Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
 Co
CoLokotko, T.*; Leblond, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Poves, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Authelet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:69.78(Physics, Nuclear)The structures of the neutron-rich  Co isotopes were investigated via (
Co isotopes were investigated via ( ) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the
) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the 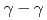 coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the
coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the  Co isotopes.
Co isotopes.
Nakayoshi, Akira; Journeau, C.*; Rempe, J.*; Barrachin, M.*; Bottomley, D.; Nauchi, Y.*; Song, J. H.*
Proceedings of 2019 International Workshop on Post-Fukushima Challenges on Severe Accident Mitigation and Research Collaboration (SAMRC 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2019/11
 decay of
decay of 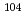 Te with a novel recoil-decay scintillation detector
Te with a novel recoil-decay scintillation detectorXiao, Y.*; Go, S.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Orlandi, R.; Andreyev, A. N.; Asai, Masato; Bentley, M. A.*; de Angelis, G.*; Gross, C. J.*; Hausladen, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(3), p.034315_1 - 034315_8, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:84.48(Physics, Nuclear) Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,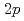 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
, 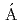 *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.15(Physics, Nuclear)The nuclear structure of the  Ni nucleus was investigated by (
Ni nucleus was investigated by ( ,
,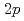 ) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt
) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt  rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by
rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by 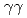 and
and 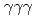 coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
 =28 and
=28 and  =50; Spectroscopy of
=50; Spectroscopy of 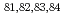 Zn
ZnShand, C. M.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; G
k, Zs.*; G rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 773, p.492 - 497, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:87.36(Astronomy & Astrophysics)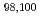 Kr
KrFlavigny, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Delaroche, J.-P.*; Girod, M.*; Libert, J.*; Rodriguez, T. R.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Calvet, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_6, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:86.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Chen, S.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Rodriguez, T. R.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Calvet, D.*; Ch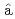 teau, F.*; Corsi, A.*; Delbart, A.*; et al.
teau, F.*; Corsi, A.*; Delbart, A.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(4), p.041302_1 - 041302_6, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:88.02(Physics, Nuclear)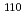 Zr
ZrPaul, N.*; Corsi, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Bally, B.*; Bender, M.*; Calvet, D.*; Ch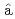 teau, F.*; et al.
teau, F.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(3), p.032501_1 - 032501_7, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:88.64(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ajimura, Shuhei*; Bezerra, T. J. C.*; Chauveau, E.*; Enomoto, T.*; Furuta, Hisataka*; Harada, Masahide; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hiraiwa, T.*; Igarashi, Yoichi*; Iwai, Eito*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(6), p.063C01_1 - 063C01_19, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The J-PARC E56 experiment aims to search for sterile neutrinos at the J-PARC Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). In order to examine the feasibility of the experiment, we measured the background rates of different detector candidate sites, which are located at the third floor of the MLF, using a detector consisting of plastic scintillators with a fiducial mass of 500 kg. The gammas and neutrons induced by the beam as well as the backgrounds from the cosmic rays were measured, and the results are described in this article.
Schwehr, K. A.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Merchel, S.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Zhang, S.*; Xu, C.*; Li, H.-P.*; Ho, Y.-F.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Santschi, P. H.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 497-498, p.671 - 678, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:38.98(Environmental Sciences)A new, accurate and simple pH-dependent solvent extraction method combined with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) measurement for  I/
I/ I isotopes and iodine speciation (iodide, iodate, and organo-I) quantification in liquids of any ionic strength has been developed. We then validated the AMS method for activity concentration measurements with a recently developed gas chromatography mass spectrometry method for
I isotopes and iodine speciation (iodide, iodate, and organo-I) quantification in liquids of any ionic strength has been developed. We then validated the AMS method for activity concentration measurements with a recently developed gas chromatography mass spectrometry method for  I concentrations of 1 Bq/L or higher. This technique was applied to
I concentrations of 1 Bq/L or higher. This technique was applied to  I-contaminated groundwater from the Savannah River Site, USA, and demonstrated changes of
I-contaminated groundwater from the Savannah River Site, USA, and demonstrated changes of  I and
I and  I concentrations and speciation along a pH, redox potential, and organic carbon gradient. The data suggest that
I concentrations and speciation along a pH, redox potential, and organic carbon gradient. The data suggest that  I/
I/ I and species distribution is strongly pH dependent. The new method can now be applied to a wide range of chemically-diverse aquatic systems, including uncontaminated environments.
I and species distribution is strongly pH dependent. The new method can now be applied to a wide range of chemically-diverse aquatic systems, including uncontaminated environments.
