water cooling panel of the vessel cooling system (VCS) is controlled under the allowable working temperature during the safety demonstration test because the water cooling panel temperature rises due to stop of cooling water circulation pumps. Therefore, several temporary thermocouples are relocated to the side cooling panel outlet ring header of VCS and the water cooling panel near the stabilizers of RPV in order to observe the temperature change of VCS. The relocated thermocouples can measure the temperature change with starting of the water circulation pumps of VCS. So it is confirmed that the relocated thermocouples can observe the VCS temperature change in the safety demonstration test.
Naito, Hiroyuki; Itagaki, Wataru; Okazaki, Yoshihiro; Imaizumi, Kazuyuki; Ito, Chikara; Nagai, Akinori; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Shamoto, Naoki*; Takeshima, Yoshiyuki*
JAEA-Technology 2012-009, 100 Pages, 2012/05
The radiation characteristics of image fiber and light guide fiber were evaluated to develop a high radiation resistant fiberscope for the fast reactor in-vessel observation. It is known that a pure silica core fiber has a high radiation resistance and radiation resistance is influenced with impurities in silica. Moreover it is necessary to change the clad material of the light guide fiber because that of the current light guide fiber is acrylate, which is weak against radiation. Hence the improved fibers consist of a pure silica core with 1,000 ppm OH and fluorine-doped silica clad. As a result of a  irradiation test, we confirm that OH inhibits the generation of the precursor by
irradiation test, we confirm that OH inhibits the generation of the precursor by  irradiation. About the clad material, we confirmed that the transmission loss of the fluorine-doped silica clad fiber is smaller than that of the acrylate clad fiber. About the mechanical strength of a fiber, we confirmed that there is no weakening the strength of the fiber and no exfoliation of the coating from the glass. In this study, we discovered the fiber which consists of a pure silica core with 1,000 ppm OH and fluorine-doped silica clad has a high radiation resistance and it is possible to observe using this fiber under the 200
irradiation. About the clad material, we confirmed that the transmission loss of the fluorine-doped silica clad fiber is smaller than that of the acrylate clad fiber. About the mechanical strength of a fiber, we confirmed that there is no weakening the strength of the fiber and no exfoliation of the coating from the glass. In this study, we discovered the fiber which consists of a pure silica core with 1,000 ppm OH and fluorine-doped silica clad has a high radiation resistance and it is possible to observe using this fiber under the 200  C after 5
C after 5 10
10 Gy irradiation.
Gy irradiation.
Inoue, Shuichi; Omuro, Tadao; Nabeya, Hideaki; Matsui, Yoshinori; Iida, Kazuhiro; Ito, Kazuyuki; Kimura, Akihiro; Kanno, Masaru
JAEA-Technology 2010-010, 27 Pages, 2012/05
In fuel irradiation transient tests using a boiling water capsule, a dilution tube has been installed in the boiling water capsule in order to detect fission products (FP) from an irradiated fuel, in case of the fuel failure during the transient, by a radiation monitor located outside the reactor. When the fuel failure occurs, the released FP flows out from the capsule through the dilution tube. The dilution tube is designed to minimize the released FP that can be detected by the radiation monitor located outside the reactor. This report summarized the measurement results of the dilution tube installed in the boiling water capsule.
Mine and Laboratories Section, Tono Geoscience Center
JAEA-Review 2012-016, 196 Pages, 2012/05
The technical committee was organized for examination of validity of the dose assessment associated with closure activity of the Tono Mine in FY2010. This report summaries the material presented and minutes at each meeting.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; Kokubun, Yuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-015, 166 Pages, 2012/05
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2010 to March 2011. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on Tokyo Electric Power Co. in 2011 March. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data exceeded the normal range of fluctuation by the accidental release was evaluated in the appendices.
Asano, Norikazu; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Kusunoki, Hidehiko; Sato, Shinichi
JAEA-Review 2012-014, 37 Pages, 2012/05
In the refurbishment of JMTR, facilities were classified into which (1) were all updated, (2) were partly updated, and (3) were continuance used by the considerations of the maintenance history, the change parts availability and the latest technology. The JMTR pure water facility was classified into all updated facility based on the consideration. The Update construction was conducted in between FY2007 and FY2008. The refurbishment of JMTR pure water facility is summarized in this report.
Sato, Isamu; Arima, Tatsumi*; Nishina, Masahiro*; Tanaka, Kosuke; Onose, Shoji; Idemitsu, Kazuya*
JAEA-Research 2012-006, 66 Pages, 2012/05
As one of the important properties for fuel manufacturability and burning behavior, the diffusion behavior of actinides in oxide fuels was investigated by both the experimental and the molecular dynamics simulation (MD). Using diffusion couples consisted of an Am containing mixed oxide fuel and a UO fuel, the diffusion tests were performed. The diffusion coefficients were estimated to be 10
fuel, the diffusion tests were performed. The diffusion coefficients were estimated to be 10 m
m /s
/s  10
10 m
m /s. In addition, the difference between Pu and Am diffusion coefficients was vanishingly small. The temperature dependence of bulk diffusion coefficients of actinides in mixed oxide fuels could be evaluated by MD. An evaluation technique for the grain boundary diffusion could be established based on the coincidence site lattice theory. The practical diffusion coefficients were obtained by combining data from the experiments with those predicted from MD. The practical diffusion coefficients obtained was discussed for use of a fuel behavior analysis code.
/s. In addition, the difference between Pu and Am diffusion coefficients was vanishingly small. The temperature dependence of bulk diffusion coefficients of actinides in mixed oxide fuels could be evaluated by MD. An evaluation technique for the grain boundary diffusion could be established based on the coincidence site lattice theory. The practical diffusion coefficients were obtained by combining data from the experiments with those predicted from MD. The practical diffusion coefficients obtained was discussed for use of a fuel behavior analysis code.
Ezure, Toshiki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Tobita, Akira; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Kamide, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2012-005, 56 Pages, 2012/05
In the design of JSFR, a two-loop cooling system and a compact reactor vessel are employed to achieve the economical improvement. However, these innovative designs lead to the increase of coolant velocity. As the results, strong vortices at the H/L intake may cause the cavitation (vortex cavitation). Therefore, the evaluation of occurrence behavior of vortex cavitation is the important issue for the structural integrity of reactor. In the present study, fundamental water experiments were performed in the cylindrical tank geometry. The water temperature was varied from 10 C to 80
C to 80 C to clarify the influence of kinematic viscosity,
C to clarify the influence of kinematic viscosity,  . The occurrences behaviors of vortex cavitation were evaluated quantitatively by visualization measurement and image analysis. As the results, it was clarified that there was little dependence on
. The occurrences behaviors of vortex cavitation were evaluated quantitatively by visualization measurement and image analysis. As the results, it was clarified that there was little dependence on  under the small
under the small  conditions, while it was relatively obvious under the large
conditions, while it was relatively obvious under the large  conditions.
conditions.
Okura, Takehisa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Taki, Mitsumasa; Shibanuma, Yukio; Kikuchi, Masamitsu; Akino, Hitoshi; Kikuta, Yasuaki; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Saegusa, Jun; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-010, 37 Pages, 2012/05
Due to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant caused by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake occurred at 11th March 2011, the emergency environmental radiation monitoring was conducted at Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). This report provides the monitoring results of ambient  -ray dose rate and atmospheric radioactivity concentration until the beginning of June 2011. Some anthropogenic radionuclides such as Cs-134, Cs-137, I-131, I-132, Te-132, Xe-133 and others were detected from air samples. The atmospheric radioactivity concentrations varied with some peaks corresponded with that of ambient
-ray dose rate and atmospheric radioactivity concentration until the beginning of June 2011. Some anthropogenic radionuclides such as Cs-134, Cs-137, I-131, I-132, Te-132, Xe-133 and others were detected from air samples. The atmospheric radioactivity concentrations varied with some peaks corresponded with that of ambient  -ray dose rate after 15th March 2011. Composition of each peak showed various characteristic. Internal exposure caused by inhalation was estimated from the observed atmospheric radioactivity.
-ray dose rate after 15th March 2011. Composition of each peak showed various characteristic. Internal exposure caused by inhalation was estimated from the observed atmospheric radioactivity.
Editorial Committee of Refining and Conversion Facility Decommissioning Results
JAEA-Technology 2012-005, 64 Pages, 2012/04
The Refining and Conversion Facility located in the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center had the natural uranium conversion process and reprocessed uranium conversion process. The construction of this facility was started in 1979 and completed in October 1981. Dismantling of equipments in radiation controlled area of this facility was started from 2008. Equipments in radiation controlled area (excluding ventilating equipment and liquid waste treatment equipment) will be dismantled by the 2011 fiscal year, and ventilating equipment and liquid waste treatment equipment will be dismantled by the 2014 fiscal year. This report describes the master plan of this decommissioning and shows as the progress in first half year of 2011FY, the actual time schedule, the method of decommissioning, the decommissioning progress appearance with photographs, work rates of each room / each worker class, and the quantity of dismantled materials and secondary wastes.
Tobita, Kenji
JAEA-Review 2012-009, 62 Pages, 2012/04
The JMTR refurbishment started from FY2007 had been completed on the end of the FY2010. The refurbishment works carried out on about 60 items nuclear reactor systems, about 40 of facilities and about 20 constructions with no trouble. This report review the basic policy of JMTR refurbishment, such as a selection of facilities/equipments for the refurbishment and the determination method of specifications for repairs. The deliberation and discussion by the safety review committee of Oarai Research and Development Center in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency and nuclear regulatory procedure are included in this report.
