Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Takahashi, Naoya; Niwa, Masakazu
JAEA-Testing 2017-001, 52 Pages, 2017/03
It is essential to understand the activity of faults in and around a target area to assess the long-term geosphere stability for geological isolation. Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) dating of fault gouge has been conducted in Tono Geoscience Center as one of the dating technique for faulting. This report includes methods for sample preparation, analyses, and age calculation on the K-Ar dating. This can contribute to an evaluation of calculated K-Ar ages.
Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2017-007, 18 Pages, 2017/03
Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) facility have been utilized for fuel irradiation experiments to study the behaviors of nuclear fuels under reactivity initiated accident conditions. Unirradiated test fuels used in fuel irradiation experiments and flesh driver fuel elements for reactor operation are stored in the fuel building of the facility. In response to the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, the impact of NSRR's nuclear fuel material usage facilities on external events beyond design requirements was evaluated. The subcriticality of the flesh fuel storage was confirmed in consideration of earthquake and tsunami as superimposed event.
Mori, Airi; Tanabe, Tsutomu; Wada, Takao; Kato, Mitsugu
JAEA-Technology 2017-006, 38 Pages, 2017/03
Large quantities of radioactive materials were released into the environment as a result of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. Residential areas and forest areas near the power station were contaminated with the radioactive materials. Outside of the houses, schools and the other buildings are being decontaminated by national authority and local government. On the other hand, the materials (such as walls, floors, or windows) which constitute the houses are not decontaminated officially. In order to prepare decontamination methods that can be applied easily, we conducted examinations of decontamination for various materials in houses. Fibrous materials, woods, glasses, concretes, plastics, vinyl chloride materials, metals and synthetic leathers were used in our examinations. These materials were collected from houses in difficult-to-return zone, and were contaminated by radioactive materials released by the accident. Dry methods (suction, wiping, adsorption and peelable coating), wet methods (wiping, brushing, polishing and washing) and physical method (peeling of materials) were used for decontamination. As a result of our examinations, materials with low water permeability, such as glasses, concretes, vinyl chloride materials and metals, were able to be decontaminated efficiently (about 90% reduction) by using wet methods. Materials with high water permeability like woods were relatively well decontaminated by peelable coating (about 60%-70% reduction). In addition to the examination described above, the difference of contamination reduction effect between chemical properties of detergents and the effect of rubbing of peelable coating were also examined. Finally, the most effective method was summarized based on these examinations.
Toguri, Satohito*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Yahagi, Ryoji*; Yamada, Toshiko*; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Aoyagi, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2017-005, 43 Pages, 2017/03
The study on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project roughly consists of (1) development of design and construction planning technologies, (2) development of construction technology, (3) development of countermeasure technology, (4) development of technology for security, and (5) development of technologies regarding restoration and mitigating of the excavation effect. In FY2015, as a part of the important issues on the research program, water-tight grouting method has been developed. Grouting methods utilized in the MIU were evaluated and the post-excavation grouting at the -500m Access/Research Gallery-South was planned based on these evaluation results. Also, technology development from the viewpoint of geological disposal was summarized, and information on the alternative method to the grouting method was collected and organized.
Mizuta, Naoki; Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Shibata, Taiju
JAEA-Technology 2017-004, 22 Pages, 2017/03
Confirmation of feasibility of fabrication technology and characterization of the high-packing fraction fuel compact of High Temperature Gas Reactor (HTGR) fuel were carried out. Fuel compacts were fabricated with CFP packing fraction targeted at 33 percent by the same manufacturing condition of HTTR fuel compact. SiC-defective fraction, compressive strength and internal CFP distribution of the compact, important parameters to guarantee its integrity, were evaluated. The high-packing fuel compacts showed as same level of SiC-defective fraction as that of HTTR first loading fuel, 8 10
10 , and larger compressive strength than the HTTR fuel criteria, 4,900N. The feasibility of fabrication technology and the performance for the high-packing fraction fuel compact was confirmed.
, and larger compressive strength than the HTTR fuel criteria, 4,900N. The feasibility of fabrication technology and the performance for the high-packing fraction fuel compact was confirmed.
Nuclear Transmutation Division, J-PARC Center
JAEA-Technology 2017-003, 539 Pages, 2017/03
JAEA is pursuing R&D on volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste based on the "Strategic Energy Plan" issued in April 2014. Construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility is under planning as one of the second phase facilities in the J-PARC program to promote R&D on the transmutation technology with using accelerator driven systems (ADS). The TEF consists of two facilities: ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) and Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). Development of spallation target technology and study on target materials are to be conducted in TEF-T with impinging a high intensity proton beam on a lead-bismuth eutectic target. Whereas in TEF-P, by introducing a proton beam to minor actinide loaded subcritical cores, physical properties of the cores are to be studied, and operation experiences are to be acquired. This report summarizes results of technical design for construction of one of two TEF facilities, TEF-T.
