Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Do, S.-H.*; Kaneko, Koji; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Stone, M. B.*; Lin, J. Y. Y.*; Ito, Shinichi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Samolyuk, G. D.*; Dagotto, E.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(18), p.L180403_1 - L180403_6, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:87.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Otto, T.*; Hertel, N. E.*; Bartlett, D. T.*; Behrens, R.*; Bordy, J.-M.*; Dietze, G.*; Endo, Akira; Gualdrini, G.*; Pelliccioni, M.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 180(1-4), p.10 - 16, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:89.32(Environmental Sciences)Report Committee 26 of the ICRU proposes a set of operational quantities for radiation protection for external radiation, directly based on effective dose and for an extended range of particles and energies. It is accompanied by new quantities for estimating deterministic effects to the eye lens and the local skin. The operational quantities are designed to overcome the conceptual and technical shortcomings of those presently in use. This paper describes the proposed operational quantities, and highlights the improvements with respect to the present legal monitoring quantities.
Toigo, V.*; Zanotto, L.*; Bigi, M.*; Decamps, H.*; Ferro, A.*; Gaio, E.*; Guti rrez, D.*; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
rrez, D.*; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.956 - 959, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:79.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper reports the progress in the reference design of the Acceleration Grid Power Supply (AGPS) of the ITER Neutral Beam Injector (NBI). The design of the AGPS is very challenging, as it shall be rated to provide about 55 MW at 1 MV dc in quasi steady-state conditions; moreover, the procurement of the system is shared between the European Domestic Agency (F4E) and the Japanese Domestic Agency (JADA), resulting in additional design complication due to the need of a common definition of the interface parameters. A critical revision of the main design choices is presented also in light of the definition of some key interface parameters between the two AGPS subsystems. Moreover, the verification of the fulfillment of the requirements in any operational conditions taking into account the tolerance of the different parameters is also reported and discussed.
Sugawara, Takanori; Sarotto, M.*; Stankovskiy, A.*; Van den Eynde, G.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 38(5), p.1098 - 1108, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)The XT-ADS, an accelerator-driven system for an experimental demonstration, has been investigated in the framework of IP EUROTRANS FP6 project. In this study, the sensitivity and uncertainty analyses were performed to comprehend the reliability of the XT-ADS neutronic design. For the sensitivity analysis, it was found that the sensitivity coefficients were significantly different by changing the geometry models and calculation codes. For the uncertainty analysis, it was confirmed that the uncertainties deduced from the covariance data varied significantly by changing them. The uncertainties deduced from the covariance data for the XT-ADS criticality were 0.94%, 1.9% and 1.1% by the SCALE 44-group, TENDL-2009 and JENDL-3.3 data, respectively. When the target accuracy of 0.3%dk for the criticality was considered, the uncertainties did not satisfy it. To achieve this accuracy, the uncertainties should be improved by experiments under an adequate condition.
Sugawara, Takanori; Stankovskiy, A.*; Sarotto, M.*; Van den Eynde, G.*
NEA/NSC/DOC(2011)4, p.27 - 35, 2011/00
A flexible fast spectrum research reactor MYRRHA able to operate in subcritical (driven by a proton accelerator) and critical modes is being developed in SCK CEN. In the framework of IP EUROTRANS programme the XT-ADS model has been investigated for MYRRHA. In this study, the sensitivity and uncertainty analysis was performed to comprehend the reliability of the XT-ADS neutronics design. The calculated sensitivity coefficients for neutronics parameters varied significantly between calculation models. The uncertainties deduced from the covariance data strongly depend on the original covariance data. The calculated nuclear data uncertainties could not meet the target accuracy. To improve uncertainties, the integral experiments in adequate conditions are expedient.
CEN. In the framework of IP EUROTRANS programme the XT-ADS model has been investigated for MYRRHA. In this study, the sensitivity and uncertainty analysis was performed to comprehend the reliability of the XT-ADS neutronics design. The calculated sensitivity coefficients for neutronics parameters varied significantly between calculation models. The uncertainties deduced from the covariance data strongly depend on the original covariance data. The calculated nuclear data uncertainties could not meet the target accuracy. To improve uncertainties, the integral experiments in adequate conditions are expedient.
