Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 422, p.113088_1 - 113088_24, 2024/06
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 414, p.112574_1 - 112574_20, 2023/12
Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Nagae, Yuji; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Mizokami, Shinya; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Koyama, Shinichi
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 53 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technologies for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Estimation Technologies of RPV Damaged Condition, etc.) in 2022JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:93.95(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Shimomura, Kenta; Yamashita, Takuya; Nagae, Yuji
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-012, 270 Pages, 2023/03
In a light water reactor, which is a commercial nuclear power plant, a severe accident such as loss of cooling function in the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and exposure of fuel rods due to a drop in the water level in the reactor can occur when a trouble like loss of all AC power occurs. In the event of such a severe accident, the RPV may be damaged due to in-vessel conditions (temperature, molten materials, etc.) and leakage of radioactive materials from the reactor may occur. Verification and estimation of the process of RPV damage, molten fuel debris spillage and expansion, etc. during accident progression will provide important information for decommissioning work. Possible causes of RPV failure include failure due to loads and restraints applied to the RPV substructure (mechanical failure), failure due to the current eutectic state of low-melting metals and high-melting oxides with the RPV bottom members (failure due to inter-material reactions), and failure near the melting point of the structural members at the RPV bottom. Among the failure factors, mechanical failure is verified by numerical analysis (thermal hydraulics and structural analysis). When conducting such a numerical analysis, the heat transfer properties (thermal conductivity, specific heat, density) and material properties (thermal conductivity, Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, tensile, creep) of the materials (zirconium, boron carbide, stainless steel, nickel-based alloy, low alloy steel, etc.) constituting the RPV and in-core structures to near the melting point are required to evaluate the creep failure of the RPV. In this document, we compiled data on the properties of base materials up to the melting point of each material constituting the RPV and in-core structures, based on published literature. In addition, because welds exist in the RPV and in-core structures, the data on welds are also included in this report, although they are limited.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 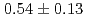 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Saito, Naohito; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2571 - 2574, 2019/06
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. Further improvement of the measurement system is needed to guarantee the required accuracy. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Otani, Masashi*; Sue, Yuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Iijima, Toru*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1067(5), p.052012_1 - 052012_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:47.2(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have measured the muon beam profile after acceleration using a radio frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). Positive muons are injected to an aluminum degrader and negative muoniums (Mu ) are generated. The generated Mu
) are generated. The generated Mu s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu
s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
Bae, S.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 21(5), p.050101_1 - 050101_6, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.82(Physics, Nuclear)Muons have been accelerated by using a radio-frequency accelerator for the first time. Negative muonium atoms (Mu ), which are bound states of positive muons and two electrons, are generated from through the electron capture process in an aluminum degrader. The generated Mu
), which are bound states of positive muons and two electrons, are generated from through the electron capture process in an aluminum degrader. The generated Mu 's are initially electrostatically accelerated and injected into a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). In the RFQ, the Mu
's are initially electrostatically accelerated and injected into a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). In the RFQ, the Mu 's are accelerated to 89 keV. The accelerated Mu
's are accelerated to 89 keV. The accelerated Mu 's are identified by momentum measurement and time of flight. This compact muon linac opens the door to various muon accelerator applications including particle physics measurements and the construction of a transmission muon microscope.
's are identified by momentum measurement and time of flight. This compact muon linac opens the door to various muon accelerator applications including particle physics measurements and the construction of a transmission muon microscope.
Kitamura, Ryo*; Otani, Masashi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.100 - 103, 2017/12
Muon acceleration is an important technique in exploring the new frontier of physics. A new measurement of the muon dipole moments is planned in J-PARC using the muon linear accelerator. The low-energy (LE) muon source using the thin metal foil target and beam diagnostic system were developed for the world's first muon acceleration. Negative muonium ions from the thin metal foil target as the LE muon source was successfully observed. Also the beam profile of the LE positive muon was measured by the LE-dedicated beam profile monitor. The muon acceleration test using a Radio-Frequency Quadrupole linac (RFQ) is being prepared as the first step of the muon accelerator development. In this paper, the latest status of the first muon acceleration test is described.
Terada, Kentaro*; Sato, Akira*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kawashima, Yoshitaka*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yoshida, Go*; Kawai, Yosuke*; Osawa, Takahito; Tachibana, Shogo*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.15478_1 - 15478_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:68.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Electron- or X-ray-induced characteristic X-ray analysis has been widely used to determine chemical compositions of materials in vast research fields. In recent years, analysis of characteristic X-rays from muonic atoms, in which a muon is captured, has attracted attention because both a muon beam and a muon-induced characteristic X-ray have high transmission abilities. Here we report the first non-destructive elemental analysis of a carbonaceous chondrite using one of the world-leading intense direct current muon beam source (MuSIC; MUon Science Innovative Channel). We successfully detected characteristic muonic X-rays of Mg, Si, Fe, O, S and C from Jbilet Winselwan CM chondrite, of which carbon content is about 2 wt percent, and the obtained elemental abundance pattern was consistent with that of CM chondrites.
