Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Grazzi, F.*; Cialdai, C.*; Manetti, M.*; Massi, M.*; Morigi, M. P.*; Bettuzzi, M.*; Brancaccio, R.*; Albertin, F.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; et al.
Rendiconti Lincei. Scienze Fisiche e Naturali, 32(3), p.463 - 477, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.01(Multidisciplinary Sciences) decay of
decay of 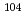 Te with a novel recoil-decay scintillation detector
Te with a novel recoil-decay scintillation detectorXiao, Y.*; Go, S.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Orlandi, R.; Andreyev, A. N.; Asai, Masato; Bentley, M. A.*; de Angelis, G.*; Gross, C. J.*; Hausladen, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(3), p.034315_1 - 034315_8, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:84.48(Physics, Nuclear) induced by H
induced by H O
O and
and  -irradiation
-irradiationKumagai, Yuta; Fidalgo, A. B.*; Jonsson, M.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123(15), p.9919 - 9925, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.54(Chemistry, Physical)Radiation-induced oxidative dissolution of uranium dioxide (UO ) is one of the most important chemical processes of U driven by redox reactions. We have examined the effect of UO
) is one of the most important chemical processes of U driven by redox reactions. We have examined the effect of UO stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution of UO
stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution of UO induced by hydrogen peroxide (H
induced by hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) and
) and  -ray irradiation. By comparing the reaction kinetics of H
-ray irradiation. By comparing the reaction kinetics of H O
O between stoichiometric UO
between stoichiometric UO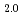 and hyper-stoichiometric UO
and hyper-stoichiometric UO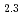 , we observed a significant difference in reaction speed and U dissolution kinetics. The stoichiometric UO
, we observed a significant difference in reaction speed and U dissolution kinetics. The stoichiometric UO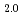 reacted with H
reacted with H O
O much faster than the hyper-stoichiometric UO
much faster than the hyper-stoichiometric UO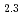 . The U dissolution from UO
. The U dissolution from UO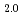 was initially much lower than that from UO
was initially much lower than that from UO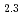 , but gradually increased as the oxidation by H
, but gradually increased as the oxidation by H O
O proceeded. The
proceeded. The  -ray irradiation induced the U dissolution that is analogous to the kinetics by the exposure to a low concentration (0.2 mM) of H
-ray irradiation induced the U dissolution that is analogous to the kinetics by the exposure to a low concentration (0.2 mM) of H O
O . The exposure to higher H
. The exposure to higher H O
O concentrations caused lower U dissolution and resulted in deviation from the U dissolution behavior by
concentrations caused lower U dissolution and resulted in deviation from the U dissolution behavior by  -ray irradiation.
-ray irradiation.
 is not a prerequisite for the core/shell ion tracks or ion shaping
is not a prerequisite for the core/shell ion tracks or ion shapingAmekura, Hiroshi*; Kluth, P.*; Mota-Santiago, P.*; Sahlberg, I.*; Jantunen, V.*; Leino, A. A.*; Vazquez, H.*; Nordlund, K.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Okubo, Nariaki; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 2(9), p.096001_1 - 096001_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:37.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)When a swift heavy ion (SHI) penetrates amorphous SiO , a core/shell (C/S) ion track is formed due to vaporization, where the ion track consists of a lower-density core and a higher-density shell. Here we reexamine this hypothesis. The MD simulations indicate that the vaporization is not induced under 50-MeV Si irradiation (
, a core/shell (C/S) ion track is formed due to vaporization, where the ion track consists of a lower-density core and a higher-density shell. Here we reexamine this hypothesis. The MD simulations indicate that the vaporization is not induced under 50-MeV Si irradiation (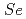 = 3 keV/nm), but the C/S tracks and the ion shaping of nanoparticles are nevertheless induced. Thus, the vaporization is not a prerequisite for the C/S tracks and the ion shaping.
