Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maurer, C.*; Galmarini, S.*; Solazzo, E.*; Ku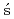 mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar
mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar , J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
, J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.106968_1 - 106968_27, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.8(Environmental Sciences)After performing multi-model exercises in 2015 and 2016, a comprehensive Xe-133 atmospheric transport modeling challenge was organized in 2019. For evaluation measured samples for the same time frame were gathered from four International Monitoring System stations located in Europe and North America with overall considerable influence of IRE and/or CNL emissions. As a lesion learnt from the 2nd ATM-Challenge participants were prompted to work with controlled and harmonized model set ups to make runs more comparable, but also to increase diversity. Effects of transport errors, not properly characterized remaining emitters and long IMS sampling times (12 to 24 hours) undoubtedly interfere with the effect of high-quality IRE and CNL stack data. An ensemble based on a few arbitrary submissions is good enough to forecast the Xe-133 background at the stations investigated. The effective ensemble size is below five.
 -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of  Mg via direct reactions
Mg via direct reactionsKitamura, Noritaka*; Wimmer, K.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Bader, V. M.*; Bancroft, C.*; Barofsky, D.*; Baugher, T.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(3), p.034318_1 - 034318_17, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Mg
MgKitamura, Noritaka*; Wimmer, K.*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Bader, V. M.*; Bancroft, C.*; Barofsky, D.*; Baugher, T.*; Bazin, D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 822, p.136682_1 - 136682_7, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:71.66(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Mg explored via in-beam
Mg explored via in-beam  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyKitamura, Noritaka*; Wimmer, K.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Bader, V. M.*; Bancroft, C.*; Barofsky, D.*; Baugher, T.*; Bazin, D.*; Berryman, J. S.*; Bildstein, V.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(5), p.054318_1 - 054318_13, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.12(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Dimitriou, P.*; Basunia, S*; Bernstein, L.*; Chen, J.*; Elekes, Z.*; Huang, X.*; Hurst, A.*; Iimura, Hideki; Jain, A. K.*; Kelley, J.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15004_1 - 15004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF) includes the most extensive and comprehensive set of nuclear structure and decay data evaluations performed by the international network of Nuclear Structure and Decay Data evaluators (NSDD) under the auspices of the IAEA. In this report we describe some of the recent NSDD activities and provide future perspectives.
Hendriks, J. N.*; Gregg, A. W. T.*; Jackson, R. R.*; Wensrich, C. M.*; Wills, A.*; Tremsin, A. S.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Luzin, V.*; Kirstein, O.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 3(11), p.113803_1 - 113803_11, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:45.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) states in
states in  Ni probed via two-neutron transfer
Ni probed via two-neutron transferFlavigny, F.*; Elseviers, J.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Bauer, C.*; Bildstein, V.*; Blazhev, A.*; 31 of others*
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054332_1 - 054332_6, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:64.15(Physics, Nuclear)Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Schulz, F.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Kantor, R. S.*; Shih, P.*; Sharon, I.*; Santini, J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Amano, Yuki; Thomas, B. C.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.463_1 - 463_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:86.04(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Maurer, C.*; Bar , J.*; Kusmierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Crawford, A.*; Eslinger, P. W.*; Seibert, P.*; Orr, B.*; Philipp, A.*; Ross, O.*; Generoso, S.*; et al.
, J.*; Kusmierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Crawford, A.*; Eslinger, P. W.*; Seibert, P.*; Orr, B.*; Philipp, A.*; Ross, O.*; Generoso, S.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 192, p.667 - 686, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:65.58(Environmental Sciences)It is very important to understand the impact for CTBT stations caused by radioxenon emitted from medical isotope production facilities for detection of underground nuclear tests. Predictions of the impact on six CTBT radionuclide stations in the Southern Hemisphere of radioxenon emitted from the medical isotope production facility in Australia were carried out by participants from ten nations using ATM (Atmospheric Transport Modeling) based on the emission data of radioxenon from this facility, as part of study on impact of radioxenon emitted from medical isotope production facilities on CTBT radionuclide stations.