Shimo, Michito*; Kumamoto, So*; Kosaka, Hiroshi; Onoe, Hironori; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Mizuno, Takashi; Oyama, Takuya
JAEA-Research 2012-004, 126 Pages, 2012/04
One of the goals of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is to develop technical basis for investigation, analysis and evaluation technologies for understanding deep underground geological environment in various scales. Understanding groundwater flow system is one of the important issues in the project, and to achieve this purpose, technologies for a hydrogeological model and the groundwater flow simulation technique, have to be established. In this study, hydrogeological modeling and groundwater flow simulations have been carried out in order to predict hydraulic and geochemical impacts around the MIU Construction Site and inflow rate into the MIU facilities. As a result of this study, the significant hydrogeological structures could be estimated. The inflow rate into the MIU facilities and hydraulic and geochemical impacts with the MIU facilities construction could be predicted. The effect of pre-grouting to the MIU facilities could be also confirmed.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2012-003, 34 Pages, 2012/04
A rock mass is a complex entity, including several classes of discontinuities and numerous heterogeneous and anisotropic minerals. From investigations of rock samples, we know that crystalline rock is a complex mix of minerals, grain boundaries and microcracks. Deformation and failure mechanisms may be more completely understood if we are able to correctly characterize the microscale composition and grain boundary properties. Amongst the rock-forming minerals, especially quartz and biotite in granite, numerous microcracks are developed. It is important to study coupled mechanical and chemical factors in crystalline rock for long-term behavior study. This report presents the results of the following FY2010 activities. (1) Explanation of nonlinear fracture mechanics, (2) Pressure dissolution experiments of using specimens of single quartz, (3) Theory study on the rate of quartz dissolution, (4) Homogenization theory for fractured rock
Nakanishi, Yoshiki; Aoyama, Yoshio; Nonaka, Kazuharu; Sone, Tomoyuki; Nakazawa, Osamu; Tashiro, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Testing 2011-008, 31 Pages, 2012/03
Steam reforming technology has been developed to reduce the volume of liquid uranium waste such as a Tri-n-butyl phosphate adding n-dodecane solvent (TBP/nDD), which is difficult to incinerate. The localized corrosion like pitting corrosion occurred on the inner surface of the gasification chamber of the demonstration scale steam reforming system during the treatment of TBP/nDD. Therefore we conducted the corrosion tests to identify the form of corrosion. It is found that the form of corrosion is crevice corrosion which caused by the residues generated by treatment of TBP/nDD. The cathodic protection system using a galvanic anode was selected as the corrosion protection method of the gasification chamber. The continuous treatment test of TBP/nDD was conducted using the steam reforming system with the cathodic protection system. As a result, the crevice corrosion did not occur during 600 hours continuous treatment of TBP/nDD, and the effectiveness of the protection method was verified.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Oto, Tsutomu; Magome, Hirokatsu; Izumo, Hironobu; Hori, Naohiko
JAEA-Technology 2012-011, 53 Pages, 2012/03
A simulator of irradiation test reactors has been developed since JFY 2010 for understanding reactor behavior and for upskilling in order to utilize for a nuclear human resource development (HRD) and to promote partnership with developing countries which have a plan to introduce nuclear power plant. The simulator is designed based on the one of the irradiation test reactors, the JMTR, and it simulates operating, irradiation tests and various kinds of accidents caused in the reactor and the irradiation facility. The development of the simulator is sponsored by the Japanese government as one of the specialized projects of advanced research infrastructure in order to promote basic as well as applied researches. The training of operation using the simulator will be started for the nuclear HRD from JFY 2012. This report summarizes the result of the conceptual design of the simulator in JFY 2010.
Takahashi, Kiyoshi; Hanawa, Hiroshi; Onuma, Yuichi; Hosokawa, Jinsaku; Kanno, Masaru
JAEA-Technology 2012-007, 31 Pages, 2012/03
The Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), achieving first criticality in March 1968, has been used in testing the durability and integrity of reactor fuels and components, basic nuclear research, the production of radioisotopes, and other purposes. The JMTR, however, stopped in August 2006 after its 165th operation cycle, and is currently under going partial renewal of reactor facilities and installation of new irradiation facilities, geared toward being restarted in 2012. Now, the installation of two new irradiation facilities under the LWR irradiation environment were finished until 2011FY. One is a power ramping test facility of high-burnup fuel. Another one is a material irradiation facility for IASCC research under the LWR irradiation environment. And another irradiation facility (Hydraulic rabbit irradiation facility) maintenance is carried out on 2011FY. This report is described the installed new irradiation facilities and established irradiation facility until 2011FY in JMTR.
 Mo production in JMTR
Mo production in JMTRTakita, Kenji; Iimura, Koichi; Tomita, Kenji; Endo, Yasuichi; Kanno, Masaru
JAEA-Technology 2012-006, 41 Pages, 2012/03
At JAEA Oarai Research and Developnment Establishment (JAEA Oarai), JAEA Oarai was proceeding a plan to repair JMTR, which is to re-operate in fiscal 2012. Additionally, as an effective utilizati of JMTR, JAEA Oarai is planning to manufacture  Mo, which is a parent nuclide of
Mo, which is a parent nuclide of  Tc.
Tc.  Tc is most commonly used as a radiopharmaceution in the field of nuclear medicine. Currently
Tc is most commonly used as a radiopharmaceution in the field of nuclear medicine. Currently  Mo supply is dependent only on foreign imports, so JAEA is aiming for working on partially manufacturing
Mo supply is dependent only on foreign imports, so JAEA is aiming for working on partially manufacturing  Mo domestically with industrial circles in Japan. In this article, this report described the choice and fabric of irradiathion facility named Hydraulic Rabbit Facility for manufacturing
Mo domestically with industrial circles in Japan. In this article, this report described the choice and fabric of irradiathion facility named Hydraulic Rabbit Facility for manufacturing  Mo, the technical study of fabrication technique.
Mo, the technical study of fabrication technique.
Ono, Masato; Tochio, Daisuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Yanagi, Shunki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2012-004, 46 Pages, 2012/03
Tohoku-Pacific Ocean Earthquake occurred on March 11th 2011 and the earthquake intensity of an upper 5 on the Japanese scale was observed in Oarai town. HTTR conducted the confirmation test on cold state in order to ensure the facilities/instruments of reactor building operate normally. In this test, the plant data in the facilities/instruments start up phase and continue steady operation phase were measured and compared with the previous operation data, and the soundness of facilities/instruments is evaluated. As a result, the facilities/instruments operate normally and keep safety and performance of the HTTR were ensured. This paper reports the evaluation of the plant data.
Horiguchi, Hironori; Nakamura, Takemi; Motohashi, Jun; Kashimura, Takanori; Ichimura, Shigeju; Sasajima, Fumio
JAEA-Technology 2012-003, 38 Pages, 2012/03
Clinical trials of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for malignant brain tumors and head and neck cancers have been performed at the research reactor JRR-4. BNCT is a kind of radiation therapy using a nuclear reaction with thermal neutrons and boron ( B) elements administered to a patient. The design specifications of all types of reflector elements were changed due to a trouble of a reflector element in JRR-4. In the production of the new reflector elements, they were designed with the influence for the neutron beam facility by the analytical calculation. After the installation of the new reflector elements, the performance of the neutron beam facility was verified by measurement such as a free air experiment and a water phantom experiment. The calculation error used in the treatment planning for BNCT can be estimated by comparing the results of our calculation with the corresponding experimental data.
B) elements administered to a patient. The design specifications of all types of reflector elements were changed due to a trouble of a reflector element in JRR-4. In the production of the new reflector elements, they were designed with the influence for the neutron beam facility by the analytical calculation. After the installation of the new reflector elements, the performance of the neutron beam facility was verified by measurement such as a free air experiment and a water phantom experiment. The calculation error used in the treatment planning for BNCT can be estimated by comparing the results of our calculation with the corresponding experimental data.
Hanaki, Tatsumi; Nagasaki, Yasushi; Suzuki, Hajime
JAEA-Technology 2012-002, 8 Pages, 2012/03
In the "Plan for meeting the midterm goal (Midterm plan, April 1st, 2010 to March 31st, 2015)" by JAEA, it is planned that the closure activities of the Tono Mine will be started during the period of the Midterm plan. The closure activities at the Tono Mine were reviewed and "Plan for Closure Activities of the Tono Mine; Mine Closure Activities under Review" was developed in June 2010. This report presents detailed closure activities of the facilities and equipment of the Tono Mine.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Takeda, Masaki; Ueno, Takashi; Daimaru, Shuji; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Onoe, Hironori; Shingu, Shinya; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-001, 134 Pages, 2012/03
Tono Geoscientific Research Unit of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is performing the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in order to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock. The borehole investigations (two boreholes; 10MI22 borehole and 10MI23 borehole) have been carried out to obtain information on geological, hydrological and hydrochemical characteristics in and around the Main-shaft fault. These investigations provided that features of fracture and alteration on rock mass in and around the Main-shaft fault. Hydrological and hydrochemical properties based on the geological features were also obtained.
Kawakami, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Fukumoto, Masahiro
JAEA-Technology 2011-042, 56 Pages, 2012/03
This work evaluated the dynamic traffic flow of evacuees' cars during the evacuation drill with family car conducted in the Ibaraki Prefecture Comprehensive Nuclear Disaster Exercise 2010. The opinion survey was also conducted to participants to get the data of choice of measures for evacuation. Consideration based on the survey of this drill revealed important outcomes as follows. (1) The evacuation routes should be chosen more than one per one residential district from the roads including low capacity road to ease traffic congestion and to secure substitute route. (2) Taking into account traffic control and guiding at the intersections on the evacuation routes by policemen and staffs is very important to make the vehicles of evacuees running smoothly. (3) Considering of the capacity and the gate size of the parking of reception center is very important to make the stream of vehicles smooth when Reception centers are chosen. (4) Considering of the effect from experiments of participants is important for the opinion surveys to get the choice of measures of evacuation. (5) The opinion surveys about evacuation from nuclear disaster should be done in the wide area including the outside of the evacuation zone.
Suwa, Masayuki; Isaka, Koji; Ouchi, Satoshi; Goto, Shingo; Ikekame, Yoshinori; Terakado, Yoshibumi
JAEA-Technology 2011-041, 35 Pages, 2012/03
JRR-3 process control computer system is used to monitor and control various process parameters such as flow rates, temperatures, pressures and so on, and operate many reactor components such as cooling pumps and valves. The system has been under aging degradation at this time and the renewal of the system has become indispensable. The renewal work has planned, paying a due consideration to minimizing renewal costs and duration, to be separated in three stages. This paper describes the renewal plan and renewal works of main part of the system.
Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakui, Takashi; Matsui, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Teshigawara, Makoto; Meigo, Shinichiro; Seki, Masakazu; Sakamoto, Shinichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-040, 154 Pages, 2012/03
In the MLF, relatively high level irradiated components will be generated. Therefore, these components can not be kept in standard facilities. For the irradiated components at the MLF, the storage plan using the facilities in the Nuclear Science Research Institute has been studied, but the concrete plan is not decided yet. In this report, outline of the components, prehistory of the studying for storage, schedule of the component generation and status of the possible facility, which is a hot laboratory, are described. Resulting from the comparison between the generation schedule and the plan of the hot laboratory, the difference is very large. Present status of the hot laboratory and the cost estimation of the modification to use for storage of the MLF components were studied. Using the hot laboratory seems not to have advantage from the view point of cost and modification method. Therefore, the study on a new storage facility construction will be started as soon as possible.
