Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Murakami, Masashi; Hoshino, Yuzuru; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Fukumura, Nobuo*; Sanda, Toshio*; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2019-003, 50 Pages, 2019/06
Toward the establishment of a common approach to determine the radioactivity concentrations in dismantling wastes arising from research reactors, radionuclide concentrations in the reactor structure materials of aluminum, carbon steel, shield concrete, and graphite of TRIGA Mark II reactor at Rikkyo University, Japan, were evaluated with both radiochemical analysis and theoretical calculation. The measured nuclides by the radiochemical analysis were  H,
H,  Co, and
Co, and  Ni in aluminum,
Ni in aluminum,  H,
H,  Co,
Co,  Ni, and
Ni, and  Eu in carbon steel,
Eu in carbon steel,  H,
H,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu in shield concrete, and
Eu in shield concrete, and  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Ni, and
Ni, and  Eu in graphite. Neutron-flux distributions and neutron-induced activities were computed with DORT and ORIGEN-ARP codes, respectively. Using the results of material composition analysis, radioactivity concentrations were conservatively predicted with good accuracy except for graphite material.
Eu in graphite. Neutron-flux distributions and neutron-induced activities were computed with DORT and ORIGEN-ARP codes, respectively. Using the results of material composition analysis, radioactivity concentrations were conservatively predicted with good accuracy except for graphite material.
Ishikawa, Makoto; Ikegami, Tetsuo*; Sanda, Toshio*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 178(3), p.335 - 349, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Under the IRPhEP framework, nine ZPPR critical experimental cores performed as the cooperative JUPITER program between the USA and Japan are established in the benchmarks to study large FBR core physics. These benchmarks cover a wide variety of core concepts including homogeneous and heterogeneous configurations, clean and engineering-mockup cores of 600-1,000 MW(electric)-class sizes, and various kinds of core parameters. Detailed experimental information has recently been dug out from the ANL original documents and scrutinized very carefully to establish the benchmark model and to evaluate the experimental uncertainty quantitatively. The benchmarks supply users with the heterogeneous cell model and three-dimensional core configuration with preserving the important physical features of the ZPPR cores. Further, the benchmark handbook includes the as-built information of the ZPPR cores as a complete set of electrical form, therefore, a user can develop his own benchmark model if necessary. The analysis of the benchmark with the latest method demonstrates the usefulness both for the improvement of analytical methods and for the validation of nuclear data.
Sanda, Toshio*; Ishikawa, Makoto
International Handbook of Evaluated Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments (CD-ROM), 233 Pages, 2010/03
The International Reactor Physics Experiment Evaluation Project (IRPhEP) is an international cooperative effort hosted by OECD/NEA to provide integral benchmark data with high quality for method and data validation in the reactor physics field. JAEA is actively contributing this important project so far. The ZPPR-10B benchmark is one of the JUPITER program series which was a joint research program between the United States and Japan using the ZPPR (Zero Power Plutonium Reactor) facility at Argonne National Laboratory (ANL)-West in Idaho to study the nuclear characteristics of large Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) cores. The JUPITER program consisted of twenty-one experimental cores built between 1978 and 1988 and is considered as one of the most important data sources in the current FBR core study because (1) it included the largest experimental core in FBR history, (2) it covered a wide variety of core concepts and structures, (3) various kinds of core parameters were measured, (4) it had excellent experimental technology, and (5) documentation was precisely recorded by the experimenters. The ZPPR-10B experiments performed at ANL-West in 1979, was an engineering mock up of a 650 MWe-class sodium-cooled MOX-fueled FBR homogeneous core with two enrichment zones, control rods and control rod positions. As the core parameters, criticality, reaction rate distribution and ratio, control rod worth and sodium void reactivity were measured and evaluated as the IRPhEP benchmarks. The ZPPR-10B benchmark is expected to be used as a standard experiment to validate the nuclear characteristics of large FBR core analyses and design works in future.
