Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogura, Koichi; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kado, Masataka; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(10), p.570 - 574, 2009/10
For accurate control of relativistic laser-plasma interaction under the repetitive operation, we have to measure and control the laser irradiation conditions such as laser parameters, the target shooting accuracy and so on as well as measuring proton parameter on each laser shot. The displacement of the laser shooting position on a tape target, that are used in the high energy proton generation using an ultra-short Ti:sapphire laser system, is measured by observing an X-ray image from laser plasma with an X-ray pinhole camera for each laser shot. The displacement of the shooting position on the target is about 20micron and the accuracy of the target positioning is within 20micron which is small enough for present laser focusing optics with an F number of 3.6 (f=179mm). The technique contributes to accurate control of a repetitive laser driven proton accelerators.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Bulanov, S. V.; Bolton, P. R.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 37(6), p.449 - 454, 2009/06
The acceleration of protons driven by a high-intensity laser is comprehensively investigated via control of the target density by using ASE just before the time of the main-laser interaction. Two cases were investigated for which the ASE intensity differed by three orders of magnitude: In the low contrast case the beam centre for higher energy protons is shifted closer to the laser-propagation direction of 45 , while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
, while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.39(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Bulanov, S. V.; Nemoto, Koshichi*; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physical Review E, 77(1), p.016401_1 - 016401_6, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:97.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The duration-controlled amplified spontaneous emission with intensity of 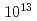 W/cm
W/cm is used to convert a 7.5
is used to convert a 7.5  m thick polyimide foil into a near-critical plasma, in which the
m thick polyimide foil into a near-critical plasma, in which the  -polarized, 45 fs,
-polarized, 45 fs, 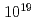 W/cm
W/cm laser pulse generates 3.8 MeV protons, emitted at some angle between the target normal and the laser propagation direction of 45
laser pulse generates 3.8 MeV protons, emitted at some angle between the target normal and the laser propagation direction of 45 . Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the efficient proton acceleration is due to generation of the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure inducing and sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the efficient proton acceleration is due to generation of the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure inducing and sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nemoto, Koshichi*; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 112, p.042034_1 - 042034_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:55.15(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In this work, we present a new method to enhance the proton generation by a 10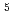 -contrast laser. High-energy protons up to 3.8 MeV are observed with 7.5-
-contrast laser. High-energy protons up to 3.8 MeV are observed with 7.5- m-thick insulator (Polyimide) target irradiated by a laser pulse having energy of 0.8 J and an intensity of 10
m-thick insulator (Polyimide) target irradiated by a laser pulse having energy of 0.8 J and an intensity of 10 -W/cm
-W/cm . Using two time-of-flight (TOF) spectrometers simultaneously in different directions, we measure the direction dependency of proton-energy spectra. As a result, we find that high-energy component of proton beam is shifted away from the target normal toward the laser-propagation direction, when the laser is focused with 45
. Using two time-of-flight (TOF) spectrometers simultaneously in different directions, we measure the direction dependency of proton-energy spectra. As a result, we find that high-energy component of proton beam is shifted away from the target normal toward the laser-propagation direction, when the laser is focused with 45 incident angle. The TOF measurements over 130 laser shots confirm that the generation of the high-energy protons, which are steered away from the target normal, depends strongly on the laser-focusing condition.
incident angle. The TOF measurements over 130 laser shots confirm that the generation of the high-energy protons, which are steered away from the target normal, depends strongly on the laser-focusing condition.
