Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Cheng, S.; Matsuba, Kenichi; Isozaki, Mikio; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 85, p.740 - 752, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:90.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi
Hokeikyo Nyusu, (56), p.2 - 4, 2015/10
JP, 2010-166333 Licensable Patent Information Database
Licensable Patent Information Database In our study, we focused on a nondestructive inspection method by cosmic-ray muons which could be used to observe the internal reactor from outside the RPV and the CV. We conducted an observation test on the HTTR to evaluate the applicability of the method to the internal visualization of a reactor. We also analytically evaluated the resolution of existing muon telescopes to assess their suitability for the HTTR observation, and were able to detect the major structures of the HTTR based on the distribution of the surface densities calculated from the coincidences measured by the telescopes. Our findings suggested that existing muon telescopes could be used for muon observation of the internal reactor from outside the RPV and CV.
 nanocubes by solvothermal synthesis
nanocubes by solvothermal synthesisYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Nakashima, Koichi*; Nagata, Hajime*; Wada, Satoshi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(10S), p.10NC01_1 - 10NC01_6, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.63(Physics, Applied)The atomic-scale structure of KNbO nanopowder synthesized by solvothermal method has been studied using high-energy X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and the atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) technique. It was found that the local structure of KNbO
nanopowder synthesized by solvothermal method has been studied using high-energy X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and the atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) technique. It was found that the local structure of KNbO nanoparticles deviates from the average structure. The local structure was found to be rhombohedral structure though the average structure was tetragonal structure. The rhombohedral distortion of NbO
nanoparticles deviates from the average structure. The local structure was found to be rhombohedral structure though the average structure was tetragonal structure. The rhombohedral distortion of NbO octahedra was maintained in the annealed sample.
octahedra was maintained in the annealed sample.
Sudo, Ayako; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Shirasu, Noriko; Takano, Masahide; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1308 - 1312, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)For understanding the control blade degradation mechanism of BWR, the thermodynamic database for the fuel assembly materials is a useful tool. Although iron, boron, and carbon ternary system is a dominant phase diagram, phase relation data is not sufficient for the region in which the boron and carbon compositions are richer than the eutectic composition. The phase relations of three samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope and energy dispersed X-ray spectrometry. The results indicate that Fe (B,C) phase only exists in the intermediate region at 1273 K and that the solidus temperature widely maintains at about 1400 K for all three samples, which are different from the calculated data using previous thermodynamic database. The difference might be originated from the over-estimations of the interaction parameter between boron and carbon in Fe
(B,C) phase only exists in the intermediate region at 1273 K and that the solidus temperature widely maintains at about 1400 K for all three samples, which are different from the calculated data using previous thermodynamic database. The difference might be originated from the over-estimations of the interaction parameter between boron and carbon in Fe (B,C).
(B,C).
Takaya, Shigeru; Watanabe, Daigo*; Yokoi, Shinobu*; Kamishima, Yoshio*; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Asayama, Tai
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 137(5), p.051802_1 - 051802_7, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.54(Engineering, Mechanical)The minimum wall thickness required to prevent seismic buckling of a reactor vessel in a fast reactor is derived using the System Based Code (SBC) concept. One of the key features of SBC concept is margin optimization; to implement this concept, the reliability design method is employed, and the target reliability for seismic buckling of the reactor vessel is derived from nuclear plant safety goals. Input data for reliability evaluation, such as distribution type, mean value, and standard deviation of random variables, are also prepared. Seismic hazard is considered to evaluate uncertainty of seismic load. Minimum wall thickness required to achieve the target reliability is evaluated, and is found to be less than that determined from a conventional deterministic design method. Furthermore, the influence of each random variable on the evaluation is investigated, and it is found that the seismic load has a significant impact.
Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.196 - 200, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the J-PARC synchrotrons, Magnetic Alloy (MA) cores loaded RF cavities are employed to achieve a high field gradient. We are successful to increase the shunt impedance of the MA cores for the Main Ring synchrotron RF cavities by applying a transverse magnetic field during annealing. The shunt impedances of the cores with transverse field annealing are around 50% higher than the cores without one. By applying the transverse magnetic field during annealing, the magnetization processes occur by mainly magnetization rotations, and consequently the core loss is reduced and the relative complex permeability shows an excellent frequency behavior. The MA core shunt impedance is increased by those improvements of the magnetic properties.
Hiroki, Akihiro
Cellulose Communications, 22(3), p.143 - 145, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Ouchi, Noriyuki
Evolution of Ionizing Radiation Research, p.41 - 62, 2015/09
Quantitative approach in radiation biology based on the clonogenic method and obtained cell survival curves as a dose-response relationship, are introduced. Generally, cell survival curves seem to have a universality on its function, i.e. functional form of survival curve seems to be unchanged under various conditions including different species. Various factors affecting the radiosensitivity have been introduced to find macroscopic nature of living organisms. Many mathematical models describing cell survival curves have been presented, however, functional form of cell survival curves derived from, based on biological mechanism does not yet exist. Finally, the possibility that the structural change of chromosome affects the repair process is discussed.
Shibata, Keiichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(9), p.1174 - 1185, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron nuclear data on 6 isotopes of iodine have been evaluated for the next release of JENDL general purpose file in the energy region from 10 eV to 20 MeV. Except for
eV to 20 MeV. Except for  I, the thermal capture cross sections were determined from a simplified formula. Unresolved resonance parameters were obtained for self-shielding calculations. On the other hand, a statistical model code CCONE was applied to calculate cross sections above the resolved resonance region. Coupled-channel optical-model potentials were employed for the interaction between neutrons and nuclei. The
I, the thermal capture cross sections were determined from a simplified formula. Unresolved resonance parameters were obtained for self-shielding calculations. On the other hand, a statistical model code CCONE was applied to calculate cross sections above the resolved resonance region. Coupled-channel optical-model potentials were employed for the interaction between neutrons and nuclei. The  -ray strength functions for iodine isotopes were determined so as to reproduce measured
-ray strength functions for iodine isotopes were determined so as to reproduce measured  -ray spectrum for
-ray spectrum for  I. The presently evaluated results are consistent with available experimental data, and found to be much better than the JENDL-4.0 evaluation. The evaluated data are compiled into ENDF formatted data files.
I. The presently evaluated results are consistent with available experimental data, and found to be much better than the JENDL-4.0 evaluation. The evaluated data are compiled into ENDF formatted data files.
