Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Jiang, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:88.89(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)As a promising environment-friendly alternative to current vapor-compression refrigeration, solid-state refrigeration based on the barocaloric effect has been attracting world wide attention. Generally, both phases in which a barocaloric effect occurs are present at ambient pressure. Here, instead, we demonstrate that KPF exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
 BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:56.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Grsic, Z.*; Halsall, C.*; Heinrich, G.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Ku a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2001, 226 Pages, 2022/06
The IAEA organized a programme from 2012 to 2015 entitled Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA), which aimed to improve capabilities in the field of environmental radiation dose assessment by acquiring improved data, model testing and comparison of model inputs, assumptions and outputs, reaching a consensus on modelling philosophies, aligning approaches and parameter values, developing improved methods and exchanging information. This publication describes the activities of Working Group 2, Exposures in Contaminated Urban Environments and Effect of Remedial Measures.
Thiessen, K. M.*; Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Federspiel, L.; Gra i
i , B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
, B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020502_1 - 020502_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:83.25(Environmental Sciences) decay of
decay of 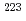 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:78.75(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Li, B.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kawamura, Seiko; Sugahara, Takeshi*; Wang, H.*; Wang, J.*; Chen, Y.*; Kawaguchi, Saori*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Ohara, Koji*; et al.
Nature, 567(7749), p.506 - 510, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:182 Percentile:99.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Refrigeration is of vital importance for modern society for example, for food storage and air conditioning- and 25 to 30% of the world's electricity is consumed for refrigeration. Current refrigeration technology mostly involves the conventional vapour compression cycle, but the materials used in this technology are of growing environmental concern because of their large global warming potential. As a promising alternative, refrigeration technologies based on solid-state caloric effects have been attracting attention in recent decades. However, their application is restricted by the limited performance of current caloric materials, owing to small isothermal entropy changes and large driving magnetic fields. Here we report colossal barocaloric effects (CBCEs) (barocaloric effects are cooling effects of pressure-induced phase transitions) in a class of disordered solids called plastic crystals. The obtained entropy changes in a representative plastic crystal, neopentylglycol, are about 389 joules per kilogram per kelvin near room temperature. Pressure-dependent neutron scattering measurements reveal that CBCEs in plastic crystals can be attributed to the combination of extensive molecular orientational disorder, giant compressibility and highly anharmonic lattice dynamics of these materials. Our study establishes the microscopic mechanism of CBCEs in plastic crystals and paves the way to next-generation solid-state refrigeration technologies.
Li, B.; Wang, H.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Zhang, Q.*; Feygenson, M.*; Yu, H. L.*; Wu, D.*; Ohara, Koji*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Nature Materials, 17(3), p.226 - 230, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:124 Percentile:96.83(Chemistry, Physical)Kim, S. H.*; Hwang, S.; Ahn, J. K.*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hong, B.*; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Kim, M. H.*; Lee, J. Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 795, p.39 - 44, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sako, Hiroyuki; Ahn, J. K.*; Baek, K. H.*; Bassalleck, B.*; Fujioka, H.*; Guo, L.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hicks, K.*; Honda, R.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(4), p.C04009_1 - C04009_10, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.93(Instruments & Instrumentation)A TPC has been developed for J-PARC E42 experiment to search for H-dibaryon in (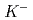 ,
, 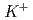 ) reaction. An event with 2
) reaction. An event with 2 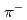 and 2 protons decaying from H-dibaryon is searched for inside the TPC. The TPC has octagonal prism shape drift volume with about 50 cm diameter with 55 cm drift length filled with Ar-CH
and 2 protons decaying from H-dibaryon is searched for inside the TPC. The TPC has octagonal prism shape drift volume with about 50 cm diameter with 55 cm drift length filled with Ar-CH (90:10) gas. At the end of the drift volume, 3-layer GEMs are equipped. In order to analyze momenta of produced particles, the TPC is applied with 1 T dipole magnetic field parallel to the drift electric field with a superconducting Helmholz magnet. In order to maximize the acceptance of H-dibaryon events, a diamond target is installed inside the TPC drift volume, in a cylindrical hole opened from the top to the middle of the drift volume. Since extremely high-rate
(90:10) gas. At the end of the drift volume, 3-layer GEMs are equipped. In order to analyze momenta of produced particles, the TPC is applied with 1 T dipole magnetic field parallel to the drift electric field with a superconducting Helmholz magnet. In order to maximize the acceptance of H-dibaryon events, a diamond target is installed inside the TPC drift volume, in a cylindrical hole opened from the top to the middle of the drift volume. Since extremely high-rate 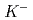 beam is directly injected into the TPC drift volume to the target, a gating grid and GEMs are adopted to suppress positive-ion feedback.
beam is directly injected into the TPC drift volume to the target, a gating grid and GEMs are adopted to suppress positive-ion feedback.