 m thick copper tape target irradiated by s-, circularly-, and p-polarized 55-fs laser pulses
m thick copper tape target irradiated by s-, circularly-, and p-polarized 55-fs laser pulsesLi, Z.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Bulanov, S. V.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Physics Letters A, 369(5-6), p.483 - 487, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The energy spectra of energetic protons emitted in the normal direction from a 5- m thick copper tape irradiated by p-, circularly-, and s-polarized 55-fs laser pulses with intensity of 8-9
m thick copper tape irradiated by p-, circularly-, and s-polarized 55-fs laser pulses with intensity of 8-9 10
10 W/cm
W/cm are measured together with the angular distribution and energy spectra of hot electrons by the target normal direction. The protons with energy up to 1.34 MeV in the rear target normal direction and hot electrons in the laser propagation direction are found. The characters of protons and electrons driven by the circularly-polarized irradiation are close to that driven by the p-polarized one, which is much different from the case at laser intensity of 2-3
are measured together with the angular distribution and energy spectra of hot electrons by the target normal direction. The protons with energy up to 1.34 MeV in the rear target normal direction and hot electrons in the laser propagation direction are found. The characters of protons and electrons driven by the circularly-polarized irradiation are close to that driven by the p-polarized one, which is much different from the case at laser intensity of 2-3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Li, Z.*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 46(9A), p.5853 - 5858, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:54.91(Physics, Applied)A laser-driven proton beam with a maximum energy of a few MeV is stably obtained using an ultra-short and high-intensity Titanium Sapphire laser. At the same time, keV X-ray is also generated at almost the same place where protons are emitted. Here, we show the successful demonstration of simultaneous proton and X-ray projection images of a test sample placed close to the source with a resolution of  10
10 m, which is determined from the source sizes. Although the experimental configuration is very simple, the simultaneity is better than a few hundreds of ps. A CR-39 track detector and imaging plate, which are placed as close as possible to the CR-39, are used as detectors of protons and X-ray. The technique is applicable to the precise observation of microstructures.
m, which is determined from the source sizes. Although the experimental configuration is very simple, the simultaneity is better than a few hundreds of ps. A CR-39 track detector and imaging plate, which are placed as close as possible to the CR-39, are used as detectors of protons and X-ray. The technique is applicable to the precise observation of microstructures.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; Fukumi, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 51(1), p.442 - 446, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The recent progress of the laser driven accelerators which include high power laser driven electrons and ions are reviewed. The studies at JAEA Kansai are mainly described. Based on the recent progres, the various aspects of the applications are also reviewed.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.043104_1 - 043104_6, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:88.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Fast protons are observed by a newly-developed  time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides
time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides 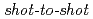 proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of
proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of 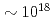 W/cm
W/cm onto a 5-
onto a 5- m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10
m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10 to 10
to 10 W/cm
W/cm . Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15
. Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15  m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
Noda, Akira*; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Soda, Hikaru*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kado, Masataka; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 21(3&4), p.319 - 330, 2007/02
Laser ion production has been studied for downsizing of the accelerator dedicated for cancer therapy. For optimization of various parameters such as pre-pulse condition, target position, laser spot size on target, laser pulse width and so on, time of flight (TOF) measurement utilizing the detected signal by a plastic scintillation counter played an essential role for real time measurement. Protons up to 900 keV and 600 keV are produced from the thin foil targets of Ti 3 micron and 5 micron in thickness, respectively. Modification of the energy distribution of the laser-produced ions with Maxwell distribution by utilizing an RF electric field synchronized to the pulse laser, which is the rotation of the ion beam in the longitudinal phase space (phase rotation), has been demonstrated for the first time.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Ma, J.-L.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Pacific Rim Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO-PR 2007) (CD-ROM), p.77 - 79, 2007/00
We are developing a proton accelerator using an intense lasers with a focused intensity of  10
10 W/cm
W/cm . To monitor proton energy spectra as well as plasma parameters at each laser shot, we are using real time detectors. The proton energy of MeV is stably obtained for applications.
. To monitor proton energy spectra as well as plasma parameters at each laser shot, we are using real time detectors. The proton energy of MeV is stably obtained for applications.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Li, Z.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2006; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.115, p.595 - 605, 2007/00
At present, using ultra-short high intensity lasers at APRC, JAEA Kansai photon research institute, we are developing laser driven multiple quantum beams such as protons, X-rays, electrons and THz waves. These beams are perfectly synchronized with each other. The pulse duration of each beam is lass than a pico-second. They have sharp directionality with high brightness. If we properly combined these, we have new pump-probe techniques for various applications.
Sagisaka, Akito; Utsumi, Takayuki*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Takai, Mamiko; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; et al.