Sakai, Kenji; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Naoe, Takashi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Tatsumoto, Hideki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-039, 121 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates the behavior, damage and restoration of a neutron source station of the MLF at the Great East Japan Earthquake and verified the safety design for emergency accidents in the neutron source station. In the MLF, after an occurrence of the Earthquake, strong quakes were detected at the instruments, the external power supply was lost, all of the circulators shut down automatically, and the hydrogen gas was released. The leakages of mercury, hydrogen and radio-activation gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between the shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines by subsidence around the building. But significant damages to the components were not found though the pressure drop of compressed air lines influenced on a target trolley lock system and so on. These results substantiated the validity of the safety design for emergency accidents in the source station, and suggested several points of improvement.
Nakata, Hisakazu; Amazawa, Hiroya; Sakai, Akihiro; Yamamoto, Masayuki*; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2011-036, 195 Pages, 2012/03
The waste package, which Japan Atomic Energy Agency plans to dispose, must be satisfied the technical standard specified by Law for the Regulations of Nuclear Source Material, Nuclear Fuel Material and Reactors. One of the technical standards is that it must have enough strength to withstand the load when the waste package is disposed finally by a burial method. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is required to prove the compliance of the waste package with the technical standard. Accordingly we conducted the actual load test of waste containers and imitated waste package in order to evaluate the anti-load strength of them by collecting strain and displacement data. The test was carried out by the compression apparatus which can imitate the supposed loading condition in a concrete pit type disposal facility. Based on the loading test result, we evaluate that 200 liter drum (M-class) has a minimum strength of 18 kN and 1 m cubic container has a maximum strength of 400 kN.
cubic container has a maximum strength of 400 kN.
Watahiki, Shunsuke; Hanawa, Yoshio; Asano, Norikazu; Hiyama, Kazuhisa; Ito, Sachito; Tsuboi, Kazuaki; Fukasaku, Akitomi
JAEA-Review 2012-013, 92 Pages, 2012/03
This replacement work was carried out under refurbishment plan of JMTR for beryllium distortion draw to acceptable limit. And gamma-ray shield refurbishment was carried out the view point of prevention maintenance in consideration of operation plan. Fabrication of beryllium frame and gamma-ray shield was spent for two years it was finished in February, 2010. It took five months to replacement work from January 2010. In this report is presented fabrication and replacement work of beryllium frame and gamma-ray shield.
Imaizumi, Tomomi; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Izumo, Hironobu; Ide, Hiroshi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Sozawa, Shizuo; Hori, Naohiko
JAEA-Review 2012-012, 25 Pages, 2012/03
A training course using JMTR and the related facilities was newly organized for domestic students and young engineers from FY 2010 from a viewpoint of nuclear Human Resource Development (HRD) in order to support global expansion of nuclear power industry. In FY2010, preparation for the training course was curried out and the 1st training course was held on February 14 to 25, 2011 with ten domestic students as a trainie. In this training course, mainly carried out was practical training of neutronic calculation for an irradiation test about the hydraulic rabbit irradiation facility which is one of the irradiation facilities in the JMTR. This report summarizes outline of training course using cutting-edge research infrastructure JMTR and the related facilities and result of the 1st training course.
Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Yanai, Tomohiro; Sugaya, Naoto; Kusunoki, Hidehiko; Sato, Shinichi; Fukasaku, Akitomi
JAEA-Review 2012-011, 35 Pages, 2012/03
The Japan materials testing reactor (here-in-after "JMTR") was used for irradiation experimental facility such as fuels and materials for commercial reactor. And the JMTR renewal work was started in 2006 and was completed in 2011. In this report, a part of renewal work for (1) freezer and its accompanying pipe and electricity facilities which the purpose of humidification and air-conditioning in the reactor and hot laboratory building, (2) boiler and its accompanying facilities which the purpose of humidification and heating in the reactor, hot laboratory and Alpha Gamma Facility (AGF) is summarized.
Onoue, Ryuji; Kawamata, Takanori; Otsuka, Kaoru; Sekine, Katsunori; Koike, Sumio; Gorai, Shigeru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Fukasaku, Akitomi
JAEA-Review 2012-010, 116 Pages, 2012/03
JMTR is a light water moderated and cooled tank-type reactor, and its thermal power is 50 MW. The JMTR is categorized as high flux testing reactors in the world. The JMTR has been utilized for irradiation experiments of nuclear fuels and materials, as well as for radioisotope productions since the first criticality in March 1968 until August 2006. JAEA is decided to refurbish the JMTR as an important fundamental infrastructure to promote the nuclear research and development. And The JMTR refurbishment work is carried out for 4 years from 2007. Before refurbishment work, from August 2006 to March 2007, all concerned renewal facilities were selected from evaluation on their damage and wear in terms of aging. Facilities which replacement parts are no longer manufactured or not likely to be manufactured continuously in near future, are selected as renewal ones. Replace priority was decided with special attention to safety concerns. A monitoring of aging condition by the regular maintenance activity is an important factor in selection of continuous using after the restart. In this report, renewal of the cooling system within refurbishment facilities in the JMTR is summarized.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsujikawa, Shigeo*; Hattori, Shigeo*; Yoshii, Tsuguyasu*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-007, 404 Pages, 2012/03
There are many LWRs which have been operated for more than 20 years in Japan and it is expected that technique corresponding to aging plants are necessary established for safety operation in LWRs. A lot of troubles related to SCC are reported and many investigations are concerned with SCC mechanism and technical evaluation. In this paper, those research data were collected as possible widely and reviewed systematically. Current circumstances concerned with SCC in LWRs were reviewed specifically as follows: SCC incidents, SCC evaluation methods for crack initiation and propagation, the investigations concerned with SCC mechanism and monitoring technique for corrosive environment. Influences with reactor types (BWR, PWR), materials (stainless steels, Ni alloys) and SCC evaluating methods (laboratories and actual plants) were summarized as graphs and tables easy to understand in common/difference points concerned with SCC. From these arranged results, future themes were considered and remarked SCC phenomenon was summarized in actual plants. As for SCC evaluations under the accelerate conditions in the laboratory test, it was suggested that a computational prediction and modeling including statistical technique and microscopic analysis in crack initiation were important. Furthermore it was suggested that monitoring techniques predicting SCC initiation and grasping plant circumstance in operation and feasibility in actual plants were important.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Hiyama, Yoshinori; Yoshii, Hideki*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Goto, Ichiro*
JAEA-Review 2012-006, 114 Pages, 2012/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and byelaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2010, from 1st April 2010 to 31st March 2011. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Ito, Kimio; Ono, Takayuki; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawasaki, Satoru
JAEA-Review 2012-005, 44 Pages, 2012/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Ningyo-toge) performs the environmental monitoring around the Ningyo-toge and the waste rock sites according to the agreements with local governments, Okayama and Tottori prefectures. Environmental monitoring of plutonium has been also performed around the Ningyo-toge regarding the practical application study on the reprocessed uranium conversion, which was carried out from 1994 to 1999 at the Ningyo-toge. Each prefectural committee on the environmental monitoring evaluates the monitoring data annually. This report summarized the results of the environmental monitoring in Okayama prefecture in the fiscal year 2010. The results show that the levels of the radiation doses and the radioactive concentrations in the environment were within natural variations, and the committee concluded that the environmental impacts from the sites were negligible. Therefore, the site of the JAEA Ningyo-toge has been well operated, and the waste rock sites have been well maintained.
Ito, Kimio; Ono, Takayuki; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawasaki, Satoru
JAEA-Review 2012-004, 20 Pages, 2012/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency performs the environmental monitoring around the Ningyo-toge and the waste rock sites according to the agreements with local governments, Okayama and Tottori prefectures. Each prefectural committee on the environmental monitoring evaluates the monitoring data annually. This report summarized the results of the environmental monitoring in Tottori prefecture in the fiscal year 2010. The results show that the levels of the radiation doses and the radioactive concentrations in the environment were within natural variations, and the waste rock sites have been well maintained. The committee concluded that the environmental impacts from the sites were negligible.
Itabashi, Keizo
JAEA-Review 2012-003, 52 Pages, 2012/03
The history and library statistics of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency library activity were summarized. Former Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the former Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute merged in October, 2005, and Japan Atomic Energy Agency is established. Properly speaking, the library statistics of old two corporations should have been summarized, but statistics of the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute is not yet obtained. Then, although it is stated as the Japan Atomic Energy Agency library, it limits to the description about the old Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute library, before 2004.
Department of Radiation Protection, Nuclear Science Research Institute; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institut; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Kansai Photon Science Institute; Operation Safety Administration Section, Mutsu Office, Aomori Research and Development Center; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Naka Fusion Institute
JAEA-Review 2012-001, 181 Pages, 2012/03
This annual report describes the activities of Radiation Protection Sector in Department of Radiation Protection in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Safety Section in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Safety Section in Kansai Photon Science Institute, Operation Safety Administration Section in Aomori Research and Development Center and Safety Section in Naka Fusion Institute.
Nuclear Human Resource Development Center
JAEA-Review 2011-055, 73 Pages, 2012/03
This annual report summarizes the activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center (NuHRDeC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the fiscal year 2010. In this fiscal year, NuHRDeC flexibly designed and conducted new training courses upon requests while conducting the annually scheduled training programs, and actively enhanced the collaboration with academia and cooperation with international organizations.
Department of JMTR Operation
JAEA-Review 2011-054, 30 Pages, 2012/03
Refurbishment works of the JMTR was carried out in plans from FY2007 to FY2010 and finished all refurbishment work on schedule in this year. Regarding the management and operation of the JMTR, the periodical inspection of facilities based on the law, maintenance and partial renewal works of facilities were carried out, and the fabrication of the fuel for restart has been carried out. As for the management and operation of irradiation facilities, maintenance and partial renewal works of facilities were also carried out. In the hot laboratory, voluntary periodical inspection, maintenance and post-irradiation examinations of irradiated materials were carried out. As for the radiation control at the JMTR facility, irradiation facility and hot laboratory facility, the limit of the radiation exposure dose defined by the safety regulation works were carried out safely under far below. This report describes the FY2010 activities on above mentions.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2011-053, 234 Pages, 2012/03
The Department of Research Reactors and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3, JRR-4, NSRR and Tandem Accelerator. This report is a summary of technical developments of The Department of Research Reactors and Tandem Accelerator in 2010.
Research Reactor Utilization Section
JAEA-Review 2011-050, 404 Pages, 2012/03
In the fiscal year 2007 the research reactor (JRR-3, JRR-4) conducted a user experiment with the use and exposure (including outside JAEA) received the submission of the results from this is put together.