Johnson, B. E.*; Santschi, P. H.*; Chuang, C.-Y.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Addleman, R. S.*; Douglas, M.*; Rutledge, R. D.*; Chouyyok, W.*; Davidson, J. D.*; Fryxell, G. E.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 46(20), p.11251 - 11258, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:85 Percentile:88.92(Engineering, Environmental)Effective collection of trace-level lanthanides and actinides is advantageous for recovery and recycling of valuable resources, environmental remediation, chemical separations, and in situ monitoring. Using isotopic tracers, we have evaluated a number of conventional and nanoporous sorbent materials for their ability to capture and remove selected lanthanides (Ce and Eu) and actinides (Th, Pa, U, and Np) from fresh and salt water systems. In general, the nanostructured materials demonstrated a higher level of performance and consistency. Nanoporous silica surface modified with 3,4-hydroxypyridinone provided excellent collection and consistency in both river water and seawater.
 O
O -dependent iodide oxidation
-dependent iodide oxidationLi, H.-P.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Brinkmeyer, R.*; Zhang, S.*; Ho, Y.-F.*; Xu, C.*; Jones, W. L.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Roberts, K. A.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 46(9), p.4837 - 4844, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:77.77(Engineering, Environmental)In order to develop an understanding of the role that microorganisms play in the transport of  I in soil-water systems, naturally occurring bacteria isolated from the F-area subsurface of the Savannah River Site (SRS) were assessed for iodide oxidizing activity. Spent liquid medium from a number of SRS bacterial cultures enhanced iodide oxidation 2-10 fold in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H
I in soil-water systems, naturally occurring bacteria isolated from the F-area subsurface of the Savannah River Site (SRS) were assessed for iodide oxidizing activity. Spent liquid medium from a number of SRS bacterial cultures enhanced iodide oxidation 2-10 fold in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ). From a time-series measurements of peroxidase activities and organic acid concentrations, it was hypothesized that microbial organic acid exudate promoted iodide oxidation via following mechanisms; (1) organic acids interact with H
). From a time-series measurements of peroxidase activities and organic acid concentrations, it was hypothesized that microbial organic acid exudate promoted iodide oxidation via following mechanisms; (1) organic acids interact with H O
O to form strong iodide oxidizing agents, peroxy carboxylic acids, and (2) organic acid secretion led to enhanced rates of H
to form strong iodide oxidizing agents, peroxy carboxylic acids, and (2) organic acid secretion led to enhanced rates of H O
O -dependent iodide oxidation by lowering the pH of the culture medium.
-dependent iodide oxidation by lowering the pH of the culture medium.
 I) by soil organic matter and possible consequences of the remedial action at Savannah River Site
I) by soil organic matter and possible consequences of the remedial action at Savannah River SiteXu, C.*; Miller, E. J.*; Zhang, S.*; Li, H.-P.*; Ho, Y.-F.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Roberts, K. A.*; Brinkmeyer, R.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 45(23), p.9975 - 9983, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:83.22(Engineering, Environmental)In order to investigate accumulation process of iodine-129 ( I) in a contaminated F-Area groundwater plume of the US Savannah River Site, soil resuspension experiments simulating surface runoff and erosion events were conducted. Results showed that 72
I) in a contaminated F-Area groundwater plume of the US Savannah River Site, soil resuspension experiments simulating surface runoff and erosion events were conducted. Results showed that 72 77% of the newly-introduced iodide was irreversibly sequestered into the organic-rich soil, while the rest was transformed into colloidal and dissolved organo-iodine by the soil. Laboratory iodination of the soil indicated a preferential incorporation of inorganic iodine into soil organic matter (SOM) at acidic pH (3
77% of the newly-introduced iodide was irreversibly sequestered into the organic-rich soil, while the rest was transformed into colloidal and dissolved organo-iodine by the soil. Laboratory iodination of the soil indicated a preferential incorporation of inorganic iodine into soil organic matter (SOM) at acidic pH (3 4), except for the iodination catalyzed by lactoperoxidase, which favors more alkaline conditions. From this result, we concluded that under very acidic conditions, abiotic iodination of SOM was predominant, while under less acidic conditions (pH
4), except for the iodination catalyzed by lactoperoxidase, which favors more alkaline conditions. From this result, we concluded that under very acidic conditions, abiotic iodination of SOM was predominant, while under less acidic conditions (pH  5), microbial enzymatically-assisted iodination took over.
5), microbial enzymatically-assisted iodination took over.
 I) at the Savannah River Site?
