Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombinationSato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Ishaque, A. M.*; Oba, Hirofumi*; Yamada, Mitsugu; Tejima, Kohei; Onodera, Takefumi; Narumi, Issei
DNA Repair, 11(4), p.410 - 418, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:59.62(Genetics & Heredity)In an effort to gain insights into the role of  RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination, we generated
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination, we generated 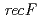 ,
, 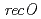 and
and 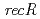 disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. Disruption of
disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. Disruption of 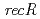 resulted in severe reduction of the transformation efficiency. On the other hand, the
resulted in severe reduction of the transformation efficiency. On the other hand, the 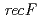 disruptant strain was the most sensitive phenotype to
disruptant strain was the most sensitive phenotype to  rays, UV irradiation and mitomycin C among the three disruptants. In the
rays, UV irradiation and mitomycin C among the three disruptants. In the 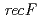 disruptant strain, the intracellular level of the LexA1 protein did not decrease following
disruptant strain, the intracellular level of the LexA1 protein did not decrease following  irradiation. These results demonstrate that the RecF protein plays a crucial role in the homologous recombination repair process by facilitating RecA activation. Thus, the RecF and RecR proteins are involved in the RecA activation and the stability of incoming DNA, respectively, during RecA-mediated homologous recombination processes that initiated the ESDSA pathway in
irradiation. These results demonstrate that the RecF protein plays a crucial role in the homologous recombination repair process by facilitating RecA activation. Thus, the RecF and RecR proteins are involved in the RecA activation and the stability of incoming DNA, respectively, during RecA-mediated homologous recombination processes that initiated the ESDSA pathway in  .
.