Nishitani, Takeo; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Nozawa, Takashi; Hayashi, Kimio; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; M slang, A.*; Baluc, N.*; Pizzuto, A.*; et al.
slang, A.*; Baluc, N.*; Pizzuto, A.*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.405 - 410, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The establishment of the breeding blanket technology is one of the most important engineering issues on the DEMO development. For the DEMO blanket, developments of the structural materials and functional materials such as tritium breeder and neutron multiplier. Which should be used under the savior circumstance such as high neutron fluence, high temperature and strong magnetic field, are urgent issues. In the Broader Approach activities initiated by EU and Japan, developments of reduced activation ferritic martensitic steels as a DEMO blanket structural material, SiC/SiC composites, advanced tritium breeders and neutron multiplier for DEMO blankets, are planed as common interest issues of EU and Japan. This paper describes the overview of the development program.
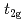 -orbital Hubbard model
-orbital Hubbard modelXavier, J. C.*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Hotta, Takashi; Dagotto, E.*
Physical Review B, 73(1), p.014405_1 - 014405_9, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present the zero-temperature phase diagram of the one-dimensional 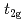 -orbital Hubbard model, by using the density-matrix renormalization group and Lanczos techniques. Emphasis is given to the case for the electron density
-orbital Hubbard model, by using the density-matrix renormalization group and Lanczos techniques. Emphasis is given to the case for the electron density  =5, of relevance to Co-based compounds. Several other cases for electron densities between
=5, of relevance to Co-based compounds. Several other cases for electron densities between  =3 and 6 are also studied. At
=3 and 6 are also studied. At  =5, our results indicate a first-order transition between a paramagnetic (PM) insulator phase and a ferromagnetic (FM) state by tuning the Hund's coupling. The results also suggest a transition from the
=5, our results indicate a first-order transition between a paramagnetic (PM) insulator phase and a ferromagnetic (FM) state by tuning the Hund's coupling. The results also suggest a transition from the  =5 PM insulator phase to a metallic regime by changing the electron density. The behavior of the spin, charge, and orbital correlation functions in the FM and PM states are discussed.
=5 PM insulator phase to a metallic regime by changing the electron density. The behavior of the spin, charge, and orbital correlation functions in the FM and PM states are discussed.
Roth, J.*; Kirschner, A.*; Bohmeyer, W.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Cambe, A.*; Casarotto, E.*; Doerner, R.*; Gauthier, E.*; Federici, G.*; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.970 - 974, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:98.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In the frame work of the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity an attempt was made to establish a possible dependence of the chemical erosion yield of carbon on the ion flux,  , involving ion beam experiments, plasma simulators, and fusion devices. After data normalization a fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with
, involving ion beam experiments, plasma simulators, and fusion devices. After data normalization a fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with 
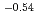 at high ion fluxes. With this dependence on ion flux a comprehensive description is available for chemical erosion as function of energy, temperature and ion flux. Using this dependence the erosion and redeposition of carbon in the ITER divertor can be calculated using the ERO code and the steady-state plasma scenario given by the ITER team. The resulting gross and net erosion rates are compared to previous estimates using a constant erosion yield of 1.5%. The use of the complete parameter dependence results in an order of magnitude lower erosion, most strongly determined by the temperature dependence and the reduction at the highest fluxes.
at high ion fluxes. With this dependence on ion flux a comprehensive description is available for chemical erosion as function of energy, temperature and ion flux. Using this dependence the erosion and redeposition of carbon in the ITER divertor can be calculated using the ERO code and the steady-state plasma scenario given by the ITER team. The resulting gross and net erosion rates are compared to previous estimates using a constant erosion yield of 1.5%. The use of the complete parameter dependence results in an order of magnitude lower erosion, most strongly determined by the temperature dependence and the reduction at the highest fluxes.
Roth, J.*; Preuss, R.*; Bohmeyer, W.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Cambe, A.*; Casarotto, E.*; Doerner, R.*; Gauthier, E.*; Federici, G.*; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(11), p.L21 - L25, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:94 Percentile:91.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Chemical erosion of carbon has been studied in ion beam experiments, and the yield values are available as a function of ion energy and surface temperature. ITER divertor condition, however, cannot be simulated by ion beam. For extrapolating to ITER, the erosion must be investigated in plasma simulators and in SOL or divertors of present fusion devices. In the past, erosion values were reported, but the values showed a wide scatter as a function of ion flux,  . Therefore, a joint attempt was made through the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) to clarify the flux dependence. For each data point the local plasma conditions were normalized to impact energy of 30 eV, the data were selected for a surface temperature close to the maximum yield or to room temperature, and the diagnostic was calibrated in-situ. Through this procedure, the previous large scatter could be drastically reduced. A fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with
. Therefore, a joint attempt was made through the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) to clarify the flux dependence. For each data point the local plasma conditions were normalized to impact energy of 30 eV, the data were selected for a surface temperature close to the maximum yield or to room temperature, and the diagnostic was calibrated in-situ. Through this procedure, the previous large scatter could be drastically reduced. A fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with 
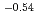 at high ion fluxes.
at high ion fluxes.