 -edge resonant inelastic X-ray Scattering in La
-edge resonant inelastic X-ray Scattering in La CuO
CuO on the basis of detailed electronic band structure
on the basis of detailed electronic band structureNomura, Takuji
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(9), p.094704_1 - 094704_13, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We study theoretically resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at the Cu  -edge in a typical parent compound of high-
-edge in a typical parent compound of high- cuprate superconductors La
cuprate superconductors La CuO
CuO on the basis of a detailed electronic band structure. We construct a realistic and precise tight-binding model by employing the maximally-localized Wannier functions derived from a first-principles electronic structure calculation, and then take account of the Coulomb repulsion between
on the basis of a detailed electronic band structure. We construct a realistic and precise tight-binding model by employing the maximally-localized Wannier functions derived from a first-principles electronic structure calculation, and then take account of the Coulomb repulsion between  electrons at each Cu site. The antiferromagnetic ground state is described within the Hartree-Fock approximation, and take account of electron correlations in the intermediate states of RIXS within the random-phase approximation (RPA). Calculated RIXS spectra agree well with the experimentally observed features including low-energy magnon excitation,
electrons at each Cu site. The antiferromagnetic ground state is described within the Hartree-Fock approximation, and take account of electron correlations in the intermediate states of RIXS within the random-phase approximation (RPA). Calculated RIXS spectra agree well with the experimentally observed features including low-energy magnon excitation,  -
- excitations, and charge-transfer excitations, over a wide excitation-energy range. In particular, we stress the importance of photon polarization dependence: the intensity of magnon excitation and the spectral structure of
excitations, and charge-transfer excitations, over a wide excitation-energy range. In particular, we stress the importance of photon polarization dependence: the intensity of magnon excitation and the spectral structure of  -
- excitations depend significantly not only on the polarization direction of incident incoming photons but also that of outgoing photons.
excitations depend significantly not only on the polarization direction of incident incoming photons but also that of outgoing photons.
 As
As )
)
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kuroki, Kazuhiko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(9), p.093702_1 - 093702_4, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Itami, Toshio*; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
Metals, 5(3), p.1212 - 1240, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:4.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A new kind of suspension liquid was developed by dispersing Ti nanoparticles (10 nm) in liquid Na, which was then determined by TEM (transmission electron microscopy) analysis. The volume fraction was estimated to be 0.0088 from the analyzed Ti concentration (2 at.%) and the densities of Ti and Na. This suspension liquid, Liquid Sodium containing nanoparticles of titanium (LSnanop), shows, despite only a small addition of Ti nanoparticles, many striking features, namely a negative deviation of 3.9% from the ideal solution for the atomic volume, an increase of 17% in surface tension, a decrease of 11% for the reaction heat to water, and the suppression of chemical reactivity to water and oxygen. The decrease in reaction heat to water seems to be derived from the existence of excess cohesive energy of LSnanop. The excess cohesive energy was discussed based on simple theoretical analyses, with particular emphasis on the screening effect. The suppression of reactivity is discussed with the relation to the decrease of heat of reaction to water or the excess cohesive energy, surface tension, the action as a plug of Ti oxide, negative adsorption on the surface of LSnanop, and percolation.
Fukaya, Yuji; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Masuro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(3), p.189 - 201, 2015/09
A study on reduction of potential radiotoxicity for spent fuel by using High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) have been performed. Unlike Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T), the reactor concept is investigated from the viewpoint of reduction of the radiotoxicity generation itself. To reduce the radiotoxicity,  U, which generates Pu, Am and Cm, should be excluded. Therefore, we proposed HTGR fueled by new concept fuels with alternative fuel matrix instead of
U, which generates Pu, Am and Cm, should be excluded. Therefore, we proposed HTGR fueled by new concept fuels with alternative fuel matrix instead of  U. Those are Yttria Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) and thorium, and the fissile material is Highly Enriched Uranium (HEU) with the enrichment of 93%. With the HEU, the radiotoxicity can be significantly reduced, and the cooling time to decay to a natural uranium level can be shorted down to approximately 800 years. Fuel integrity and proliferation resistance can be remained by the dilution using YSZ, and neutronic characteristics of self-regulation is remained by the loading of erbium. The fuel can generate heat as same amount as ordinary uranium fuel. The electricity generation cost is as cheap as ordinary GTHTR300. It is concluded that the proposed reactor concept can reduce the cooling time less than 1% from 100 thousand years to a 800 years without additional technology development.
U. Those are Yttria Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) and thorium, and the fissile material is Highly Enriched Uranium (HEU) with the enrichment of 93%. With the HEU, the radiotoxicity can be significantly reduced, and the cooling time to decay to a natural uranium level can be shorted down to approximately 800 years. Fuel integrity and proliferation resistance can be remained by the dilution using YSZ, and neutronic characteristics of self-regulation is remained by the loading of erbium. The fuel can generate heat as same amount as ordinary uranium fuel. The electricity generation cost is as cheap as ordinary GTHTR300. It is concluded that the proposed reactor concept can reduce the cooling time less than 1% from 100 thousand years to a 800 years without additional technology development.
Sasaki, Yuji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Shirasu, Noriko; Morita, Keisuke; Suzuki, Tomoya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(3), p.202 - 212, 2015/09
We have been developing the new partitioning method of high-level radioactive waste by single-cycle extraction process. This process is composed of extraction of actinides (An) and fission products (FP, e.g., Pd, Ru, Mo and Tc), and mutual separation by back-extraction. The extractant employed in this process is required to extract soft, hard acid metals and oxonium anions simultaneously. The NTAamide (hexaoctyl-nitrilotriacetamide) is one of the candidate extractants. After extraction of An and FP, the mutual separation by back-extraction should be set up. Pd and Ru extracted by NTAamide can be back-extracted by complexing agents such as thiourea, systeine, diethylenetriamine, and trisaminoethylamine, and the back-extraction of Mo can be performed by methylimino-diethylacetamide (MIDEA), NTAamide(C2) and iminodimethylphosphoric acid, and Re can be done by aqueous phase with high pH.
Sugimoto, Takanori*; Mori, Michiyasu; Toyama, Takami*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review B, 92(12), p.125114_1 - 125114_6, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Hg formed in fusion reactions of
Hg formed in fusion reactions of  Ar +
Ar +  Sm
SmNishio, Katsuhisa; Andreyev, A. N.*; Chapman, R.*; Derkx, X.*; D llmann, C. E.*; Ghys, L.*; He
llmann, C. E.*; Ghys, L.*; He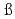 berger, F. P.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Ikezoe, Hiroshi*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Ikezoe, Hiroshi*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 748, p.89 - 94, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:92.9(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Ichimaru, Satoshi*; Takenaka, Hisataka*; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Maruyama, Momoko; Oku, Satoshi*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(9), p.093106_1 - 093106_7, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)A graded and broadband Mo/Si multilayer mirror for EUV spectroscopy is demonstrated. This mirror has an average reflectivity profile of 16% in the wavelength region from 15 nm to 17 nm and an effective area of 1100 - 1500 mm . This reflectivity is about 4 times larger than that of a standard Mo/Si multilayer mirror on a 1 in. diameter substrate, showing that the mirror can be used for measuring EUV fluorescence at wavelengths in the region around 15 nm to 17 nm.
. This reflectivity is about 4 times larger than that of a standard Mo/Si multilayer mirror on a 1 in. diameter substrate, showing that the mirror can be used for measuring EUV fluorescence at wavelengths in the region around 15 nm to 17 nm.
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Izumi, Toshinori
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.417 - 421, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1The interaction between alkali metals and oxides has attracted much attention as heterogeneous catalysis, chemical reaction promoters, and high intensity electron emitter. Also the interaction of cesium and oxides has become important subject, because radioactive cesium trapped in minerals such as clay and soil may cause health risks. In the present study, we analyzed chemical states of ultra-trace amount of cesium on oxide surfaces by total reflection X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (TR-XPS) exited by synchrotron radiation. For the adsorbed cesium thicker than 0.01 layer, cesium is weakly bound with oxide through Van-der-Waals force. On the other hand, for ultra-thin layer about 0.002 layer, the chemical bond changes to covalent bond. It is suggested that this change in the chemical bonding state is one of the reasons why radioactive cesium is hard to be released from minerals.
