Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kusumoto, Tamon*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Baba, Kentaro*; Ogawara, Ryo*; Akselrod, M. S.*; Harrison, J.*; Fomenko, V.*; Kai, Takeshi; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Hasegawa, Sumitaka*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 132, p.106256_1 - 106256_4, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Internal radiation therapy with Cu-64 concentrates energy deposition in tumor cells by virtue of released Auger electrons with low energy. In our previous study, we have attached the solutions at the surface of Fluorescent Nuclear Track Detector (FNTD) and succeeded in measuring the absorbed doses of Auger electrons registered in FNTD. However, because there are several types of radiation emitted from the source, i.e., beta rays, positron etc., the contribution degree of Auger electron to energy concentration remain uncertain. In this study, we quantitatively analyzed the spatial dose distribution in the FNTD based on Monte Carlo simulation with PHITS and GEANT4, and evaluated high dose deposited by Auger electrons. The dose distribution calculated by the PHITS code is exactly equivalent to that by Geant4. Also, the simulations are well agreement with experimental results. If the contribution of Auger electrons is ignored, the significantly high absorbed dose proximal to the source is not properly reduced. These findings demonstrate that Auger electrons work very effectively to kill cancer cells proximal to Cu-64 source while minimizing damage effects on normal cells distal to the source.
Al-Shayeb, B.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Ward, F.*; Munk, P.*; Devoto, A.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Amano, Yuki; et al.
Nature, 578(7795), p.425 - 431, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:220 Percentile:99.5(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kristo, M. J.*; Williams, R.*; Gaffney, A. M.*; Kayzar-Boggs, T. M.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Lagerkvist, P.*; Vesterlund, A.*; Rameb ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.425 - 434, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.7(Chemistry, Analytical)In a recent international exercise, 10 international nuclear forensics laboratories successfully performed radiochronometry on three low enriched uranium oxide samples, providing 12 analytical results using three different parent-daughter pairs serving as independent chronometers. The vast majority of the results were consistent with one another and consistent with the known processing history of the materials. In general, for these particular samples, mass spectrometry gave more accurate and more precise analytical results than decay counting measurements. In addition, the concordance of the  U-
U-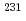 Pa and
Pa and  U-
U- Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Gin, S.*; Abdelouas, A.*; Criscenti, L.*; Ebert, W.*; Ferrand, K.*; Geisler, T.*; Harrison, M.*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Mueller, K. T.*; et al.
Materials Today, 16(6), p.243 - 248, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:377 Percentile:99.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The nations producing borosilicate glass as a confinement material for high-level waste resulting from spent fuel reprocessing have decided to reinforce scientific collaboration in order to obtain consensus on the mechanisms controlling the long-term dissolution rate of glass. This goal is the most important issue for developing reliable predictive models usable for performance assessment and safety demonstration of geological storage of such materials. This collaboration involves numerous laboratories working either in fundamental or applied research and using all the modern tools available in material science. We present first the situation of the six countries involved in the project regarding their history in nuclear waste vitrification, current policy, and geological disposal project development. This provides an understanding of the common and country specific needs regarding the issue of long-term behavior of glass. Then main proposals and first results are briefly presented.
Nakajima, Hideo; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Iguchi, Masahide; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Matsui, Kunihiro; Chida, Yutaka; Kajitani, Hideki; Takano, Katsutoshi; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
The ITER organization and 6 Domestic Agencies (DA) have been implementing the construction of ITER superconducting magnet systems. Four DAs have already started full scale construction of Toroidal Field (TF) coil conductors. The qualification of the radial plate manufacture has been completed, and JA and EU are ready for full scale construction. JA has qualified full manufacturing processes of the winding pack with a 1/3 prototype and made 2 full scale mock-ups of the basic segments of TF coil structure to optimize and industrialize the manufacturing process. Preparation and qualification of the full scale construction of the TF coil winding is underway by EU. Procurement of the manufacturing equipment is near completion and qualification of manufacturing processes has already started. The constructions of other components of the ITER magnet systems are also going well towards the main goal of the first plasma in 2020.
Ostermeyer, M.*; Kong, H.-J.*; Kovalev, V. I.*; Harrison, R. G.*; Fotiadi, A. A.*; M gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 26(3), p.297 - 362, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:55.6(Physics, Applied) by the dynamic extinction of neutron radiation
by the dynamic extinction of neutron radiationLiss, K. D.; Kabra, S.*; Thoennessen, L.*; Harjo, S.; Reid, M.*; Yan, K.*; Harrison, R.*; Dippenaar, R. J.*
no journal, ,
Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Bellamy, M.*; Bolch, W. E.*; Eckerman, K. F.*; Endo, Akira; Hertel, N.*; Hunt, J.*; Jansen, J.*; Kim, C. H.*; Lee, C.*; et al.
no journal, ,
A Task Group of the Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP, is currently working on the estimation of effective dose and organ dose coefficients for members of the public due to environmental external exposures to photons and electrons. The JAEA is contributing to the Task Group by calculating the doses with the radiation transport code PHITS which has been developed in the JAEA. Those calculations were performed using the ICRP adult and pediatric male and female reference computational phantoms for the environmental radiation sources in air, soil, and water. The obtained results of effective dose and organ dose are normalized to radioactivity concentration, ambient dose equivalent, and air kerma, and summarize in a database of the dose coefficients. Furthermore, dose coefficients for radionuclides in the environment are also evaluated by using the most recent nuclear decay data.