Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
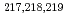 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero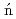 , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:77.09(Physics, Nuclear) T
T As
As (
( = Co,Ni)
= Co,Ni)Tam, D. M.*; Song, Y.*; Man, H.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Yin, Z.*; Lu, X.*; Wang, W.*; Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Gong, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(6), p.060505_1 - 060505_6, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)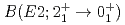 value in
value in  Kr
KrR gis, J.-M.*; Jolie, J.*; Saed-Samii, N.*; Warr, N.*; Pfeiffer, M.*; Blanc, A.*; Jentschel, M.*; K
gis, J.-M.*; Jolie, J.*; Saed-Samii, N.*; Warr, N.*; Pfeiffer, M.*; Blanc, A.*; Jentschel, M.*; K ster, U.*; Mutti, P.*; Soldner, T.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Mutti, P.*; Soldner, T.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 90(6), p.067301_1 - 067301_4, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:80.23(Physics, Nuclear)Fischer, U.*; Iida, Hiromasa; Li, Y.*; Loughlin, M.*; Sato, Satoshi; Serikov, A.*; Tsige-Tamirat, H.*; Tautges, T.*; Wilson, P. P.*; Wu, Y.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 56(2), p.702 - 709, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Several approaches have been recently developed to make available CAD geometry data for Monte Carlo calculations with the MCNP code. Among these are conversion tools for the automatic generation of geometry models in MCNP representation such as MCAM of China, McCad of Germany, and GEOMIT of JAEA, as well as the direct DAG-MCNPX approach developed by USA. An extensive benchmark exercise has been conducted on ITER between 2005 and 2007 with the objective to test and validate the different approaches and thereby check the maturity level for ITER design applications. The exercise encompassed the generation of a dedicated neutronics CATIA model based on available engineering CAD design data, the conversion into MCNP geometry, the verification of the converted models, and a number of calculations to compare the different approaches with regard to the performance and the validity of the results obtained. The paper briefly reviews the different approaches and provides a detailed description of the ITER benchmark effort, its results and conclusions. As a key issue, the recommendations are discussed that need to be followed when generating a neutronics CAD model for ITER design calculations. This is considered essential since the ITER quality assurance requirements will request the consistency of the analysis models and the underlying engineering CAD models.
Snyder, P. B.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085035_1 - 085035_8, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:170 Percentile:98.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The pressure at the top of the edge transport barrier impacts fusion performance, while large ELMs can constrain material lifetimes. Investigation of intermediate wavelength MHD mode has led to improved understanding of the pedestal height and the mechanism for ELMs. The combination of high resolution diagnostics and a suite of stability codes has made edge stability analysis routine, and contribute both to understanding, and to experimental planning and performance optimization. Here we present extensive comparisons of observations to predicted edge stability boundaries on several tokamaks, both for the standard (Type I) ELM regime, and for small ELM and ELM-free regimes. We further discuss a new predictive model for the pedestal height and width (EPED1), developed by self-consistently combining a simple width model with peeling-ballooning stability calculations. This model is tested against experimental measurements, and used in initial predictions of the pedestal height for ITER.
Snyder, P. B.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Investigation of intermediate wavelength MHD modes has led to improved understanding of important constraints on the pedestal height and the mechanism for ELMs. The combination of high resolution pedestal diagnostics and a suite of highly efficient stability codes, has made edge stability analysis routine on several major tokamaks, contributing both to understanding, and to experimental planning and performance optimization. Here we present extensive comparisons of observations to predicted edge stability boundaries on several tokamaks, both for the standard ELM regime, and for small ELM and ELM-free regimes. We further use the stability constraint on pedestal height to test models of the pedestal width, and self-consistently combine a simple width model with MHD stability calculations to develop a new predictive model (EPED1) for the pedestal height and width. This model is tested against experimental measurements, and used in initial predictions of the pedestal height for ITER.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Fujita, Takaaki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Chu, M. S.*; Snyder, P. B.*; Wilson, H. R.*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.010_1 - 010_8, 2007/04
Numerical method for the stability analysis of ideal MHD modes is invented by using the physical model based on the two-dimensional Newcomb equation in combination with the conventional ideal MHD model. The MARG2D code built on this numerical method realizes to analyze the stability of wide  range of ideal MHD modes. The validity of MARG2D has been confirmed with the benchmarking test with the DCON code by identifying the stability boundary of low-
range of ideal MHD modes. The validity of MARG2D has been confirmed with the benchmarking test with the DCON code by identifying the stability boundary of low- modes, and that with the ELITE code by comparing the growth rates of intermediate to high
modes, and that with the ELITE code by comparing the growth rates of intermediate to high  modes. With the MARG2D code, the edge stability of JT-60SA, the complementally experiment of ITER, is investigated.
modes. With the MARG2D code, the edge stability of JT-60SA, the complementally experiment of ITER, is investigated.
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Leonard, A. W.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Boedo, J. A.*; Becoulet, M.*; Counsell, G. F.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Herrmann, A.*; Horton, L. D.*; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A149 - A162, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:78.1(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This report summarizes Type I edge localized mode (ELM) dynamics measurements from a number of tokamaks. Several transport mechanisms are conjectured to be responsible for ELM transport, including convective transport due to filamentary structures ejected from the pedestal, parallel transport due to edge ergodization or magnetic reconnection and turbulent transport driven by the high edge gradients when the radial electric field shear is suppressed. The experimental observations are assessed for their validation, or conflict, with these ELM transport conjectures.
B coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An
coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An , J.-M.*; et al.
, J.-M.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12A), p.A93 - A113, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:91.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Maekawa, Fujio; Von-Moellendorff, U.*; Wilson, P. P. H.*; Wada, Masayuki*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Reactor Dosimetry: Radiation Metrology and Assessment (ASTM STP 1398), p.417 - 424, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Von-Moellendorff, U.*; Maekawa, Fujio; Giese, H.*; Wilson, P. P. H.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 51-52(Part.B), p.919 - 924, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Maekawa, Fujio; Wada, Masayuki*; Von-Moellendorff, U.*; Wilson, P. P. H.*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 51-52(Part.B), p.815 - 820, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English