Okafuji, Takashi*; Miura, Kazuhiro*; Sago, Hiromi*; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Kubo, Koji*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Wakai, Takashi; Shimomura, Kenta
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2017 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.591 - 595, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Kenta; Kato, Shoichi; Wakai, Takashi; Ando, Masanori; Hirose, Yuichi*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/05
This paper describes experimental and analytical works to confirm that the design standard for SFR components sufficiently covers possible failure mechanisms. Creep-fatigue damage evaluation method in JSME design standard for SFR components has been constructed based on experiments and/or numerical analyses of conventional austenitic stainless steels, such as 304SS. Since the material characteristics of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel are substantially different from those of austenitic stainless steels, it is required to verify the applicability of the design standards to the SFR components made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. A series of uni-axial creep-fatigue tests were conducted using double-ended notch bar specimens made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel under displacement controlled condition with 30 minute holding. The curvature radii of the specimens were 1.6mm, 11.2mm and 40.0mm. The specimen having 1.6mm notch and 11.2mm notch failed from outer surface but the specimen having 40.0mm notch showed obvious internal crack nucleation. In addition, though total duration time of the creep-fatigue test was only 2,000 hours, a lot of creep voids and inter granular crack growth were observed. To clarify the cause of such peculiar failure, some additional experiments were performed, as well as some numerical analyses. We could point out that such a peculiar failure aspect might result from corresponding stress distribution in the cross section. As a result of a series of investigations, possible causes of such peculiar failure could be narrowed down. A future investigation plan was proposed to clarify the most significant cause.
Shimomura, Kenta; Garcia Rodriguez, D.*
no journal, ,
There is a longstanding interest to improve the in-service inspection (ISI) of nuclear power plants in general, and sodium fast reactors (SFR) in particular. With the goal of improving both safety and economic performance, a risk-informed approach to in-service inspection (RI-ISI) has therefore been earmarked for future commercial-scale SFR. A reliable RI-ISI, however, can only be established based on a rich operational experience record. For long, JAEA has compiled information about SFR troubles, but up to now such effort had been limited to specific types of troubles or components, while lacking the reliability and completeness required for the RI-ISI approach. In this paper we introduce recent work aiming to develop a comprehensive SFR trouble database based on original information sources, which both expands and improves any previously available documentation.
Shimomura, Kenta; Onizawa, Takashi; Kato, Shoichi; Ando, Masanori; Wakai, Takashi
no journal, ,
This paper describes the formulation of material characteristics of austenitic stainless steels at extremely high temperature which meets in some kinds of severe accidents of nuclear power plants. After the severe accident in Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants, it has been supposed to be very important not only to prevent the occurrence of abnormal conditions, i.e. from the first to the third layer safety, but also to prevent the expansion of the accident conditions, i.e. the fourth layer safety. In order to evaluate the structural integrity under the severe accident condition, material characteristics which can be used in the numerical analyses, such as finite element analysis, were required. However, there were no material characteristics applicable to the structural integrity assessment at extremely high temperature. Therefore, a series of tensile and creep tests was performed for austenitic stainless at extremely high temperature which meets in some kinds of severe accidents of nuclear power plants, namely up to 1000 C. Based on the acquired data from the tests, monotonic stress-strain equation and creep rupture equation applicable to the structural analysis at extremely high temperature, up to 1000
C. Based on the acquired data from the tests, monotonic stress-strain equation and creep rupture equation applicable to the structural analysis at extremely high temperature, up to 1000 C were formulated. As a result, these formulae make it possible to conduct the structural integrity assessment using numerical analysis techniques, such as finite element method.
C were formulated. As a result, these formulae make it possible to conduct the structural integrity assessment using numerical analysis techniques, such as finite element method.
Okuda, Takahiro; Yamashita, Hayato; Toyota, Kodai; Shimomura, Kenta; Onizawa, Takashi; Kato, Shoichi
no journal, ,
This study describes the setting of the material property equations of 316FR steel at an extremely high temperature which can be applied to severe accident conditions of generation IV fast reactors. 316FR steel will be applied to structural materials, e.g. reactor vessel, in the generation IV fast reactors. After the severe accident in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, the evaluation of structural integrity was found to be very important severe accident condition. The development of the generation IV fast reactors requires the material properties of 316FR steel at the extremely high temperature. However, such data has not been acquired. Therefore, tensile and creep tests were carried out in the temperature range over 700 C for 316FR steel. Based on the acquired data from the tests, the equations that can evaluate the material properties of 316FR steel at the extremely high temperature were set up. They are an elasto-plastic stress-strain equation, a creep rupture equation and a creep strain equation.
C for 316FR steel. Based on the acquired data from the tests, the equations that can evaluate the material properties of 316FR steel at the extremely high temperature were set up. They are an elasto-plastic stress-strain equation, a creep rupture equation and a creep strain equation.
Onizawa, Takashi; Shimomura, Kenta; Kato, Shoichi; Wakai, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English