Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -wave direct capture and interference effect observed in the
-wave direct capture and interference effect observed in the  O
O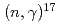 O reaction
O reactionNagai, Yasuki*; Kinoshita, Mitsutaka*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Nobuhara, Yuriko*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mengoni, A.*
Physical Review C, 102(4), p.044616_1 - 044616_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.12(Physics, Nuclear)Teshigawara, Makoto; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke*; Ichikawa, Go*; Takata, Shinichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Harada, Masahide; Oi, Motoki; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Kai, Tetsuya; Kawamura, Seiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 929, p.113 - 120, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:86.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)A nano-diamond is an attractive neutron reflection material below cold neutron energy. The total neutron cross section of a nano-diamond was derived from a neutron transmission measurement over the neutron energy range of 0.2 meV to 100 meV because total neutron cross section data were not available. The total cross section of a nano-diamond with particle size of approximately 5 nm increased with a decrease in neutron energy to 0.2 meV. It was approximately two orders of magnitude larger than that of graphite at 0.2 meV. The contribution of inelastic scattering to the total cross section was to be shown negligible small at neutron energies of 1.2, 1.5, 1.9, 2.6, and 5.9 meV in the inelastic neutron scattering measurement. Moreover, small-angle neutron scattering measurements of the nano-diamond showed a large scattering cross section in the forward direction for low neutron energies.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
 and
and 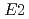 cross sections of the
cross sections of the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction at
O reaction at 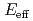
 1.2 MeV using pulsed
1.2 MeV using pulsed  beams
beamsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Fujimoto, Shinya*; Segawa, Mariko; Mishima, Kenji*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Igashira, Masayuki*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1269, p.283 - 288, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of
O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of 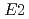 cross section to
cross section to  one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed
one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed  beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the
beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the  -ray from the
-ray from the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction with high statistics. We determined the
O reaction with high statistics. We determined the  and
and 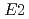 cross section down to
cross section down to 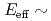 1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
 and
and 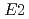 cross sections of the
cross sections of the  C
C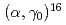 O reaction using pulsed
O reaction using pulsed  beams
beamsMakii, Hiroyuki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Segawa, Mariko; Mishima, Kenji*; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*
Physical Review C, 80(6), p.065802_1 - 065802_16, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:83.95(Physics, Nuclear)We measured the  -ray angular distribution from
-ray angular distribution from  C
C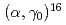 O to the ground state of
O to the ground state of  O using a pulsed
O using a pulsed  beam at
beam at 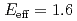 and 1.4 MeV. True events of
and 1.4 MeV. True events of  C
C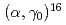 O were discriminated from background events due to neutrons from
O were discriminated from background events due to neutrons from  C(
C(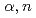 )
) O with a time-of-flight method. The obtained
O with a time-of-flight method. The obtained  -ray spectrum with anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers showed a characteristic line shape from
-ray spectrum with anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers showed a characteristic line shape from  C
C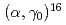 O: the Doppler broadening and energy loss of
O: the Doppler broadening and energy loss of  particles in
particles in  C targets. The astrophysical S factors for
C targets. The astrophysical S factors for  and
and 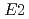 ,
, 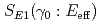 and
and 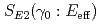 , derived from the present cross sections are in excellent agreement with the values derived by
, derived from the present cross sections are in excellent agreement with the values derived by  -matrix calculation of the
-matrix calculation of the  -delayed
-delayed  spectrum of
spectrum of  N, and by using the asymptotic normalization constant in the
N, and by using the asymptotic normalization constant in the  -matrix fit.
-matrix fit.
