Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shirai, Nobutoshi; Miura, Yasushi; Tachibana, Ikuya; Omori, Satoru; Wake, Junichi; Fukuda, Kazuhito; Nakano, Takafumi; Nagasato, Yoshihiko
JAEA-Technology 2016-007, 951 Pages, 2016/07
The periodic safety review of TRP is to confirm the safety activities and get effective additional measures the facility safety and its reliability. We implemented 4 items; for (1) evaluation of safety activity implementation, we confirmed we are adequately expanding its safety activities by the necessary documents and schemes. For (2) evaluation of status of safety activities reflecting the latest technical knowledges, we confirmed we reflect latest knowledges for improvement of safety and reliability. For (3) technical evaluation about aging degradation, we can keep the safety of the facilities important to safety and the sea discharge line, under assumption of the present maintenance, because of "focuses for aging degradation". For (4) planning measures about a 10-years-plan that the operator shall implement to keep the facility condition, by the technical evaluation, we found no additional safety plans into maintenance strategies.
 -ray irradiated neutral water condition
-ray irradiated neutral water conditionYamamoto, Masahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of 17th Asian Pacific Corrosion Control Conference (APCCC-17) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2016/01
In Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, decommissioning procedures are continuing more than 30 years until fuel debris removal. It is important to keep soundness of primary container vessel (PCV), made of carbon steel, during these procedures. Corrosion of carbon steel is well-known to be controlled by cathodic reaction, in usual, oxygen reduction reaction. Corrosion of carbon steel could be mitigated by nitrogen injection procedure. However, a lot of radioactive materials exist in cooling water, an effect of radiolysis product on corrosion is an important problem. Clarifying an irradiation effect for corrosion of carbon steel, corrosion test was conducted in  Co
Co  -ray irradiated condition. Electrochemical measurements were conducted to determine cathodic current density of samples. Corrosion rates of carbon steel decrease with time in both
-ray irradiated condition. Electrochemical measurements were conducted to determine cathodic current density of samples. Corrosion rates of carbon steel decrease with time in both  -ray irradiated and non-irradiated conditions. Measured values of cathodic current density gradually decreased with time and then stayed at constant value.
-ray irradiated and non-irradiated conditions. Measured values of cathodic current density gradually decreased with time and then stayed at constant value.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(3), p.181 - 188, 2015/09
In relation to the consideration for long-term storage of spent Cs adsorption vessels containing zeolites in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of the vessel material in the spent Cs adsorption vessel is one of important issues. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (SUS 316L) in the zeolites containing artificial seawater under  -ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential (
-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ( ) and critical pitting potential (
) and critical pitting potential (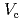 ), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after
), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after  -ray irradiation. The
-ray irradiation. The  , defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing
, defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing  was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H
was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H O
O in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H
in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H O
O . There was good relationship between
. There was good relationship between  and the concentration of H
and the concentration of H O
O . The
. The 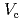 of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl
of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the
ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the 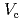 in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing
in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing  under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
 -ray irradiated condition
-ray irradiated conditionYamamoto, Masahiro; Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of European Corrosion Congress 2015 (EUROCORR 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2015/09
In Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, decommissioning procedures are continuing and it will take more than 30 years. As some structures are made of carbon steel, degradation by corrosion is large problem for structural reliability. To clarify an irradiation effect for corrosion of carbon steel, corrosion test was con-ducted in  Co
Co  -ray irradiated condition. Corrosion test results showed that corrosion rates of
-ray irradiated condition. Corrosion test results showed that corrosion rates of  -ray irradiated condition increased with
-ray irradiated condition increased with  -ray dose rates. The oxidant concentrations were also increased with
-ray dose rates. The oxidant concentrations were also increased with  -ray dose rate. From these results, a new estimation method for corrosion rate of carbon steel in water with
-ray dose rate. From these results, a new estimation method for corrosion rate of carbon steel in water with  -ray irradiated condition using radiolysis calculation is introduced and discussed.
-ray irradiated condition using radiolysis calculation is introduced and discussed.