Sanda, Toshio*; Ishikawa, Makoto
International Handbook of Evaluated Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments (CD-ROM), 180 Pages, 2010/03
The International Reactor Physics Experiment Evaluation Project (IRPhEP) is an international cooperative effort hosted by OECD/NEA to provide integral benchmark data with high quality for method and data validation in the reactor physics field. JAEA is actively contributing this important project so far. The ZPPR-10C benchmark is one of the JUPITER program series which was a joint research program between the United States and Japan using the ZPPR (Zero Power Plutonium Reactor) facility at Argonne National Laboratory (ANL)-West in Idaho to study the nuclear characteristics of large Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) cores. The JUPITER program consisted of twenty-one experimental cores built between 1978 and 1988 and is considered as one of the most important data sources in the current FBR core study because (1) it included the largest experimental core in FBR history, (2) it covered a wide variety of core concepts and structures, (3) various kinds of core parameters were measured, (4) it had excellent experimental technology, and (5) documentation was precisely recorded by the experimenters. The ZPPR-10C experiments performed at ANL-West in 1979, was an engineering mock up of an 800 MWe-class sodium-cooled MOX-fueled FBR homogeneous core with two enrichment zones and control rod positions. As the core parameters, criticality, reaction rate distribution and ratio, control rod worth and sodium void reactivity were measured and evaluated as the IRPhEP benchmarks. The ZPPR-10C benchmark is expected to be used as a standard experiment to validate the nuclear characteristics of large FBR core analyses and design works in future.
Hanaki, Hiroshi*; Sanda, Toshio*; Ohashi, Masahisa*
JAEA-Review 2008-047, 266 Pages, 2008/10
It is thought to improve the prediction accuracy for burnup characteristics using many burnup data of "Joyo" effectively. It is thought the best way to adjust cross-sections using sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics to utilize burnup data of "Joyo". Therefore in this work computer codes for analyzing sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics had been prepared since 1992. The results are as follows: (1) The computer codes which could analyze sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics taking into consideration plural cycles and refueling were prepared, therefore it came to be able to adjust cross-sections using burnup data and to estimate the accuracy for design of large LMFBR cores. (2) The adequacy of prepared codes was made sure by comparing with direct calculations. (NB: This document is a translation of PNC TJ9124 94-007 Vol.2 published in March 1997.)
Sanda, Toshio; Yamashita, Takumi; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
A conceptual core design study is performed on Pb-Bi cooled fast reactor with forced circulation (FC) cooling in the Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System (FS) in Japan. From the viewpoint of Pb-Bi eutectic alloy application as reactor coolant, Pb-Bi/core material compatibility is one of the most significant issues. The previous core design study assumes that the maximum acceptable fuel pin cladding temperature is to be 650 deg-C and applies provisional cladding corrosion correlation based on a little available information of ferritic/martensitic steel-Pb(-Bi) compatibility studies. Recently new cladding corrosion correlation was proposed based on recent material corrosion tests in the Pb-Bi eutectic alloys, which suggests that the acceptable fuel pin cladding temperature is to be 570 deg-C. The core design is performed under the new corrosion conditions for 750MWe Pb-Bi cooled reactor. The designed core without upper axial and radial blanket achieves the target of the FS, such as 1.1 of breeding ratio and core average burnup of 150GWd/t, filling the demand from a plant design. And shielding structures around the core are set, shielding performance is checked.