Tanno, Takeo; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Hikima, Ryoichi; Matsui, Hiroya; Tada, Hiroyuki*; Goke, Mitsuo*; Kumasaka, Hiroo*; Ishii, Takashi*
JAEA-Research 2012-002, 86 Pages, 2012/03
The Crack tensor model which is a kind of equivalent continuum model has been studied in rock mechanical investigation in the MIU. The fractured rock mass is modeled as the elastic continuum model with the crack tensor. In this study, crack tensor based on the geological observation in the MIU project was calculated, and REV (Representative Elementary Volume) in the shafts and research galleries was studied based on the relative error of the crack tensor. The correlation between the crack density, the trace length of crack and the trace of crack tensor and the rock mass classification was also studied.
Inoue, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suto, Mitsuo
JAEA-Research 2011-057, 100 Pages, 2012/03
Corrosion resistance of fuel pin cladding tube materials is one of the most important properties to design aqueous reprocessing process. The martensitic oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steel, names as "9Cr-ODS" steel, is the primary candidate of high burnup fuel pin cladding tube for fast reactor cycle. Because 9Cr-ODS steel contains lower chromium than stainless steels, oxidizing species in nitric acid medium needs to reduce its corrosion rate. In spent fuel dissolvers, although both nitric acid and metallic ions concentrations change, corrosion potential of 9Cr-ODS steel tends to increase gradually and stabilize protective passive layer effectively.
Inagaki, Manabu*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Maekawa, Keisuke; Shibata, Masahiro
JAEA-Research 2011-056, 37 Pages, 2012/03
In Japan, a step-wise approach is applied in the site selection process for the geologic disposal site. Preliminary surface-based investigations will be followed by detailed investigations. The basic repository concept, including underground design and layout, will be discussed at the end of surface-based investigations. The repository concept will depend on the spatial extent of the candidate rock formation(s) and their barrier performance. However, information obtained from the surface is limited and includes uncertainties. It is thus important to assess host rock performance considering uncertainties. In this study, methodology for evaluation of geological conditions has been developed that focuses on determining the usable volume of host rock with specific performance characteristics. Initially, multiple performance indices have been discussed and defined from the viewpoint of barrier performance. Then the evaluation procedure is illustrated by using the dataset obtained from the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project. Finally the proposed procedure is reviewed and future challenges are extracted.
Sanada, Masanori; Kishi, Hirokazu; Hayashi, Katsuhiko*; Takebe, Atsuji*
JAEA-Research 2011-055, 79 Pages, 2012/03
In order to refine and rationalize a design method of multi tunnels in the deep geological repository, various study have been conducted. In this study, an effect of procedure for excavating multi-tunnels on extent of EDZ was examined by 3D FEM analysis. In modeling the multi tunnels and setting cases of analysis, workability, cost and safeness under construction were considered. Results of 3D FEM analysis showed that 3D effect of procedure for excavating such as a gap of progress with tunnel faces can be considered by 3D FEM and extent of EDZ is demonstrated more practically compared with 2D FEM. Another 2D FEM analysis modeling for crystalline rock (granite) was executed and the results showed that plastic zone did not appear in all cases.
Sakai, Ryutaro; Munakata, Masahiro; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2011-054, 19 Pages, 2012/03
In the safety assessment for a geological disposal of radioactive waste, it is important to establish validation methods for deep groundwater flow system to estimate radionuclide migration to human environment through groundwater flow. This study discussed the method which estimates groundwater mixing condition and groundwater flow process using principal component analysis (PCA) to groundwater chemistry and isotopic compositions, together with data of groundwater age and trace element in case of Horonobe area. The results show that hydrochemical system can be divided into two systems: (1) three deep groundwater mixing system at depths greater than 200 to 400 m, (2) mixing area of deep groundwater and surface water at depths less than 200 to 400 m. Groundwater in the deep aquifer is suggested to be discharged at surface through Omagari Fault.
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi; Amano, Yuki; Kunimaru, Takanori; Semba, Takeshi
JAEA-Research 2011-049, 68 Pages, 2012/03
This report summarizes technical basis and the Know-how on hydrochemical investigations for deep underground as a part of METI project "Development of Information Synthesis and Interpretation System (ISIS)". We describe the procedures and methods of hydrochemical investigation in following stages; (1) initial analysis of previous information, (2) planning of borehole investigation, (3) borehole investigation at field, and (4) construct the "hydrochemical model" representing hydrochemical condition and the evolution process. The contents of this report are inputted to "Expert system" developed by METI project and are available via WEB system (internet).
Nanjo, Isao; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Kunimaru, Takanori; Murakami, Hiroaki; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Morikawa, Keita
JAEA-Research 2011-048, 162 Pages, 2012/03
The observation technique of hydrochemical condition in low permeable sedimentary rock around the facility is one of R&D subjects. We report, (1) development of hydrochemical monitoring system to observe water pressure, pH, electric conductivity, dissolved oxygen, redox potential and temperature, (2) hydrochemical observation results around URL under construction. The applicability of the hydrochemical monitoring system is evaluated for low permeable sedimentary rock bearing abundant dissolved gases. The hydrochemical observation during facility construction demonstrates that pH and redox potential of groundwater almost did not changed even at hydraulic disturbed zone (water pressure decreased zone).
Oguri, Tomomi*; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-026, 25 Pages, 2012/03
The simplified shielding calculation (SSCAT) system is a calculation system for radiation shielding design of high energy proton accelerator facilities, based on Moyer's and Tesch's formulae for bulk shielding and Stapleton's formula for neutron skyshine. SSCAT was originally developed for conceptual shielding design calculations of the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) facilities, and was recently revised in order to cope with safety analysis for the licensing of the J-PARC facilities and shielding design for other proton accelerator facility. This report describes the recent status of SSCAT.
Katakura, Junichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-025, 73 Pages, 2012/03
The decay and fission yield data of fission products were compiled as JENDL FP decay data file 2011 (JENDL/FPD-2011) and JENDL FP fission yields data file 2011 (JENDL/FPY-2011). After the release of the JENDL FP decay data file 2000 file which was released in 2000, new measured data have been accumulated and new TAGS (Total Absorption  -ray Spectroscopy) data have been published. The JENDL/FPD-2011 file was then compiled to reflect the new measured data. In order to keep the consistency between the number of the nuclides contained, fission yields file, JENDL/FPY-2011 was also compiled. The decay heat calculations for various kinds of fissioning nuclides were performed to confirm the validity of the JENDL/FPD-2011 and JENDL/FPY-2011 files. The calculated results showed good agreement with the measured data. The uncertainty analyses of the decay heat calculation were carried out with the method of sensitivity analysis.
-ray Spectroscopy) data have been published. The JENDL/FPD-2011 file was then compiled to reflect the new measured data. In order to keep the consistency between the number of the nuclides contained, fission yields file, JENDL/FPY-2011 was also compiled. The decay heat calculations for various kinds of fissioning nuclides were performed to confirm the validity of the JENDL/FPD-2011 and JENDL/FPY-2011 files. The calculated results showed good agreement with the measured data. The uncertainty analyses of the decay heat calculation were carried out with the method of sensitivity analysis.
Suyama, Tadahiro; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-022, 34 Pages, 2012/03
The present report focuses on updating of the sorption database (JAEA-SDB) by adding Kd data for various systems including soil and cement systems, to apply JAEA-SDB for the PA-related Kd setting for disposal of low level radioactive wastes including TRU wastes and the evaluation of radionuclide transport in surface soil systems. The updated data includes Kd data for soil and cement systems extracted from mainly previous published database, and Kd data related to our recent activities on the Kd setting and mechanistic model development. As a result, 16,000 Kd data from 334 references are added, total Kd values in the JAEA-SDB are about 46,000. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for the performance assessment of various types of radioactive waste.
Ishihara, Masahiro; Suzuki, Masahide
JAEA-Conf 2011-003, 297 Pages, 2012/03
This report is the Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Materials Testing Reactors hosted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The 4th symposium was originally scheduled to be held INVAP in Argentina. However, the aftermath of volcanic explosion at Chili forced the symposium to change place. Total 111 participants attended from Argentina, Belgium, France, Germany, Indonesia, Malaysia, Korea, South Africa, Switzerland, the United State and Japan. This symposium addressed the general topics of "status and future plan of materials testing reactors", "advancement of irradiation technology", "expansion of industry use(RI)", "facility, upgrade, aging management", "new generation MTR", "advancement of PIE technology", "development of advanced driver fuel", and "nuclear human resource development(HRD) for next generation", and 39 presentations were made.
Ouchi, Satoshi; Suwa, Masayuki; Isaka, Koji; Ikekame, Yoshinori; Terakado, Yoshibumi
JAEA-Testing 2011-006, 43 Pages, 2012/02
JRR-3 has been utilized for various researches such as neutron irradiation experiment, neutron beam experiment and so on as a high performance research reactor with thermal power of 20 MW since the first criticality in March, 1990. Process data needed for JRR-3 operation such as temperatures, pressures, and flow rates, etc. had been processed by JRR-3 process computer system which consisted of several computer systems and several application softwares. The system needed complicated data administration and conservation. Also there was a problem in the administration of recording data. Data discrepancy among computers used in the system was taken place since the system was not so designed as to synchronize the process timing among the computers. Therefore, we developed a program to synchronize among all of the computers. This paper reports the development of data processing computer system.
Kochiyama, Mami; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Technology 2011-038, 26 Pages, 2012/02
A nondestructive measurement of gamma-ray emitting nuclides has been studied and Multiple gamma-ray Detection Instrument is newly constructed with 4 detection units consisting of Ge and BGO detectors. Compton scattering was decreased by the combination of Ge and BGO detectors. This instrument was applied to the detection of interested nuclides in radioactive waste sample, which contains significant amount of Co-60, and detection limit of the interested gamma-ray emitting nuclides were improved by a factor of 4 to 12 times than single gamma-ray spectrometer. As for Nb-94, the radioactivity determined from measurements using Multiple gamma-ray Detection Instrument in this sample was agreed with that determined by radiochemical analysis within 15%. It was confirmed that the instrument are useful for radioactivity determination of gamma-ray emitting nuclides in radioactive waste.
Nojima, Takehiro; Yasuda, Ryo; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Iikura, Hiroshi; Sakai, Takuro; Matsubayashi, Masahito
JAEA-Technology 2011-037, 33 Pages, 2012/02
We have equipped fuel cell operation system for TNRF at JRR-3 in order to visualize on performance of PEFC. Our system, which is aimed to be used in nuclear facility, is composed by various equipments that give safety in experiments such as hydrogen diluting system and purge system, etc. We confirmed normal operation of our system with JARI-standard fuel cell, and succeeded in visualizing water distribution of fuel cell on performance by our system with neutron radiography.
