Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.8(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
 isomers in
isomers in  Cf
CfOrlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Ito, Yuta; Suzaki, Fumi; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064301_1 - 064301_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.99(Physics, Nuclear) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.53(Astronomy & Astrophysics) O
O
Allenspach, S.*; Biffin, A.*; Stuhr, U.*; Tucker, G. S.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko; Voneshen, D. J.*; Boehm, M.*; Normand, B.*; Laflorencie, N.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(17), p.177205_1 - 177205_7, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Ge
Ge
Wo, H.*; Wang, Q.*; Shen, Y.*; Zhang, X.*; Hao, Y.*; Feng, Y.*; Shen, S.*; He, Z.*; Pan, B.*; Wang, W.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.217003_1 - 217003_5, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zr(
Zr( )
)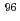 Zr cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on
Zr cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on  -process nucleosynthesis
-process nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Karakas, A. I.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mohr, P.*; Su, J.*; Li, Y. J.*; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 848(2), p.98_1 - 98_8, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.26(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 67(Part A), p.168 - 184, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:62.14(Thermodynamics)An experimental study on upward bubbly air-water flows in a vertical large-diameter square duct have been performed by mainly using four-sensor probes. Local measurements of interfacial area concentration (IAC), void fraction, 3D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter at 3 axial positions were conducted. Although the interfacial area transport equation (IATE) and its bubble coalescence and breakup models have already played an important role in predicting the IAC in general two-phase flow fields, they are mainly developed based on the two-phase flow experimental data taken in round pipes or small diameter channels. To confirm their usability in large-diameter square duct, this study has evaluated the 1D one-group IATE with its 6 sets of bubble coalescence and breakup models with the presently-obtained database. It was found the relative error between the best prediction and the database was 25%.
Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17) (USB Flash Drive), 14 Pages, 2017/09
An experimental study on the upward bubbly air-water flows in a vertical large-diameter square duct have been performed by using four-sensor probes. The four-sensor probe were applied in the local measurements at 3 axial positions along the flow direction to obtain interfacial area concentration, 3-D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter. The obtained void fraction, interfacial area concentration, 3-D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter provided valuable insight into the flow structure and will serve as a valuable database to develop the mechanistic models for interfacial area transport equation sources and sinks.
Kikkawa, Takashi*; Shen, K.*; Flebus, B.*; Duine, R. A.*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Qiu, Z.*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review Letters, 117(20), p.207203_1 - 207203_6, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:148 Percentile:97.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zr(n,
Zr(n, )
) Zr cross section with
Zr cross section with 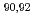 Zr(
Zr( O,
O, O)
O)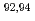 Zr reactions
Zr reactionsYan, S. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Su, J.*; Li, Y. J.*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Hirose, Kentaro; Han, Y. L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(1), p.015804_1 - 015804_5, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.35(Physics, Nuclear)Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 89, p.140 - 158, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:89.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)An experimental study was performed on the local structure of upward air-water two-phase flow in a vertical large diameter square duct by using a four-sensor probe. The four-sensor probe method classifying spherical and non-spherical bubbles was applied as a key measurement way to obtain local parameters such as 3-D bubble velocity vector, bubble diameter and interfacial area concentration. Both the local void fraction and interfacial area concentration indicated radial core-peak and wall-peak distributions at low and high liquid flow rates respectively. The 2 components of the bubble velocity vector in the cross-section revealed that there exists a rotating secondary flow in the octant symmetric triangular area and the magnitude of the rotating secondary flow increases with the liquid flow rate. Some of constitutive correlations of drift-flux model and interfacial area concentration are reviewed to study their predictabilities against the present data.
 n eigenmodes
n eigenmodesKonovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Kovalishen, E. A.*; Ozeki, Takahisa
Physics of Plasmas, 11(9), p.4531 - 4534, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:53.19(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Kovalishen, E. A.*; Kamenets, F. F.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Shirokov, M. S.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tsypin, V. S.*
Doklady Physics, 49(7), p.405 - 408, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.77(Mechanics)Effect of feedback system, placed outside the vacuum vessel, on neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) in tokamaks is analytically studied. External matching parameters for magnetic island chain are derived for the simplest case of step profile of equilibrium parallel current. The structure of dynamical equations for the island width and island rotation frequency in terms of matching parameters is explained. It is shown that such a feedback system can lead to essential shift of the island rotation, in particular, for stabilization of NTMs by the polarization current effect.
Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Kovalishen, E. A.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Konovalov, S. V.; Tsypin, V. S.*; Kamenets, F. F.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori
Physics of Plasmas, 11(2), p.666 - 676, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Analytical treatment of magnetic islands with high poloidal mode numbers and widths smaller than ion Larmor radius (microislands) is presented. The profile functions and rotation frequencies of microislands are investigated with the two-fluid magnetohydrodynamics. The microislands are described in terms of two profile functions, one of which characterizes the electric field and perturbed plasma density, and second the perturbed electron temperature. The problem of rotation frequencies of microislands is discussed.
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Tsypin, V. S.*; Kovalishen, E. A.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori
Physics Letters A, 318(4-5), p.429 - 434, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English

Hua, Y.*; Narumi, Issei; Gao, G.*; Tian, B.*; Sato, Katsuya; Kitayama, Shigeru; Shen, B.*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306(2), p.354 - 360, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:95.76(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have identified a unique deinococcal gene,  , as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which
, as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which  is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with
is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with  . In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of
. In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of  and
and  and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.