Michel-Sendis, F.*; Gauld, I.*; Martinez, J. S.*; Alejano, C.*; Bossant, M.*; Boulanger, D.*; Cabellos, O.*; Chrapciak, V.*; Conde, J.*; Fast, I.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 110, p.779 - 788, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:99.16(Nuclear Science & Technology) and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sediments
and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sedimentsHernsdorf, A. W.*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ise, Kotaro; Suzuki, Yohei*; Anantharaman, K.*; Probst, A. J.*; Burstein, David*; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 11, p.1915 - 1929, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:95.92(Ecology)To evaluate the potential for interactions between microbial communities and disposal systems, we explored the structure and metabolic function of a sediment-hosted subsurface ecosystem associated with Horonobe Underground Research Center, Hokkaido, Japan. Overall, the ecosystem is enriched in organisms from diverse lineages and many are from phyla that lack isolated representatives. The majority of organisms can metabolize H , often via oxidative [NiFe] hydrogenases or electron-bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenases that enable ferredoxin-based pathways, including the ion motive Rnf complex. Many organisms implicated in H
, often via oxidative [NiFe] hydrogenases or electron-bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenases that enable ferredoxin-based pathways, including the ion motive Rnf complex. Many organisms implicated in H metabolism are also predicted to catalyze carbon, nitrogen, iron, and sulfur transformations. Notably, iron-based metabolism was predicted in a bacterial lineage where this function has not been predicted previously and in an ANME-2d archaeaon that is implicated in methane oxidation. We infer an ecological model that links microorganisms to sediment-derived resources and predict potential impacts of microbial activity on H
metabolism are also predicted to catalyze carbon, nitrogen, iron, and sulfur transformations. Notably, iron-based metabolism was predicted in a bacterial lineage where this function has not been predicted previously and in an ANME-2d archaeaon that is implicated in methane oxidation. We infer an ecological model that links microorganisms to sediment-derived resources and predict potential impacts of microbial activity on H accumulation and radionuclide migration.
accumulation and radionuclide migration.
Eslinger, P. W.*; Bowyer, T. W.*; Achim, P.*; Chai, T.*; Deconninck, B*; Freeman, K.*; Generoso, S.*; Hayes, P.*; Heidmann, V.*; Hoffman, I.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 157, p.41 - 51, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:72.19(Environmental Sciences)It is very important to understand the impact for CTBT stations caused by radioxenon emitted from nuclear facilities and medical isotope production facilities for detection of underground nuclear tests. Predictions of the impact on the CTBT radionuclide station in Germany of radioxenon emitted from the medical isotope production facility in Belgium were carried out by participants from seven nations using ATM (Atmospheric Transport Modeling) based on the emission data of radioxenon from this facility, as part of study on impact of radioxenon emitted from medical isotope production facilities on CTBT radionuclide stations.
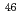 Ar by the (
Ar by the (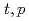 ) two-neutron transfer reaction
) two-neutron transfer reactionNowak, K.*; Wimmer, K.*; Hellgartner, S.*; M cher, D.*; Bildstein, V.*; Diriken, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; Gaffney, L. P.*; Gernh
cher, D.*; Bildstein, V.*; Diriken, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; Gaffney, L. P.*; Gernh user, R.*; Iwanicki, J.*; et al.
user, R.*; Iwanicki, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(4), p.044335_1 - 044335_10, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:77.39(Physics, Nuclear)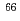 Ni(
Ni( ,
, )
) Ni one-neutron transfer reaction
Ni one-neutron transfer reactionDiriken, J.*; Patronis, N.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Antalic, S.*; Bildstein, V.*; Blazhev, A.*; Darby, I. G.*; De Witte, H.*; Eberth, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(5), p.054321_1 - 054321_15, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.97(Physics, Nuclear) =40;
=40;  Cu
CuSahin, E.*; Doncel, M.*; Sieja, K.*; De Angelis, G.*; Gadea, A.*; Quintana, B.*; G rgen, A.*; Modamio, V.*; Mengoni, D.*; Valiente-Dob
rgen, A.*; Modamio, V.*; Mengoni, D.*; Valiente-Dob n, J. J.*; et al.
n, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(3), p.034302_1 - 034302_9, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:84.43(Physics, Nuclear)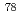 Ni; Spectroscopy of the N=49 isotope
Ni; Spectroscopy of the N=49 isotope  Zn
ZnOrlandi, R.; M cher, D.*; Raabe, R.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Pain, S. D.*; Bildstein, V.*; Chapman, R.*; De Angelis, G.*; Johansen, J. G.*; Van Duppen, P.*; et al.
cher, D.*; Raabe, R.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Pain, S. D.*; Bildstein, V.*; Chapman, R.*; De Angelis, G.*; Johansen, J. G.*; Van Duppen, P.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 740, p.298 - 302, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:85.36(Astronomy & Astrophysics) d
d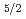 orbital in
orbital in 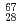 Ni
Ni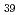 using one-neutron transfer reactions
using one-neutron transfer reactionsDiriken, J.*; Patronis, N.*; Andreyev, A. N.*; Antalic, S.*; Bildstein, V.*; Blazhev, A.*; Darby, I. G.*; De Witte, H.*; Eberth, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 736, p.533 - 538, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.61(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Sushkov, O. P.*; Milstein, A. I.*; Mori, Michiyasu; Maekawa, Sadamichi
EPL; A Letters Journal Exploring the Frontiers of Physics, 103(4), p.47003_1 - 47003_6, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.72(Physics, Multidisciplinary)He, R.-H.*; Hashimoto, Makoto*; Karapetyan, H.*; Koralek, J. D.*; Hinton, J. P.*; Testaud, J. P.*; Nathan, V.*; Yoshida, Yoshiyuki*; Yao, H.*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; et al.
Science, 331(6024), p.1579 - 1583, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:276 Percentile:98.66(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The nature of the pseudogap phase of cuprate high-temperature superconductors is a major unsolved problem in condensed matter physics. We studied the commencement of the pseudogap state at temperature 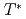 using three different techniques (angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, polar Kerr effect, and time-resolved reflectivity) on the same optimally doped Bi2201 crystals. We observed the coincident, abrupt onset at
using three different techniques (angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, polar Kerr effect, and time-resolved reflectivity) on the same optimally doped Bi2201 crystals. We observed the coincident, abrupt onset at 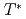 of a particle-hole asymmetric antinodal gap in the electronic spectrum, a Kerr rotation in the reflected light polarization, and a change in the ultrafast relaxational dynamics, consistent with a phase transition. Upon further cooling, spectroscopic signatures of superconductivity begin to grow close to the superconducting transition temperature (
of a particle-hole asymmetric antinodal gap in the electronic spectrum, a Kerr rotation in the reflected light polarization, and a change in the ultrafast relaxational dynamics, consistent with a phase transition. Upon further cooling, spectroscopic signatures of superconductivity begin to grow close to the superconducting transition temperature ( ), entangled in an energy-momentum dependent manner with the preexisting pseudogap features, ushering in a ground state with coexisting orders.
), entangled in an energy-momentum dependent manner with the preexisting pseudogap features, ushering in a ground state with coexisting orders.
Guly s, L.*; Fainstein, P. D.*; Shirai, Toshizo
s, L.*; Fainstein, P. D.*; Shirai, Toshizo
Physical Review A, 65(5), p.052720_1 - 052720_9, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:58.28(Optics)We perform an extension of the continuum-distorted-wave (CDW) approximation for single electron capture by introducing model potentials to describe the interaction of the active electron with the residual-target and projectile ions. The cross sections for electron transfer in collisions of bare and dressed projectile ions with H and He atoms are calculated and compared with experimental data and previous CDW calculations that make use of approximate analytical wave functions to represent the active electron initial and final states. For electron capture in proton-He collisions into definite final states the present calculations are in better agreement with experiments. We trace the differences in the results from both models to a different behavior at projectile scattering angles close to the Thomas peak.