Neutron Source Section Materials and Life Science Division
JAEA-Technology 2011-035, 536 Pages, 2012/02
One of the experimental facilities in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) is the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF), where high-intensity neutron beams are used as powerful probes for basic research on materials and life science, as well as research and development in industrial engineering. Neutrons are generated with nuclear spallation reaction by bombarding a mercury target with high-intensity proton beams. The neutrons are slowed down with supercritical hydrogen moderators and then extracted as beams to each experimental apparatus. The principal design of the spallation neutron source is compiled in this comprehensive report.
Shibata, Akira; Ito, Masayasu; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Nakatsuka, Masafumi*; Ohara, Hiroshi*; Kodama, Mitsuhiro*; Tanimoto, Masataka; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Technology 2011-034, 67 Pages, 2012/02
Reflector elements made from metal beryllium is widely used as neutron reflectors to increase neutron flux in test reactors. When beryllium reflector elements are irradiated by neutron, bending of reflector elements caused by swelling occurs, and beryllium reflector elements must be replaced in several years. In this report, investigation for non-destructive inspection method of metal Beryllium and experiments for Preliminary inspection to establish post irradiation examination method for research of characteristics of metal beryllium under neutron irradiation were reported.
Tochio, Daisuke; Saito, Kenji; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
JAEA-Technology 2011-033, 43 Pages, 2012/02
Thermal load fluctuation test of the heat utilization system using the HTTR are planned in order to demonstrate the reactor system stability in the case of thermal load fluctuation of the heat utilization system in the HTGR hydrogen production system. In the previous report, the investigation on the ACL fan stopping tests were conducted, and it was confirmed that the tests can be conducted under several conditions and provide the data needed to verify the plant dynamics simulation code for future HTGR. In this report, the investigations on the ACL pressurized water flow rate fluctuation tests were conducted. As the result, it is confirmed that the ACL pressurized water flow rate fluctuation tests can be conducted under several conditions and provide the data needed to verify the plant dynamics simulation code for future HTGR.
Ishikawa, Hiroyuki; Tate, Akihiro; Murakami, Tadashi*
JAEA-Technology 2011-030, 62 Pages, 2012/02
In the J-PARC network, yet we already have several kinds of systems to detect and protect network information security threats, it is also important and necessary to countermeasure security vulnerabilities or holes at servers connected to the network. For such purposes, server host vulnerability inspection system is suitable. The system scans target server systems, checks running OS and server software versions on them and warns server administrators against known software vulnerabilities, if there exists. However, we suppose that it is not enough to inspect only at once at the server installation time. Regularly server administrators should do inspection, apply software patches according to its result during the server lives. In this point of view, we developed a web portal system to easily control this continual improve process of server side information security countermeasures by server administrators themselves.
Information Technology Systems' Management and Operating Office
JAEA-Review 2011-052, 231 Pages, 2012/02
JAEA conducts research and development (R&D) in various fields related to nuclear power as a comprehensive institution of nuclear energy R&Ds, and utilizes computational science and technology in many activities. In March 2010, CCSE introduced the nation's largest system and started operations to meet growing demand of calculation. Although the performance of new system is 14 times higher than that of old system, the utilization of new system reached 90% in the first three days, bearing out the strong demand of calculation in JAEA. This report presents a great amount of R&D results accomplished by using the system in its the first year of operation (FY2010), as well as user support structure, operational records and overviews of the system, and so on.
Environmental Management Section, Safety Administration Department
JAEA-Review 2011-051, 208 Pages, 2012/02
In September, 2011 Japan Atomic Energy Agency published the Environmental Report 2011 concerning the activities of FY 2010 under "Law Concerning the Promotion of Business Activities with Environmental Consideration by Specified Corporations, etc, by Facilitating Access to Environmental Information, and Other Measures". This report has been edited to show detailed environmental performance data in FY 2010 as the base of the Environmental Report 2011. This report would not only ensure traceability of the data in order to enhance the reliability of the environmental report, but also make useful measures for promoting activities of environmental considerations in JAEA.
Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities
JAEA-Review 2011-048, 35 Pages, 2012/02
This document describes the activity record in the Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities against the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku earthquake. This Part I includes the damage situations and the emergency activities on 11th March for the 11 nuclear facilities managed by the department. The subsequent activities, such as the repairs or restorations, are described in the Part II. Despite the enormous damages for some of these facilities, such as the Research Hot Laboratory or the Reactor Fuel Examination Facility, there was no victim or no release of the radioactive materials out to the facilities. It was the great deal of the periodic patrol for the safety and health which is based on the manual procedure for the earthquake countermeasures executed since 1st January 2011.
Kobayashi, Takanori; Sakon, Miyoji; Takada, Osamu; Hatori, Masakazu; Sakamoto, Tsutomu; Sato, Toshiyuki; Kazama, Akihito*; Ishizawa, Yoshihiro*; Igawa, Katsuhisa*; Nakae, Hideo*
JAEA-Review 2011-047, 48 Pages, 2012/02
I confirmed a leak of the effluent gas from cylinder part during a load examination after the check of the emergency generator C unit on December 28, 2010 of the facilities check average and confirmed crack in No.8 cylinder liner part. As a result, because it was not performed oil pressure management properly without attaching an oil pressure gauge when I removed cylinder liner about the cause, crack occurred by having been able to write excessive stress for the cylinder liner and reached damage. By a process of this investigation, a fall of the materials strength of some cylinder liner was confirmed, but because a lead ingredient got mixed with materials by a casting process at the time of the production of the cylinder liner, as for this, Widmannst tten graphite occurred, and it became clear that materials strength fell. In addition, I performed inspection by the supersonic wave velocity measurement as technique to distinguish this Widmannst tten graphite easily and confirmed that I was effective.
Kawata, Koji; Matsuki, Takuo*; Miyahara, Shinya
JAEA-Review 2011-046, 42 Pages, 2012/02
Sodium spray fire tests at an initial sodium temperature of 250 C were conducted under the atmospheric conditions of air and 3% oxygen containing nitrogen to determine both the sodium burning rate and the aerosol release fraction.
C were conducted under the atmospheric conditions of air and 3% oxygen containing nitrogen to determine both the sodium burning rate and the aerosol release fraction.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi
JAEA-Review 2011-045, 101 Pages, 2012/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) has been conducting a geoscientific studies in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. Information and Opinion Exchange Conference on Geoscientific Study has been held by TGC annually. The conference provides technical information and an opportunity for peer review and exchange of opinions on the geoscientific studies conducted at TGC. Research specialists and engineers from Japanese universities, research organizations and private companies usually participate in the conference. This document compiles research presentations, posters of the conference at Mizunami on November 1, 2011.
Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities
JAEA-Review 2011-044, 100 Pages, 2012/02
This report describes the operation and management of eleven facilities under the Department of Hot Laboratories and Facilities during a fiscal year of 2010. In Reactor Fuel Examination Facility, various post-irradiation examinations were performed regarding the advanced light water reactor fuel performance and safety research program, and the development of vessel material for spallation target of neutron scattering facility. In order to update and install new equipment, the license revision for the use of nuclear fuel materials was applied and its facility inspection by the ministry was accepted. In Waste Safety Testing Facility, various examinations were performed regarding the irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking behavior for nuclear power plant materials, corrosion properties for stainless steel against the dense uranyl solution, and properties of minor actinide bearing fuels. In order to perform the autoclave test for fuel claddings, the license revision for the use of nuclear fuel materials was applied and accepted. Since 2010, chemical analyses have been made by request at No.4 Research Laboratory, including maintenance of shared instruments and the technical assistance. In Research Hot Laboratory, the decontamination of hot cells and the dismantling of auxiliary equipment were performed at the lead cells on the decommissioning schedule of a fiscal year 2010. In addition, the facility management was carried out of No.1 Plutonium Laboratory, No.2 Research Laboratory, Analytical Chemistry Laboratory, Uranium Enrichment Laboratory, Simulation Test for Environmental Radionuclide Migration, Clean Laboratory for Environmental Analysis and Research, and Fuel Storage.
Kawamura, Hiroshi; Chakrov, P.*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Gizatulin, S.*; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Chakrova, Y.*; Kimura, Akihiro; Ludmila, C.*; Tanimoto, Masataka; Asset, S.*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-042, 46 Pages, 2012/02
Based on the implementing agreement between National Nuclear Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan (NNC) and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) for the Nuclear Technology on Testing/Research Reactors in the cooperation in Nuclear Energy Research and Development in Nuclear Energy and Technology, four specific topics of cooperation (STC) have been carried out from June, 2009. Four STCs are as follows; (1) STC No.II-1: International Standard of Instrumentation, (2) STC No.II-2: Irradiation Technology of RI Production, (3) STC No.II-3: Lifetime Expansion of Beryllium Reflector, (4) STC No.II-4: Irradiation Technology for NTD-Si. The information exchange, personal exchange and cooperation experiments are carried out under these STCs. The status in the field of nuclear technology on testing/research reactors in the implementing arrangement is summarized, and future plans of these specific topics of cooperation are described in this report.
Shimizu, Ryo; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Sakurai, Satoshi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Yamamura, Tsukasa; Naoi, Yosuke; Kuno, Yusuke
JAEA-Review 2011-038, 116 Pages, 2012/02
International forum on peaceful use of nuclear energy and nuclear non-proliferation was held at Gakushi-kaikan, Tokyo on February 2-3, 2011 in cooperation with The Japan Institute of International Affairs (JIIA) and The University of Tokyo Global COE. In our International Forum, we would like to encourage active discussion of international challenges to and solutions for compatibility between peaceful use of nuclear energy and nuclear non-proliferation, and international cooperation for emerging nuclear energy states. It was successfully carried out with as many as 310 participants and a lot of discussions. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summary of panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Sato, Hisashi; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2011-052, 55 Pages, 2012/02
In order to obtain the hydraulic property, mass transport property and three-dimensional fracture void geometry which need for elucidate the permeability and mass transport phenomena in a single fracture, we conducted a flow test, measurement of fracture shape, aperture measurement by optical method, tracer test by optical method for three transparent replica specimens. As a result, the flow rate of two-dimensional seepage flow analysis based on LCL became about 1.5 to 2 times of the flow test results, which results was consistent with previously reported results. To investigate the influence of fracture shape for the flow analysis results, corrected the transmissivity using the acquired data of aperture distribution and fracture shape data. As a results, the fracture permeability by applying the corrected transmissivity considering local slope of the fracture was decreased which is closer to the flow test results.