= 3 keV/nm), but the C/S tracks and the ion shaping of nanoparticles are nevertheless induced. Thus, the vaporization is not a prerequisite for the C/S tracks and the ion shaping.
 O
O and UO
and UO
Fidalgo, A. B.*; Kumagai, Yuta; Jonsson, M.*
Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 71(11-13), p.1799 - 1807, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:88.5(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In this work, we have studied the reaction between H O
O and UO
and UO with particular focus on the nature of the hydroxyl radical formed as an intermediate. Experiments were performed to study the kinetics of the reaction at different initial H
with particular focus on the nature of the hydroxyl radical formed as an intermediate. Experiments were performed to study the kinetics of the reaction at different initial H O
O concentrations. The results show that the consumption rates at a given H
concentrations. The results show that the consumption rates at a given H O
O concentration are different depending on the initial H
concentration are different depending on the initial H O
O concentration. This is attributed to an alteration of the reactive interface, likely caused by blocking of surface sites by oxidized U/surface-bound hydroxyl radicals. The U dissolution yield decreases with increasing initial H
concentration. This is attributed to an alteration of the reactive interface, likely caused by blocking of surface sites by oxidized U/surface-bound hydroxyl radicals. The U dissolution yield decreases with increasing initial H O
O concentration. This is expected from the mechanism of catalytic decomposition of H
concentration. This is expected from the mechanism of catalytic decomposition of H O
O on oxide surfaces. As the experiments were performed in solutions containing 10 mM and a strong concentration dependence was observed in the 0.2 - 2.0 mM H
on oxide surfaces. As the experiments were performed in solutions containing 10 mM and a strong concentration dependence was observed in the 0.2 - 2.0 mM H O
O concentration range, we conclude that the intermediate hydroxyl radical is surface bound rather than free.
concentration range, we conclude that the intermediate hydroxyl radical is surface bound rather than free.
Michel-Sendis, F.*; Gauld, I.*; Martinez, J. S.*; Alejano, C.*; Bossant, M.*; Boulanger, D.*; Cabellos, O.*; Chrapciak, V.*; Conde, J.*; Fast, I.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 110, p.779 - 788, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:99.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)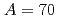 isobars from the
isobars from the  island of inversion
island of inversionMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, T.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 765, p.328 - 333, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:91.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Peri
 ez, R.*; Bezhenar, R.*; Brovchenko, I.*; Duffa, C.*; Iosjpe, M.*; Jung, K. T.*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Lamego, F.*; Maderich, V.*; Min, B. I.*; et al.
ez, R.*; Bezhenar, R.*; Brovchenko, I.*; Duffa, C.*; Iosjpe, M.*; Jung, K. T.*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Lamego, F.*; Maderich, V.*; Min, B. I.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 569-570, p.594 - 602, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:63.89(Environmental Sciences)State-of-the art dispersion models were applied to simulate  Cs dispersion from Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant disaster fallout in the Baltic Sea and from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant releases in the Pacific Ocean after the 2011 tsunami. Models were of different nature, from box to full three-dimensional models, and included water/sediment interactions. Agreement between models was very good in the Baltic. In the case of Fukushima, results from models could be considered to be in acceptable agreement only after a model harmonization process consisting of using exactly the same forcing (water circulation and parameters) in all models. It was found that the dynamics of the considered system (magnitude and variability of currents) was essential in obtaining a good agreement between models. The difficulties in developing operative models for decision-making support in these dynamic environments were highlighted.
Cs dispersion from Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant disaster fallout in the Baltic Sea and from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant releases in the Pacific Ocean after the 2011 tsunami. Models were of different nature, from box to full three-dimensional models, and included water/sediment interactions. Agreement between models was very good in the Baltic. In the case of Fukushima, results from models could be considered to be in acceptable agreement only after a model harmonization process consisting of using exactly the same forcing (water circulation and parameters) in all models. It was found that the dynamics of the considered system (magnitude and variability of currents) was essential in obtaining a good agreement between models. The difficulties in developing operative models for decision-making support in these dynamic environments were highlighted.
