Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(1), p.147 - 152, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Chemistry, Analytical)A heterogeneous partition coefficient for Ra in BaCO (witherite) was determined from a coprecipitation experiment using the free drift method. The initial solution was bubbled with 100% CO
(witherite) was determined from a coprecipitation experiment using the free drift method. The initial solution was bubbled with 100% CO (g) and equilibrated with witherite. After a small amount of Ra was added into the solution, a coprecipioitation reaction was induced by increase of pH caused by degassing of CO
(g) and equilibrated with witherite. After a small amount of Ra was added into the solution, a coprecipioitation reaction was induced by increase of pH caused by degassing of CO (g). A kinetic reaction of precipitation was restricted to be slow due to slow degassing of CO
(g). A kinetic reaction of precipitation was restricted to be slow due to slow degassing of CO (g). Precipitation rate was observed to be enough low comparing with values of low precipitation rates to derive equilibirium partitioning of elements in coprecipitation experiments with CaCO
(g). Precipitation rate was observed to be enough low comparing with values of low precipitation rates to derive equilibirium partitioning of elements in coprecipitation experiments with CaCO (calcite). The
(calcite). The  -value derived for Ra was
-value derived for Ra was  = (1.3
= (1.3 0.7)
0.7) 10
10 . This value was similar to that of Ra in CaCO
. This value was similar to that of Ra in CaCO (calcite). It indicated that partitioning behavior of Ra in carbonate minerals did not depend on affinity in radius of a cation in host carbonate.
(calcite). It indicated that partitioning behavior of Ra in carbonate minerals did not depend on affinity in radius of a cation in host carbonate.
Shimoda, Satoko*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Tachi, Yukio; Seida, Yoshimi*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1665, p.179 - 184, 2014/09
The potential effect of alkaline perturbation caused by the cementitious materials must be evaluated in the performance assessment for HLW geological disposal. In this study, sorption of Cs, Ni and Th was investigated using the altered and unaltered samples of sedimentary rock from Horonobe underground research laboratory. The K values of Cs, Ni and Th measured by batch method using synthetic groundwater changed as a function of degrees of alteration. The K
values of Cs, Ni and Th measured by batch method using synthetic groundwater changed as a function of degrees of alteration. The K values of Cs increased with increasing degrees of alteration, indicating secondary minerals contributes to the increase in Cs sorption by ion exchange mechanism. On the other hand, the K
values of Cs increased with increasing degrees of alteration, indicating secondary minerals contributes to the increase in Cs sorption by ion exchange mechanism. On the other hand, the K values of Ni and Th decreased with the increase of degrees of alteration. This change may be caused by dissolution of clay minerals controlling Ni and Th sorption by surface complexation. These results imply that the effect of alkaline perturbation on K
values of Ni and Th decreased with the increase of degrees of alteration. This change may be caused by dissolution of clay minerals controlling Ni and Th sorption by surface complexation. These results imply that the effect of alkaline perturbation on K values of rocks depend on the surface property of the altered rock and sorption mechanism.
values of rocks depend on the surface property of the altered rock and sorption mechanism.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Morikawa, Keita; Tachi, Yukio; Kuno, Yoshio*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Shimoda, Satoko*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ikuse, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Masako*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-013, 96 Pages, 2012/07
For the purpose to understand the relationship between characteristic of mass transport and characteristic of fracture, the following experiments were carried out using core sample, which was sampled from the -300 m Stage. This paper compiled the results of these experiment. (1) Diffusion experiments of Cs, Sr, I and uranin in granite samples (2) Sorption experiments of Cs and Sr on crushed granite (3) Measurement of pore physicality by Mercury Intrusion and water saturation
Tachi, Yukio; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ochs, M.*; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Seida, Yoshimi; Yamada, Norikazu*; Yui, Mikazu
Radiochimica Acta, 98(9-11), p.711 - 718, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:84.21(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Diffusion and sorption of radionuclides in compacted bentonite are the key processes in the safe geological disposal. The effects of carbonate and salinity on Np(V) diffusion and sorption in compacted montmorillonite were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusion coefficients (
 ) and distribution coefficients (
) and distribution coefficients (
 ) of Np in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m
) of Np in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m were measured under four conditions with different salinities (0.05/0.5 M NaCl) and carbonate concentrations (0/0.01 M NaHCO
were measured under four conditions with different salinities (0.05/0.5 M NaCl) and carbonate concentrations (0/0.01 M NaHCO ). The
). The 
 for carbonate-free conditions decreased as salinity increased, and those for carbonate conditions showed the opposite dependency. The
for carbonate-free conditions decreased as salinity increased, and those for carbonate conditions showed the opposite dependency. The 
 decreased by one order of magnitude under high carbonate condition. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted by coupling the thermodynamic aqueous speciation, the thermodynamic sorption model based on ion exchange and surface complexation, and the diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory in narrow pores. The mechanistic model could be useful in predicting the sorption and diffusion behavior of complex species in compacted systems.