Yamagishi, Hideshi*; To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Research 2011-051, 19 Pages, 2012/02
An ASD-ASIC (Amplifier-Shaper-Discriminator ASIC) with fast response and low noise performances has been designed for two-dimensional position sensitive neutron gas detectors (InSPaD). The InSPaD is a 2D neutron detector system with  He gas and provides a high spatial resolution by making distinction between proton and triton particles generated in the gas chamber. The new ASD-ASIC is required to have very low noise, a wide dynamic range, good output linearity and high counting rate. The new ASD-ASIC has been designed by using CMOS and consisted of 64-channel ASDs, a 16-channel multiplexer with LVTTL drivers and sum amplifier system for summing all analog signals. The performances were evaluated by the Spice simulation. It was confirmed that the new ASD-ASIC had very low noise performance, wide dynamic range and fast signal processing functions.
He gas and provides a high spatial resolution by making distinction between proton and triton particles generated in the gas chamber. The new ASD-ASIC is required to have very low noise, a wide dynamic range, good output linearity and high counting rate. The new ASD-ASIC has been designed by using CMOS and consisted of 64-channel ASDs, a 16-channel multiplexer with LVTTL drivers and sum amplifier system for summing all analog signals. The performances were evaluated by the Spice simulation. It was confirmed that the new ASD-ASIC had very low noise performance, wide dynamic range and fast signal processing functions.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Nishimaki, Yuichiro*
JAEA-Research 2011-047, 105 Pages, 2012/02
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. Conventional ISD model is unsatisfactory because for multivalent cation/anion and complex ion model predictions disagree with experimental data, and because the model contains additional non-physical fitting parameter. Accordingly we extract the factors influencing the assessment from fundamental assumptions of the conventional ISD model. In this report we incorporated the excluded volume effect, the dielectric saturation effect and the fluctuation potential effect caused by ion-ion electrostatic interaction into ISD model. As results of numerical analysis of these models the considering factors influence hardly the effective diffusivity. Therefore it does not mean that the disagreement with experimental data are caused by considering factors in this report.
Ishitoya, Kimihide; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Funabashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2011-046, 32 Pages, 2012/02
Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan (NSC) issued "Policy of the Safety Assessment of Sub-surface Disposal after the Period for Active Control" (April 1, 2010). Then, we investigated the parameters for dose assessment in tunnel excavation scenario and large-scale land use scenario which were described in the "Policy of the Safety Assessment", in order to perform the assessment based on actual conditions. To be concrete, we investigated the tunnel excavating speeds in Japan for the former scenario, and investigated technical standards of the filling for the latter scenario. We studied the realistic parameters for the dose assessment with the results of those investigations.
Iwamae, Atsushi*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori
JAEA-Research 2011-045, 11 Pages, 2012/02
In order to investigate reflection properties on plasma-facing material in ITER, the bi-directional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) of a tungsten block sample has been measured. On the machining surface of the block, one-directional machining lines are engraved. Two laser diodes  652 nm and
652 nm and  473 nm were used to simulate H
473 nm were used to simulate H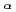 and H
and H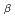 emissions, respectively. The reflected light is affected by the machining surface. The reflected light traces a line when the incident light is injected in the perpendicular direction to the engraved line. On the other hand the reflected light traces an arc shape when the incident light is injected in the parallel direction to the engraved lines. Ray tracing simulation qualitatively explains the experimental results.
emissions, respectively. The reflected light is affected by the machining surface. The reflected light traces a line when the incident light is injected in the perpendicular direction to the engraved line. On the other hand the reflected light traces an arc shape when the incident light is injected in the parallel direction to the engraved lines. Ray tracing simulation qualitatively explains the experimental results.
FBR Safety Unit
JAEA-Research 2011-044, 185 Pages, 2012/02
JAEA has been developing a flow-induced vibration methodology applied to the JSFR piping under the FaCT project. As part of this development, flow pattern in the single-elbow pipe has been investigated with the measurement of fluid force induced by turbulence flow and of the flow-induced vibration response. The experimental results have served to the development and vibration of the flow-induced vibration evaluation methodology. Based on these outcomes, JAEA has established a working group on a guideline of large-diameter piping flow-induced vibration evaluation under the JAEA's Thermal-Hydraulic Research Committee for creating the JAEA internal guideline. The first proposal of the guideline was summarized from the achievements of the working group activity. Since technical discussion has been made deeply in developing the guideline, this report summarizes technical background and understanding for the guideline.
Sugita, Yutaka; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Aizawa, Takao*; Ito, Shunichiro*
JAEA-Research 2011-043, 25 Pages, 2012/02
A simplified seismic velocity survey system was developed for the repeat performance of surveys in conjunction with tunnel excavation, to monitor the various changes that occur in a rock mass around tunnels or galleries as they are excavated in the deep underground. The simplified seismic velocity survey system developed consists of a hammer to transfer seismic energy to the borehole wall and receivers installed and anchored in the borehole, and then backfilled. The hammer is operated with compressed air, necessitated by the potential presence of flammable gas such as methane. The system developed was used in the EDZ Experiment in a horizontal tunnel in the Horonobe URL. Changes in seismic velocity were monitored during and after excavation of the tunnel and the tomograms obtained are high quality. These results show that the system developed can provide the information needed to monitor the development and the variations in an EDZ.
Yamamoto, Yoichi; Maekawa, Keisuke; Yokota, Hideharu; Yamazaki, Masanori
JAEA-Research 2011-042, 97 Pages, 2012/02
The surface hydrogeological investigation has been carried out in and around the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory area as a part of Horonobe URL project. Observations of meteorological, river flux, water quality, soil moisture and groundwater level have been continued in order to understand the groundwater recharge rate and groundwater flow in the shallow part, which are required for the setting of boundary and initial condition of the groundwater flow analysis. This report shows the summary of the surface hydrogeological investigation and results of recharge rates of investigation basins from December 2004 to November 2009 are calculated by using the water budget method. Spatial estimation of hydrological quantities for the groundwater recharge rate is demonstrated by the runoff analysis. As a result, average of the groundwater recharge rate of whole basins is estimated to 131mm/yr. Suggestive observations related to hydraulic properties of the geology and faults are obtained from consideration to the groundwater recharge rate for each basin.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Research 2011-041, 62 Pages, 2012/02
We have proposed a hydrogen supply-chain system, which is a storage/supply system of large amount of hydrogen produced by HTGR-IS hydrogen production system. The organic chemical hydride method is one of the candidate techniques in the system for hydrogen storage and transportation. In this study, properties of organic hydrides and conventional hydrogen storage/supply system were examined to help the conceptual design of the hydrogen supply system using an organic hydrides method with VHTR-IS hydrogen production process (hydrogen production: 85,400 Nm /h). Conceptual specifications of the main apparatus were designed for the hydrogen supply system with hydrogenation and dehydrogenation process. It was also clarified the problems of hydrogen supply system, such as efficiency of energy and system optimization.
/h). Conceptual specifications of the main apparatus were designed for the hydrogen supply system with hydrogenation and dehydrogenation process. It was also clarified the problems of hydrogen supply system, such as efficiency of energy and system optimization.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Fukui, Katsunori*; Hashiba, Kimihiro*; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2011-040, 54 Pages, 2012/02
With respect to high-level radioactive waste disposal, knowledge of the long-term mechanical stability of shafts and galleries excavated in rock are required, not only during construction and operation but also over a period of thousands of years after closure. Therefore, it is very important to understand the time-dependent behavior of rock for evaluating long-term mechanical stability. This report describes the results of the activities in FY2010. In Chapter 1, we provide an overview and the background to this study. In Chapter 2, the results of a long-term creep test on Tage tuff, started in FY1997 are described. In Chapter 3, the relation of loading-rate dependency of strength and stress dependency of creep life, the relationship of time dependency and probability distribution of strength or creep life and size effects are discussed to indicate more clearly the meaning of the value of "n" to express the degree of time dependency of the rock. In Chapter 4, failure criterions of a rock mass considering time dependency are discussed. In Chapter 5, the FEM analysis implemented with a generalized variable-compliance-type constitutive equation considering the change of "n" in confining pressure and strength distribution of rock mass carried out to clarify the long-term behavior of Toki granite is described. Finally, based on the numerical analysis, an in situ testing method is proposed.
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kato, Shoichi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Yamamoto, Masaya; Sekine, Takashi; Ito, Chikara
JAEA-Research 2011-039, 20 Pages, 2012/02
Application of zirconium alloy as a neutron reflector around the driver fuel region of the Japanese experimental fast reactor JOYO has been planned for a further increase of core average burn-up. In order to investigate the compatibility of the zirconium alloys with high-temperature sodium which is coolant of the JOYO, corrosion test in sodium and tensile test of the exposed alloys were performed. The corrosion test was done at 500 C and 650
C and 650 C in stagnant/flowing sodium for two kinds of zirconium alloys, and then weight change measurement and metallurgical observation were carried out. The tensile test was performed in air at the same temperature with the sodium exposure.
C in stagnant/flowing sodium for two kinds of zirconium alloys, and then weight change measurement and metallurgical observation were carried out. The tensile test was performed in air at the same temperature with the sodium exposure.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-033, 126 Pages, 2012/02
The next advancements for the research of radioactive waste repository was started to improve and systematize the investigation and evaluation techniques on geological environment in consideration of intra-field of science and technology. Intra-field means the various fields among each study area of (a) geological environment, (b) design and engineering, (c) safety evaluation for radioactive waste repository, here. The following items were studied and discussed this year. (1) To Reconstruct Near Field (NF) Concept in consideration of coupled phenomena on geological environment. (2) To develop systematic investigation techniques on the geological environment in consideration of intra-field among each study area above mentioned (a), (b) and (c). Regarding (1), examination of NF concept focused on the realistic crystalline rock was carried out. Also through the overall discussion in the committee, comments from the all commissioners in relation to the intra-field of their study area were made to reflect on reconstruction of NF concept. Regarding (2), the research and development in consideration of NF and intra-field among each study area were conducted.
Tatebe, Kazuaki; Suzuki, Yurina; Shirato, Seiichi; Sato, Yoshinori
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-024, 84 Pages, 2012/02
The recent society requires business activities with environmental consideration to every enterprise. Also, Japanese laws require those activities. For example, "Environmental Consideration Law" mandates publication of a report relating to the activities of environmental consideration to each enterprise over a certain size. "Act on the Rational Use of Energy" mandates the report of the results of energy consumption and the long-term plan of the rational use of energy. Moreover, "Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures" mandates the report of the greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to those, "Water Pollution Control Law" and other environmental laws as well as environmental ordinances require business activities with environmental consideration to all companies. So, it is very important for JAEA to report business activities with environmental consideration in order to build up trustful relations with the people and communities. The Environmental Data Management System has been developed as the data base of business activities with environmental consideration at JAEA and the means to promote the activities at every site and office of JAEA. This report summarizes the structure of the environmental data management system, kinds of environmental performance data treated by the system, and gathering methods of the data.