Hotta, Takashi; Dagotto, E.*
Physical Review Letters, 92(22), p.227201_1 - 227201_4, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:80.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ground-state properties of layered nickelates are investigated based on the orbital-degenerate Hubbard model coupled with lattice distortions, by using numerical techniques. The N el state composed of spin
el state composed of spin  =1 ions is confirmed in the undoped limit
=1 ions is confirmed in the undoped limit  =0. At
=0. At  =1/2, novel antiferromagnetic states, called CE- and E-type phases, are found by increasing the Hund's coupling. (
=1/2, novel antiferromagnetic states, called CE- and E-type phases, are found by increasing the Hund's coupling. (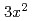

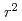 /
/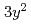

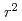 )-type orbital ordering is predicted to occur in a checkerboard-type charge-ordered state. At
)-type orbital ordering is predicted to occur in a checkerboard-type charge-ordered state. At  =1/3,
=1/3, 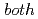 Coulombic and phononic interactions are found to be important, since the former stabilizes the spin stripe, while the latter leads to the striped charge-order.
Coulombic and phononic interactions are found to be important, since the former stabilizes the spin stripe, while the latter leads to the striped charge-order.
Hotta, Takashi; Moraghebi, M.*; Feiguin, A.*; Moreo, A.*; Yunoki, Seiji*; Dagotto, E.*
Physical Review Letters, 90(24), p.247203_1 - 247203_4, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:91.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Novel ground-state spin structures in undoped and doped manganites are here investigated based on the orbital-degenerate double-exchange model, by using mean-field and numerical techniques. In undoped manganites, a new antiferromagnetic (AFM) state, called the E-type phase, is found adjacent in parameter space to the A-type AFM phase. Its structure is in agreement with recent experimental results. This insulating E-AFM state is competing with a ferromagnetic metallic phase as well, suggesting that large magneto-resistant effects could exist even in undoped manganese oxides. For doped layered manganites, the phase diagram includes another new AFM phase of the 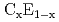 -type. Experimental signatures of the new phases are discussed.
-type. Experimental signatures of the new phases are discussed.
Hotta, Takashi; Dagotto, E.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 312-313(1-4), p.700 - 702, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.65(Physics, Condensed Matter)The crucial role of the orbital degree of freedom is here discussed in order to understand the complex spin and charge structures of transition metal oxides. For manganites, it is shown that diagonal charge stripes in the ferromagnetic phase are induced by the staggered orbital ordered pattern, while for ruthenates, a novel orbital ordering is found to exist in the G-type antiferromagnetic structure, with a hole arrangement as recently observed in X-ray experiments.
Hotta, Takashi; Dagotto, E.*
Physical Review Letters, 88(1), p.017201_1 - 017201_4, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:80 Percentile:90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The key role of the orbital degree of freedom to understand the magnetic properties of layered ruthenates is here discussed. In the G-type antiferromagnetic (AFM) phase of Ca RuO
RuO , recent X-ray experiments reported the presence of 0.5 hole per site in the
, recent X-ray experiments reported the presence of 0.5 hole per site in the 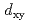 orbital, while the
orbital, while the 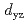 and
and 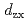 orbitals contain 1.5 holes. This unexpected
orbitals contain 1.5 holes. This unexpected 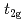 hole distribution is explained by a novel state with orbital ordering (OO), stabilized by a combination of Coulomb interactions and lattice distortions. In addition, the rich phase diagram presented here suggests the possibility of large magnetoresistance effects, and predicts a new ferromagnetic OO phase in ruthenates.
hole distribution is explained by a novel state with orbital ordering (OO), stabilized by a combination of Coulomb interactions and lattice distortions. In addition, the rich phase diagram presented here suggests the possibility of large magnetoresistance effects, and predicts a new ferromagnetic OO phase in ruthenates.
Onishi, Hiroaki; Gonzalez, I.*; Melko, R.*; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Hiroaki; Gonzalez, I.*; Melko, R.*; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,
Onishi, Hiroaki; Gonzalez, I.*; Melko, R.*; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Hiroaki; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Hiroaki; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Hiroaki; Gonzalez, I.*; Melko, R.*; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Hiroaki; Dagotto, E.*
no journal, ,