Fujie, Yutaro*; Kojima, Yuka*; Nagaya, Shun
Daigaku Toshokan Kenkyu, (102), p.34 - 43, 2015/08
no abstracts in English
Buesseler, K. O.*; German, C. R.*; Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Black, E. E.*; Kawakami, Hajime*; Manganini, S. M.*; Pike, S.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(16), p.9807 - 9816, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.84(Engineering, Environmental)A three year time-series of particle fluxes is presented from sediment traps deployed at 500 and 1000 m at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. The accident-derived radiocesium were enhanced in flux peaks that, given variations in trap  Cs/
Cs/ Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from
Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from  120 to
120 to  500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
Niwa, Masakazu; Mizuochi, Yukihiro*; Tanase, Atsushi*
Geofluids, 15(3), p.387 - 409, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.67(Geochemistry & Geophysics)It is expected that in some cases water-rock interaction in fault zones can strongly affect nuclide migration. In this study, we analyzed the chemical composition of well-exposed fault rocks from the Atera Fault, Central Japan, to understand the variability and behavior of major and some selected trace elements. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in fault gouges, and carbon and oxygen isotope ratios in carbonates indicate that the two major clay-rich zones formed in bedrock at near surficial depth, consistent with observed deformation structures. Based on the analyses of chemical compositions, we identified depletion of SiO , Na
, Na O, K
O, K O, and light rare earth elements associated with the formation of smectite and kaolinite, and increase of CaO, MnO, and heavy rare earth elements associated with carbonate precipitation caused by the mixing of allochthonous basalt fragments during fault activities.
O, and light rare earth elements associated with the formation of smectite and kaolinite, and increase of CaO, MnO, and heavy rare earth elements associated with carbonate precipitation caused by the mixing of allochthonous basalt fragments during fault activities.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sato, Kaoru; Endo, Akira; Ono, Koji*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Hasegawa, Takayuki*; Katsunuma, Yasushi*; Yoshitake, Takayasu*; Kai, Michiaki*
Health Physics, 109(2), p.104 - 112, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.13(Environmental Sciences)A dosimetry system, named WAZA-ARI, is developed to assess accurately radiation doses to persons from Computed Tomography (CT) examination patients in Japan. Organ doses were prepared to application to dose calculations in WAZA-ARI by numerical analyses using average adult Japanese human models with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Experimental studies clarified the radiation configuration on the table for some multi-detector row CT (MDCT) devices. Then, a source model in PHITS could specifically take into account for emissions of X-ray in each MDCT device based on the experiment results. Numerical analyses with PHITS revealed a concordance of organ doses with human body size. The organ doses by the JM phantoms were compared with data obtained using previously developed systems. In addition, the dose calculation in WAZA-ARI were verified with previously reported results by realistic NUBAS phantoms and radiation dose measurement using a physical Japanese model. The results implied that analyses using the Japanese phantoms and PHITS including source models can appropriately give organ dose data with consideration of the MDCT device and physiques of typical Japanese adults.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Isotope News, (736), p.47 - 50, 2015/08
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira
Isotope News, (736), p.34 - 37, 2015/08
Japanese translation of ICRP Publication 116 entitled "Conversion Coefficients for Radiological Protection Quantities for External Radiation Exposures" was published by the Japan Radioisotope Association in March 2015. The book gives fluence to dose conversion coefficients for both effective dose and organ absorbed doses for various types of external exposures, consistent with the 2007 Recommendations of the ICRP. A complete set of conversion coefficients is provided in an accompanying CD in ASCII format and Microsoft Excel software. This article overviews ICRP Publication 116 and its impact to practice of radiation protection.
Ishiyama, Shintaro; Imahori, Yoshio*; Itami, Jun*; Koivunoro, H.*
Journal of Cancer Therapy, 6(8), p.759 - 766, 2015/08
From the concentration of 10BPA drug was intravenously injected into the tumor and normal cells of brain tumor patients measured by dynamic PET method, the CBE factor for the BNCT treatment can be calculated by using ISHIYAMA-IMAHORI model.
 , Na
, Na , I
, I and HTO in granodiorite; Laboratory-scale results and their extrapolation to the in situ condition
and HTO in granodiorite; Laboratory-scale results and their extrapolation to the in situ conditionTachi, Yukio; Ebina, Takanori*; Takeda, Chizuko*; Saito, Toshihiko*; Takahashi, Hiroaki*; Ouchi, Yuji*; Martin, A. J.*
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 179, p.10 - 24, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:73.48(Environmental Sciences)Matrix diffusion and sorption are important processes in the assessment of radionuclide transport in crystalline rocks. Diffusion and sorption parameters for Cs , Na
, Na , I
, I and HTO were determined by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments using granodiorite samples from the Grimsel Test Site, Switzerland. The De values were in the order Cs
and HTO were determined by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments using granodiorite samples from the Grimsel Test Site, Switzerland. The De values were in the order Cs , Na
, Na , HTO, I
, HTO, I . The capacity factor and Kd values show the same trends. The dual depth profiles for Cs
. The capacity factor and Kd values show the same trends. The dual depth profiles for Cs and Na
and Na can be interpreted by a near-surface Kd increment. The microscopic analysis indicated that this is caused by high porosity and sorption capacities in disturbed biotite minerals on the sample surface. The Kd values derived from the dual profiles are likely to correspond to Kd dependence on the grain sizes of crushed samples in the batch experiments. The results of the in situ LTD experiments were interpreted reasonably well by using transport parameters derived from laboratory data and extrapolating them to in situ conditions.
can be interpreted by a near-surface Kd increment. The microscopic analysis indicated that this is caused by high porosity and sorption capacities in disturbed biotite minerals on the sample surface. The Kd values derived from the dual profiles are likely to correspond to Kd dependence on the grain sizes of crushed samples in the batch experiments. The results of the in situ LTD experiments were interpreted reasonably well by using transport parameters derived from laboratory data and extrapolating them to in situ conditions.
Soler, J. M.*; Landa, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Tachi, Yukio; Ebina, Takanori*; Sardini, P.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Eikenberg, J.*; Martin, A. J.*
, V.*; Tachi, Yukio; Ebina, Takanori*; Sardini, P.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Eikenberg, J.*; Martin, A. J.*
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 179, p.89 - 101, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:81.5(Environmental Sciences)Matrix diffusion is a key process for radionuclide retention in crystalline rocks. An in-situ diffusion experiment in granite matrix was performed at the Grimsel Test Site (Switzerland). Several tracers (HTO, Na , Cs
, Cs ) were circulated through a borehole and the decrease in tracer concentrations was monitored for 2.5 years. Then, the borehole section was overcored and the tracer profiles in the rock were analyzed. Transport distances in the rock were 20 cm for HTO, 10 cm for Na
) were circulated through a borehole and the decrease in tracer concentrations was monitored for 2.5 years. Then, the borehole section was overcored and the tracer profiles in the rock were analyzed. Transport distances in the rock were 20 cm for HTO, 10 cm for Na and 1 cm for Cs
and 1 cm for Cs . The dataset was analyzed with diffusion-sorption models by different teams using different codes, with the goal of obtaining effective diffusivities (De) and rock capacity factors. There was a rather good agreement between the values from different teams, implied that De and capacity factors in the borehole damaged zone are larger than those in the bulk rock. However, HTO seems to display large discrepancies between measured and modeled results.