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.1281 - 1284, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Yukio; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Matsukado, Koji*; Mori, Michiaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Chen, L.-M.; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 121(2), p.99 - 107, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.68(Environmental Sciences)The authors obtain a new equation to estimate the forward component of a photon dose which is generated through the interaction between a target and a short pulse high power laser. As the equation is quite simple, it is useful for calculating the photon dose. The equation shows that the photon dose is proportional to the electron temperature for the range of its temperature  3 MeV, and proportional to square of the electron temperature for the range of its temperature
3 MeV, and proportional to square of the electron temperature for the range of its temperature  3 MeV. The dose estimated with this method is roughly consistent with the result of Monte Carlo simulation. On someassumptions and corrections, it can reproduce experimental results obtained and the dose result calculated at other laboratories.
3 MeV. The dose estimated with this method is roughly consistent with the result of Monte Carlo simulation. On someassumptions and corrections, it can reproduce experimental results obtained and the dose result calculated at other laboratories.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; et al.
Applied Physics B, 84(3), p.415 - 419, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:64.73(Optics)no abstracts in English
Mori, Michiaki; Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Yoshimura, Norihisa; Ogura, Koichi; Takai, Mamiko; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 1(9), p.042_1 - 042_4, 2006/09
A new detection device for evaluating ion energy distributions for laser-plasma ion source is demonstrated. The Imaging Plate (IP) with no protective layer as ion detector device for the Thomson Parabola spectrometeris used. The Imaging Plate Thomson Parabola spectrometer (IPTPS) is applicable for the analysis of the energydistribution of the laser-driven ion beam using an opto-electric digitizing technique.
Sagisaka, Akito; Utsumi, Takayuki*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Takai, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; et al.
Reza Enerugigaku Kenkyu Senta Heisei-17-Nendo Kyodo Kenkyu Seika Hokokusho (Heisei-17-Nen 4-Gatsu  Heisei-18-Nen 3-Gatsu), p.61 - 62, 2006/07
Heisei-18-Nen 3-Gatsu), p.61 - 62, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Kado, Masataka; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Applied Physics B, 83(4), p.487 - 489, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.92(Optics)We present experimental results on protons accelerated up to 950 keV from a 3- m thick tantalum foil with a 133-nm thick polystyrene layer on its rear surface, irradiated with a laser pulse having the duration of 70 fs and the intensity of
m thick tantalum foil with a 133-nm thick polystyrene layer on its rear surface, irradiated with a laser pulse having the duration of 70 fs and the intensity of 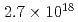 W/cm
W/cm . The energy distribution of fast protons was measured simultaneously with that of the hot-electrons from the rear surface. The proton yield from the polystyrene-coated target is about 10 times as high as that from the uncoated metal target. This enhancement of the proton yield is roughly proportional to the increase of hydrogen atoms given by the 133-nm thick polystyrene layer, assuming a contaminant layer of
. The energy distribution of fast protons was measured simultaneously with that of the hot-electrons from the rear surface. The proton yield from the polystyrene-coated target is about 10 times as high as that from the uncoated metal target. This enhancement of the proton yield is roughly proportional to the increase of hydrogen atoms given by the 133-nm thick polystyrene layer, assuming a contaminant layer of  10-nm thickness is on the metal surface without coating. This result shows that the polystyrene layer contributes to the yield enhancement.
10-nm thickness is on the metal surface without coating. This result shows that the polystyrene layer contributes to the yield enhancement.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Mori, Michiaki; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; Nakamura, Shu*; et al.
Acta Physica Hungarica B, 26(3-4), p.327 - 333, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Takai, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Proceedings of RCNP-JAEA Workshop on Nuclear Photon Science "Hadron-nuclear physics probed by photon", p.195 - 200, 2006/00
High energy ions, electrons, and X-ray are generated from ultrashort pulse high-intensity laser-matter interactions. High-energy protons are observed with a thin-foil target irradiated with a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser at the peak intensity of  2.7
2.7 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . The maximum proton energy is
. The maximum proton energy is  900 keV.
900 keV.