Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Oketani, Kazuki*; Fujii, Hirokazu*; Zhao, Y.*; Kato, Masaji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya; Kono, Masanori*
Zairyo, 73(3), p.220 - 225, 2024/03
The fractures in the rock are the main pass of groundwater flow and solute transport. The filling of fine-grained particle, such as clay minerals, was confirmed to decrease the permeability of rock by laboratory experiment. This research aimed to verify the occurance of the phoenomena in the fild. The water containing the clay minerals was injected into the rock at the 200m stage of the Mizunami undearground research laboratory. The hydraulic conductivity decreased two order before and after the injection. This result suggested that the decrease of hydraulic conductivity by the filling of fine-grained particle in the fractures occured in the real field.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical) titanium alloys strong and ductile
titanium alloys strong and ductileChong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Guo, B.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Zhao, G.*; Yoshida, Shuhei*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 257, p.119165_1 - 119165_14, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:84.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable  titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable
titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable  titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced
titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced  martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent
martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent  phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the
phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the  martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of
martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of  martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of
martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of 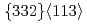 deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable
deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable  titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.73(Microbiology) X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.7(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Civil)Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary) BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Wang, Q.*; Hu, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, T.*; Ilavsky, J.*; Kuzmenko, I.*; Ma, B.*; Tachi, Yukio
International Journal of Coal Geology, 261, p.104093_1 - 104093_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:69.58(Energy & Fuels) ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; Kaneko, Tatsuya*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
 K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Zhao, Y.*; Suzuki, T.*; Iimori, T.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J. R.*; Horio, Masafumi*; Sato, Yusuke*; Fukaya, Yuki; Kanai, T.*; Okazaki, K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115304_1 - 115304_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yang, J.*; Ren, W.*; Zhao, X.*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Miao, P.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Zhang, Z.*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 99, p.55 - 60, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-entropy alloys are characteristic of extensive atomic occupational disorder on high-symmetric lattices, differing from traditional alloys. Here, we investigate magnetic and thermal transport properties of the prototype face-centered-cubic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi by combining physical properties measurements and neutron scattering. Direct-current (dc) and alternating-current (ac) magnetizations measurements indicate a mictomagnetic behavior with coexisting antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic interactions in the entire temperature region and three anomalies are found at about 80, 50, and 20 K, which are related to the paramagnetic to antiferromagnetic transition, the antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic transition, and the spin freezing, respectively. The electrical and thermal conductivities are significantly reduced compared to Ni and the temperature dependence of lattice thermal conductivity exhibits a glass-like plateau. Inelastic neutron scattering measurements suggest weak anharmonicity so that the thermal transport is expected to be dominated by the defect scattering.
 Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fukaya, Yuki; Zhao, Y.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J.-R.*; Fukidome, Hirokazu*; Matsuda, Iwao*
Physical Review B, 104(18), p.L180202_1 - L180202_5, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:69.8(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Miyabe, Masabumi; Satou, Yukihiko; Wakaida, Ikuo; Terabayashi, Ryohei*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Tomita, Hideki*; Zhao, Y.*; Sakamoto, Tetsuo*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 54(14), p.145003_1 - 145003_8, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Optics)Two-color two-step photoionization optogalvanic spectroscopy was performed using high-repetition-rate titanium sapphire lasers and a uranium hollow cathode lamp to find the two-step resonance ionization schemes of uranium. Many ionization transitions were observed by exciting uranium atoms in a ground state into five, even parity, excited levels with the first-step laser and by scanning the second-step laser wavelengths. By blocking the first-step laser, single-color, two-photon ionization transitions were also identified. From these results, we have found more than 50 odd-parity autoionizing levels of uranium in the energy, ranging from the ionization potential (49958.4 cm ) to 51150 cm
) to 51150 cm . The determined energy levels are within 1 cm
. The determined energy levels are within 1 cm of previously reported values.
of previously reported values.

Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Y.*; Jia, G.*; Cui, X.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Q.*; Gu, L.*; Zheng, L.*; Li, L. H.*; Wu, Q.*; Singh, D. J.*; et al.
Chem, 7(2), p.436 - 449, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:194 Percentile:99.8(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)