. The dataset was analyzed with diffusion-sorption models by different teams using different codes, with the goal of obtaining effective diffusivities (De) and rock capacity factors. There was a rather good agreement between the values from different teams, implied that De and capacity factors in the borehole damaged zone are larger than those in the bulk rock. However, HTO seems to display large discrepancies between measured and modeled results.
Nagae, Yuji; Takaya, Shigeru; Asayama, Tai
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 137(4), p.041407_1 - 041407_5, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Mechanical)Yamashita, Yuji*; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Nagano, Tetsushi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Naganawa, Hirochika
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 305(2), p.583 - 587, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.96(Chemistry, Analytical)We propose a method for the decontamination and waste volume reduction of cesium-contaminated soil. The soils were solidified with an interpolyelectrolyte complex solution and classified into several size fractions by wet sieving.  -ray spectrometry of these fractions showed that the distribution ratio of the activity concentration of coarse soil particles decreased, whereas that of soil particles under 0.075 mm increased relative to reference samples. Results show that the fine soil particles, on which radioactive cesium accumulates, were removed from the surface of the coarse soil particles during, and remained in the washing water.
-ray spectrometry of these fractions showed that the distribution ratio of the activity concentration of coarse soil particles decreased, whereas that of soil particles under 0.075 mm increased relative to reference samples. Results show that the fine soil particles, on which radioactive cesium accumulates, were removed from the surface of the coarse soil particles during, and remained in the washing water.
Yoneya, Masayuki; Sanada, Yukihisa
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(8), p.517 - 522, 2015/08
, 57(8), p.517 - 522, 2015/08
no abstracts in English
 C
COgawa, Tatsuhiko; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Satoh, Daiki; Tsuda, Shuichi; Niita, Koji*
Physical Review C, 92(2), p.024614_1 - 024614_14, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:92.28(Physics, Nuclear)For prediction of radiological impact of heavy ions in accelerator facilities, space missions and cancer therapy, nuclear reaction models play a fundamental role. As one of such models, JAERI Quantum molecular dynamics (JQMD) has been successfully used to describe production of residue and secondary particles in nucleus-nucleus collisions. However, it has been pinpointed that JQMD underestimates projectile-like fragments produced in peripheral collisions. Moreover, no cross section data systematically measured over a wide energy range are not available, which makes it difficult to benchmark the reaction models. In this study, we develop a method to measured fragmentation cross sections using a thick target and detecting fragments produced from incident ions fragmented in the target using telescope detectors. Thus we obtained fragmentation cross sections systematically over a wide energy range. We also revise the description of reaction mechanism and ground-state nuclear structure in JQMD to take into account for peripheral collisions accurately. So far, ground-state nuclei got excited and sometimes disintegrated owing to frame transform from the laboratory system to the center-of-mass system. Fragment production cross sections calculated by the revised JQMD (JQMD2.0) are in better agreement with the literature data.
Naito, Osamu
Physics of Plasmas, 22(8), p.084505_1 - 084505_5, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An analytic formula has been derived for the relativistic incoherent Thomson backscattering spectrum for a drifting anisotropic plasma when the scattering vector is parallel to the drifting direction. The shape of the scattering spectrum is insensitive to the electron temperature perpendicular to the scattering vector, but its amplitude may be modulated. As a result, while the measured temperature correctly represents the electron distribution parallel to the scattering vector, the electron density may be underestimated when the perpendicular temperature is higher than the parallel temperature. Since the scattering spectrum in shorter wavelengths is greatly enhanced by the existence of drift, the diagnostics might be used to measure local electron current density in fusion plasmas.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hirota, Makoto*
Physics of Plasmas, 22(8), p.082512_1 - 082512_9, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.03(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A mechanism exciting magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instabilities in rotating tokamak plasmas is found numerically for the first time. This mechanism is the interplay between a resistive wall mode (RWM) and a stable MHD mode. When the plasma has a stable discrete eigenmode, a reversed shear Alfv n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv
n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency. With a dispersion relation, it was shown explicitly that plasma rotation switches the unstable mode from the RWM to the ideal MHD mode destabilized by wall resistivity.
n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency. With a dispersion relation, it was shown explicitly that plasma rotation switches the unstable mode from the RWM to the ideal MHD mode destabilized by wall resistivity.
Fukano, Yoshitaka; Nishimura, Masahiro; Yamada, Fumiaki
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.5687 - 5698, 2015/08
The following safety criteria for anticipated operational occurrences are commonly and uniformly employed for all the DBAs in the Japanese prototype sodium-cooled fast reactor to prevent fuel melting and cladding failure:(a) Maximum fuel temperature shall be below the melting point,(b) Maximum cladding temperature shall be below 830 C, and (c) Maximum coolant temperature shall be below the boiling point. Cladding failure is allowed, on the contrary to that, in beyond DBAs (BDBAs) or severe accidents (SAs), whereas the core cooling capability is also needed to be secured as in DBAs. No fuel melting enables this by keeping the core in a coolable geometry, and is thus conservatively required even under such a condition. Protected loss-of-heat-sink (PLOHS) events are identified as one of the most dominant sequences. Safety margins for significant core damage in PLOHS events were therefore studied in this paper assuming fuel cladding failure. The following three possible mechanisms leading to degradation of the core were then identified to be scrutinized by a thorough and state-of-the-art review of open papers on the phenomena anticipated to occur under cladding failure conditions:(1) Fuel melting due to fuel-sodium reaction product (FSRP) formation, (2) Thermal transient due to FP gas impingement from adjacent failed fuel pins, and (3) Mechanical load due to the same FP gas impingement. It was clarified through simulation analyses on each phenomenon mentioned above using the FUCA code that there was no significant core damage at the coolant temperatures of up to 950
C, and (c) Maximum coolant temperature shall be below the boiling point. Cladding failure is allowed, on the contrary to that, in beyond DBAs (BDBAs) or severe accidents (SAs), whereas the core cooling capability is also needed to be secured as in DBAs. No fuel melting enables this by keeping the core in a coolable geometry, and is thus conservatively required even under such a condition. Protected loss-of-heat-sink (PLOHS) events are identified as one of the most dominant sequences. Safety margins for significant core damage in PLOHS events were therefore studied in this paper assuming fuel cladding failure. The following three possible mechanisms leading to degradation of the core were then identified to be scrutinized by a thorough and state-of-the-art review of open papers on the phenomena anticipated to occur under cladding failure conditions:(1) Fuel melting due to fuel-sodium reaction product (FSRP) formation, (2) Thermal transient due to FP gas impingement from adjacent failed fuel pins, and (3) Mechanical load due to the same FP gas impingement. It was clarified through simulation analyses on each phenomenon mentioned above using the FUCA code that there was no significant core damage at the coolant temperatures of up to 950 C. It was therefore concluded that large safety margins are provided during PLOHS events even in failure of fuel cladding.
C. It was therefore concluded that large safety margins are provided during PLOHS events even in failure of fuel cladding.
Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Chino, Masamichi; Katata, Genki; Mikami, Satoshi; Saito, Kimiaki
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.4044 - 4052, 2015/08
JAEA has estimated the atmospheric releases of radionuclide during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FNPS1) accident by comparing measurements of air concentration of a radionuclide or its dose rate in the environment with the ones calculated by atmospheric transport and deposition model (ATDM). To improve our source term, we are trying to develop more sophisticated estimation method and use new information from severe accident analysis and observation data. As the first step of new trial, we used  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratios of inventories in FNPS1 reactors Unit 1 to 3 and those in surface deposition. By considering temporal change in
Cs ratios of inventories in FNPS1 reactors Unit 1 to 3 and those in surface deposition. By considering temporal change in  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio of released plume and ATDM simulations, spatial distribution of
Cs ratio of released plume and ATDM simulations, spatial distribution of  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio in surface deposition was explained. This result can be used to specify from which reactor the dominant release occurred for each time period, and consequently provide useful information to severe accident analysis for the FNPS1 case.
Cs ratio in surface deposition was explained. This result can be used to specify from which reactor the dominant release occurred for each time period, and consequently provide useful information to severe accident analysis for the FNPS1 case.
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C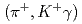 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 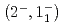 was measured to be
was measured to be 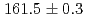 (stat)
(stat)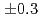 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 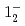 and
and 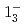 states were measured to be
states were measured to be  , keV and
, keV and 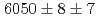 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Takaya, Shigeru; Kamishima, Yoshio*; Machida, Hideo*; Watanabe, Daigo*; Asayama, Tai
Transactions of 23rd International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-23) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2015/08
In our previous study, a new process for determination of in-service inspection (ISI) requirements was proposed on the basis of the System Based Code concept. The proposed process consists of two complementary evaluations, one focusing on structural integrity and the other on plant safety. In this study, ISI requirements for a reactor guard vessel and a core support structure of the prototype sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor in Japan, Monju, were investigated according to the proposed process. The proposed process is expected to contribute to realize effective and rational ISI by properly taking into account plant-specific features.
Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Kawakami, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Matsukawa, Keisuke*; Oshima, Masami*; Izuchi, Hisao*
Transactions of 23rd International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-23) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2015/08
The digital shaking table is introduced to carry out numerical experiments for the so called STRUCTURE of a petroleum plant. In numerical experiments, STRUCTURE was precisely modelled as it is designed and meshed into fine finite elements. The components of STRUCTURE were meshed one by one, and the code of a finite element analysis for structure of assembly gathered every meshed components to run time domain response analysis. Four waves are applied to the analysis to determine its behaviour. Four waves are namely as El Centro, Taft, Hachinohe, and Geiyo. The results of experiments are discussed by comparing accumulating data in the past. It is concluded to reconfirm the methodology of gathering meshed components and a finite element analysis for structure of assembly with the STRUCTURE.
Nishida, Akemi; Choi, B.; Itoi, Tatsuya*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*; Furuya, Osamu*; Muramatsu, Ken*
Transactions of 23rd International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-23) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2015/08
This study focused on uncertainty-assessment frameworks and the development of relevant software to improve the reliability of seismic probabilistic risk assessment (SPRA) for NPP and promote its further use. This research aimed at contributing to development of implementation guidelines on epistemic uncertainty. Some sensitivity analyses were performed using a three dimensional reactor-building model and a conventional evaluation model by using 3D vibration simulator for NPP of JAEA, and the results were provided to the experts for expert-opinion elicitation. The results of the sensitivity analyses were related to the uncertainty evaluation of the buildings and soil to evaluate the fragility of the equipment. In this paper, those results will be shown in comparison with a conventional evaluation model.
Igarashi, Sayaka*; Sakamoto, Shigehiro*; Uchiyama, Yasuo*; Yamamoto, Yu*; Nishida, Akemi; Muramatsu, Ken; Takada, Tsuyoshi*
Transactions of 23rd International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-23) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2015/08
In the preceding study, the methodology to generate ground-motion time histories for advanced PRA of NPPs was proposed by Nishida et al.. They are consistent with seismic hazard at reference site, and incorporate uncertainties of seismic-source characteristics. The ground motions utilized in conventional PRA are generated to fit to specified spectra such as UHS, and they are often generated without considering the variation of spectra. Even if it is considered, their inter-period correlations are generally assumed to be 1.0. In this paper, the authors prepared some cases of ground-motions sets. Ground motions are generated to fit to the response spectra calculated from hazard-consistent ground motions. While the target response spectra have the same median for all case, they have different variation and inter-period correlation. The response analyses of general RC structure and PWR building are conducted and the damage frequencies of simplified equipment system are compared.
Muta, Hitoshi*; Muramatsu, Ken*; Furuya, Osamu*; Uchiyama, Tomoaki*; Nishida, Akemi; Takada, Tsuyoshi*
Transactions of 23rd International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-23) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2015/08
Seismic PRA is an effective measure to consider the countermeasures and improvement plans to secure the further safety of nuclear power plants regarding to seismic risk for the earthquake exceeding the reference ground motion. However, the application of the seismic PRA has not been utilized sufficiently so far. One of the reasons is that there is not enough consensus among stakeholders regarding to the evaluation methods and consideration of uncertainty for decision-making. This study proposes the mathematic framework to treat the uncertainty properly related to the evaluation of Core Damage Frequency induced by earthquake, the method to evaluate the fragility utilizing expert knowledge, the probabilistic model to cope with the aleatory uncertainty as well as the development of analyzing code including these considerations for the improvement of the reliability of the method and enhancement of utilization of the products of Seismic PRA.
V zquez-Campos, X.*; Kinsela, A. S.*; Collins, R. N.*; Neilan, B. A.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Waite, T. D.*
zquez-Campos, X.*; Kinsela, A. S.*; Collins, R. N.*; Neilan, B. A.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(14), p.8487 - 8496, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:67.81(Engineering, Environmental)The uptake and binding of uranium by a moderately acidophilic fungus, 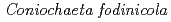 , recently isolated from a uranium mine site, is examined in this work in order to better understand the potential impact of organisms such as this on uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical systems. Our results show that the viability of the fungal biomass is critical to their capacity to remove uranium from solution. Indeed, live biomass were capable of removing 16 mg U/g dry weight in contrast with dead biomass which removed 45 mg U/g dry weight after 2 h. Furthermore, the uranium binds with different strength, with a fraction ranging from 20-50 % being easily leachable from the exposed biomass by a 10 min acid washing. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements show that the strength of uranium binding is strongly influenced by cell viability, with live cells showing a more well-ordered uranium bonding environment, while the distance to carbon or phosphorus second neighbours is similar in all samples. When coupled with laser spectroscopy, the importance of organic acids and phosphates, and polysaccharides, likely released with fungal cell death, appear to be the primary determinants of uranium binding in this system. These results provide an important progression to our understanding with regard to uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical applications.
, recently isolated from a uranium mine site, is examined in this work in order to better understand the potential impact of organisms such as this on uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical systems. Our results show that the viability of the fungal biomass is critical to their capacity to remove uranium from solution. Indeed, live biomass were capable of removing 16 mg U/g dry weight in contrast with dead biomass which removed 45 mg U/g dry weight after 2 h. Furthermore, the uranium binds with different strength, with a fraction ranging from 20-50 % being easily leachable from the exposed biomass by a 10 min acid washing. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements show that the strength of uranium binding is strongly influenced by cell viability, with live cells showing a more well-ordered uranium bonding environment, while the distance to carbon or phosphorus second neighbours is similar in all samples. When coupled with laser spectroscopy, the importance of organic acids and phosphates, and polysaccharides, likely released with fungal cell death, appear to be the primary determinants of uranium binding in this system. These results provide an important progression to our understanding with regard to uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical applications.