Yamashita, Takumi; Sanda, Toshio; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2005-039, 88 Pages, 2005/08
In "Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Breeder Reactor Cycle System(FS)", various types of fast breeder reactor using different coolant have been studied, in which lead-bismuth is one of the subject. In this study, design studies of medium size forced circulation (FC) reactor were carried out using newly proposed correlation in evaluation for clad outside surface corrosion and in restriction on the maximum clad outside surface temperature to 570 C based on the design in JFY 2003. The influence of changes in foregoing design conditions on core performances of the FC reactor was smaller than that of natural circulation (NC) reactor, and consequently, design of the FC core (outputs were 1980MWt, 750MWe) was performed to meet demands for coolant velocity, bundle pressure loss and so on. The designed core was larger than that designed in JFY 2002 because of increase in fuel pin diameter and fuel pin pitch. The main specifications for the designed core were as follows; with no radial blanket, fuel pin diameter of 8.0mm, core height of 70cm, core equivalent diameter of 4.43m, envelope diameter of radial shielding region of 5.35m. The main core performances were as follows; operation period of 18 months, burn-up of over 150GWd/t, and breeding ratio of 1.10 for the breeding core and 1.04 for the break even core. They achieved the performance targets in the FS within the condition where envelope diameter of radial shielding region was less than 5.5m. Fast fluence was not restricted in anticipation of improvements on materials in the future. When it was restricted to the development target of ODS steel and PNC-FMS steel (5
C based on the design in JFY 2003. The influence of changes in foregoing design conditions on core performances of the FC reactor was smaller than that of natural circulation (NC) reactor, and consequently, design of the FC core (outputs were 1980MWt, 750MWe) was performed to meet demands for coolant velocity, bundle pressure loss and so on. The designed core was larger than that designed in JFY 2002 because of increase in fuel pin diameter and fuel pin pitch. The main specifications for the designed core were as follows; with no radial blanket, fuel pin diameter of 8.0mm, core height of 70cm, core equivalent diameter of 4.43m, envelope diameter of radial shielding region of 5.35m. The main core performances were as follows; operation period of 18 months, burn-up of over 150GWd/t, and breeding ratio of 1.10 for the breeding core and 1.04 for the break even core. They achieved the performance targets in the FS within the condition where envelope diameter of radial shielding region was less than 5.5m. Fast fluence was not restricted in anticipation of improvements on materials in the future. When it was restricted to the development target of ODS steel and PNC-FMS steel (5 10
10 n/cm
n/cm , E
, E 0.1Mev), the burn-up was about 125GWd/t. From these results, prospect of possibility of core manufacture was gained within the new design conditions of clad corrosion and temperature.
0.1Mev), the burn-up was about 125GWd/t. From these results, prospect of possibility of core manufacture was gained within the new design conditions of clad corrosion and temperature.
Sanda, Toshio; Okano, Yasushi; Naganuma, Masayuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2005-035, 83 Pages, 2005/08
The core design study has been performed for small fast reactors at two main features of long-life core and enhanced passive safety as part of the "Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System (FS)".
Yamashita, Takumi; Sanda, Toshio; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2004-065, 93 Pages, 2004/11
In "Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Breeder Reactor Cycle System(FS)", various types of fast breeder reactor using different coolant are studied, in which lead-bismuth is one of the subject. In JFY 2003 study of FS phase-II, design studies of medium scale forced /natural circulation nitride fuel core (FC/NC core) were carried out considering DDI (duct-duct interaction) which was not considered in JFY 2001 studies. The prospect of satisfying a design target of the core performance was acquired by improved design. By comparing properties of FC core (750MWe) and NC core (550MWe), we recommended the FC core as a hopeful one to design. The FC core was superior to the NC core in the following points, (1)Larger average burn-up (core and blanket) (2)Less Pu-fissile loaded weight (3)Smaller core equivalent diameter in spite of larger generating power (4)The NC core has much problems from the viewpoint of earthquake-resistant design. A design target of high burn-up of 150 GWd/t was satisfied, but fast fluence on clad is over the development target of ODS steel and PNC-FMS stee1 (5 10
10 n/cm
n/cm , E
, E 0.1Mev). Cores in which fast fluence was restricted to less than the target were also designed. MOX fuel and metal fuel cores were studied, and the effect of composition of TRU fuel recovered from LWR to core performance was also investigated to show flexibility and diversity in the lead-bismuth cooled core. In recent studies, it is becoming clear that the present evaluation for the clad corrosion in lead-bismuth gives non-conservative result and lowering the highest clad temperature will be required in core design. The lowering of temperature was permissible according to preliminary analysis using the present corrosion correlation.