Amano, Yuki; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Nanjo, Isao; Murakami, Hiroaki; Yokota, Hideharu; Yamazaki, Masanori; Kunimaru, Takanori; Oyama, Takahiro*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-023, 312 Pages, 2012/02
In the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project, ground water from boreholes, river water and precipitation have been analyzed for the environmental monitoring since the fiscal year 2001. This report shows the data set of water chemistry since the fiscal year 2001 to the fiscal year 2010.
Suto, Toshiyuki; Fukushima, Manabu*
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-021, 91 Pages, 2012/02
Future reprocessing facilities are considered to treat not only LWR uranium fuels but also LWR-MOX fuels and even FBR fuels. These spent fuels have various enrichments, isotopic compositions of plutonium. In order to make reasonable design and management of criticality safety for such multi-fuel reprocessing facilities, there needs to be critiricality safety data with a multiple of enrichments, isotopic compositions of plutonium. The authors calculated subcritical dimensions of uranium/plutonium mixed nitrate solution with a multiple set of enrichments and isotopic compositions of plutonium for cylinder, slab, and annular geometries and arranged the results in tables and graphs which are usable for the criticality safe design study of future reprocessing facilities. In addition, some findings useful for selecting criticality safety control methods were summarized.
Okumura, Keisuke; Okamoto, Tsutomu
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-020, 193 Pages, 2012/02
Accurate information on nuclide inventories of spent fuels from Light Water Reactors (LWRs) is important for evaluations of criticality, decay heat, radioactivity, toxicity, and so on, in the safety assessments of storage, transportation, reprocessing and waste disposal of the spent fuels. So, a lot of lattice burn-up calculations were carried out for the possible fuel specifications and irradiation conditions in Japanese commercial LWRs by using the latest nuclear data library JENDL-4.0 and a sophisticated lattice burn-up calculation code MOSRA-SRAC. As a result, burn-up changes of nuclide inventories and their possible ranges were clarified for 21 heavy nuclides and 118 fission products, which are important from the viewpoint of impacts to nuclear characteristics and nuclear fuel cycle and environment.
Takeyasu, Masanori; Takeishi, Minoru*
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-019, 23 Pages, 2012/02
A computer code system (SIERRA-II) has been developed to estimate the environmental radiological impact of accidental releases of radionuclides from a nuclear facility in real time. The SIERRA-II is based on a three-dimensional mass-conserving wind field model and a particle dispersion model with a nesting function to calculate with high spatial resolution in the vicinity of the facility. Input includes on-line local meteorological and effluent data observed and monitored at the site of the facility, and local meteorological data as predicted by an atmospheric dynamic model. The SIERRA-II was validated using environmental monitoring data for ambient dose rate as observed at monitoring posts around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant when Kr-85 was discharged during its operation. The observed increase of the dose rate was simulated well. The agreement of calculated and observed dose rate was within a factor of 5 for 74 % of observations.
Takeda, Masaki; Sato, Atsuya*; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-007, 38 Pages, 2012/02
At the Tono Geoscientific Research Unit, the subsurface water balance observation has been carried out in order to estimate groundwater recharge rate for setting the upper boundary conditions on groundwater flow simulation and to obtain data for the calibration of the hydrogeological model. In the water balance observations, precipitation metrological data for the estimation of evapotranspiration, river flow rate, and groundwater table and soil moisture have been observed in the Sheba river area, the Sheba river model area and MIU Construction Site. After missed data and data error in the monitoring data from the fiscal year 2008 were complemented or corrected, the data was compiled in data set. Both of the observation data and compiled data are included in the data set, and the data set is recorded on DVD-ROM.
Takeda, Masaki; Sato, Atsuya*; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-006, 21 Pages, 2012/02
At the Tono Geoscientific Research Unit, the subsurface water balance observation has been carried out in order to estimate groundwater recharge rate for setting the upper boundary conditions on groundwater flow simulation and to obtain data for the calibration of the hydrogeological model. In the water balance observations, precipitation metrological data for the estimation of river flow rate, and groundwater table have been observed in the Garaishi river area and the Hiyoshi river area. The missed data and data error in the monitoring data from the fiscal year 2008 were complemented or corrected the data was compiled in data set. Both of the observation data and compiled data are included in the data set, and the data set is recorded on DVD-ROM.
Ichikawa, Shoichi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Haga, Hiroyuki; Kajima, Hisashi*; Sakurai, Satoshi*; Katsuyama, Kozo; Maeda, Koji; Nishinoiri, Kenji
JAEA-Technology 2011-032, 46 Pages, 2012/01
The assembly technique to the capsular irradiation rig newly developed was established. In the irradiation examination, the assembling disassembling and reassembling to PFB110 "B11(1), B11(2)" and PFB140 "B14" that built in Am-MOX fuel pin was achieved. The reassembly technique by recycling the irradiation material was established in the assembly of B11(2). This time, the assembly and disassembly of B11 (1) were reported. Moreover, the assembly of B14 which improved the assembly technology of B11 (1) was reported.
Imaizumi, Tomomi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Ito, Masayasu; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Nagata, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Naka, Michihiro; Kawamata, Kazuo; Yamaura, Takayuki; Ide, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-031, 123 Pages, 2012/01
The number of research reactors in the world is decreasing because of their aging. However, the planning to introduce the nuclear power plants is increasing in Asian countries. In these Asian countries, the key issue is the human resource development for operation and management of nuclear power plants after constructed them, and also the necessity of research reactor, which is used for lifetime extension of LWRs, progress of the science and technology, expansion of industry use, human resources training and so on, is increasing. From above backgrounds, the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center began to discuss basic concept of a multipurpose low-power research reactor for education and training, etc. This design study is expected to contribute not only to design tool improvement and human resources development in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center but also to maintain and upgrade the technology on research reactors in nuclear power-related companies. This report treats the activities of the working group from July 2010 to June 2011 on the multipurpose low-power research reactor in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center and nuclear power-related companies.
Sato, Sohei; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Muto, Shigeo; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Katagiri, Hiromi
JAEA-Review 2011-049, 77 Pages, 2012/01
The Tohoku District-off the Pacific Ocean Earthquake occurred at 14:46 on March 11, 2011. Tsunami caused by the earthquake attacked the Fukushima Dai-ichi and Fukushima Dai-ni Nuclear Power Stations of Tokyo Electric Power Company and nuclear accidents involving release of radioactive material occurred. Since the earthquake, Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) has served as a base of support activities conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). After nearly half a year has passed since the occurrence of the accident, we compiled the support activities of NEAT. NEAT's lessons learned and recommendations based on the experiences of support activities to the accident should be very helpful in considering the structure of nuclear emergency preparedness and response. We summarized them in this time. We hope that this report helps further developing nuclear emergency preparedness and response in the future.
Kojima, Takuji
JAEA-Review 2011-043, 207 Pages, 2012/01
JAEA Takasaki annual report 2010 describes research and development activities performed from April 1, 2010 to March 31, 2011 with Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA), and electron/ -ray irradiation facilities at Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Takasaki). These activities are classified into four research fields: (1) Space, Nuclear and Energy Engineering, (2) Environmental Conservation and Resource Exploitation, (3) Medical and Biotechnological Application, and (4) Advanced Materials, Analysis and Novel Technology. This annual report contains 159 reports consisting of 151 research papers and 8 status reports on operation/maintenance of the irradiation facilities described above, and a list of publications, patents, related press-releases, TV broadcasting, and the type of research collaborations as Appendices.
-ray irradiation facilities at Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Takasaki). These activities are classified into four research fields: (1) Space, Nuclear and Energy Engineering, (2) Environmental Conservation and Resource Exploitation, (3) Medical and Biotechnological Application, and (4) Advanced Materials, Analysis and Novel Technology. This annual report contains 159 reports consisting of 151 research papers and 8 status reports on operation/maintenance of the irradiation facilities described above, and a list of publications, patents, related press-releases, TV broadcasting, and the type of research collaborations as Appendices.
Otani, Hiroshi; Matsushima, Akira; Mori, Naoto; Kutsuna, Hideki; Higashiura, Norikazu
JAEA-Review 2011-041, 55 Pages, 2012/01
In planning and carrying out decommissioning technical development of Fugen, "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning", which consists of the members well-informed, is established, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened inside and outside the country, as the central point in the energy research and development base making project of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report compiles presentation materials "Current Situation of Fugen Decommissioning", "Radioactive Corrosion Products Decontamination Experiment with using Heavy Water System Equipment", "Laser Cutting Test on Dust Behavior in Cutting Work in Air", "Preparatory Situation for Operation of Clearance System" of this committee.
 method
methodSuzuki, Satoshi*; Komatsuzaki, Takashi*; Tadokoro, Hideaki*; Oki, Koichi
JAEA-Review 2011-039, 74 Pages, 2012/01
This report summarizes outline, methods and measurement results of actual wastes of nondestructive measurement system using the passive  method applied to the evaluation of the quantity of uranium in the drum waste (0.2 m
method applied to the evaluation of the quantity of uranium in the drum waste (0.2 m ) and container waste (1 m
) and container waste (1 m ). The following are the results. (1) The measurement number of drum wastes was 18,884 (4,703 of the number were pit wastes), at the end of March, 2011. (2) The measurement number of container wastes was 749 (110 of the number were pit wastes), at the end of March, 2011. (3) About 60% of drum wastes and about 80% of container wastes were metal and concrete. (4) 75% of drum wastes were less than detection limit, and average of radioactivity is 3.4 Bq (U-238)/g. Then 17% of container wastes were less than detection limit, and average of radioactivity is 2.3 Bq (U-238)/g. (5) If clearance level is 1.0 Bq (U-238)/g (IAEA RS-G-1.7), about 80% of wastes are below the clearance level.
). The following are the results. (1) The measurement number of drum wastes was 18,884 (4,703 of the number were pit wastes), at the end of March, 2011. (2) The measurement number of container wastes was 749 (110 of the number were pit wastes), at the end of March, 2011. (3) About 60% of drum wastes and about 80% of container wastes were metal and concrete. (4) 75% of drum wastes were less than detection limit, and average of radioactivity is 3.4 Bq (U-238)/g. Then 17% of container wastes were less than detection limit, and average of radioactivity is 2.3 Bq (U-238)/g. (5) If clearance level is 1.0 Bq (U-238)/g (IAEA RS-G-1.7), about 80% of wastes are below the clearance level.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2011-038, 26 Pages, 2012/01
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project has been implemented to establish the techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment and to develop a range of engineering techniques for application deep underground. In this paper, results of differential strain curve analysis (DSCA) and elastic wave measurements using polyhedral specimens at the 08MI13 and 09MI20 boreholes in -300 m stage are described. The objectives of this work are to evaluate in situ stress condition on the -300 m stage.