Ishihara, Keisuke; Kanazawa, Shingo; Kozawa, Masachiyo; Mori, Masakazu; Kawahara, Takahiro
JAEA-Technology 2017-002, 27 Pages, 2017/03
At radioactive waste management facilities in the Nuclear Science Research Institute, solid radioactive wastes are stored by using containers such as 200L drums and pallets to tier containers in 2 to 4 stacks in the height direction in waste storage facilities (Waste Storage Facility No.1, Waste Storage Facility No.2 and Waste Size Reduction and Storage Facility). On March 11, 2011, the Great East Japan Earthquake was happened, and some waste packages dropped from their pallets and large number of waste packages moved from their original position and inclined due to the influence of the earthquake in the waste storage facilities. There was no experience of rearrangement works to set those dropped and unbalanced waste packages in their original position and it was necessary to prepare detailed work procedures and progress for this task to prevent the occurrence of industrial accidents. Therefore, we prepared detailed work manual and repeatedly carried out mock-up test. And then, we started rearrangement work from April 2011 after confirmation of workers skill and adequacy of the work manual. Finally, all rearrangement works for stored waste packages took about four and half years and were completed in September 2015 without any accident and shutdown of storage function. This report summarizes the countermeasures to reduce exposure doses of workers and to prevent the occurrence of industrial accidents during the rearrangement works.
Totsuka, Masayoshi; Kurosawa, Ryohei*; Sakai, Akihiro; Nakata, Hisakazu; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Amazawa, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2017-001, 40 Pages, 2017/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is planning for the near surface disposal of low level radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities industry in Japan. This document provides the values of radioactivity concentrations equivalent to dose criterion for trench-type disposal. These values are derived based on the safety assessment for ground water scenarios by using a model which describes the release of radionuclides from wastes to a cover soil caused by elution. These concentrations are compared with the one calculated by a model that describes the nuclide release mechanisms as solid-liquid partitioning equilibrium. Additionally, the change in the concentrations is evaluated when the amount of water percolating into a disposal facility varies.
Miyai, Hiromitsu; Suzuki, Miho; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2016-041, 46 Pages, 2017/03
In the Reactor Fuel Examination Facility (RFEF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Post Irradiation Examinations (PIEs) have been carried out for a long time in order to verify the reliability and the safety of the nuclear fuels irradiated in nuclear power plants. Samples for the PIEs are small and have various shapes. In order to facilitate the handling of the samples using a manipulator, the several kinds of jigs have been used for PIEs at RFEF those jigs are usually manufactured by machining process. We tried to make the jigs, which is PLA resin, with 3D printer and instead of machining process for the reduction of the manufacturing time and the improvement of the dimensional accuracy of the jig this time. It became clear that the actual dimensions of the jigs manufactured with 3D printer were roughly smaller at the concave section and larger at the convex section compared with the dimensions of the plan. So it is necessary to make a plan for the jigs after consideration of the characteristic of the 3D printer. The jigs can be applied to SEM observation, because the deposition of carbon film onto the jigs was well. And the jigs can be used to for the metallography, because the jigs were applicable without any harmful effects on polishing and etching processes.
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Goto, Minoru; Takada, Shoji
JAEA-Technology 2016-040, 16 Pages, 2017/03
To study the packing effects of the truncated coated fuel particle on the criticality for the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), four alternative models including the truncated uniform model, the non-truncated uniform model, the truncated random model and the non-truncated random model for the arrangement of CFP in fuel compact were used, and the neutronic and criticality calculation were performed by using Monte Carlo MCNP6 code with ENDF/B-VII.1 cross section library. The results showed that the infinite multiplication factors (k ) in the truncated models were lower than those of the non-truncated models regardless of the uniform or random arrangement, and the four factors in the four-factor-formula showed that the difference of k
) in the truncated models were lower than those of the non-truncated models regardless of the uniform or random arrangement, and the four factors in the four-factor-formula showed that the difference of k was mainly attributed to the resonance escape probability. The difference in resonance escape probability is caused by the increase of capture reactions in the resonance region as the influence of spatial-self-shielding-effect. It is because the equivalent kernel diameter of the CFP for the truncated model is smaller than that of the non-truncated model.
was mainly attributed to the resonance escape probability. The difference in resonance escape probability is caused by the increase of capture reactions in the resonance region as the influence of spatial-self-shielding-effect. It is because the equivalent kernel diameter of the CFP for the truncated model is smaller than that of the non-truncated model.
Segawa, Yukari; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nakada, Masami; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Tamura, Yukito*; Okamoto, Hisato; Otomo, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-039, 64 Pages, 2017/03
The laboratory building No.1 for the plutonium research program (Bldg. Pu1) was chosen as one of the facilities to decommission by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform in September, 2013. The research groups, users of Bldg. Pu1, were driven by necessity to remove used equipment and transport nuclear fuel to other facilities from Bldg. Pu1. Research Group for Radiochemistry proactively established the Used Equipment Removal Team for the smooth operation of the removal in April, 2015. The team classified six types of work into the nature of the operation, removal of used equipment, disposal of chemicals, stabilization of mercury, stabilization of nuclear fuel, transportation of nuclear fuel and radioisotope, and survey of contamination status inside the glove boxes. These works were completed in December, 2015. This report circumstantially shows six works process, with the exception of the approval of the changes on the usage of nuclear fuel in Bldg. Pu1 to help prospective decommission.