Mishima, Kenji*; Ino, Takashi*; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Sato, Hiromi*; Otake, Yoshie*; Omori, Hitoshi*; Muto, Suguru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.342 - 345, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:85.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new beamline for a fundamental physics experiment is under construction at BL05 port in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), this beamline is designed using novel techniques of neutron optics and it is termed "Neutron Optics and Physics". The beam from the moderator is deflected by multi-channel supermirrors and split into three branches for individual experiments. In this study, we have optimized the design of the beam optics and shields using the Monte Carlo simulation package PHITS. The neutron fluxes of beams are expected to be 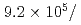 cm
cm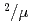 str
str s
s MW,
MW, 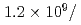 cm
cm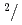 s
s MW,
MW, 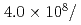 cm
cm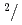 s
s MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
 and
and 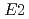 cross sections of the
cross sections of the  C(
C(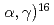 O reaction at
O reaction at 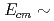 1.4 MeV using pulsed
1.4 MeV using pulsed  beams
beamsMakii, Hiroyuki; Nagai, Yasuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Segawa, Mariko; Shima, Tatsushi*; Ueda, Hitoshi; Igashira, Masayuki*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1016, p.215 - 220, 2008/05
The  C(
C(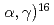 O reaction plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the
O reaction plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the 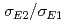 ratio. We have installed a new system to measure the
ratio. We have installed a new system to measure the  -ray angular distribution of the
-ray angular distribution of the  C(
C(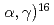 O reaction to accurately determine the
O reaction to accurately determine the 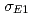 and
and 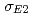 . In this experiment, we used high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers to detect a
. In this experiment, we used high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers to detect a  -ray from the reaction with a large S/N ratio, intense pulsed
-ray from the reaction with a large S/N ratio, intense pulsed  beams to discriminate true events from neutron induced background with a time-of-flight method, and the monitoring system of target thickness. We succeeded in removing a background due to neutrons and could clearly detect the
beams to discriminate true events from neutron induced background with a time-of-flight method, and the monitoring system of target thickness. We succeeded in removing a background due to neutrons and could clearly detect the  -ray from the
-ray from the  C(
C(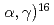 O reaction with high statics.
O reaction with high statics.
 Os,
Os,  Os, and
Os, and 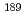 Os and the Re-Os chronology
Os and the Re-Os chronologySegawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Goriely, S.*; Koning, A.*; Hilaire, S.*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1016, p.448 - 450, 2008/05
 Re-
Re- Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of
Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of  Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,
Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,  Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of
Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of  Os. Secondly,
Os. Secondly,  Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of
Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of  Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for
Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and 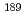 Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for
Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for  Os off the ground state of
Os off the ground state of  Os to its 9.75 keV first excited state in the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV.
Os to its 9.75 keV first excited state in the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV.
 -ray detector in a
-ray detector in a  C(
C(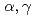 )
) O reaction study
O reaction studyMakii, Hiroyuki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Mishima, Kenji*; Segawa, Mariko; Shima, Tatsushi*; Igashira, Masayuki*
Physical Review C, 76(2), p.022801_1 - 022801_5, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:67.84(Physics, Nuclear)Neutron-induced background events occurring within a  -ray detector in the
-ray detector in the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction study are discussed by comparing a spectrum taken by a NaI(Tl) detector with a pulsed
O reaction study are discussed by comparing a spectrum taken by a NaI(Tl) detector with a pulsed  -beam with that taken previously by a Ge detector using a continuous
-beam with that taken previously by a Ge detector using a continuous  -beam. Both spectra contain such background events induced by neutrons from the
-beam. Both spectra contain such background events induced by neutrons from the 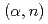 reaction on
reaction on  C and/or
C and/or  Be contained in enriched
Be contained in enriched  C targets. These observations together with a calculated
C targets. These observations together with a calculated  -ray spectrum of the neutron-induced reaction by Ge isotopes indicate the thus-produced background events, which would be hardly reduced by using shield materials, become significant background in the
-ray spectrum of the neutron-induced reaction by Ge isotopes indicate the thus-produced background events, which would be hardly reduced by using shield materials, become significant background in the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction study at low
O reaction study at low  -beam energy.
-beam energy.