Matsuo, Mamoru; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Frontiers in Physics (Internet), 3, p.54_1 - 54_10, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2Nakajima, Norihiro; Miyamura, Hiroko; Kawakami, Yoshiaki; Kawamura, Takuma
Kashika Joho Gakkai-Shi, 35(Suppl.1), p.233 - 238, 2015/07
no abstracts in English
Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/07
Japanese seismic conditions are getting severer and natural frequencies of components are getting lower due to the enlargements of components' size, therefore response accelerations and buckling margins of reactor vessels were parametrically surveyed with attention to thicknesses, diameters, and isolation frequencies for reviewing necessary isolation specification. RV installed floor responses and buckling margins were calculated based on this seismic condition. Expansion characteristic of isolation system was evaluated by parametric acceleration response analyses. Japanese seismic design condition may become severer than present one, and a natural frequency of main component may decrease. However based on the buckling margin with present plant specifications and the expansion characteristic of isolation system, the advanced isolation system with 8Hz vertical natural frequency was selected as the isolation system of JSFR at still present occasion.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ozu, Akira; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Seya, Michio
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/07
The new program "Development of active neutron NDA techniques" has started for non-proliferation applications. The final purpose of this program is to establish the measurement techniques for the high radioactive special nuclear material such as MA-Pu fuel for transmutation of minor actinide. In this program, the JAEA will conduct the R&D on active neutron non-destructive measurement techniques, DDA, NRTA, PGA/NRCA and DGS in collaboration with EC-JRC.
Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Mimura, Hitoshi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 82, p.69 - 73, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kurosaki, Yuzuru
Shototsu, 12(4), p.114 - 125, 2015/07
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Hiroshi
Gakujutsu No Doko, 20(6), p.32 - 38, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Iimura, Hideki; M ller, P.*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Sagawa, Hiroyuki*; Iwamoto, Akira*
ller, P.*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Sagawa, Hiroyuki*; Iwamoto, Akira*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030102_1 - 030102_4, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 784, p.194 - 197, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)A novel ceramics insulated detector element was developed for neutron measurement. The developed detector element consists of a ceramics insulator, cathode lines on the insulator, and ball-shaped anodes. The incident neutrons are usually scattered by the detector element itself because it acts as scatterer. To estimate the effects of scattering, we calculated the amount of neutrons scattered by the developed element. By the calculation results by a Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS, it is found that the developed element is effective to reduce the scattered neutrons. The number of scattered neutrons of the developed element is 40% smaller than that of polymer insulated element, which is widely used in micro-pattern element. Finally, neutron-induced signals were clearly observed using the developed detector element.
Yuri, Yosuke; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Yoshida, Kenichi; Ishibori, Ikuo; Okumura, Susumu
Proceedings of 6th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '15) (Internet), p.236 - 238, 2015/06
Tanaka, Kosuke; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Obayashi, Hiroshi; Koyama, Shinichi
Energy Procedia, 71, p.282 - 292, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:83.55(Energy & Fuels)Americium-containing MOX (Am-MOX) fuels were subjected to heating tests using thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA) measurements in a flowing gas atmosphere of dry air to investigate the effect of Am addition on oxidation behavior of MOX fuel.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Shimokawa, Tomotsugu*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/05
The influence of dislocation density on yield strength, which is a key factor in the anomalous deformation behavior in ultrafine-grained (UFG) metals, was investigated by huge scale atomistic simulations. Polycrystalline models with intragulanular Frank-Read sources were constructed to elucidate the relationship between the inter- and intra-granular plastic deformation processes and the mechanical properties. Then the uniaxial tension and compression were applied to the polycrystalline copper. Consequently it was found that Frank-Read sources were activated prior to intergranular dislocation emission, and the yield event of the whole system seems to occur when some dislocation sources activated. The yield stress is strongly influenced by the number of intragranular dislocation sources, i.e., dislocation density. Additionally, the Bauschinger effect of UFG metals is caused by the change in dislocation density in the process of forward and backward deformation.
 at
at 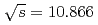 GeV
GeVGarmash, A.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*
Physical Review D, 91(7), p.072003_1 - 072003_16, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:92.84(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Senzaki, Masao; Naoi, Yosuke; Kuribayashi, Toshihiro; Okumura, Yukiko
Book of Abstracts, Presentations and Papers of Symposium on International Safeguards; Linking Strategy, Implementation and People (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA has supported to HRD of mainly Asian countries in the field of SGs and SSAC, and works closely with governmental organizations in Japan, and with the IAEA, the US DOE, EC, the flame work of FNCA, APSN. This paper presents the efforts, contributions and future challenges of JAEA to HRD regarding SGs and SSAC, through international cooperation, which have been taking place for around 20 years.
Seya, Michio; Kobayashi, Naoki; Naoi, Yosuke; Hajima, Ryoichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Harada, Hideo
Book of Abstracts, Presentations and Papers of Symposium on International Safeguards; Linking Strategy, Implementation and People (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA-ISCN has been implementing basic development programs of the advanced NDA technologies for nuclear material (NM) since 2011JFY (Japanese Fiscal Year), which are (1) NRF (Nuclear resonance fluorescence) NDA technology using laser Compton scattered (LCS)  -rays (intense mono-energetic
-rays (intense mono-energetic  -rays), (2) Alternative to
-rays), (2) Alternative to  He neutron detection technology using ZnS/B
He neutron detection technology using ZnS/B O
O ceramic scintillator, and (3) NRD (Neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (Neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (Neutron resonance capture analysis). These programs are going to be finished in 2014JFY and have demonstration tests in February - March 2015.
ceramic scintillator, and (3) NRD (Neutron resonance densitometry) using NRTA (Neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (Neutron resonance capture analysis). These programs are going to be finished in 2014JFY and have demonstration tests in February - March 2015.
Nakamura, Hironobu; Mukai, Yasunobu; Kurita, Tsutomu
Book of Abstracts, Presentations and Papers of Symposium on International Safeguards; Linking Strategy, Implementation and People (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/03
The Distributed Source-Term Analysis (DSTA) technique has been used in a variety of safeguards applications to determine location and quantity of material contained within large sample volumes. By applying this method, JAEA developed and applied two different neutron measurement techniques in order to improve own MC&A. The first advanced technique is a Glove Box Cleanout Assistance Tool (BCAT). It is used by operator during cleanout just before PIT to increase recovered material, to decrease unmeasured inventory, and to perform the cleanout activity effectively. The BCAT is being introduced to the actual cleanout since 2011. The second advanced technique is a dynamic cross-talk correction (DCTC) method. The DCTC can obtain actual doubles signal cross-talk between multiple gloveboxes. In order to assay Pu amount in the holdup correctly, we implemented an improved HBAS system using DCTC. Two advanced holdup measurement technologies provide appropriate safety and safeguards environment to conduct nuclear cycle with operator and inspector.
 rays-irradiation
rays-irradiationKawahara, Yutaka*; Sekiguchi, Takahiro*; Nishikawa, Yukihiro*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu
Nihon Shiruku Gakkai-Shi, 23, p.67 - 69, 2015/03
Silk aerogel has been prepared from liquid silk, and the influences of the  ray-irradiation on its mechanical property have been investigated. The formation of crosslinking structure in the sericin component by the
ray-irradiation on its mechanical property have been investigated. The formation of crosslinking structure in the sericin component by the  ray-irradiation should induced the hardening of the silk aerogel.
ray-irradiation should induced the hardening of the silk aerogel.