 ion production by electron attachment using cesium sputter ion source
ion production by electron attachment using cesium sputter ion sourceUsui, Aya; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke
JAEA-Technology 2016-034, 21 Pages, 2017/03
In the TIARA (Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application), in order to propel the studies on the swift cluster ions, a novel technique was developed to increase the beam intensity of the fullerene ions which would have a considerably larger irradiation effect than any cluster ions. As a new method of negative ion production, the ionization mechanism by electron attachment was introduced as an alternative to the traditional method with the cesium sputtering to the existing cesium sputter type ion source (SNICS). In consequence, the intensity of the negative C ion beam produced using an existing ion source with a novel technique was increased thousand times as high as those using the previous one for 12 hour operation. In this report, we describe the problems in the traditional ionization method and explain the production technique of the negative C
ion beam produced using an existing ion source with a novel technique was increased thousand times as high as those using the previous one for 12 hour operation. In this report, we describe the problems in the traditional ionization method and explain the production technique of the negative C ions ionized via electron attachment process, which solves that only by the minor changes in SNICS.
ions ionized via electron attachment process, which solves that only by the minor changes in SNICS.
Eguchi, Shohei; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Tanimoto, Masataka; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2017-007, 32 Pages, 2017/03
A practical training course using the JMTR and other research infrastructures was held from July 25th to August 5th in 2016 for domestic and foreign young researchers and engineers. This course aims to enlarge the number of high-level nuclear researchers/engineers in Japan and foreign countries which are planning to introduce a nuclear power plant, and to promote the use of facilities in future. In this year, 13 young researchers and engineers joined the course from 7 countries. This course consists of lectures, which are related to irradiation test research, safety management of nuclear reactors, nuclear characteristics of the nuclear reactors, etc., practical training and technical tour of nuclear facilities on nuclear energy. At the end of the course, the trainees discussed the energy policy and prospect of each country, each country's research reactor, and trainee's current research. The content of this course in FY 2016 is reported in this paper.
Kawase, Keiichi; Kitano, Mitsuaki; Watanabe, Masanori; Yoshimura, Shuichi; Kikuchi, Shiro; Nishino, Katsumi*
JAEA-Review 2017-006, 173 Pages, 2017/03
Survey of a transition of the air and surface dose rate was conducted for the area where the Cabinet Office decontamination model demonstration project was implemented. The area includes 15 districts in 9 municipalities identified by the Ministry of the Environment. We investigated 11 times from October, 2012 to October, 2015. Measurement of the air dose rate in this study was carried out in two methods using the fixed-point measurement and gamma plotter H using a NaI scintillation survey meter etc. As fixed-point measurement, set measurement point in the first survey for (fixed point), it was subjected to measurement of the surface dose rate to continue (1cm height) and space dose rate (1m height). In addition surface specific dose rate distribution measurement using a gamma plotter H (5cm and 1m height) was also performed together. As a result of the fixed-point measurement and gamma plotter H surface measurements, space dose rate from the first survey to the 11th survey shows the downward trend. We consider that there is no movement of radioactive pollutants from outside decontamination model project area into decontamination model project area.
Li, Y.; Hayashi, Shotaro*; Itabashi, Yu*; Nagai, Masaki*; Kanto, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Masahide*; Masaki, Koichi*
JAEA-Review 2017-005, 80 Pages, 2017/03
For the improvement of the structural integrity assessment methodology on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs), the probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed and improved in JAEA based on latest knowledge. The PASCAL code evaluates the failure probabilities and frequencies of Japanese RPVs under transient events such as pressurized thermal shock considering neutron irradiation embrittlement. In order to confirm the reliability of the PASCAL as a domestic standard code and to promote the application of PFM on the domestic structural integrity assessments of RPVs, it is important to verify the probabilistic variables, functions and models incorporated in the PASCAL and summarize the verification processes and results as a document. On the basis of these backgrounds, we established a working group, composed of experts on this field besides the developers, on the verification of the PASCAL3 which is a PFM analysis module of PASCAL, and the source program of PASCAL3 was released to the members of working group. Through one year activities, the applicability of PASCAL in structural integrity assessments of domestic RPVs was confirmed with great confidence. This report summarizes the activities of the working group on the verification of PASCAL in FY2015.
Motooka, Takafumi; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Review 2017-004, 157 Pages, 2017/03
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) is responsible to promote international cooperation in the R&D activities on the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and to develop the necessary human resources. CLADS held the Research Conference on Post-accident Waste Management Safety (RCWM2016) was held on November 7th, 2016 and the Technical Seminar on Safety Research for Radioactive Waste Storage was held on November 8th, 2016. This report compiles the abstracts and the presentation materials in the above conference and seminar.
 CEN and JAEA for Partitioning and Transmutation through Accelerator-Driven System
CEN and JAEA for Partitioning and Transmutation through Accelerator-Driven SystemWorking Group for Collaboration between SCK CEN and JAEA for P&T through ADS
CEN and JAEA for P&T through ADS
JAEA-Review 2017-003, 44 Pages, 2017/03
This technical report reviews Research and Development (R&D) programs for the Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) technology through Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) at Studiecentrum voor Kernenergie/Centre d'Etude de l' nergie Nucl
nergie Nucl aire (SCK
aire (SCK CEN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The results obtained in the present Collaboration Arrangement between the two organizations for the ADS are also summarized, and possible further collaborations and mutual realizations in the future are sketched.