Ban, Yasutoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Research 2011-037, 11 Pages, 2012/01
Adsorption of Cs with five types of inorganic adsorbents (CST: Crystalline SilicoTitanate) powder, CST grain, synthetic mordenite powder, synthetic mordenite grain, and natural mordenite) was carried out by batch methods in the aqueous solution of NaCl at room temperature, respectively. The concentration of Cs after the batch experiments decreased compared with the initial concentration of Cs when the ratio of the solution volume (ml) to the amount of the adsorbent (g) was 100 ml/g, and it was confirmed that the adsorbents used in the present study adsorbed Cs ion in the presence of Na
ion in the presence of Na and Cl
and Cl ions.
ions.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sugino, Kazuteru; Numata, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Research 2011-036, 64 Pages, 2012/01
An analytical study of minor actinide (MA) transmutation systems was conducted using JENDL-4.0, with a comparison to JENDL-3.3 in terms of reactor physics parameters (criticality, void reactivity and the Doppler reactivity) and those uncertainties. As objects of the analyses, Accelerator driven system (ADS) and MA loaded fast reactor (FR) were assumed. It was found that there were considerable changes for both systems. As the results of the sensitivity and uncertainty analysis, we found that the difference of the parameters of ADS is due mainly to the inelastic scattering cross sections of lead isotopes and several reactions of  Am. For FR, a large difference of the void reactivity uncertainty results primarily from the covariance data of the inelastic cross section of
Am. For FR, a large difference of the void reactivity uncertainty results primarily from the covariance data of the inelastic cross section of  Na.
Na.
Hyakutake, Toru*; Muto, Akinori*; Sasakura, Mariko*; Minowa, Hirotsugu*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Takahashi, Nobuo; Hata, Haruhi; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Research 2011-035, 53 Pages, 2012/01
System decontamination has been generally carried out with the aim of reducing the amount of radioactive waste generated and minimizing exposure to radiation released from nuclear fuel facilities. At the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, metal surfaces that are contaminated by uranium are dry decontaminated by using iodine heptafluoride (IF ) as a system decontaminator. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination techniques is required. In the present study, the efficiency of a dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of uranium hexafluoride.
) as a system decontaminator. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination techniques is required. In the present study, the efficiency of a dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of uranium hexafluoride.
FBR Plant Engineering Center; Fast Breeder Reactor Research and Development Center, Tsuruga Head Office; Policy Planning and Co-ordination Department, Tsuruga Head Office
JAEA-Evaluation 2011-004, 132 Pages, 2012/01
The logical adequacy of the safety measures in Monju, coolability of the reactor core and the ex-vessel storage tank by natural circulation, and coolability of the spent fuel storage pool, considering Tohoku district - off the Pacific Ocean Earthquake were explained by Japan Atomic Energy Agency and reviewed in the above-titled committee. Main conclusions by the chairman of the committee are summarized as follows: (1) Natural circulation cooling is secured in the reactor after station blackout (SBO) as far as flow path exist. Therefore, the reactor core will never melt because of the decay heat removal as far as the natural circulation is reserved after the reactor shutdown; (2) Spent fuels will never melt due to temperature rise in the ex-vessel fuel storage system, since natural circulation cooling can be expected even after SBO; (3) It is possible to take sufficient countermeasures such as water supply against the spent fuel pool because it takes approximately two month before the top of the spent fuel cans which contain spent fuels are exposed by evaporation of the water.
Sugino, Kazuteru
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-018, 125 Pages, 2012/01
Transport calculation codes for 3D hexagonal geometry have been developed: nodal code NSHEX, hexagonal-mesh finite difference code MINIHEX, and triangle-mesh finite difference code MINISTRI, which can perform neutron transport calculations with high accuracy for fast reactor cores. NSHEX is improved by extending the polynomial expansion order of intranode fluxes for better accuracy. MINIHEX is modified in the process of negative flux fix-up. In addition, MINISTRI is newly produced by changing the basic algorithm of MINIHEX. NSHEX, MINIHEX, and MINISTRI are applied to various fast reactor cores. It is found that these codes show satisfactory performance in terms of calculation accuracy. However, reduction of calculation time and improvement of convergence performance are required for all the codes by such measure as introduction of suitable acceleration technique. Further, development of post process functions is desired, which is represented by perturbation calculation scheme.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Hazama, Taira; Numata, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-017, 44 Pages, 2012/01
Fast reactor group constant sets UFLIB.J40 and JFS-3-J4.0 were prepared, which are based on the latest Japanese evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. Concerning UFLIB.J40, several fine group constant sets, which covered 70-group, 73-group, 175-group and 900-group structures, and the ultra fine group constant set were prepared. The number of nuclides for cross-sections of lumped fission products was extended so as to follow the extension of the number of fissile species for fission yield data.
Shinohara, Masanori; Yanagi, Shunki; Tochio, Daisuke; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Nojiri, Naoki; Owada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Nao; Sagawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Masayuki
JAEA-Technology 2011-029, 39 Pages, 2011/12
JAEA plans and performs the safety demonstration test using the HTTR to develop High Temperature Gas Reactor technologies. Cold test of the loss of forced cooling was conducted prior to the safety demonstration test, to check test procedure and plant behavior. Cold test consists of two phases, Phase1, 1 or 2 Vessel Cooling System (VCS) terminates, in the Phase2, all 3 Gas circulators and 1 VCS terminates. Cold test could confirm test process, and obtain data necessary to analysis and 2-dimensional horizontal sectional model analysis was verified to simulate actual measurement value.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2011-040, 119 Pages, 2011/12
JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility has been utilized by researchers from universities, research institutes, industrial companies as well as from in-house research groups in the fields of nuclear science, materials science etc. This report covers development of accelerators and research activities carried out in the period of April 1, 2010 to March 31, 2011. Thirty-six summary reports are categolized into seven research fields; (1) Accelerator operation and development, (2) Nuclear structure, (3) Nuclear reaction, (4) Nuclear chemistry, (5) Nuclear theory, (6) Atomic physics and solid-state physics and (7) Radiation effect in materials. This report also lists publications, meetings, personnel, committee members, cooperative researches and common use programs.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Sawahata, Masayoshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-037, 66 Pages, 2011/12
When a Nuclear emergency occurs, Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies emergency equipment and materials to the National Government and local governments. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. NEAT also researches on nuclear disaster prevention and cooperates with international organizations. Concerning about the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake at 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its full scale effort. NEAT served as the center of these supporting activities of JAEA.
Kawakami, Takeshi; Tasaki, Takashi
JAEA-Review 2011-028, 47 Pages, 2011/12
The International Search and Consequence Management Workshop (ISCM-WS) that was organized by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) took place from May 17th to May 20th, 2010. The Aim of this Workshop is to build and enhance the global capacity to prevent and respond to nuclear and radiological emergencies, and it directly supports the aims of global initiative to combat nuclear terrorism. DOE brought together 92 officials from 26 countries and 3 officials from IAEA in this Workshop. DOE introduced two matters in USA, First is response against nuclear and radiological terrorisms and second is technology, systems, activity for consequence management. This review report summarized the observation in the ISCM-WS including activity of DOE/NNSA's Search Response Team and activity of consequence management.
Kawakubo, Yoko; Inoue, Naoko; Senzaki, Masao
JAEA-Review 2011-024, 75 Pages, 2011/12
Revision 5 of the "Evaluation Methodology for Proliferation Resistance and Physical Protection of Generation IV Nuclear Energy Systems" is also known as the Rev. 5 report. The Rev. 5 report provides an important evaluation framework that was developed with consensus-based discussions, and published by the OECD-NEA in November, 2006. The activities of PR&PP WG has contributed to establish PR&PP culture. Japan has to develop the future nuclear cycle system with sufficient proliferation resistance and physical protection features and demonstrate and explain about its effectiveness to the domestic and international society. For these reasons, and recognizing the usefulness of the Revision-5 Report, it was translated and published here as a Japanese-language edition with the concurrence of the OECD-NEA. The original report in English language can be downloaded at the OECD-NEA website.
Chiba, Go*; Hazama, Taira; Kinjo, Hidehito*; Nishi, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Takayuki
JAEA-Research 2011-034, 42 Pages, 2011/12
Uncertainty of Doppler coefficient is quantified for a Monju core, reflecting present knowledge. Various uncertainty sources are evaluated: (1) Nuclear data and numerical method, (2) Fission product nuclear data, (3) Control rod position, (4) Approximated treatment of temperature dependence, (5) Averaged fuel temperature, (6) Approximated treatment of temperature spatial distribution, etc. Resulting uncertainty for Doppler coefficient is estimated at 11.7% for the 2  reliability.
reliability.
Doke, Ryosuke; Yasue, Kenichi; Nakayasu, Akio; Niizato, Tadafumi; Tanikawa, Shinichi; Tanaka, Takenobu*; Aoki, Michinori*; Sekiya, Ayako*
JAEA-Research 2011-031, 109 Pages, 2011/12
In this study, existing information related to methods for the estimation of the beginning age of the faulting in the present faulting pattern on the active fault were collected and reviewed. A principle of method, noticing points and technical know-hows in the application of the methods, data uncertainty, and so on were extracted from the existing information. Based on these extracted information, task-flows indicating working process on the estimation of the beginning age for the faulting of the active fault were illustrated on each method. Additionally, the distribution map of the beginning age with accuracy of faulting in the present faulting pattern on the active fault was illustrated.
Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Shibata, Taiju; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-016, 10 Pages, 2011/12
We have developed Code-B-1 for the prediction of the failure probabilities of the coated fuel particles for the high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) under operation by modification of an existing code. A finite element method (FEM) is employed for the stress calculation part and Code-B-1 can treat the plastic deformation of the coating layer of the coated fuel particles which the existing code cannot treat.
Fukaya, Yuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-015, 99 Pages, 2011/12
The conceptual studies for the Next Generation Simulation Code (NGSC) to simulate various fields of phenomena had been performed. As a result, the development of a next generation reactor analysis code system, MARBLE version 1.0, was developed. At this stage, the ability of the MARBLE version 1.0 is only to estimate the nuclear characteristics of FBRs. However, the plan of the NGSC includes LWR analysis and coupling calculations to connect various fields of estimation. In this context, the HARP has been developed as a thermal hydraulic module in the part of the MARBLE. With this module, the temperature, which is essential to estimate power coefficient of reactivity, can be estimated only by the MARBLE system. It is expected to profit for the evolution of the MARBLE as the platform for coupling calculations, because the HARP is the first thermal hydraulic solver of the MARBLE.