Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nisawa, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Go*; Murakami, Hironori*; Okajima, Yuka*; Yamamoto, Kenichiro*; Semba, Yasunori*; Uesugi, Kentaro*; Tanaka, Yoshihito*; Yamamoto, Masaki*; et al.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(2), p.219 - 225, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)A Si(111) winged crystal has been designed to minimize anticlastic bending and improve sagittal focusing efficiency. The crystal was thin with wide stiffening wings. The length-to-width ratio of the crystal was optimized by finite element analysis, and the optimal value was larger than the "golden value". The analysis showed that the slope error owing to anticlastic bending is less than the Darwin width. The X-rays were focused two-dimensionally using the crystal and a tangentially bent mirror. The observed profiles of the focal spot agreed well with the results of a ray-tracing calculation in the energy range from 8 to 17.5 keV. X-ray diffraction measurements with a high signal-to-noise ratio using this focusing system were demonstrated for a small protein crystal.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-020, 178 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II. And Phase III started in 2010 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2010, as a part of the Phase II based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002.
Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Tanai, Kenji; Matsumoto, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Haruo; Ueno, Kenichi; Tetsu, Takeshi*
JNC TN8430 2003-002, 47 Pages, 2003/03
By the second progress report(H12) on research and development for the geological disposal of HLW in Japan, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) extended the database on basic properties of compacted bentonite, and this was mainly obtained by using distilled water as test fluid. This report presents influence of dry densities, silica sand content and temperature on the hydraulic properties of compacted bentonite under condition of marine-based groundwater, which was simulated by use of synthesized seawater. We found that hydraulic conductivity increases with increasing temperature, and the relationship between effective clay density and intrinsic permeability is obtained by the following equation.  = exp(-47.155 + 15.138
= exp(-47.155 + 15.138  -7.878
-7.878 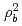 ) where
) where  is intrinsic permeability[m
is intrinsic permeability[m ],
],  is effective clay density[Mg/m
is effective clay density[Mg/m ]. Intrinsic permeability using synthetic seawater as test fluid is about ten times higher then that under distilled water condition. Difference between them however becomes smaller with increasing dry density. We also examined the smectite layers distance after test samples, but remarkable change was not found between them.
]. Intrinsic permeability using synthetic seawater as test fluid is about ten times higher then that under distilled water condition. Difference between them however becomes smaller with increasing dry density. We also examined the smectite layers distance after test samples, but remarkable change was not found between them.
Ura, Tamaki*; Takamasa, Tomoji*; Nishimura, Hajime*; Aoki, Taro*; Ueno, Michio*; Maeda, Toshio*; Nakamura, Masato*; Shimazu, Shunsuke*; Tokunaga, Sango*; Shibata, Yozo*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-049, 154 Pages, 2001/07
JAERI has studied on design and operation of a nuclear powered submersible research vessel, which will navigate under sea in the Arctic Ocean, as a part of the design study of advanced marine reactors. This report describes operation conditions and an operating system of the vessel those were discussed by the specialists of hull design, sound positioning, ship motions and oceanography, etc. The design conditions on ship motions for submersible vessels were surveyed considering regulations in our country, and ship motions were evaluated assuming the observation activities in the Arctic Ocean. A submarine transponder system and an on ice communication buoy system were examined as a positioning and communication system supposing the activity under ice. Procedures to secure safety of nuclear powered submersible research vessel were discussed based on the investigation of accidents. These results were reflected to the concept of the nuclear powered submersible research vessel, and subjects fto be settled in the next step were clarified.
*; *; *; Ara, Katsuyuki
Journal of Applied Physics, 69(8), p.4925 - 4927, 1991/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.21(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
Electron state analysis of pure Iron with Hydrogen atom was conducted using ab-initio calculation. From work function and dipole moment of the system, we have obtained that surface potential change might occurs by changes of surface dipole moment and inner work function.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
Hydrogen embrittlement has become important because of demand for higher strength steel. To clarify the mechanism, it is one of the important issues to evaluate hydrogen distribution in steel. Recently, metal surface potential mapping has used to evaluate hydrogen distribution in metal using surface potential lowering by hydrogen adsorption on metal surface. However, the mechanism of that behavior has been unclear. To elucidate the surface potential lowering mechanism of iron by hydrogen atom, work function and electric dipole moment analysis by density functional theory (DFT) calculation method were carried out. In the study, Fe(100) clean surface and oxygen adsorbed surface were prepared. Hydrogen atoms were adsorbed on surface or penetrated into interior of iron slab in the model. There was a negative correlation between work function and electric dipole. In addition, the surface potential decreased due to hydrogen adsorption on oxygen adsorption surface. It is suggested that electronic state around surface was changed by hydrogen atom adsorption and then surface potential was lowered by the electric dipoles on the surface generated.