CEN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The results obtained in the present Collaboration Arrangement between the two organizations for the ADS are also summarized, and possible further collaborations and mutual realizations in the future are sketched.
Yamaguchi, Mika; Hidaka, Akihide; Ikuta, Yuko; Murakami, Kenta*; Tomita, Akira*; Hirose, Hiroya*; Watanebe, Masanori*; Ueda, Kinichi*; Namaizawa, Ken*; Onose, Takatoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-002, 60 Pages, 2017/03
Since 2010, IAEA has held the NEM School to develop future leaders who plan and manage nuclear energy utilization in their county. Since 2012, JAEA together with Japan Nuclear HRD Network, University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Industrial Forum and JAIF International Cooperation Center have cohosted the school in Japan in cooperation with IAEA. Since then, the school has been held in Japan every year. In 2006, Japanese nuclear technology and experience, such as lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, were provided to offer a unique opportunity for the participants to learn about particular cases in Japan. Through the school, we contributed to the internationalization of Japanese young nuclear professionals, development of nuclear human resource of other countries including nuclear newcomers, and enhanced cooperative relationship with IAEA. Additionally, collaborative relationship within the network was strengthened by organizing the school in Japan.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-001, 115 Pages, 2017/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2015. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Hino, Ryutaro; Takegami, Hiroaki; Yamazaki, Yukie; Ogawa, Toru
JAEA-Review 2016-038, 294 Pages, 2017/03
In the aftermath of the Fukushima nuclear accident, safety measures against hydrogen in severe accident have been recognized as a serious technical problem in Japan. Therefore, efforts have begun to form a common knowledge base between nuclear engineers and experts on combustion and explosion, and to secure and improve future nuclear energy safety. As one of such activities, we have prepared the "Handbook of Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety" under the Advanced Nuclear Hydrogen Safety Research Program funded by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. The concepts of the handbook are as follows: to show advanced nuclear hydrogen safety technologies that nuclear engineers should understand, to show hydrogen safety points to make combustion-explosion experts cooperate with nuclear engineers, to expand information on water radiolysis considering the situation from just after the Fukushima accidents and to the waste management necessary for decommissioning after the accident, etc.
Safety and Environmental Management Section, Safety and Nuclear Security Administration Department
JAEA-Review 2016-037, 218 Pages, 2017/03
In September 2016, Japan Atomic Energy Agency published a part of environmental activity in "Japan Atomic Energy Agency Report 2016" concerning the activities of FY 2015 under "Law Concerning the Promotion of Business Activities with Environmental Consideration by Specified Corporations, etc., by Facilitating Access to Environmental Information, and Other Measures". This report has been edited to show detailed environmental performance data in FY 2015 as the base of the "Japan Atomic Energy Agency Report 2016". This report would not only ensure traceability of the data in order to enhance the reliability of the environmental report, but also make useful measures for promoting activities of environmental considerations in JAEA.
Department of HTTR
JAEA-Review 2016-036, 95 Pages, 2017/03
The High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) was attained at the full power operation of 30 MW in December 2001 and achieved the 950 degrees of coolant outlet temperature at outside of the reactor pressure vessel in June 2004. This report summarizes activities and results of HTTR operation, maintenance, and several Research and developments, which were carried out in the fiscal year 2015.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Hokama, Tomonori; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Nishimura, Tomohiro; Matsubara, Natsumi; Maehara, Yushi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-035, 179 Pages, 2017/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2015 to March 2016. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and were exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Ema, Akira; Ishimori, Yuu
JAEA-Review 2016-034, 84 Pages, 2017/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has managed the decommissioning projects since 2013. In 2015, Enforcement Management System (EMS) was established to enforce the project management systematically. The project management based on EMS was started in 2015. This report summarized the state of management activities in FY 2015.
Department of Radiation Protection, Nuclear Science Research Institute; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institut; Safety and Utilities Section, Department of Administrative Services, Kansai Photon Science Institute; Operation Safety Administration Section, Mutsu Office, Aomori Research and Development Center; Safety Section, Department of Administrative Services, Naka Fusion Institute
JAEA-Review 2016-033, 180 Pages, 2017/03
This annual repost describes the activities in the 2015 fiscal year of Department of Radiation Protection in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Safety Section in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Safety and Utilities Section in Kansai Photon Science Institute, Nuclear Facilities Management Section in Aomori Research and Development Center and Safety Section in Naka Fusion Institute.
Engineering Services Department
JAEA-Review 2016-030, 107 Pages, 2017/03
The Engineering Services Department is in charge of operation and maintenance of utility facilities (water distribution systems, electricity supply systems, steam generation systems and drain water systems etc.) in whole of the institute. And also is in charge of operation and maintenance of specific systems (a receive transmitted electricity system, an emergency electric power supply system, an air/liquid waste treatment system, a compressed air supply system) in nuclear reactor facilities, nuclear fuel treatment facilities and usual facilities or buildings. In addition, the department is in charge of maintenance of buildings, design and repair of electrical/mechanical equipments. This annual report describes summary of activities, operation and maintenance data and technical developments of the department carried out in JFY 2015. We hope that this report may help future work.