 Os,
Os,  Os, and
Os, and 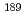 Os for the Re-Os chronology
Os for the Re-Os chronologySegawa, Mariko; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Goriely, S.*; Koning, A.*; Hilaire, S.*
Physical Review C, 76(2), p.022802_1 - 022802_5, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.66(Physics, Nuclear)Discrete as well as continuum  -ray energy spectra from the neutron capture by
-ray energy spectra from the neutron capture by  Os,
Os,  Os, and
Os, and 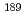 Os have been taken for the first time at 5
Os have been taken for the first time at 5  En
En  90 keV by an anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The detection of a weak discrete
90 keV by an anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The detection of a weak discrete  -ray, about 0.5% of total
-ray, about 0.5% of total  -ray strength, demonstrates the high sensitivity of the present measurement. The energy spectra enabled us to accurately determine the reaction cross sections with a small systematic uncertainty. Based on the new cross sections, we re-estimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F
-ray strength, demonstrates the high sensitivity of the present measurement. The energy spectra enabled us to accurately determine the reaction cross sections with a small systematic uncertainty. Based on the new cross sections, we re-estimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F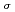 for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in
for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in  Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the Galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the Galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Oku, Takayuki; Yamada, Satoru; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Sato, Hiromi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 397(1-2), p.188 - 191, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.18(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have studied a neutron polarization method by means of a quadrupole magnet. By passing through the aperture of the quadrupole magnet (QM), positive and negative polarity neutrons are accelerated in opposite directions and spatially separated due to the magnetic field gradient. Then, by extracting one spin component, we can obtain a highly polarized neutron beam. Since polarized neutrons do not interact with any substances in this method, we can obtain the polarized neutron beam free from neutron attenuation. As a result of a cold neutron beam polarization experiment by using the QM, we obtained extremely high neutron polarization degree P0.999. In this paper, we show some experimental results of the neutron polarization experiment and discuss the application of the QM-based polarizing device to neutron scattering experiments.
Oku, Takayuki; Yamada, Satoru; Suzuki, Junichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Shinohara, Takenao*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Sato, Hiromi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Satoru; Mishima, Kenji*; Sato, Hiromi*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Shinohara, Takenao*; Morishima, Takahiro*; Ono, Masashi*; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

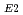 and
and 
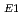 of the
of the  C(
C( ,
,  )
) O reaction obtained at E
O reaction obtained at E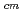 = 1.6 and 1.4 MeV
= 1.6 and 1.4 MeVMakii, Hiroyuki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Segawa, Mariko; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Satoru; Oku, Takayuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Sato, Hiromi*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Morishima, Takahiro*; Ono, Masashi*; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oku, Takayuki; Yamada, Satoru*; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Sato, Hiromi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mishima, Kenji*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Goriely, S.*; Koning, A.*; Hilaire, S.*
no journal, ,
The  Re nucleus is known to be a good chronometer to derive the stellar duration of the r-process nuceosyntheis and deduce the age of universe. However, there are several problems inherent to this chronometer. In order to solve these problems, one must know both the production and depletion rates (via the excited state as well as the ground state) of
Re nucleus is known to be a good chronometer to derive the stellar duration of the r-process nuceosyntheis and deduce the age of universe. However, there are several problems inherent to this chronometer. In order to solve these problems, one must know both the production and depletion rates (via the excited state as well as the ground state) of  Os and inelastic scattering cross section off the ground state (J
Os and inelastic scattering cross section off the ground state (J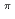 = 1/2
= 1/2 ) of
) of  Os to its excited 10 keV state (J
Os to its excited 10 keV state (J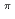 = 3/2
= 3/2 ) are needed. Hence, in the present study we aimed to accurately measure the neutron capture cross sections of
) are needed. Hence, in the present study we aimed to accurately measure the neutron capture cross sections of  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and 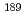 Os, and the inelastic scattering cross section for
Os, and the inelastic scattering cross section for  Os for neutrons between 10 and 90 keV by developing a new experimental method.
Os for neutrons between 10 and 90 keV by developing a new experimental method.
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Makii, Hiroyuki*; Mishima, Kenji*; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Nakayoshi, Akira*; Ota, Takeshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Re-
Re- Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of
Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of  Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,
Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,  Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of
Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of  Os. Secondly,
Os. Secondly,  Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of
Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of  Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for
Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and 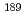 Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for
Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for  Os off the ground state of
Os off the ground state of  Os to its 9.75-keV first excited statein the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV. The measurements of the neutron capture reactions have been carried out by detecting a prompt
Os to its 9.75-keV first excited statein the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV. The measurements of the neutron capture reactions have been carried out by detecting a prompt  -ray by means fan anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The (n, n') reaction cross section for
-ray by means fan anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The (n, n') reaction cross section for  Os has been measured with use of four
Os has been measured with use of four  Li-glass scintillation detectors. Based on these new capture cross sections, we reestimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in
Li-glass scintillation detectors. Based on these new capture cross sections, we reestimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in  Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Sakai, Kenji; Muto, Suguru*; Ino, Takashi*; Yoshioka, Tamaki*; Mishima, Kenji*; Taketani, Kaoru*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English