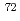 Ni
NiMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; Lorusso, G.*; Patel, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(3), p.034328_1 - 034328_14, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:85.25(Physics, Nuclear)Peri
 ez, R.*; Brovchenko, I.*; Duffa, C.*; Jung, K.-T.*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Lamego, F.*; Maderich, V.*; Min, B.-I.*; Nies, H.*; Osvath, I.*; et al.
ez, R.*; Brovchenko, I.*; Duffa, C.*; Jung, K.-T.*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Lamego, F.*; Maderich, V.*; Min, B.-I.*; Nies, H.*; Osvath, I.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 150, p.247 - 269, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.96(Environmental Sciences)A detailed intercomparison of marine dispersion models applied to the releases from Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant has been carried out in the frame of MODARIA program, of the IAEA. Models have been compared in such a way that the reasons of the discrepancies between them can be assessed. The overall idea is to harmonize models, making them run with the same forcing in a step-by-step procedure, in such a way that the main agent in producing discrepancy between models can be found. It has been found that the main reason of discrepancies between models is due to the description of the hydrodynamics. However, once this has been suppressed, some variability between model outputs remains due to intrinsic differences between models. The numerical experiments have been carried out for a perfectly conservative radionuclide and for  Cs. Model outputs for this radionuclide have also been compared with measurements in water and sediments.
Cs. Model outputs for this radionuclide have also been compared with measurements in water and sediments.
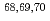 Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chain
Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chainBenzoni, G.*; Morales, A. I.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; Gargano, A.*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 751, p.107 - 112, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Polster, L.*; Schuemann, J.*; Rinaldi, I.*; Burigo, L.*; McNamara, A. L.*; Steward, R. D.*; Attili, A.*; Carlson, D. J.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Ramos M ndez, J.*; et al.
ndez, J.*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 60(13), p.5053 - 5070, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:90.68(Engineering, Biomedical)The aim of this work is to extend a widely used proton Monte Carlo tool, TOPAS, towards the modeling of relative biological effect (RBE) distributions in experimental arrangements as well as patients. Then, eight biophysical models was incorporated into TOPAS. As far as physics parameters are concerned, four of these models are based on the proton linear energy transfer (LET), while the others are based on DNA Double Strand Break (DSB) induction and the frequency-mean specific energy, lineal energy, or delta electron generated track structure. The model on the basis of lineal energy adapted a microdosimetric function developed by JAEA. This work is an important step in bringing biologically optimized treatment planning for proton therapy closer to the clinical practice.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:94.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Si
Si under intense pulsed magnetic fields up to 81T
under intense pulsed magnetic fields up to 81TScheerer, G. W.*; Knafo, W.*; Aoki, Dai*; Nardone, M.*; Zitouni, A.*; B ard, J.*; Billette, J.*; Barata, J.*; Jaudet, C.*; Suleiman, M.*; et al.
ard, J.*; Billette, J.*; Barata, J.*; Jaudet, C.*; Suleiman, M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 89(16), p.165107_1 - 165107_12, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.9(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Park, S. R.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Hamann, A.*; Lamago, D*; Pintschovius, L.*; Fujita, Masaki*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Reznik, D.*
Physical Review B, 89(2), p.020506_1 - 020506_5, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:75.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Toigo, V.*; Zanotto, L.*; Bigi, M.*; Decamps, H.*; Ferro, A.*; Gaio, E.*; Guti rrez, D.*; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
rrez, D.*; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.956 - 959, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:79.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper reports the progress in the reference design of the Acceleration Grid Power Supply (AGPS) of the ITER Neutral Beam Injector (NBI). The design of the AGPS is very challenging, as it shall be rated to provide about 55 MW at 1 MV dc in quasi steady-state conditions; moreover, the procurement of the system is shared between the European Domestic Agency (F4E) and the Japanese Domestic Agency (JADA), resulting in additional design complication due to the need of a common definition of the interface parameters. A critical revision of the main design choices is presented also in light of the definition of some key interface parameters between the two AGPS subsystems. Moreover, the verification of the fulfillment of the requirements in any operational conditions taking into account the tolerance of the different parameters is also reported and discussed.