Kuwabara, Kazumichi*; Aoyagi, Yoshiaki; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2017-002, 39 Pages, 2017/03
Authors developed a displacement meter using optical fiber sensor. The displacement meter can be set at any locations in a borehole and guarantee the measurement accuracy up to 5MPa. Total twelve displacement meters were installed in three boreholes to measure the rock mass displacement during groundwater recovery test. The measurement of the rock mass displacement was stated on March, 27, FY 2014. During the first and second groundwater recovery experiments, compressive displacements were observed close to the closure test drift wall. Magnitude of the measured displacements, except vicinity of test drift wall, was smaller than that of calculated under the assumption of it is an isotropic elastic material.
Ichikawa, Shoichi; Chiba, Yusuke; Ono, Fumiyasu; Hatori, Masakazu; Kobayashi, Takanori; Uekura, Ryoichi; Hashiri, Nobuo*; Inuzuka, Taisuke*; Kitano, Hiroshi*; Abe, Hisashi*
JAEA-Research 2017-001, 40 Pages, 2017/03
In order to reduce the influence on a plant schedule of the MONJU by the maintenance of dew point hygrometers, The JAEA examined a capacitance type dew point hygrometer as an alternative dew point hygrometer for a lithium-chloride type dew point hygrometer which had been used at the CV-LRT in the MONJU. As a result of comparing a capacitance type dew point hygrometer with a lithium-chloride type dew point hygrometer at the CV-LRT (Atmosphere: nitrogen, Testing time: 24 hours), there weren't significant difference between a capacitance type dew point hygrometer and a lithium-chloride type dew point hygrometer. As a result of comparing a capacitance dew point hygrometer with a high-mirror-surface type dew point hygrometer for long term verification (Atmosphere: air, Testing time: 24 months), the JAEA confirmed that a capacitance type dew point hygrometer satisfied the instrument specification ( 2.04
2.04 C) required by the JEAC4203-2008.
C) required by the JEAC4203-2008.
 -ray spectrometry; Application of
-ray spectrometry; Application of  pre-concentration from large volume of water sample using Powdex resin and barium sulfate coprecipitation of radium isotopes
pre-concentration from large volume of water sample using Powdex resin and barium sulfate coprecipitation of radium isotopesTomita, Jumpei; Abe, Takuya
JAEA-Research 2016-026, 12 Pages, 2017/03
An analytical method of low-level Ra isotopes in freshwater samples with combination of  pre-concentration from large volume of water sample (
pre-concentration from large volume of water sample ( 170 L) using Powdex resin and
170 L) using Powdex resin and  -ray spectrometry followed by simple coprecipitation of Ra was developed.
-ray spectrometry followed by simple coprecipitation of Ra was developed.  pre-concentration of Ra by batch method using Powder resin was examined, and it was shown that the amount of the resin required collecting Ra in the water sample could be determined by measuring the electric conductivity (EC) of water sample. It was found that coprecipitation of Ra with barium sulfate could remove more than 96% of potassium that increases the background. The validation of this method was confirmed by the analyses of 170 L of water sample containing the known amount of Ra isotopes with different EC. Among the analyses, the recovery of Ra was 98% in average and detection limits of
pre-concentration of Ra by batch method using Powder resin was examined, and it was shown that the amount of the resin required collecting Ra in the water sample could be determined by measuring the electric conductivity (EC) of water sample. It was found that coprecipitation of Ra with barium sulfate could remove more than 96% of potassium that increases the background. The validation of this method was confirmed by the analyses of 170 L of water sample containing the known amount of Ra isotopes with different EC. Among the analyses, the recovery of Ra was 98% in average and detection limits of  Ra and
Ra and 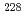 Ra were achieved to be approximately 0.3 and 0.5 mBq L
Ra were achieved to be approximately 0.3 and 0.5 mBq L , respectively.
, respectively.
Sato, Toshinori; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Eiichi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Fujita, Tomoo*; Tanai, Kenji; Nakayama, Masashi; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-025, 313 Pages, 2017/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. This report summarizes the results of the Phase II investigations carried out from April 2005 to June 2014 to a depth of 350m. Integration of work from different disciplines into a "geosynthesis" ensures that the Phase II goals have been successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to made to be addressed in the Phase II investigations Efforts are made to summarize as many lessons learnt from the Phase II investigations and other technical achievements as possible to form a "knowledge base" that will reinforce the technical basis for both implementation and the formulation of safety regulations.