decreased by one order of magnitude under high carbonate condition. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted by coupling the thermodynamic aqueous speciation, the thermodynamic sorption model based on ion exchange and surface complexation, and the diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory in narrow pores. The mechanistic model could be useful in predicting the sorption and diffusion behavior of complex species in compacted systems.
Seida, Yoshimi; Terashima, Motoki; Tachi, Yukio; Iijima, Kazuki; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Yamada, Norikazu*; Yui, Mikazu
Radiochimica Acta, 98(9-11), p.703 - 709, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.08(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Diffusion and sorption behaviors of Eu in sedimentary rock were investigated in the presence of humic substance in the present study. Sedimentary rock obtained from Horonobe URL test site in Hokkaido, Japan, (accessible pore diameter is around several to several ten nanometer) was used. The Diffusion behaviors of Eu were examined based on reservoir depletion method coupled with analysis of inner distribution of the radioactive elements in the rock. Time sequence of concentration of each radioactive element as well as the humic substance in the reservoir was obtained as a function of concentration and molecular size of humic substance. Coexistence of humic substance reduced the depletion of Eu in the reservoir, indicating complexation between the radioactive elements and the humic substance. On the contrary, obvious decrease of humic substance in the reservoir was not observed in the system. This observation suggests that the radioactive elements became hard to diffuse into the sedimentary rock due to an increase of their size through complexation with the humic substance. The sorption of Eu was reduced with increase of the humic substance although the sorption of the humic substance was not influenced by the existence of Th or Eu. The diffusion and sorption of Eu were found to be reduced in the presence of humic substance.
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Nakanishi, Takashi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 280(3), p.541 - 545, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.36(Chemistry, Analytical)Coprecipitation experiment of Ra in gypsum was done with oversaturation method. Derived partition coefficient is,0.71 0.53. Partition coefficient of Ra in gypsum was not reported. Comparing with that of Ra in barite and of Sr in gypsum, a value of partition coefficient in the present study is though to be reasonable.
0.53. Partition coefficient of Ra in gypsum was not reported. Comparing with that of Ra in barite and of Sr in gypsum, a value of partition coefficient in the present study is though to be reasonable.
Morooka, Koichi*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Yoshihiko, Saito,; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Shibata, Masahiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 2005-015, 63 Pages, 2005/08
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has developed a sorption database for bentonite and rocks in order to assess the retardation property of important radioactive elements in natural and engineered barriers in the H12 report. However, there are not enough distribution coefficient data for some radioactive elements in the database. Thus the batch sorption tests for tuff and granodiorite were performed for Samarium (Sm) in synthesized sea water and distilled water under reducing conditions. For Samarium, there are little registration numbers of JNC database and it is important element for performance assessment of HLW disposal system. The results of the experiments are summarized below;(1)Kd for tuff were approximately 0.6 m /kg in rock - distilled water leachate (Eh=-320 - -270mV) adjusted to pH 7 after 10000 MWCO filtration.(2)Kd for tuff were approximately 0.4 m
/kg in rock - distilled water leachate (Eh=-320 - -270mV) adjusted to pH 7 after 10000 MWCO filtration.(2)Kd for tuff were approximately 0.4 m /kg in rock - synthesized sea water leachate (Eh=-304 - -265mV) adjusted to pH 7 after 10000 MWCO filtration.(3)Kd for granodiorite at 1 week were approximately 3.9 m
/kg in rock - synthesized sea water leachate (Eh=-304 - -265mV) adjusted to pH 7 after 10000 MWCO filtration.(3)Kd for granodiorite at 1 week were approximately 3.9 m /kg in rock - distilled water leachate (Eh=-279 - -242mV) adjusted to pH 9 after 10000 MWCO filtration. Kd had a tendency to rise with time in the period of 1 week through 4 week.(4)Kd for granodiorite at 1 week were approximately 0.3 m
/kg in rock - distilled water leachate (Eh=-279 - -242mV) adjusted to pH 9 after 10000 MWCO filtration. Kd had a tendency to rise with time in the period of 1 week through 4 week.(4)Kd for granodiorite at 1 week were approximately 0.3 m /kg in rock - synthesized sea water leachate (Eh=-237 - -206mV) adjusted to pH 9 after 10000 MWCO filtration. Kd had a tendency to rise with time in the period of 1 week through 4 week.