0.1Mev). Cores in which fast fluence was restricted to less than the target were also designed. MOX fuel and metal fuel cores were studied, and the effect of composition of TRU fuel recovered from LWR to core performance was also investigated to show flexibility and diversity in the lead-bismuth cooled core. In recent studies, it is becoming clear that the present evaluation for the clad corrosion in lead-bismuth gives non-conservative result and lowering the highest clad temperature will be required in core design. The lowering of temperature was permissible according to preliminary analysis using the present corrosion correlation.
Konomura, Mamoru; Ogawa, Takashi; Okano, Yasushi; Yamaguchi, Hiroyuki; Murakami, Tsutomu; Takaki, Naoyuki; Nishiguchi, Youhei; Sugino, Kazuteru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Hishida, Masahiko; et al.
JNC TN9400 2004-035, 2071 Pages, 2004/06
The attractive concepts for Sodium-, lead-bismuth-, helium- and water-cooled FBRs have been created through using typical plant features and employing advanced technologies. Efforts on evaluating technological prospects of feasibility have been paid for these concepts. Also, it was comfirmed if these concepts satisfy design requierments of capability and performance presumed in the feasibilty study on commertialization of Fast Breeder Reactor Systems. As results, it was concluded that the selection of sodium-cooled reactor was most rational for practical use of FBR technologies in 2015.
Sanda, Toshio; Okano, Yasushi; Takaki, Naoyuki; Naganuma, Masayuki; Uto, Nariaki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2004-031, 154 Pages, 2004/06
Some concepts of small fast reactors have been studied as part of the "Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System (FS)", and the core design study has been performed at two main features of "long-life core " and "enhanced passive safety" in the FS phase II. Based on the previous study, 165MWe forced circulation sodium cooled reactor with control rods was studied as the promising concept from a viewpoint of economical efficiency in JFY 2003. In the present study, the fuel reloading interval of 20 years and outlet temperature of 550 deg-C are targeted under following condition as thicker metal fuel pin diameter (less than or equal) 15mm, lower pressure drop (less than or equal) 0.75kg/cm2, and smller core diameter (less than or equal) 3m by sodium void reactivity restriction relief into design conditions avoiding core melt without SASS at ATWS. The prospect of achievement of the fuel reloading interval of 20 years and outlet temperature of 550 deg-C was acquired for "Higher Temperature Core" and "Higher Temperature and Smller Core" without blanket fuels by using a sodium-cooled metal-fueled core with single Pu enrichment fuel which has high potential of small change of space distribution of power density and high breeding ratio. These cores have core height / diameter of 127/293cm and 164/260cm, fuel burnup of 77 and 80 GWd/t, burnup reactivity of 1.2 and 1.5% (delta)k/kk', breeding ratio of 1.06 and 1.07 and coolanat void reactivity of 6 and 8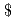 , respectively. Control rod reactivity balance, fuel soundness and shielding performance were checked that these were satisfied. Moreover, since the reactivity change due to burnup was small, the possibility of long-term operation which does not require a control rod movement was also examined. In addition, the "Higher Temperature Core" was recommended for a promising core of phase-II middle time since core melt would be avoided without SASS at ATWS. Furthermore, the applicability of the Feher heat cycl
, respectively. Control rod reactivity balance, fuel soundness and shielding performance were checked that these were satisfied. Moreover, since the reactivity change due to burnup was small, the possibility of long-term operation which does not require a control rod movement was also examined. In addition, the "Higher Temperature Core" was recommended for a promising core of phase-II middle time since core melt would be avoided without SASS at ATWS. Furthermore, the applicability of the Feher heat cycl
Okano, Yasushi; Takaki, Naoyuki; Sanda, Toshio; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2004-027, 203 Pages, 2004/06
He-cooled fast reactor employing coated-particle nitride fuel has been taken an interest as a part of feasibility study project of fast reactor reactor designs. Two fuel assembly (F/A) configurations have been considered as candidates. One configuration is 'Horizontal flow cooling compartment F/A', the other is 'Ascending flow cooling block F/A'. This MS deals with the best-to-date core designs with 120GWd/t average core discharge burnup to compare core/safety performances of two configuration designs. as an annual report of JFY2003.