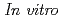 studies on cellular binding and stability of
studies on cellular binding and stability of  Cu-labeled peptide for tumor imaging
Cu-labeled peptide for tumor imagingSugo, Yumi; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Sasaki, Ichiro; Ishioka, Noriko
Peptide Science 2014, p.303 - 306, 2015/03
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Takayanagi, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.394 - 398, 2015/03
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hayashi, Naoki; Okabe, Kota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Hashimoto, Yoshinori*; Toyama, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.278 - 282, 2015/03
Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC) is providing more than 300 kW of proton beam to Material and Life science Facility (MLF) and Main Ring (MR). Last summer shutdown, a new ion source was installed to increase output power to 1 MW. In order to achieve reliable operation of 1 MW, we need to reduce beam loss as well. Beam quality of such higher output power is also important for users. Therefore we developed new monitors that can measure the halo with higher accuracy. We present beam monitor systems for these purposes.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Toyama, Takeshi*; Chin, Y. H.*; Takata, Koji*
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.74 - 78, 2015/03
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Saha, P. K.; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Chin, Y. H.*; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.369 - 373, 2015/03
Hotchi, Hideaki
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.6 - 11, 2015/03
The J-PARC 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) is the world's highest class of high-power pulsed proton driver aiming at 1-MW output beam power. In the last summer shutdown of 2013, the injection energy from the linac was upgraded from 181 MeV to the design value of 400 MeV. In addition, in this summer shutdown of 2014, the maximum peak current of the injection beam was increased from 30 mA to the design value of 50 mA. In October 2014 after completing these series of the injector linac upgrades, we have started the final stage of beam tuning toward the design output beam power of 1 MW. The most important issues in realizing such a high power 1 MW beam operation are control and minimization of beam loss. This talk will present our approaches to beam loss issues that we faced on the process of the beam power ramp-up.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Meigo, Shinichiro; Hotchi, Hideaki
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2015/03
The 3-GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of J-PARC is designed for a high-intensity output beam power of 1MW. The RCS is extracted 2 bunches by using 8 pulsed kicker and 3 septum magnets with 25Hz repetition. The extracted beam is simultaneously delivered to the Material and Life science Facility (MLF) as well as the 50-GeV synchrotron. The kicker magnets have the ringing of flat-top field and the ringing causes the position displacement. The displacement is big issue because it directly causes an emittance growth of the extracted beam. In the beam tuning, we performed a timing scan of each kicker magnet by using a shorter pulse beam and understood the characteristics of ringing field. We then carefully optimized timing of each kicker for the ringing cancellation. The displacement was reduced to be less than 1mm as compared to that of 15mm with no ringing correction. The present correction method and experimental results will be reported.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.143 - 147, 2015/03
Transverse beam halo is one of the most important beam parameters due to limit the performance of the high intensity beam accelerator. Therefore the transverse beam halo measurement is required to increase the beam power of the J-PARC 3-GeV RCS. In the beam profile, there are the beam core which is a high density area, the beam tail which is a low density area around the beam core, and the beam halo which is the area outside of the beam tail and in which few particles are straggling. Generally, the beam halo intensity is less than 1/100000  1/1000000 of the beam core. Therefore, the dynamic range of the beam halo is required typically an order of 10
1/1000000 of the beam core. Therefore, the dynamic range of the beam halo is required typically an order of 10 , but it is difficult to achieve this ultra wide dynamic range by any one diagnostics. Then, new beam halo monitor, which is combined a wire type beam scraper and some beam loss monitors, are developed and installed in the extraction beam transport line. Each beam loss monitor has not more than 10
, but it is difficult to achieve this ultra wide dynamic range by any one diagnostics. Then, new beam halo monitor, which is combined a wire type beam scraper and some beam loss monitors, are developed and installed in the extraction beam transport line. Each beam loss monitor has not more than 10 order of the dynamic range. However, to use some beam loss monitors with a plurality of different sensitivity range, its ultra wide dynamic range can be achieved and beam profile including both of the beam core, beam tail, and beam halo can be obtained.
order of the dynamic range. However, to use some beam loss monitors with a plurality of different sensitivity range, its ultra wide dynamic range can be achieved and beam profile including both of the beam core, beam tail, and beam halo can be obtained.
 collisions at
collisions at 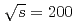 GeV
GeVImai, Kenichi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; PHENIX Collaboration*
Physical Review D, 91(3), p.032001_1 - 032001_13, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:41.91(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 573(1), p.012028_1 - 012028_4, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:79.08(Engineering, Biomedical)Polymer gel dosimeters based on radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose gel were prepared, which comprised 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (9G) as less toxic monomers and tetrakis (hydroxymethyl) phosphoniumu chloride (THPC) as an antioxidant. The dosimeters exposed to  Co
Co  -rays became cloudy at only 1 Gy. The irradiated dosimeters were optically analyzed by using a UV-vis spectrophotometer to evaluate dose response. Absorbance of the dosimeters linearly increased in the dose range from 0 to 10 Gy. The dose sensitivity increased with increasing 9G concentration. The dosimeter with 2 wt% HEMA, 3 wt% 9G, and 0.16 wt% THPC exhibited about 0.04 Abs Gy
-rays became cloudy at only 1 Gy. The irradiated dosimeters were optically analyzed by using a UV-vis spectrophotometer to evaluate dose response. Absorbance of the dosimeters linearly increased in the dose range from 0 to 10 Gy. The dose sensitivity increased with increasing 9G concentration. The dosimeter with 2 wt% HEMA, 3 wt% 9G, and 0.16 wt% THPC exhibited about 0.04 Abs Gy of the dose sensitivity. The dose sensitivity of the dosimeters was also enhanced by increment in THPC, reached about 0.06 Abs Gy
of the dose sensitivity. The dose sensitivity of the dosimeters was also enhanced by increment in THPC, reached about 0.06 Abs Gy at 0.40 wt% THPC.
at 0.40 wt% THPC.
 Si crystals with XAS and XPS
Si crystals with XAS and XPSYamamoto, Hiroyuki; Nojima, Takehiro; Esaka, Fumitaka
Photon Factory Activity Report 2014, Part B, P. 112, 2015/00
In order to develop silicon-based electronic devices, metal silicides are widely studied. Information of the surface chemical states of metal silicides is important to obtain homo-epitaxial films with excellent quality. In this work, depth analysis of surface chemical states of Mg Si crystals is carried by XPS. Depth analysis is also performed in XAS measurement with a partial electron yield (PEY) mode. The Si 1s XPS spectra of the cleaved surface of the Mg
Si crystals is carried by XPS. Depth analysis is also performed in XAS measurement with a partial electron yield (PEY) mode. The Si 1s XPS spectra of the cleaved surface of the Mg Si crystal indicates that SiO is formed on the surface of the Mg
Si crystal indicates that SiO is formed on the surface of the Mg Si crystal. Here, no peak assigned to SiO
Si crystal. Here, no peak assigned to SiO structure is observed. The Si K-edge XAS spectra obtained with the PEY mode show a peak at 1843.7 eV, which can be assigned to SiO structure.
structure is observed. The Si K-edge XAS spectra obtained with the PEY mode show a peak at 1843.7 eV, which can be assigned to SiO structure.