Hayashida, Kazuki; Kato, Toshihiro; Munemoto, Takashi; Aosai, Daisuke*; Inui, Michiharu*; Kubota, Mitsuru; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-008, 52 Pages, 2017/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the effect on excavating and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2015. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method, analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Kuwagaki, Kazuki*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-007, 27 Pages, 2017/03
The integral benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 for U-233 systems using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP was conducted. The previous benchmark test was performed only for U-233 thermal solution and fast metallic systems in the ICSBEP handbook. In this study, MVP input files were prepared for uninvestigated benchmark problems in the handbook including compound thermal systems (mainly lattice systems) and integral benchmark test was performed. The prediction accuracy of JENDL-4.0 was evaluated for effective multiplication factors (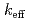 's) of the U-233 systems. As a result, a trend of underestimation was observed for all the categories of U-233 systems. In the benchmark test of ENDF/B-VII.1 for U-233 systems with the ICSBEP handbook, it is reported that a decreasing trend of calculated
's) of the U-233 systems. As a result, a trend of underestimation was observed for all the categories of U-233 systems. In the benchmark test of ENDF/B-VII.1 for U-233 systems with the ICSBEP handbook, it is reported that a decreasing trend of calculated 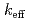 values in association with a parameter ATFF (Above-Thermal Fission Fraction) is observed. The ATFF values were also calculated in this benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 and the same trend as ENDF/B-VII.1 was observed.
values in association with a parameter ATFF (Above-Thermal Fission Fraction) is observed. The ATFF values were also calculated in this benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 and the same trend as ENDF/B-VII.1 was observed.
Miyara, Nobukatsu; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-005, 34 Pages, 2017/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is performing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project, which includes a scientific study of the deep geological environment as a basis of research and development for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes (HLW), in order to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in the sedimentary rock. This report integrates geophysical logging data obtained from the deep borehole investigations (HDB-1  HDB-11) conducted in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Phase I).
HDB-11) conducted in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project (Phase I).
Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Nakajima, Junya; Yoshida, Keisuke; Kato, Saori; Nishino, Sho; Nozaki, Teo; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Tsunoda, Junichi; Sugaya, Yuki; Hasegawa, Rie; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-004, 57 Pages, 2017/03
In emergency situation of nuclear facilities, we need to estimate the radiation dose due to radiation and radioactivity to grasp the influence range of the accident in the early stage. Therefore, we prepare the case studies of dose assessment for public exposure dose and personal exposure dose and contribute them to emergency procedures. This document covers about accidents of nuclear facilities in Nuclear Science Research Institute and past accident of nuclear power plant, and it can be used for inheritance of techniques of emergency dose assessment.
Ueno, Tetsuro; Takeuchi, Ryuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-003, 46 Pages, 2017/03
Tono Geoscience Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). As for The MIU Project (Phase II) was carried out from 2004 fiscal year, and has been started the Phase III in 2010 fiscal year. The groundwater inflow monitoring into shafts and research galleries, has been maintained to achieve the Phase II goals, begins in 2004 fiscal year and follow now. This document presents the results of the groundwater inflow monitoring from fiscal year 2014 to 2015.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Shibata, Taiju
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-002, 74 Pages, 2017/03
In order to ensure the thermal integrity of fuel in High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs), it is necessary that the maximum fuel temperature in normal operation is to be lower than a thermal design target. In the core thermal-hydraulic design of block-type HTGRs, the maximum fuel temperature should be evaluated considering data such as core geometry and specifications, power density and neutron fluence distributions, and core coolant flow distribution. The fuel temperature calculation code used in the design stage of the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) presupposes to run on UNIX systems, and its operation and execution procedure are complicated and are not user-friendly. Therefore, a new fuel temperature calculation code, named FTCC, which has a user-friendly system such as a simple and easy operation and execution procedure, was developed. This report describes the calculation objects and models, the basic equations, the strong points (improvement points from the HTTR design code), the code structure, the using method of FTCC, and the result of a validation calculation with FTCC. The calculation result obtained by FTCC provides good agreement with that of the HTTR design code, and then FTCC will be used as one of the design codes for high temperature gas-cooled reactors. In addition, the effect of hot spot factors and fuel cooling forms on reducing the maximum fuel temperature is investigated with FTCC. As a result, it was found that the effect of center hole cooling for hollow fuel compacts and gapless cooling with monolithic type fuel rods on reducing the temperature is very high.
Asami, Makoto*; Takahatake, Yoko; Myodo, Masato; Tobita, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Kiwami; Hayakawa, Misa; Usui, Yuka; Watahiki, Hiromi; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-001, 78 Pages, 2017/03
At Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station owned by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Incorporated (TEPCO), contaminated water (accumulated, treated) secondary waste from water treatment, rubble and soil were collected and analyzed. The data already opened to public was collected as this report. The analytical data reported by TEPCO, Japan Atomic Energy Agency and International Research Institute for Nuclear Decommissioning until the end of March, 2016, was collected. Information on the samples and values of radioactive nuclide concentration and others were tabulated, besides figures, which show change in radioactive nuclide concentration for major nuclides, are contained. And, English translation and the collected data are provided as electric data.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sakurai, Akitaka; Niunoya, Sumio*
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-022, 91 Pages, 2017/03
The objective of this report is to investigate the three dimensional stress state in the 350 m Loop Gallery (East) at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. For the measurement, three boreholes, which are 17.0 m in length, were drilled. Hydraulic fracturing was applied as a stress measurement method. For the analysis, shut-in pressure of a transverse fractures, reopening pressure of longitudinal fractures and stress condition causing borehole breakouts were integrated into the equation; then stress state was calculated by inversion technique. As a result, considering the stress condition causing breakouts, the value of the maximum principal stress was 3.73 MPa, which is much smaller than the overburden pressure (about 6.0 MPa). The orientation of the maximum horizontal stress is almost vertical. The stress state is normal faulting.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Tamamura, Shuji*; Nakata, Kotaro*; Hasegawa, Takuma*
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-021, 60 Pages, 2017/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been involved in ongoing research in the Horonobe area for the purposes of geoscientific research, and research and development (R&D) on technologies to be used for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The chemistry of groundwater and dissolved gas from deep boreholes has been obtained since H13 fiscal year for R&D on technologies related to geological characterization. Horonobe Research Institute for the Subsurface Environment (H-RISE) has investigated a resources development on promoting effective use of coal bed buried in Hokkaido including the Horonobe area using microbial communities. The data of dissolved gas from the Horonobe groundwater have also been obtained along with the microbiological research by H-RISE. Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) has conducted R&D on technology of groundwater geochronology which is one of technologies to be used for the geological disposal, and noble gas data from the Horonobe groundwater have been obtained by CRIEPI. This report shows a data set which comprises gas data obtained from the Horonobe underground research project during the period from H13 fiscal year to H27 fiscal year.