/kg in rock - synthesized sea water leachate (Eh=-237 - -206mV) adjusted to pH 9 after 10000 MWCO filtration. Kd had a tendency to rise with time in the period of 1 week through 4 week.
Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*; Yoshihiko, Saito,; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Shibata, Masahiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 2004-023, 67 Pages, 2005/01
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has developed the sorption database for dentonite and rocks in order to assess the retardation capacities of important radioactive elements in natural and engineered barriers in the H12 report. However, there are not enough distribution coefficient data for radioactive elements in saline type groundwater in the database. Thus the batch sorption tests were performed for uranium(U) and thorium(Th) in saline type groundwater. For these elements, there are little registration numbers in the JNC's sorption database, and also these elements are important to evaluate the safety of disposal system. The experiments for each radioactive element were performed on the following conditions; *U:Kd measurements using the solutions (synthesized sea water and distilled water) reacted with sand stone as a function of carbonate concentration, under reducing conditions. *Th:Kd measurements using the solutions (synthesized sea water and distilled water) reacted with sand stone.
Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*; Muroi, Masayuki*; Shibata, Masahiro; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 2003-039, 44 Pages, 2004/02
We carried out the batch sorption experiments for Sn, Pb and Th in saline type groundwater to obtain the distribution coefficient (Kd) data that were lack in the JNC sorption database. As the results, the following data were obtained. Sn: in artificial sea water, Kd=1 m3/kg on sand stone, Pb: in artificial sea water, Kd=2 m3/kg on sand stone and Kd=4-10 m3/kg on tuff, Th: in artificial sea water, Kd=1-8 m3/kg on sand stone, in artificial sea water with high carbonate concentration, Kd=0 m3/kg on sand stone.
Ueta, Shinzo*; *; *; Muroi, Masayuki*; *; Izumi, Jun*; *
JNC TJ8400 2001-025, 130 Pages, 2001/03
As concern the study on the property of Iodine-129 waste-forms, the solubilities of iodine-sodalite and tourmaline and leachabilities of hidroxy-apatite and fluoro-apatite were measured last year. The results in this year are summarized as follows. (1)Solubility and Leachability of lodine-sodalite were measured under the condition of Leachabilities and solubilities of the synthesized iodine-sodalite were measured by means of a long-term leach test in the solution with chloride ions and high pH (12.5). The measured solubilities were within a range of 10 - 10
- 10 M. It showed a tendency to increase with increasing temperature. The lieachabilities showed a tendency to decrease as time passed, and were within a range of 10
M. It showed a tendency to increase with increasing temperature. The lieachabilities showed a tendency to decrease as time passed, and were within a range of 10 - 10
- 10 g/cm
g/cm /d(10
/d(10 - 10
- 10 m/y). After the leach test, the solid phases were analyzed and the alternation was not observed. It was confirmed by the experiments that the sodalite waste form had a certain capability to contain iodine even though the chloride ion existence. (2)Leaching property of high density apatite sample The following results were obtained by the manufacture examination of high density apatite sample and leaching experiments; (a)As a manufacture technology for apatite molding body, Plasma-hotpress technology was applied. To the porosity which aims 5%, the porosity of hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite was under 2%. (b)Ca and P leaching concentration from hydroxyapatite reached 10
m/y). After the leach test, the solid phases were analyzed and the alternation was not observed. It was confirmed by the experiments that the sodalite waste form had a certain capability to contain iodine even though the chloride ion existence. (2)Leaching property of high density apatite sample The following results were obtained by the manufacture examination of high density apatite sample and leaching experiments; (a)As a manufacture technology for apatite molding body, Plasma-hotpress technology was applied. To the porosity which aims 5%, the porosity of hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite was under 2%. (b)Ca and P leaching concentration from hydroxyapatite reached 10 M order, which was same order solubility estimated by PHREEQE code. From this test results, it was indicated that apatite material has a possibility for a waste of low-Leachability and high density performance.