 H2AX foci caused by heavy ion particle traversal; Distribution between core track versus non-track damage
H2AX foci caused by heavy ion particle traversal; Distribution between core track versus non-track damageNakajima, Nakako*; Brunton, H.*; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Shrikhande, A.*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; Fujimori, Akira*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Okayasu, Ryuichi*; Jeggo, P.*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 8(8), p.e70107_1 - e70107_14, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:91.05(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Heavy particle irradiation can produce complex DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) within the particle trajectory. Additionally, secondary electrons, termed delta-electrons, can create low linear energy transfer (LET) damage distant from the track. Using imaging with deconvolution, we show that at 8 hours after exposure to Fe ions,  H2AX foci forming at DSBs within the particle track are large and encompass multiple smaller and closely localised foci, which we designate as clustered
H2AX foci forming at DSBs within the particle track are large and encompass multiple smaller and closely localised foci, which we designate as clustered  H2AX foci. We also identified simple
H2AX foci. We also identified simple  H2AX foci distant from the track. They are rapidly repaired. Clustered
H2AX foci distant from the track. They are rapidly repaired. Clustered  H2AX foci induced by heavy particle radiation cause prolonged checkpoint arrest compared to simple
H2AX foci induced by heavy particle radiation cause prolonged checkpoint arrest compared to simple  H2AX foci. However, mitotic entry was observed when
H2AX foci. However, mitotic entry was observed when  10 clustered foci remain. Thus, cells can progress into mitosis with multiple clusters of DSBs following the traversal of a heavy particle.
10 clustered foci remain. Thus, cells can progress into mitosis with multiple clusters of DSBs following the traversal of a heavy particle.
Tillack, M. S.*; Turnbull, A. D.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Garofalo, A. M.*; Holland, C.*; Koch, F.*; Linsmeier, Ch.*; Lisgo, S.*; Maingi, R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 53(2), p.027003_1 - 027003_23, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.97(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This review summarizes the presentations and discussions by experts in the fields of edge plasma physics and plasma material interactions at a workshop organized for the purpose of evaluating current status and extrapolating forward to the post-ITER power plant regime. The topics included physics, modelling, experimental results, benchmarking and programme planning.
Burr, T.*; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Howell, J.*; Jongo, C. E.*; Hamada, M. S.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 640(1), p.200 - 212, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Process monitoring (PM) is increasingly important in nuclear safeguards as a complement to mass-balance based nuclear materials accounting (NMA). Typically, PM involves more frequent but lower quality measurements than NMA. While NMA estimates special nuclear material (SNM) mass balances and uncertainties, PM often tracks SNM attributes qualitatively or in the case of solution monitoring (SM) tracks bulk mass and volume. Automatic event marking is used in several nuclear safeguards PM systems. All methods are evaluated on both raw and smoothed data, and several smoothing options are compared, including standard filters, hybrid filters, and local kernel smoothing. The main finding is that for real and simulated examples considered, a two-step strategy is most effective. First, any reasonably effective initial smoother is used to provide a good initial guess at change point locations. Second, PLR is applied, looking for one change point at a time.
 Mg sheds new light on the
Mg sheds new light on the  =20 island of inversion
=20 island of inversionKanungo, R.*; Nociforo, C.*; Prochazka, A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aumann, T.*; Boutin, D.*; Cortina-Gil, D.*; Davids, B.*; Diakaki, M.*; Farinon, F.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 685(4-5), p.253 - 257, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:86.72(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English