 -ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral water
-ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral waterYamamoto, Masahiro; Nakano, Junichi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/11
Corrosion protection of RPV and PCV is an important issue for the long term maintenance until the end of the decommissioning procedures. One of the uncertain factors for the issue is an effect of radioactivity on corrosion of LAS and CS. Corrosion tests using LAS and CS were conducted in  -rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by
-rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by  -rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with
-rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with  -ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H
-ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H O
O was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in
was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in  -ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
-ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
As a part of consideration for long-term storage of spent zeolite adsorption vessels in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of vessel material in the spent zeolite adsorption vessel is one of important issue. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (type 316L) in the zeolite containing artificial seawater under  -ray irradiation. Steady spontaneous potential (Esp) and pitting potential (VC), of type 316L was measurement.
-ray irradiation. Steady spontaneous potential (Esp) and pitting potential (VC), of type 316L was measurement.  Co
Co  -rays source was used under irradiation. Dose rate of
-rays source was used under irradiation. Dose rate of  -ray irradiation was controlled for 5 kGy/h and 400 Gy/h. In anode polarization curves, there was no clear difference under irradiation and non-irradiation. The corrosion potential of type 316L increased with increasing time after
-ray irradiation was controlled for 5 kGy/h and 400 Gy/h. In anode polarization curves, there was no clear difference under irradiation and non-irradiation. The corrosion potential of type 316L increased with increasing time after  -ray irradiation. The Esp was shifted to nobler by
-ray irradiation. The Esp was shifted to nobler by  -rays irradiation, while increasing Esp was suppressed by contacted with zeolite.
-rays irradiation, while increasing Esp was suppressed by contacted with zeolite.
 atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under
atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under  -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.977 - 986, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Seawater was injected into the reactor cores in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Corrosion of reactor vessel steels is considered to progress. To evaluate durability of the reactor vessel steels, corrosion tests were conducted in diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  -rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N
-rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N H
H were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N
were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N H
H , weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N
, weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N H
H was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N
was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N H
H . When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N
. When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N , weight loss in the vessel steels, and O
, weight loss in the vessel steels, and O and H
and H O
O concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
Yamagishi, Isao; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kato, Chiaki; Morita, Keisuke; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kamiji, Yu; Hino, Ryutaro; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.1044 - 1053, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)For safe storage of zeolite wastes generated by treatment of radioactive saline water at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, properties of the Herschelite adsorbent were studied and its adsorption vessel was evaluated for hydrogen production and corrosion. Hydrogen production depends on its water level and dissolved species because hydrogen is oxidized by radicals in water. It is possible to evaluate hydrogen production rate in Herschelite submerged in seawater or pure water by taking into account of the depth effect of the water. The reference vessel of decay heat 504 W with or without residual pure water was evaluated for the hydrogen concentration by thermal hydraulic analysis using obtained fundamental properties. Maximum hydrogen concentration was below the lower explosive limit (4 %). The steady-state corrosion potential of a stainless steel 316L increased with absorbed dose rate but its increase was repressed by the presence of Herschelite. At 750 Gy/h and  60
60 C which were values evaluated at the bottom of the vessel of 504 W, the localized corrosion of SUS316L contacted with Herschelite would not immediately occur under 20,000 ppm of Cl
C which were values evaluated at the bottom of the vessel of 504 W, the localized corrosion of SUS316L contacted with Herschelite would not immediately occur under 20,000 ppm of Cl concentration.
concentration.
 -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(1), p.1 - 6, 2014/03
The seawater was injected into reactor cores of Units 1, 2 and 3 in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. To investigate effects of  rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50
rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N
rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N H
H ) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N
) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N H
H , the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N
, the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N H
H were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N
were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N H
H . When N
. When N was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during
was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during  rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 444(1-3), p.454 - 461, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cracking growth tests were conducted in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H
) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H O
O , the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H
, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H O
O on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 441(1-3), p.348 - 356, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crack growth tests were performed in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) to evaluate the relationships between the crevice structure and H
) to evaluate the relationships between the crevice structure and H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) growth morphology of stainless steel (SS). Small compact tension (CT) specimens with different fatigue pre-crack lengths were prepared. 20
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) growth morphology of stainless steel (SS). Small compact tension (CT) specimens with different fatigue pre-crack lengths were prepared. 20 300 ppb H
300 ppb H O
O was injected into the high-temperature water at 561 K. Intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near the side grooves of the CT specimens. Owing to pre-crack shortening, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens. The effects of H
was injected into the high-temperature water at 561 K. Intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near the side grooves of the CT specimens. Owing to pre-crack shortening, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens. The effects of H O
O on SS appeared intensely near the surfaces exposed to high levels of H
on SS appeared intensely near the surfaces exposed to high levels of H O
O . The calculations for the percentage of H
. The calculations for the percentage of H O
O remaining showed that the effects of H
remaining showed that the effects of H O
O flowed from both sides of the crack were more obvious than those flowed from the crack mouth.
flowed from both sides of the crack were more obvious than those flowed from the crack mouth.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio*; Shibata, Akira; Nakano, Junichi; Tsukada, Takashi; Takakura, Kenichi*; Nakata, Kiyotomo*
International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering, 2(3), p.65 - 71, 2012/09
Crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been conducted with neutron irradiated compact tension (CT) specimens. The specimens were irradiated in the core region of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in simulated BWR water environments at 288  C from 0.37 to 5.55
C from 0.37 to 5.55 10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E 1 MeV) (0.62 to 9.2 dpa). The CGRs of base metals in high electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition with 10
1 MeV) (0.62 to 9.2 dpa). The CGRs of base metals in high electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition with 10  stress intensity factor, K
stress intensity factor, K  30 MPam
30 MPam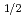 , increased with increasing neutron fluence until 2 dpa and the CGRs were almost the same from 2 to 10 dpa. We investigated the influence of microstructure on CGR by microstructure observation and local strain measurement around the precipitate. This paper will discuss the relationship between CGR and microstructure, radiation hardening, radiation induced segregation.
, increased with increasing neutron fluence until 2 dpa and the CGRs were almost the same from 2 to 10 dpa. We investigated the influence of microstructure on CGR by microstructure observation and local strain measurement around the precipitate. This paper will discuss the relationship between CGR and microstructure, radiation hardening, radiation induced segregation.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 2012 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2012) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2012/09
It has been reported that the corrosion behavior of stainless steels in high temperature water with hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) was different from those with O
) was different from those with O . To evaluate the effect of H
. To evaluate the effect of H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SCC growth tests were conducted in high temperature water injected with H
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC), SCC growth tests were conducted in high temperature water injected with H O
O . In 100 ppb H
. In 100 ppb H O
O at 561 K, an intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only small portion of area near the side grooves of the CT specimen. In 100 ppb H
at 561 K, an intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only small portion of area near the side grooves of the CT specimen. In 100 ppb H O
O at 453 K, however, IGSCC extended to the central region of the CT specimen. Effects of H
at 453 K, however, IGSCC extended to the central region of the CT specimen. Effects of H O
O on SCC growth behavior appeared stronger at lower temperature due to a reduction of the thermal decomposition of H
on SCC growth behavior appeared stronger at lower temperature due to a reduction of the thermal decomposition of H O
O . Moreover, outer oxide layer of oxide film formed on the crack of the CT specimen was examined to estimate environmental situations in the cracks and a thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
. Moreover, outer oxide layer of oxide film formed on the crack of the CT specimen was examined to estimate environmental situations in the cracks and a thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsujikawa, Shigeo*; Hattori, Shigeo*; Yoshii, Tsuguyasu*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-007, 404 Pages, 2012/03
There are many LWRs which have been operated for more than 20 years in Japan and it is expected that technique corresponding to aging plants are necessary established for safety operation in LWRs. A lot of troubles related to SCC are reported and many investigations are concerned with SCC mechanism and technical evaluation. In this paper, those research data were collected as possible widely and reviewed systematically. Current circumstances concerned with SCC in LWRs were reviewed specifically as follows: SCC incidents, SCC evaluation methods for crack initiation and propagation, the investigations concerned with SCC mechanism and monitoring technique for corrosive environment. Influences with reactor types (BWR, PWR), materials (stainless steels, Ni alloys) and SCC evaluating methods (laboratories and actual plants) were summarized as graphs and tables easy to understand in common/difference points concerned with SCC. From these arranged results, future themes were considered and remarked SCC phenomenon was summarized in actual plants. As for SCC evaluations under the accelerate conditions in the laboratory test, it was suggested that a computational prediction and modeling including statistical technique and microscopic analysis in crack initiation were important. Furthermore it was suggested that monitoring techniques predicting SCC initiation and grasping plant circumstance in operation and feasibility in actual plants were important.
Shibata, Akira; Nakano, Junichi; Omi, Masao; Kawamata, Kazuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 422(1-3), p.14 - 19, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To simulate Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) behavior by in-pile experiments, it is necessary to irradiate specimens up to a neutron fluence that is higher than the IASCC threshold fluence. Pre-irradiated specimens must be relocated from pre-irradiation capsules to in-pile capsules. Hence, a remote welding machine has been developed. And the integrity of capsule housing for a long term irradiation was evaluated by tensile tests in air and slow strain rate tests in water. Two type specimens were prepared. Specimens were obtained from the outer tubes of capsule irradiated to 1.0-3.9  10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E 1 MeV). And specimens were irradiated in a leaky capsule to 0.03-1.0
1 MeV). And specimens were irradiated in a leaky capsule to 0.03-1.0  10
10 n/m
n/m . Elongation more than 15% in tensile test at 423 K was confirmed and no IGSCC fraction was shown in SSRT at 423 K which was estimated as temperature at the outer tubes of the capsule under irradiation.
. Elongation more than 15% in tensile test at 423 K was confirmed and no IGSCC fraction was shown in SSRT at 423 K which was estimated as temperature at the outer tubes of the capsule under irradiation.
Nakano, Junichi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Uchimoto, Tetsuya*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.883 - 886, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To examine the effects of minor elements on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) susceptibility of low carbon stainless steels with work hardened layer, a high purity type 304 stainless steel was fabricated and minor elements, Si, S, P, C or Ti, were added. Work hardened layer was introduced by shaving on the surface of stainless steels. The specimens were exposed to a boiling 42% MgCl solution for 20 hours and the number and the length of initiated cracks were examined. SCC susceptibility of the specimen with P was the highest and that of the specimen with C was the lowest in all specimens. By magnetic force microscope examination, magnetic phase expected to be martensitic phase was detected near surface. Since corrosion resistance of martensite is lower than that of austenite, the minor elements additions would affect SCC susceptibility through the amount of the transformed martensite, i.e. austenite stability.
solution for 20 hours and the number and the length of initiated cracks were examined. SCC susceptibility of the specimen with P was the highest and that of the specimen with C was the lowest in all specimens. By magnetic force microscope examination, magnetic phase expected to be martensitic phase was detected near surface. Since corrosion resistance of martensite is lower than that of austenite, the minor elements additions would affect SCC susceptibility through the amount of the transformed martensite, i.e. austenite stability.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
To evaluate the effects of hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behavior of stainless steels (SSs), crack growth tests and in-situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in high temperature water injected with H
) on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behavior of stainless steels (SSs), crack growth tests and in-situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in high temperature water injected with H O
O were carried out. On the fracture surface of a compact tension (CT) specimen exposed 100 ppb H
were carried out. On the fracture surface of a compact tension (CT) specimen exposed 100 ppb H O
O at 561 K, intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near side grooves of the CT specimen. To increase the amount of remaining H
at 561 K, intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near side grooves of the CT specimen. To increase the amount of remaining H O
O , Chevron notches were eliminated from a CT specimen. Consequently expansion of IGSCC area was observed into the central region of the CT specimen. EIS was conducted on SS creviced corrosion specimens. Using the obtained charge transfer resistance, ratio of remaining H
, Chevron notches were eliminated from a CT specimen. Consequently expansion of IGSCC area was observed into the central region of the CT specimen. EIS was conducted on SS creviced corrosion specimens. Using the obtained charge transfer resistance, ratio of remaining H O
O inside crevice was calculated with a differential equation code. Ratio of remaining H
inside crevice was calculated with a differential equation code. Ratio of remaining H O
O in the CT specimen without Chevron notches was calculated as higher than that of the one with Chevron notches.
in the CT specimen without Chevron notches was calculated as higher than that of the one with Chevron notches.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Shibata, Akira; Ise, Hideo; Kasahara, Shigeki; Kawaguchi, Yoshihiko*; Nakano, Junichi; Omi, Masao; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of Enlarged Halden Programme Group Meeting 2011 (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
In order to load a large specimen of 0.5T-CT up to a high stress intensity factor of  30 MPa
30 MPa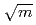 , we have adopted a lever type loading unit for in-pile irradiation-assisted stress corrosion crack (IASCC) growth tests in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In this unit, the applied load is generated by shrinking a bellows with lower inner gas pressure than surrounding water pressure and enlarged by leverage. The crack length of the specimen is monitored by potential drop method (PDM) using mineral insulator (MI) cables. In this paper, technical concerns of the in-pile crack growth test unit, especially the estimation procedure of applied load to the specimen inside the irradiation capsule and the evaluation of precision of the PDM signals are presented.
, we have adopted a lever type loading unit for in-pile irradiation-assisted stress corrosion crack (IASCC) growth tests in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In this unit, the applied load is generated by shrinking a bellows with lower inner gas pressure than surrounding water pressure and enlarged by leverage. The crack length of the specimen is monitored by potential drop method (PDM) using mineral insulator (MI) cables. In this paper, technical concerns of the in-pile crack growth test unit, especially the estimation procedure of applied load to the specimen inside the irradiation capsule and the evaluation of precision of the PDM signals are presented.
Sato, Takahiro*; Iwasaki, Atsushi*; Ishibashi, Kazuki*; Okino, Tomoya*; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; Adachi, Junichi*; Yagishita, Akira*; Yazawa, Hiroki*; Kannari, Fumihiko*; Aoyama, Makoto; et al.
Europhysics News, 42(5), P. 10, 2011/09
The resonant and non-resonant two-photon single ionization processes of He were investigated using intense free electron laser light in the extreme ultraviolet (XUV) region (53.4-61.4 nm) covering the 1s-2p and 1s-3p resonant transitions of He. On the basis of the dependences of the yield of He on the XUV light-field intensity at 53.4, 58.4, 56.0 and 61.4 nm, the absolute values of the two-photon ionization cross sections of He at the four different wavelengths and their dependence on the light-field intensity were determined for the first time.
on the XUV light-field intensity at 53.4, 58.4, 56.0 and 61.4 nm, the absolute values of the two-photon ionization cross sections of He at the four different wavelengths and their dependence on the light-field intensity were determined for the first time.
Sato, Takahiro*; Iwasaki, Atsushi*; Ishibashi, Kazuki*; Okino, Tomoya*; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; Adachi, Junichi*; Yagishita, Akira*; Yazawa, Hiroki*; Kannari, Fumihiko*; Aoyama, Makoto; et al.
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 44(16), p.161001_1 - 161001_5, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:82.78(Optics)The resonant and non-resonant two-photon single ionization processes of He were investigated using intense free electron laser light in the extreme ultraviolet (XUV) region (53.4-61.4 nm) covering the 1s-2p and 1s-3p resonant transitions of He. On the basis of the dependences of the yield of He on the XUV light-field intensity at 53.4, 58.4, 56.0 and 61.4 nm, the absolute values of the two-photon ionization cross sections of He at the four different wavelengths and their dependence on the light-field intensity were determined for the first time.
on the XUV light-field intensity at 53.4, 58.4, 56.0 and 61.4 nm, the absolute values of the two-photon ionization cross sections of He at the four different wavelengths and their dependence on the light-field intensity were determined for the first time.