Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Shinichiro; Kevin, B.*; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 10th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-10) (Internet), p.44 - 47, 2012/12
Degradation behavior of a-Si/a-SiGe/a-SiGe triple-junction solar cells irradiated with various energy protons are investigated  . It is clarified that the degradation due to proton irradiation is scaled by a unit of displacement damaged dose and thus the proton-induced degradation is mainly caused by the displacement damage effect. The performance recoveries immediately after irradiation are also investigated and it is clarified that all the parameters recover significantly at room temperature. In particular, the remarkable recovery is observed in the short-circuit current. This is thought to be due to recovery of the carrier lifetime, which is based on annealing of radiation defects.
. It is clarified that the degradation due to proton irradiation is scaled by a unit of displacement damaged dose and thus the proton-induced degradation is mainly caused by the displacement damage effect. The performance recoveries immediately after irradiation are also investigated and it is clarified that all the parameters recover significantly at room temperature. In particular, the remarkable recovery is observed in the short-circuit current. This is thought to be due to recovery of the carrier lifetime, which is based on annealing of radiation defects.
Sato, Shinichiro; Kevin, B.*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Performance degradation of a-Si/a-SiGe/a-SiGe triple-junction solar cells due to irradiation of electrons, protons, and silicon ions are investigated using an 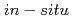 current-voltage measurement system. The room temperature annealing effects immediately after irradiation are also investigated. By analyzing the energy loss process of incident particles (ionizing energy loss and non-ionizing energy loss), the radiation degradation mechanism is discussed.
current-voltage measurement system. The room temperature annealing effects immediately after irradiation are also investigated. By analyzing the energy loss process of incident particles (ionizing energy loss and non-ionizing energy loss), the radiation degradation mechanism is discussed.