M order, which was same order solubility estimated by PHREEQE code. From this test results, it was indicated that apatite material has a possibility for a waste of low-Leachability and high density performance.
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Izumi, Jun*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; *; *; *; Ueta, Shinzo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-038, 202 Pages, 2000/02
(1)Sodalite and tourmaline are natural-occurring minerals, which can contain halide in their aluminosilicate lattices. Therefore, these materials have possibilities of immobilization of I-129. In this study, solubility measurements for these materials were carried out. It was confirmed from dissolution behaviors obtained for some kinds of sodalite and calculated results of solubilities based on thermodynamic data that dissolution of sodalite to aqueous solution could be limited by its solubility. Solubility of sodalite had tendencies of "synthesized one  natural one" and "chloride
natural one" and "chloride  iodide". Immobilized iodine in sodalite crystalline lattice was not replaced by chlolide ion in the solution. It was indicated that tourmaline has a possibility as a waste material containing I-129 from comparison of dissolution behavior of element with sodalite. (2)Leaching property of a multi-layered waste-form, that is composed of (1)iodine bearing material (zeolite), (2)coating layer (silica and apatite) and 3)low solubility matirx (apatite), was studied under reducing condition. The following results were obtained by the leaching experiments: (1)The coating layer of hidroxyapatite can reduce the iodine leaching rate by 4 order compared with that of bare iodine bearing material. (2)Ca and P concentration after one-month dipping reached the solubility estimated by the theoretical calculation using PHREEQE code. As a conclusion, it was indicated that this waste-form concept has potential to show low leaching rate.
iodide". Immobilized iodine in sodalite crystalline lattice was not replaced by chlolide ion in the solution. It was indicated that tourmaline has a possibility as a waste material containing I-129 from comparison of dissolution behavior of element with sodalite. (2)Leaching property of a multi-layered waste-form, that is composed of (1)iodine bearing material (zeolite), (2)coating layer (silica and apatite) and 3)low solubility matirx (apatite), was studied under reducing condition. The following results were obtained by the leaching experiments: (1)The coating layer of hidroxyapatite can reduce the iodine leaching rate by 4 order compared with that of bare iodine bearing material. (2)Ca and P concentration after one-month dipping reached the solubility estimated by the theoretical calculation using PHREEQE code. As a conclusion, it was indicated that this waste-form concept has potential to show low leaching rate.
Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Izumi, Jun*; Saigusa, Moriyuki*; Kitao, Hideo*; Tsuzuki, Yasuo*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Okada, Kenichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-037, 61 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Ueta, Shinzo*; *; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-002, 364 Pages, 2000/02
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) have been setting migration parameters and developing its database for the 2nd Progress Report of HLW Geological Disposal (H12 Report). In this study, experimentswere carried out to certify the reliability of parameters and scenario, and examination was carried out to survey procedures of quality management. The main contents are as follows. (1)Data acquisition for certification of migration parameters. The effect of NH complex of Pd on distribution coefficients (Kd) of Pd on both bentonite and rocks, and the effect of sulfate and carbonate complexes of Am on Kds of Am on bentonite are investigated. Kds of Pd depended on NH
complex of Pd on distribution coefficients (Kd) of Pd on both bentonite and rocks, and the effect of sulfate and carbonate complexes of Am on Kds of Am on bentonite are investigated. Kds of Pd depended on NH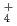 concentration in aqueous. The dependence varied with pH. Effects of sulfate and carbonate complexes on Kds of Am were not remarkable. Apparent diffusivities of Cs in bentonite saturated by saline water were measured. It was confirmed that the apparent diffusivities of Cs in saline water were similar to those in pure water. (2)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model (Hwang's model) for nuclide migration under existence of colloids and investigation of characterization of colloids in groundwater were carried out. As the results, it was indicated that the Hwang's model was appropriate, and it was found that samplingtechnique influenced concentration and size distribution of colloids. (3)Influence of organic substances on solubility. Solubility of Th was measured under the condition with humic acid and carbonate. It increased roughly in proportion to the concentration of humic acid. And it was remarkably high under the condition with carbonate. It was confirmed that Th solubility data set in H12 report was conservative, even though humic acid existed in groundwater. (4)Use of Mechanistic Models for Safety Assessment. The integrated sorption/diffusion model has been used to calculate K