Fujimura, Koji*; Sanda, Toshio*; Ogawa, Takashi*
JNC TJ9400 2001-015, 85 Pages, 2001/03
Research and development for stabilizing or shortening the radioactive wastes included in spent nuclear fuel are widely conducted in view point of reducing the environmental impact. Especially it is effective way to irradiate and transmute long-lived TRU by fast reactors. Two types of loading way were previously proposed. The former is loading relatively small amount of TRU in all commercial fast reactors and the latter is loading large amount of TRU in a few TRU burning reactors. This study has been intended to contribute to the feasibility studies on commercialized fast reactor cycle system. The transmutation and nuclear characteristics of TRU burning reactors were evaluated and compared with those of conventional transmutation system using commercial type fast reactor based upon the investigation of technical information about TRU burning reactors. Major results are summarized as follows. (1) Investigation of technical information about TRU burning reactors. Based on published reports and papers, technical information about TRU burning reactor concepts and transmutation system using conventional commercial type fast reactors were investigated. Transmutation and nuclear characteristics or R&D issue were investigated based on these results. (a) Homogeneously loading of about 5wt% MAs on core fuels in the conventional commercial type fast reactor may not cause significant impact on the nuclear core characteristics. Transmutation of MAs being produced in about five fast reactors generating the same output is feasible. (b) The helium cooled MA burning fast reactor core concept propose by JAERI attains criticality using particle type nitride fuels which contain more than 60 wt% MA. This reactor could transmute MAs being produced in more than ten 1000 MWe-LWRs. (c)Ultra-long life core concepts attaining more than 30 years operation without refueling by utilizing MA's nuclear characteristics as burnable absorber and fertile nuclides were proposed. (d)Those ...
Shirakata, Keisho; ; Nakashima, Fumiaki
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 131, p.137 - 198, 1999/00
None
*; Sanda, Toshio*
PNC TJ9124 97-002, 178 Pages, 1997/03
To develop nuclear design of LMFBR cores, they are important subjects of research and development to improve the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores and to design highly efficient core more rationally. The adjusted nuclear cross-sections library had been made by being reflected the result of critical experiment of the JUPITER, etc.effectively as much as possible. And the distinct improvement of the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores had been achieved. But, this adjusted library published in 1991 should be improved utilizing the newest results of study for the stage in which nuclear design is required higher precision such as fundamental design of demonstration FBR, because it was adjusted by using the data of only JUPITER experiment, without burnup and temperature characteristics, basing on JENDL-2 published in early 1980s, and wasn't done the adjustment of inelastic scattering matrix. Therefore the object of this work is to make unified cross-section library that will be able to use for design stage from fundamental to approval by adjusting the newest domestic library, JENDL-3.2 published in 1994 and improving precision and trust in nuclear design. For the object, it will be used for adjustment that "Monju" and "Joyo" experimental data being owned by PNC, critical experimental data of ZPPR-2,3 and MOZART, burnup characteristics, and temperature characteristics. The results of this study are as follows: (1)It was prepared each C/E values, experimental and analysis errors, correlation factors, etc. of criticality, reaction rate ratio, control rod worth, and Doppler reactivity experimented in ZPPR-2,3. (2)It was prepared the data of C/E values, experimental and analysis errors, correlation factors, etc. of isothermal temperature coefficient experimented in SEFOR. (3)JENDL-3.2 library was preparatorily adjusted using the experimental data which had been already obtained. The effect of adjustment and validity of decided errors were ...
