Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Ozaki, Toshinori*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(2), p.023001_1 - 023001_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.16(Physics, Applied)We show that Xe ion irradiation with 80 MeV to GdBa Cu
Cu Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at
Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at 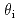 = 45
= 45 , whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (
, whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (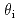 = 0
= 0 ) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density
) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density  .
.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Uraguchi, Yusei*; Suenaga, Momotaro*; Makihara, Takahiro*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Ishikawa, Norito
Physica C, 530, p.72 - 75, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.05(Physics, Applied)In order to clarify the influence of size and spatial distribution of three-dimensional pinning centers (3D-PCs) on hybrid flux pinning, columnar defects (CDs) were installed by using 200 MeV Xe ions along the  -axis direction into quasi-multilayered films consisting of YBa
-axis direction into quasi-multilayered films consisting of YBa Cu
Cu Oy layers and pseudo layers of BaSnO
Oy layers and pseudo layers of BaSnO . The positive effect of the BaSnO
. The positive effect of the BaSnO doping on the hybrid flux pinning stands out for the critical current density
doping on the hybrid flux pinning stands out for the critical current density  around
around 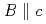 in high magnetic field and/or inclined magnetic field off the
in high magnetic field and/or inclined magnetic field off the  -axis, whereas there is little difference in the
-axis, whereas there is little difference in the  at
at 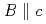 among the same growth temperature samples for low magnetic field. In the case of the in-plane distributed BaSnO
among the same growth temperature samples for low magnetic field. In the case of the in-plane distributed BaSnO nano-dots, the Jc around
nano-dots, the Jc around 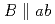 is remarkably enhanced, whereas there is a detrimental effect on the Jc around
is remarkably enhanced, whereas there is a detrimental effect on the Jc around 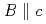 . These imply that the tuning of 3D-PCs is one of the keys to improve the
. These imply that the tuning of 3D-PCs is one of the keys to improve the  at all magnetic field orientations for the hybrid flux pinning.
at all magnetic field orientations for the hybrid flux pinning.
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Uraguchi, Yusei*; Kai, Takashi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.6603004_1 - 6603004_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.43(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To investigate the effect of discontinuity of 1-D pinning centers on the flux pinning in a wide range of magnetic field directions, discontinuous columnar defects (CDs) and continuous CDs were formed in GdBCO coated conductors using Xe-ion irradiations with 80 and 270 MeV, respectively. An overall shift upward in Jc, for the 80-MeV-irradiated sample compared to the 270-MeV-irradiated one, can be observed in every direction of magnetic field, which is more remarkable as temperature decreases. This implies a synergetic effect of the pinning interaction between the linearity and the discontinuity for the discontinuous CDs.
 -values in BaZrO
-values in BaZrO /YBa
/YBa Cu
Cu O
O quasi-multilayered films with columnar defects
quasi-multilayered films with columnar defectsSueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Mitsugi, Fumiaki*; Ikegami, Tomoaki*; Ishikawa, Norito
Physica C, 494, p.153 - 157, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.14(Physics, Applied)BaZrO /YBa
/YBa Cu
Cu Oy quasi-multilayered films, in which the size and the spatial distribution of BaZrO
Oy quasi-multilayered films, in which the size and the spatial distribution of BaZrO nano-particles were controlled, were irradiated using 200 MeV Xe ions along the c-axis direction. Whenthe BaZrO
nano-particles were controlled, were irradiated using 200 MeV Xe ions along the c-axis direction. Whenthe BaZrO nano-particles were larger in size, the flux lines not captured by CDs, such as interstitial fluxlines between CDs and double kinks of flux lines, can be pinned more effectively by the BaZrO
nano-particles were larger in size, the flux lines not captured by CDs, such as interstitial fluxlines between CDs and double kinks of flux lines, can be pinned more effectively by the BaZrO nano-particles, so that the Jc enhances for high magnetic fields and high temperature. In addition, the inverse correlation between Jc and n-value appears at high temperature in increasing magnetic field for the film with correlated rows of the nano-particles which might be curved off the c-axis. These suggest that the hybrid flux pinning depends not only on the combination of one-dimensional (1D) and three-dimensional pinning centers (3D-PCs) but also on the size and the spatial distribution of the 3D-PCs.
nano-particles, so that the Jc enhances for high magnetic fields and high temperature. In addition, the inverse correlation between Jc and n-value appears at high temperature in increasing magnetic field for the film with correlated rows of the nano-particles which might be curved off the c-axis. These suggest that the hybrid flux pinning depends not only on the combination of one-dimensional (1D) and three-dimensional pinning centers (3D-PCs) but also on the size and the spatial distribution of the 3D-PCs.