I) at the Savannah River Site?Xu, C.*; Zhang, S.*; Ho, Y.-F.*; Miller, E. J.*; Roberts, K. A.*; Li, H.-P.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Kaplan, D. I.*; Brinkmeyer, R.*; et al.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(19), p.5716 - 5735, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:83.32(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In order to understand the effect of soil organic matter (SOM) on the mobility of iodine in the vicinity of the F-area seepage basin at the U.S. Department Energy's Savannah River Site (SRS), relationships between radioiodine/iodine concentration and properties of SOM (e.g., degree of humification, aromaticity, and molecular weight) were examined. Analyses were carried out for four sequential extracts of SOM (freshwater, alkaline, glycerol, and citric-alkaline solutions). Iodine in SOM was selectively bound to a small-size aromatic subunit (less than 10 kDa), and majority of water soluble  I was associated with a low molecular weight amphiphilic organic carrier (13.5-15 kDa). From these results, it was suggested that (1) SOM behaved as a sink as well as a source for iodine at the SRS, and (2) the function of SOM varies with groundwater chemistry.
I was associated with a low molecular weight amphiphilic organic carrier (13.5-15 kDa). From these results, it was suggested that (1) SOM behaved as a sink as well as a source for iodine at the SRS, and (2) the function of SOM varies with groundwater chemistry.
 I and
I and  I species in an acidic groundwater plume at the Savannah River Site
I species in an acidic groundwater plume at the Savannah River SiteOtosaka, Shigeyoshi; Schwehr, K. A.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Roberts, K. A.*; Zhang, S.*; Xu, C.*; Li, H.-P.*; Ho, Y.-F.*; Brinkmeyer, R.*; Yeager, C. M.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 409(19), p.3857 - 3865, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:82.13(Environmental Sciences)Spatial distributions of concentrations and speciation of radioiodine ( I) and stable iodine (
I) and stable iodine ( I) in groundwater in the vicinity of the F-area seepage basin at the U.S. Department Energy of Savannah River Site were investigated.
I) in groundwater in the vicinity of the F-area seepage basin at the U.S. Department Energy of Savannah River Site were investigated.  I concentration in groundwater was 8.6 Bq/L immediately downstream of the seepage basin (well FSB-95DR), and decreased with distance from the infiltration basin.
I concentration in groundwater was 8.6 Bq/L immediately downstream of the seepage basin (well FSB-95DR), and decreased with distance from the infiltration basin.  I concentration decreased similarly to that of
I concentration decreased similarly to that of  I. Although there was no potential
I. Although there was no potential  I source in wastes in the basin,
I source in wastes in the basin,  I also showed a similar gradient to that of
I also showed a similar gradient to that of  I. High concentrations of
I. High concentrations of  I or
I or  I were not detected in groundwater collected from wells located outside of the mixed waste plume of this area. The high iodide concentrations in groundwater near the basin were presumed to be caused by dissolution of iodide from soil due to gradually increasing of pH values in the last decade.
I were not detected in groundwater collected from wells located outside of the mixed waste plume of this area. The high iodide concentrations in groundwater near the basin were presumed to be caused by dissolution of iodide from soil due to gradually increasing of pH values in the last decade.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 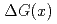 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Bauer, E. D.*; Yang, Y.-F.*; Capan, C.*; Urbano, R. R.*; Miclea, C. F.*; Sakai, Hironori; Ronning, F.*; Graf, M. J.*; Balatsky, A. V.*; Movshovich, R.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(17), p.6857 - 6861, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:81.82(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here, we report a manifestation of electronic inhomogeneity in a strongly correlated  -electron system, using CeCoIn
-electron system, using CeCoIn as an example. A thermodynamic analysis of its superconductivity, combined with nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements, shows that nonmagnetic impurities (Y, La, Yb, Th, Hg, and Sn) locally suppress unconventional superconductivity, generating an inhomogeneous electronic "Swiss cheese" due to disrupted periodicity of the Kondo lattice. Our analysis may be generalized to include related systems, suggesting that electronic inhomogeneity should be considered broadly in Kondo lattice materials.
as an example. A thermodynamic analysis of its superconductivity, combined with nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements, shows that nonmagnetic impurities (Y, La, Yb, Th, Hg, and Sn) locally suppress unconventional superconductivity, generating an inhomogeneous electronic "Swiss cheese" due to disrupted periodicity of the Kondo lattice. Our analysis may be generalized to include related systems, suggesting that electronic inhomogeneity should be considered broadly in Kondo lattice materials.