*; *; Sanda, Toshio*
PNC TJ9124 96-007, 278 Pages, 1996/03
To develop nuclear design of LMFBR cores, they are important subjects of research and development to improve the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores and to design highly efficient core more rationally. The adjusted nuclear cross-sections library had been made by being reflected the result of critical experiment of the JUPITER, etc.effectively as much as possible. And the distinctim provement of the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores had been achieved. And the computer codes for analyzing sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics had been prepared to improve the prediction accuracy for burnup characteristics using many burnup data of "Joyo" effectively. As compared with critical experiment, Doppler reactivity is one of the great characteristics of LMFBR. Doppler reactivity is very important to assure core character of self-control and it is claimed to improve the prediction accuracy for it. But it is impossible to estimate the accuracy for present codes because it is much depend on self-shielding factor. Therefore in this work the system for estimating the accuracy in nuclear design of Doppler reactivity by improving present computer codes was studied. The results are as follows: (1)The method of analyzing sensitivity coefficients of Doppler reactivity was studied and computer codes was prepared by improving present codes. (2)Uncertainty of the gradient toward temperature of self-shielding factor of U238 capture reaction which is the most important reaction for Doppler reactivity was estimated preparatorily and formalized for using adjustment. (3)Uncertainties of experiment and analysis for Doppler reactivities in ZPPR-9 were arranged. (4)It was clarifled that it is possible to improve C/E values of Doppler reactivities without affecting other neutronic characteristics by doing preparatorily adjustment.
*; *; *; Sato, Wakaei*; *; Sanda, Toshio*
PNC TN9410 95-214, 199 Pages, 1995/08
In order to improve the design method and accuracy of large fast breeder cores, extensive work has been performed to accumulate and evaluate many kinds of results of fast reactor physics experiments and analyses. As a part of efforts to develop a standard data base for LMFBR core nuclear design, the present report evaluates the physical consistency of JUPITER experimental analysis, especially concentrating on criticality. Here, the judgment of consistency is based on not only the deviation degree of C/E values from unity, but also various viewpoints such as the comparison with other cores or other nuclear characteristics by sensitivity analysis, the effect of changing nuclear data library, the analysis of FCA and JOYO which have completely different source of data from JUPITER, and the use of the Monte Carlo method as an analytical reference. (1)The C/E values of JUPITER criticality are slightly underestimated in the range of 0.993-0.999, using the JFS-3-J2 (1989) group constant set based on JENDL-2 and three-dimensional XYZ transport theory with the most detailed analytical model. There is an obvious dependency of C/Es on reactor core concepts with homogeneous or heterogeneous structure, the main cause of which is considered to be the effect of internal blanket existence and cross-section errors of JFS-3-J2, judged from sensitivity analysis. (2)The latest analytical method and model based on three-dimensional XYZ transport theory has sufficient ability to predict the relative changes of JUPITER criticality caused by the effect of reactor core size, CRP sodium channel, control rod and internal blankets. (3)The analytical error of JUPITER criticality was evaluated as approximately 0.3%dk and this seems reasonable, because the results of Monte Carlo analysis for ZPPR-9 criticality were almost identical with those of our standard analytical method. (4)The analytical results based on the latest JENDL-3.2 library were very close to those of JENDL-2 results, ...
*; Sanda, Toshio*; *
PNC TJ9124 95-005, 467 Pages, 1995/03
To develop nuclear design of LMFBR cores, they are important subjects of research and development to improve the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores and to design highly efficient core more rationally. The adjusted nuclear cross-sections library had been made by being reflected the result of critical experiment of the JUPITER, etc. effectively as much as possible. And the distinct improvement of the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores had been achieved. And the computer codes for analyzing sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics had been prepared to improve the prediction accuracy for burnup characteristics using many burnup data of "Joyo" effectively. As compared with critical experiment, Doppler reactivity is one of the great characteristics of LMFBR. Doppler reactivity is very important to assure core character of self-control and it is claimed to improve the prediction accuracy for it. But it is impossible to estimate the accuracy for present codes because it is much depend on self-shielding factor. Therefore in this work the system for estimating the accuracy in nuclear design of Doppler reactivity by improving present computer codes was studied. The results are as follows: (1)The method of analyzing sensitivity coefficients of Doppler reactivity was studied and computer codes was prepared by improving present codes. (2)Uncertainty of the gradient toward temperature of self-shielding factor of U238 capture reaction which is the most important reaction for Doppler reactivity was estimated preparatorily and formalized for using adjustment. (3)Uncertainties of experiment and analysis for Doppler reactivities in ZPPR-9 were arranged. (4)It was clarified that it is possible to improve C/E values of Doppler reactivities without affecting other neutronic characteristics by doing preparatorily adjustment.
*; Sanda, Toshio*; *
PNC TJ9124 94-007, 723 Pages, 1994/03
To develop nuclear design of LMFBR cores, they are important subjects of research and development to improve the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores and to design highly efficient core more rationally. The adjusted nuclear cross-section library has beeen made by being reflected the result of critical experiment of the JUPITER, etc. effectively as much as possible. And the distinct improvement of the accuracy in nuclear design of large LMFBR cores has been achieved. In the design of large LMFBR cores, however, it is important to accurately estimate not only nuclear characteristics, for example, reaction rate distribution and control rod worth but also burnup characteristics, for example, burnup reactivity loss, breeding ratio and so on. Therefore, it is thought to improve the prediction accuracy for burnup characteristics using many burnup data of "JOYO" effectively. It is thought the best way to adjust cross-sections using sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics to utilize burnup data of "JOYO". It is able to know the accuracy quantitatively for burnup characteristics of large LMFBR by analyzing the sensitivity coefficients. Therefore in this work computer codes for analyzing sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics had been prepared since 1992. In 1992 cross-sections adjustment was done by using the data of "JOYO" and the effect was studied. In this year the adequacy of the codes was studied with a view of applying to design of large LMFBR cores. The results are as follows: (1)The computer codes which could analyze sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics taking into consideration plural cycles and refueling were prepared, therefore it came to be able to adjust cross-section using burnup data and to estimate the accuracy for design of large LMFBR cores. The characteristics are not only burnup reactivity loss, breeding ratio but also number density, criticality, reactivity worth, reaction rate ratio, and ....
*; *; Sanda, Toshio*
PNC TJ9124 93-009, 334 Pages, 1993/03
To commertialize LMFBR, they are important subjects of research and development to improve the accuracy in neutronic design of large LMFBR cores and to make be able to design highly efficient core more rationaoy. The adjusted library has been made by being reflected the result of critical experiment of the JUPITER, etc. effectively as much as possible by using the cross-sections adjustment method based on the probabilistic theory. And the distinct improvement of the accuracy in neutronic design of large LMFBR cores has been achieved. In the design of large LMFBR cores, however, it is important to accurately estimate not only neutronic characteristics, for example, reaction rate distribution and control rod worth but also burnup characteristics, for example, burnup reactivity loss, breeding ratio and so on. Therefore the objective of the work is to improve the prediction accuracy for burnup characteristics using many burnup data of "Joyo" effectively. For the objective computer codes for analyzing sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics were prepared and cross-sections adjustment using burnup data of "Joyo" was done and the effect for the improvement of the accuracy for burnup characteristics was estimated. The results are as follows: (1)The computer codes which could analyze sensitivity coefficients of burnup characteristics of LMFBR taking into consideration plural cycles and refueling were prepared and their adequacy was made sure by comparing with direct calculations. (2)It was clarified that it is possible to improve the accuracy of burnup characteristics without affecting statically neutronic characteristics so much by applying the burnup characteristics to cross-sections adjustment.