Takai, Shizuka; Takayama, Hideki*; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-020, 40 Pages, 2017/03
In this report, another group of scenarios for occurrence of earthquake at construction stage, operation stage and closure stage of disposal facility was presented. At first, we compiled information about damage cases of tunnel by earthquake and analyzed conditions for occurrence of damage. Base on this result and the previous report, information of influence of the accidents and human factors on safety functions and information of FEP about THMC variation, we specified events to be considered, which occur by earthquake and influence engineering barriers, natural barriers and long-term safety after closure stage of disposal facility. We compiled influence of the events on safety functions after closure stage of disposal and showed the chains of the influence on long-term safety as scenarios. These results were integrated as a database that could support development of scenarios caused by application of engineering technologies to geological disposal.
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakurai, Takeshi; Mori, Takamasa
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-019, 450 Pages, 2017/03
In order to realize fast and accurate Monte Carlo simulation of neutron and photon transport problems, two Monte Carlo codes MVP (continuous-energy method) and GMVP (multigroup method) have been developed at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The codes have adopted a vectorized algorithm and have been developed for vector-type supercomputers. They also support parallel processing with a standard parallelization library MPI and thus a speed-up of Monte Carlo calculations can be achieved on general computing platforms. The first and second versions of the codes were released in 1994 and 2005, respectively. They have been extensively improved and new capabilities have been implemented. The major improvements and new capabilities are as follows: (1) perturbation calculation for effective multiplication factor, (2) exact resonant elastic scattering model, (3) calculation of reactor kinetics parameters, (4) photo-nuclear model, (5) simulation of delayed neutrons, (6) generation of group constants, etc. This report describes the physical model, geometry description method used in the codes, new capabilities and input instructions.
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakurai, Takeshi; Mori, Takamasa
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-018, 421 Pages, 2017/03
In order to realize fast and accurate Monte Carlo simulation of neutron and photon transport problems, two Monte Carlo codes MVP (continuous-energy method) and GMVP (multigroup method) have been developed at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The codes have adopted a vectorized algorithm and have been developed for vector-type supercomputers. They also support parallel processing with a standard parallelization library MPI and thus a speed-up of Monte Carlo calculations can be achieved on general computing platforms. The first and second versions of the codes were released in 1994 and 2005, respectively. They have been extensively improved and new capabilities have been implemented. The major improvements and new capabilities are as follows: (1) perturbation calculation for effective multiplication factor, (2) exact resonant elastic scattering model, (3) calculation of reactor kinetics parameters, (4) photo-nuclear model, (5) simulation of delayed neutrons, (6) generation of group constants, etc. This report describes the physical model, geometry description method used in the codes, new capabilities and input instructions.
Nomura, Katsuhiro; Tanikawa, Shinichi*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Yasue, Kenichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-015, 49 Pages, 2017/03
The uplift of the last hundred thousand years in the Japanese Islands has been acquired mainly using marine and river terraces. We arranged information regarding the uplift in a table. This data is one of the useful information for the development of the investigation technology of uplift and for the research of the landform evolution in Japanese islands.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Shibata, Kenji*
JAEA-Testing 2016-004, 40 Pages, 2017/02
X-ray fluorescence analysis is one of the methods commonly used to reveal whole-rock chemical composition, which is basic information of rock samples. This report shows methods to prepare glass beads of fused samples and to use the X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (Rigaku ZSX Primus II) housed in Tono Geoscience Center, and the evaluation of precision and accuracy of the measurement.
Shimazaki, Yosuke; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Yanagida, Yoshinori; Shinohara, Masanori; Kawamoto, Taiki; Takada, Shoji
JAEA-Technology 2016-038, 36 Pages, 2017/02
The High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) has three neutron startup sources (NSs) in the reactor core, each of which consists of  Cf with 3.7GBq The NSs are exchanged at the interval of approximately 7 years. The NS holders including NSs are transported from the dealer's hot cell to the reactor facility of HTTR using a transportation container. The loading work of NS holders to the Control Rod guide blocks is subsequently carried out in the fuel handling machine maintenance pit of HTTR. Following technical issues were extracted from the experiences in the past two exchange works of NSs to develop a safety handling procedure; (1) The reduction and prevention of radiation exposure of workers. (2) The exclusion of falling of NS holder. Then, a new transportation container special to the NSs of HTTR was developed to solve the technical issues while keeping the cost as low as that for overhaul of conventional container and satisfying the regulation of A type transportation package.
