Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuura, Masato*; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12098_1 - 12098_8, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:56.02(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nemoto, Fumiya*; Kofu, Maiko; Nagao, Michihiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Takata, Shinichi; Suzuki, Junichi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Ueki, Takeshi*; Kitazawa, Yuzo*; et al.
Journal of Chemical Physics, 149(5), p.054502_1 - 054502_11, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:70.02(Chemistry, Physical) mimFeCl
mimFeCl
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 mimFeCl
mimFeCl
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been in the spotlight due to their unique and interesting properties. It is remarkable that their physicochemical properties are controlled by varying cations and anions. Magnetic IL is an example. The first discovered magnetic IL C mimFeCl
mimFeCl is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (=
is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (= 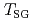 ) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C
) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C mimFeCl
mimFeCl exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below
exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below 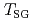 , which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. We guess that, since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized.
, which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. We guess that, since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized.
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been in the spotlight due to their unique and interesting properties. It is remarkable that their physicochemical properties are controlled by varying cations and anions. Magnetic IL is an example. The first discovered magnetic IL C mimFeCl
mimFeCl is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (=
is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (= 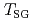 ) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C
) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C mimFeCl
mimFeCl exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below
exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below 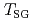 , which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. Since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin cluster.
, which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. Since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin cluster.
 mimFeCl
mimFeCl
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been in the spotlight due to their unique and interesting properties. It is remarkable that their physicochemical properties are controlled by varying cations and anions. Magnetic IL is an example. The first discovered magnetic IL C mimFeCl
mimFeCl is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (=
is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (= 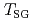 ) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C
) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C mimFeCl
mimFeCl exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below
exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below 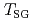 , which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. We guess that, since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin clusters.
, which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. We guess that, since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin clusters.
Kofu, Maiko; Yamamuro, Osamu*; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuura, Masato*; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English