concentration in aqueous. The dependence varied with pH. Effects of sulfate and carbonate complexes on Kds of Am were not remarkable. Apparent diffusivities of Cs in bentonite saturated by saline water were measured. It was confirmed that the apparent diffusivities of Cs in saline water were similar to those in pure water. (2)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model (Hwang's model) for nuclide migration under existence of colloids and investigation of characterization of colloids in groundwater were carried out. As the results, it was indicated that the Hwang's model was appropriate, and it was found that samplingtechnique influenced concentration and size distribution of colloids. (3)Influence of organic substances on solubility. Solubility of Th was measured under the condition with humic acid and carbonate. It increased roughly in proportion to the concentration of humic acid. And it was remarkably high under the condition with carbonate. It was confirmed that Th solubility data set in H12 report was conservative, even though humic acid existed in groundwater. (4)Use of Mechanistic Models for Safety Assessment. The integrated sorption/diffusion model has been used to calculate K , D
, D and D
and D values ...
values ...
Ueta, Shinzo*; *; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-001, 44 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ueta, Shinzo*; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-069, 41 Pages, 1999/11
As a part of the evaluation for the sorption phenomena of nuclides in compacted bentonite, apparent diffusivities for uranium, neptunium and technetium that are redox-sensitive elements, were measured under reducing conditions. Bentonite used was a sodium bentonite, Kunigel V1. Apparent diffusivities were measured by using in-diffusion method (concentration profile method), under the conditions with varying dry densities of compacted bentonite and sorts of the solution used for water saturation of bentonite in diffusion experiments. As a result of the measurements, following ranges of values for apparent diffusivities were acquired. ...
Ueta, Shinzo*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Kurosawa, Susumu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*
JNC TJ8400 99-032, 338 Pages, 1999/02
JNC is preparing the second Performance Assessment Report for high level waste disposal. This research was carried out to prepare the database and assessment model for nuclide migration analysis for the report. The main results are as follows. (1)Quality assurance of nuclide migration database. Thermodynamic database for formation and complexation of 21 elements was developed. International researchers reviewed the database. The review comments, for example the analogousness of actinide elements, were reflected on the database. (2)Modeling study for bentonite porewater chemistry. The porewater chemistry was modeled with ion exchange reaction and surface complexation reaction. The predicted chemistry was compared with the empirical data. (3)Modeling study for nuclide sorption. The sorptivity of Cs, Ra/Sr, Pb, Ni, Am was modeled with ion exchange reaction and surface complexation reaction. The predicted sorptivity was compared with the empirical data and showed the good agreements. (4)Data acquisition for reliable assessment. Hydraulic tests and colloid transport tests with altered bentonite, nuclide diffusion experiments with bentonite and sorption experiments with rocks and bentonite were carried out. The hydraulic conductivity of the altered bentonite was 1.3 5.1
5.1 10
10 m/s, the apparent diffusivities of the actinide elements were in the range of 10
m/s, the apparent diffusivities of the actinide elements were in the range of 10

 10
10 m
m /s, and distribution coefficients of Sm were approximately 6 m
/s, and distribution coefficients of Sm were approximately 6 m /kg. (5)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model for nuclide migration under existence of colloids (Hwang's model), and an analysis of nuclide migration including colloids filtration effect were carried out. As a result, it was indicated that a concept of the Hwang's model were appropriate, and it was suggested that nuclide migration was retarded by colloids filtration.
/kg. (5)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model for nuclide migration under existence of colloids (Hwang's model), and an analysis of nuclide migration including colloids filtration effect were carried out. As a result, it was indicated that a concept of the Hwang's model were appropriate, and it was suggested that nuclide migration was retarded by colloids filtration.
Ueta, Shinzo*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Kurosawa, Susumu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*
JNC TJ8400 99-030, 54 Pages, 1999/02
JNC is preparing the second Performance Assessment Report for high level waste disposal. This research was carried out to prepare the database and assessment model for nuclide migration analysis for the report. The main results are as follows. (1)Quality assurance of nuclide migration database. Thermodynamic database for formation and complexation of 21 elements was developed. International researchers reviewed the database. The review comments, for example the analogousness of actinide elements, were reflected on the database. (2)Modeling study for bentonite porewater chemistry. The porewater chemistry was modeled with ion exchange reaction and surface complexation reaction. The predicted chemistry was compared with the empirical data. (3)Modeling study for nuclide sorption. The sorptivity of Cs, Ra/Sr, Pb, Ni, Am was modeled with ion exchange reaction and surface complexation reaction. The predicted sorptivity was compared with the empirical data and showed the good agreements. (4)Data acquisition for reliable assessment. Hydraulic tests and colloid transport tests with altered bentonite, nuclide diffusion experiments with bentonite and sorption experiments with rocks and bentonite were carried out. The hydraulic conductivity of the altered bentonite was 1.3 5.1
5.1 10
10 m/s, the apparent diffusivities of the actinide elements were in the range of 10
m/s, the apparent diffusivities of the actinide elements were in the range of 10

 10
10 m
m /s, and distribution coefficients of Sm were approximately 6 m
/s, and distribution coefficients of Sm were approximately 6 m /kg. (5)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model for nuclide migration under existence of colloids (Hwang's model), and an analysis of nuclide migration including colloids filtration effect were carried out. As a result, it was indicated that a concept of the Hwang's model were appropriate, and it was suggested that nuclide migration was retarded by colloids filtration.
/kg. (5)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model for nuclide migration under existence of colloids (Hwang's model), and an analysis of nuclide migration including colloids filtration effect were carried out. As a result, it was indicated that a concept of the Hwang's model were appropriate, and it was suggested that nuclide migration was retarded by colloids filtration.
Yoshida, Yasushi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Sato, Tomofumi*
no journal, ,
To evaluate incorporation behavior of Me larger than Ca in ion radius, co-precipitation experiment were implemented. Partition coefficient is generally used to estimate co-precipitation reaction and this parameter is reported to be affected by precipitation rate of calcite. Therefore, under the condition of variety of R, D for Me
larger than Ca in ion radius, co-precipitation experiment were implemented. Partition coefficient is generally used to estimate co-precipitation reaction and this parameter is reported to be affected by precipitation rate of calcite. Therefore, under the condition of variety of R, D for Me larger than Ca into calcite was measured. For trace elements Ra and Ba were used. As a result of experiment Partition coefficient for Ba (or Ra) are decreasing toward the slow R. This tendency is consistent with the reported data. The values of D of Ba and Ra which are low imply those large radius elements are difficult to incorporated into crystal lattice and inclusion is presumably induced by distortion of lattice structure. In addition there is no notable difference of D for Ra and Ba despite difference of radius length. It indicates an extent of inclusion does not depend on a difference of ion radius between Ra and Ba.
larger than Ca into calcite was measured. For trace elements Ra and Ba were used. As a result of experiment Partition coefficient for Ba (or Ra) are decreasing toward the slow R. This tendency is consistent with the reported data. The values of D of Ba and Ra which are low imply those large radius elements are difficult to incorporated into crystal lattice and inclusion is presumably induced by distortion of lattice structure. In addition there is no notable difference of D for Ra and Ba despite difference of radius length. It indicates an extent of inclusion does not depend on a difference of ion radius between Ra and Ba.
Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Muroi, Masayuki*; Honda, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Kohei; Oda, Chie; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Yamada, Norikazu*; Takase, Toshio*
no journal, ,
In this research, the batch immersion experiment and the flow-through column experiment of granite and the artificial highperalkaline pore water were conducted, and the main geochemistry reaction was examined. A change with the lapse of time of the saturation index was calculated by the chemical equilibrium computation based on the batch immersion experiment result. The secondary mineral with the possibility of precipitation in the liquid phase based on the calculation result was extracted, and the combination was examined. In addition, the combination of these secondary minerals was applied to the flow-through column experiment result, and the liquid phase composition after the flow-through and the secondary mineral's spatial distribution were compared with geochemistry calculation (PHREEQC) result. As a result, it has been understood to have to understand the main geochemistry reaction paying attention at the precipitation rate of the secondary mineral in the future.