Cf with 3.7GBq The NSs are exchanged at the interval of approximately 7 years. The NS holders including NSs are transported from the dealer's hot cell to the reactor facility of HTTR using a transportation container. The loading work of NS holders to the Control Rod guide blocks is subsequently carried out in the fuel handling machine maintenance pit of HTTR. Following technical issues were extracted from the experiences in the past two exchange works of NSs to develop a safety handling procedure; (1) The reduction and prevention of radiation exposure of workers. (2) The exclusion of falling of NS holder. Then, a new transportation container special to the NSs of HTTR was developed to solve the technical issues while keeping the cost as low as that for overhaul of conventional container and satisfying the regulation of A type transportation package.
Iwasaki, Riyo*; Hama, Katsuhiro; Morikawa, Keita*; Hosoya, Shinichi*
JAEA-Technology 2016-037, 62 Pages, 2017/02
Mass transport study is mainly performed as part of Phase III in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project. In Phase III, the goal of mass transport study is to obtain a better understanding of mass transport phenomena in the geological environment as well as to develop technologies for measurement of the mass transport parameters, model construction, numerical analysis and validation of those technologies. This study was planned to understand the influence of the geological characteristics of fracture on the mass transport parameters.
Nagayasu, Takaaki; Taki, Tomihiro; Fukushima, Shigeru
JAEA-Technology 2016-031, 53 Pages, 2017/02
The forerunner of JAEA, found a smelter in 1964 to do industrialization tests of hydrometallurgical extraction process from domestic uranium ore to uranium tetrafluoride, extracted at Ningyo-toge. Yotsugi Mill Tailings Pond was constructed for the purpose of depositing slag and other things generated due to the operation of the smelter. Furthermore supernatant water from the deposition field had been treated appropriately at wastewater treatment facilities, which has been provided in the downstream site of the pond. We have been utilizing the Yotsugi Mill Tailings Pond as a temporary storage field of mine water generated from the old mining gallery, mainly. After filing an abolition report of facilities of the smelter, with the completion of industrial trials of refinery in 1982. Ningyo-toge environmental engineering center has studied for processing uranium and radium, in wastewater, which must be reduced more safely by advancing these processing technical development. Supernatant water of The Pond is treated at the wastewater treatment facilities before discharging to Ikegogawa-river. And those collateralize the emission standards to discharge to the river set at the Center with continuing stable processing. This document summarized the history of the wastewater treatment, technical development for the water treatment, and the current situation of the water treatment.
Safety Division, J-PARC Center
JAEA-Review 2016-032, 134 Pages, 2017/02
This annual report describes the activities on safety in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in FY 2015. Activities on radiation safety and general safety are described, and the technological developments and research on safety issues are summarized. In addition, another chapter was given to the "Activities on Promotion of Safety Culture".
Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management
JAEA-Review 2016-029, 90 Pages, 2017/02
This report describes the activities of Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management (DDWM) in Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) in the period from April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2016. The report covers organization and missions of DDWM, outline and operation/maintenance of facilities which belong to DDWM, treatment and management of radioactive wastes, decommissioning activities, and related research and development activities which were conducted in DDWM.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2016-022, 40 Pages, 2017/02
For reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in the light water reactors, the fracture toughness decreases due to the neutron irradiation embrittlement with operating years. In Japan, to prevent RPVs from a nil-ductile fracture, deterministic fracture mechanics methods in accordance with the codes provided by the Japan Electric Association are performed for assessing the structural integrity of RPVs under the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events by taking the neutron irradiation embrittlement into account. On the other hand, in recent years, probabilistic methodologies for PTS evaluation are introduced into regulations in Europe and the United States. For example, in the United States, a PTS screening criterion related to the reference temperature derived by the probabilistic method is stipulated. If the screening criterion is not satisfied, it is approved to perform the evaluation based on the probabilistic method by calculating numerical index such as through-wall crack frequency (TWCF). To reach the objectives that persons who have knowledge on the fracture mechanics can carry out the PFM analyses and obtain TWCF for a domestic RPVs by referring to this report, we develop the guideline on a structural integrity assessment method based on PFM by reflecting the latest knowledge and expertise.
Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Takahashi, Shigemi*; Seki, Kotaro*; Izumo, Sari; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-017, 53 Pages, 2017/02
Fugen Nuclear Power Station was shut down and now is under decommissioning. Many radioactivity concentration data of dismantled materials have to be accumulated to calculate the scaling factors of radioactive wastes and to verify that the cleared dismantled materials conform to the clearance levels. A simple and rapid radioactivity determination method for radioactive waste samples was developed by Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management. For its demonstration, the simple and rapid radioactivity determination method was applied to metal samples, which were taken from dismantled pipes in contact with heavy water or carbon dioxide gas of Fugen. This report summarizes the radioactivity data obtained from the analysis of those samples.