Deng, Z.*; Zhao, K.*; Gu, B.; Han, W.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Wang, X. C.*; Li, X.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Yu, R. C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 88(8), p.081203_1 - 081203_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:92.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Bruzzone, P.*; Stepanov, B.*; Wesche, R.*; Mitchell, N.*; Devred, A.*; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Tronza, V.*; Kim, K.*; Boutboul, T.*; Martovetsky, N.*; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Starting March 2007, over 60 ITER cable-in-conduit conductors (CICC) have been tested in the SULTAN test facility, Switzerland. For the NbTi CICC, the results confirm the prediction from the strand data, which are made taking the peak field over the conductor cross section as operating field. All the NbTi samples passed the supplier qualification phase. For the Nb Sn CICC, the performance prediction is not straightforward because of the irreversible degradation caused by filament damage occurring during cyclic loading. At the first run of the test campaign, the performance of all the Nb
Sn CICC, the performance prediction is not straightforward because of the irreversible degradation caused by filament damage occurring during cyclic loading. At the first run of the test campaign, the performance of all the Nb Sn samples largely meets the target for all the tested samples. Contrary to the NbTi CICC case, the n-index of the transition is substantially lower than in the strands, providing evidence of irreversible degradation. The performance loss upon load cycles and thermal cycles has a broad range among the various conductor samples.
Sn samples largely meets the target for all the tested samples. Contrary to the NbTi CICC case, the n-index of the transition is substantially lower than in the strands, providing evidence of irreversible degradation. The performance loss upon load cycles and thermal cycles has a broad range among the various conductor samples.
 implantation and subsequent thermal annealing
implantation and subsequent thermal annealingYu, R. S.*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Wang, B. Y.*; Wei, L.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 270, p.47 - 49, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.18(Instruments & Instrumentation)Deng, Z.*; Jin, C. Q.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Wang, X. C.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Feng, S. M.*; Chen, L. C.*; Yu, R. C.*; Arguello, C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 2, p.1425_1 - 1425_5, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:160 Percentile:93.76(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In a prototypical ferromagnet (Ga,Mn)As based on a III-V semiconductor, substitution of divalent Mn atoms into trivalent Ga sites leads to severely limited chemical solubility and metastable specimens available only as thin films. The doping of hole carriers via (Ga,Mn) substitution also prohibits electron doping. To overcome these difficulties, Masek et al. theoretically proposed systems based on a I-II-V semiconductor LiZnAs, where isovalent (Zn,Mn) substitution is decoupled from carrier doping with excess/deficient Li concentrations. Here we show successful synthesis of Li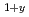 (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )As in bulk materials. We reported that ferromagnetism with a critical temperature of up to 50 K is observed in nominally Li-excess compounds, which have p-type carriers.
)As in bulk materials. We reported that ferromagnetism with a critical temperature of up to 50 K is observed in nominally Li-excess compounds, which have p-type carriers.
Ioki, Kimihiro*; Barabash, V.*; Cordier, J.*; Enoeda, Mikio; Federici, G.*; Kim, B. C.*; Mazul, I.*; Merola, M.*; Morimoto, Masaaki*; Nakahira, Masataka*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.787 - 794, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents recent results of ITER activities on Vacuum Vessel (VV), blanket, limiter, and divertor. Major results can be summarized as follows. (1) The VV design is being developed in more details considering manufacturing and assembly methods, and cost. Incorporating manufacturing studies being performed in cooperation with parties, the regular VV sector design has been nearly finalized. (2) The procurement allocation of blanket modules among 6 parties was fixed and the blanket module design has progressed in cooperation with parties. Fabrication of mock-ups for prequalification testing is under way and the tests will be performed in 2007-2008. (3) The divertor activities have progressed with the aim of launching the procurement according to the ITER project schedule.
Chiba, Satoshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Shibata, Keiichi; Yu, B.*; Kosako, Kazuaki*; Yamamuro, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(2), p.187 - 194, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Tatsuki; Guido-Garcia, F.; Kozai, Naofumi; Zhang, S.*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Yu, Q.*; Grambow, B.
no journal, ,
To understand bacterial ability to dissolve clay minerals, we isolated siderophore-producing bacteria from white clover roots grown in south Osaka, Japan. The ability to produce siderophores was evaluated by CAS plate method. llite, biotite, vermiculite and nontronite were used for testing as clay minerals. Three different bacteria strains were cultivated. Bacteria cells were centrifuged and washed before inoculation tests. Fifty mg dry weight of bacteria were inoculated into 100 mL modified Balland media and 100 mg of each clay mineral added. The suspension was sampled and new media was added. The concentrations of iron, aluminium and silicon were determined by ICP-OES. The presence of organic molecules was determined by SEC-ICP-OES. The peaks of siderophores were determined using the 405 nm absorbance. As a result, siderophore producing bacteria are able to dissolve clay. This suggests that the effect of siderophore on cesium dissolution is an indirectly process.