Kimura, Takaumi
Genshiryoku, Ryoshi, Kakuyugo Jiten, 3, p.52 - 55, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Koichi*; Iikura, Hiroshi
Nuclear Science and Techniques, 25(S1), p.S010604_1 - S010604_5, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(11), p.C11019_1 - C11019_9, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)A multiwire-type two-dimensional neutron detector system using individual line readout and optical signal transmission method is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The sensitive area was 128  128 mm
128 mm with a pitch of 1 mm in both directions (x and y), and the 256 signal lines are individually readout by signal-processing electronics. First irradiation experiments using pulsed neutrons are performed at the J-PARC/MLF. The developed detector could determine time-of-flight spectra and time-resolved two-dimensional images accurately with time range from 0 to 40 ms that arise from 25-Hz pulsed neutrons. Finally, the validity of the detector system is confirmed by a neutron reflectometry using Ni/Ti multilayer.
with a pitch of 1 mm in both directions (x and y), and the 256 signal lines are individually readout by signal-processing electronics. First irradiation experiments using pulsed neutrons are performed at the J-PARC/MLF. The developed detector could determine time-of-flight spectra and time-resolved two-dimensional images accurately with time range from 0 to 40 ms that arise from 25-Hz pulsed neutrons. Finally, the validity of the detector system is confirmed by a neutron reflectometry using Ni/Ti multilayer.
Angell, C.; Hajima, Ryoichi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Karwowski, H.*; Silano, J.*
Physical Review C, 90(5), p.054315_1 - 054315_6, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.9(Physics, Nuclear) As
As
Kodama, Katsuaki; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kiho, Kunihiro*; Lee, C.-H.*; Iyo, Akira*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Physical Review B, 90(14), p.144510_1 - 144510_5, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt
-ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea saltMotooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), seawater was injected into spent fuel pools in March 2011. Zircaloy-2 is adopted for the fuel cladding at 1F. Zirconium alloys including Zircaloy-2 are susceptible to pitting corrosion in oxidizing chloride solutions. In this study, we investigated the effect of oxide film formed during  -ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt. The pitting potentials of Zircaloy-2 were measured using the water containing artificial sea salt. Changes in the composition of water containing sea salt were analyzed before and after
-ray irradiation on pitting corrosion of fuel cladding in water containing sea salt. The pitting potentials of Zircaloy-2 were measured using the water containing artificial sea salt. Changes in the composition of water containing sea salt were analyzed before and after  -ray irradiation. The characteristics of the oxide films formed on Zircaloy-2 were evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solution analyses for water containing sea salt showed that hydrogen peroxide was generated by the irradiation. The pitting potential of Ziracloy-2 with oxide film formed under
-ray irradiation. The characteristics of the oxide films formed on Zircaloy-2 were evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solution analyses for water containing sea salt showed that hydrogen peroxide was generated by the irradiation. The pitting potential of Ziracloy-2 with oxide film formed under  -ray irradiation was higher than that with oxide film formed without irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the oxide film was composed of zirconium oxide and the growth of oxide film was enhanced during the irradiation. It could thus be explained that the enhanced growth of oxide film under
-ray irradiation was higher than that with oxide film formed without irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicated that the oxide film was composed of zirconium oxide and the growth of oxide film was enhanced during the irradiation. It could thus be explained that the enhanced growth of oxide film under  -ray irradiation caused the higher pitting potential.
-ray irradiation caused the higher pitting potential.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Kakubo, Yuta*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Nozawa, Yasuko*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Onizawa, Kunio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 452(1-3), p.235 - 240, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:95.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Microstructures and hardness of stainless steel weld overlay cladding of reactor pressure vessels subjected to the thermal aging at 400  C for 100-10,000 h were investigated using atom probe tomography and nanoindentation technique. The Cr concentration fluctuation in the
C for 100-10,000 h were investigated using atom probe tomography and nanoindentation technique. The Cr concentration fluctuation in the  -ferrite phase caused by spinodal decomposition rapidly progressed by the 100 h aging while NiSiMn clusters increased in number density at 2,000 h and coarsened at 10,000 h. The hardness of the
-ferrite phase caused by spinodal decomposition rapidly progressed by the 100 h aging while NiSiMn clusters increased in number density at 2,000 h and coarsened at 10,000 h. The hardness of the  -ferrite phase also rapidly increased at the short aging time. The Cr concentration fluctuation and the hardness were in good correlation with the degree of the Cr concentration fluctuation rather than the formation of the NiSiMn clusters. These results strongly suggested that the dominant factor of the hardening of the
-ferrite phase also rapidly increased at the short aging time. The Cr concentration fluctuation and the hardness were in good correlation with the degree of the Cr concentration fluctuation rather than the formation of the NiSiMn clusters. These results strongly suggested that the dominant factor of the hardening of the  -ferrite phase by the thermal aging was Cr spinodal decomposition.
-ferrite phase by the thermal aging was Cr spinodal decomposition.
 IrSi
IrSi
Pyon, S.*; Kudo, Kazutaka*; Matsumura, Junichi*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Matsuo, Genta*; Nohara, Minoru*; Hojo, Hajime*; Oka, Kengo*; Azuma, Masaki*; Garlea, V. O.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(9), p.093706_1 - 093706_5, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:82.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sugawara, Takanori; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; The Role of Reactor Physics toward a Sustainable Future (PHYSOR 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/09
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has the plan to construct Transmutation Physic Experimental Facility (TEF-P) under a framework of J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) project. TEF-P is a critical assembly which can load Minor Actinide (MA) fuels to perform reactor physics experiments for transmutation systems such as Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) or Fast Reactor (FR). The facility can also use proton beam from the J-PARC accelerator to investigate the controllability of ADS. Cur-rent status and activities for TEF-P are described.
Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kubo, Makoto*; Ma, H.*; Nakagawa, Akiko*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Isono, Mayu*; Kanai, Tatsuaki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Radiation Research, 182(3), p.338 - 344, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:90.66(Biology)To clarify whether high-LET radiation inhibits all repair pathways or specifically one repair pathway, studies were designed to examine the effects of radiation with different LET values on DNA DSB repair and radiosensitivity. Embryonic fibroblasts bearing repair gene KO were exposed to X rays, carbon-, iron-, neon- and argon-ion beams. Cell survival was measured with colony-forming assays. The sensitization enhancement ratio (SER) values were calculated using the 10% survival dose of wild-type cells and repair-deficient cells. Cellular radiosensitivity was listed in descending order: double-KO cells  NHEJ-KO cells
NHEJ-KO cells  HR-KO cells
HR-KO cells  wild-type cells. Although HR-KO cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ-KO cells showed a high-SER value when compared to HR-KO cells, even with increasing LET values. These results suggest that with carbon-ion therapy, targeting NHEJ repair yields higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair.
wild-type cells. Although HR-KO cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ-KO cells showed a high-SER value when compared to HR-KO cells, even with increasing LET values. These results suggest that with carbon-ion therapy, targeting NHEJ repair yields higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair.