Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kim, H.-S.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Na, Y.-S.*; Ghim, Y.-C.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Bak, J. G.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083012_1 - 083012_11, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We evaluate the characteristics of global energy confinement in KSTAR (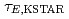 ) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database,
) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database, 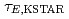 of L-mode plasmas exhibits
of L-mode plasmas exhibits 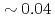 s to
s to 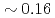 s and
s and 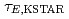 of H-mode plasmas
of H-mode plasmas 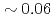 s to
s to 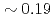 s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation
s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation  in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of
in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of 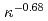 and
and 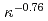 for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as
for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as  increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
Yoon, S. W.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hahn, S. H.*; Ko, W. H.*; Lee, K. D.*; Chung, J. I.*; Nam, Y. U.*; Kim, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113009_1 - 113009_9, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:79.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Typical ELMy H-mode discharges have been achieved on the KSTAR tokamak with the combined auxiliary heating of NBI and ECRH. The minimum external heating power required is about 1.1 MW at a line-averaged density higher than 1.4 10
10 m
m and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than
and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than 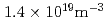 . The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
. The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
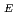 ) predicted that
) predicted that 
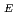 was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account,
was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account, 
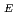 better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
Ostermeyer, M.*; Kong, H.-J.*; Kovalev, V. I.*; Harrison, R. G.*; Fotiadi, A. A.*; M gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 26(3), p.297 - 362, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:55.6(Physics, Applied)Oyama, Naoyuki; Yoon, S. W.*; Suttrop, W.*; Wolfrum, E.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Urano, Hajime; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
no journal, ,
In JT-60U, the ELM heatload can be reduced by 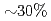 together with increasing the ELM frequency by injecting electron cyclotron wave (ECW) near the top of pedestal. In order to understand the required and optimum condition for the ELM control, edge ECW injection experiments have been performed in ASDEX Upgrade and KSTAR. As a result, clear increase in the ELM frequency was observed in all devices, but the level of ELM mitigation depends on the experimental condition.
together with increasing the ELM frequency by injecting electron cyclotron wave (ECW) near the top of pedestal. In order to understand the required and optimum condition for the ELM control, edge ECW injection experiments have been performed in ASDEX Upgrade and KSTAR. As a result, clear increase in the ELM frequency was observed in all devices, but the level of ELM mitigation depends on the experimental condition.
Suzuki, Takahiro; Kim, J. H.*; Na, Y. S.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Mueller, D.*; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Kim, H. S.*; Hahn, S. H.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Kim, W. C.*
no journal, ,
We have started advanced operation scenario development in KSTAR in this campaign, which opens up a new research area directly connecting to ITER and DEMO. The advanced scenario, which has higher performance than the standard H-mode, typically possesses lower internal inductance li (safety factor q above unity without sawtooth). In conventional KSTAR operation scenarios, divertor configuration with high elongation is realized after or near the end of Ip ramp-up, where sawtooth activity starts during the ramp-up before entering into the higher performance phase. Thus, we need a new KSTAR operation scenario without sawtooth during the Ip ramp-up and with lower li than unity. Our idea is to delay the inductive current penetration by simultaneous EC&NB heating application into the full-bore divertor plasma during the Ip ramp-up as early as possible. After the optimization, we have successfully established a start-up scenario without sawtooth throughout the Ip ramp-up. In a shot 7897, high 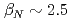 reaching an advanced scenario regime has been achieved in ELM-free H-mode (
reaching an advanced scenario regime has been achieved in ELM-free H-mode ( ) at
) at 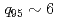 .
.
Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Yoon, S. W.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Kubo, Hirotaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O studied by
studied by  SR technique
SR techniqueKawamura, Seiko; Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Sari P., D.*; Asih, R.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Watanabe, Isao*; Nakajima, Kenji
no journal, ,
Rb Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O is a quantum spin system having zig-zag chains of the spin-1/2 Cu ions. Whereas the system is expected to exhibit an incommensurate spin-singlet state based on a ratio of the second neighbor ferromagnetic interaction
is a quantum spin system having zig-zag chains of the spin-1/2 Cu ions. Whereas the system is expected to exhibit an incommensurate spin-singlet state based on a ratio of the second neighbor ferromagnetic interaction 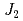 to the first neighbor antiferromagnetic interaction
to the first neighbor antiferromagnetic interaction 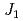 , there is no report to bare a direct evidence for the spin-singlet ground state of this system. We carried out
, there is no report to bare a direct evidence for the spin-singlet ground state of this system. We carried out  SR measurements on this system, to clarify its ground state and dynamics. In the zero-field measurement, the time spectra do not show changes with temperature from 300 K to 20 K, while the muon spin relaxation is enhanced below 20 K. The relaxation is again independent of temperature below 1.5 K. The result reveals that the ground state of Rb
SR measurements on this system, to clarify its ground state and dynamics. In the zero-field measurement, the time spectra do not show changes with temperature from 300 K to 20 K, while the muon spin relaxation is enhanced below 20 K. The relaxation is again independent of temperature below 1.5 K. The result reveals that the ground state of Rb Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O is nonmagnetic. Furthermore, the longitudinal-field
is nonmagnetic. Furthermore, the longitudinal-field  SR measurements indicate characteristic behavior of the internal field and dynamics accompanying formation of the spin singlet.
SR measurements indicate characteristic behavior of the internal field and dynamics accompanying formation of the spin singlet.