Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ioka, Ikuo
QST-M-29; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2019, P. 71, 2021/03
The objective of our research is to clarify corrosion acceleration mechanism of materials under the gamma-ray radiation environment. The irradiation experiment was conducted for 30 mins at the gamma-ray irradiation facility of Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute of QST. During the gamma-ray irradiation, pH decreases, and also the electric conductivity showed a tendency to increase. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide in water was measured after irradiation and was about 3.5 10
10 wt%. When the concentration is less than 10 wt%, the pH value decreases with increasing the concentration. A pH of 3.5
wt%. When the concentration is less than 10 wt%, the pH value decreases with increasing the concentration. A pH of 3.5 10
10 wt% hydrogen peroxide water was 5.58. This was almost same as the pH value (5.56) of purified water. It seems that the decrease of pH after irradiation is not able to explain by the production of hydrogen peroxide.
wt% hydrogen peroxide water was 5.58. This was almost same as the pH value (5.56) of purified water. It seems that the decrease of pH after irradiation is not able to explain by the production of hydrogen peroxide.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen using heat from solar power. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. The container using the hybrid material was experimentally made. The pre-oxidized container using hybrid technique was prepared for the corrosion test in boiling sulfuric acid to evaluate the corrosion characteristics of the container. There was no detaching of the surface with the weld part and the R processing. We proposed the calculation method of corrosion rate from the ions dissolved in the sulfuric acid solution after the corrosion test.
on the surface. The container using the hybrid material was experimentally made. The pre-oxidized container using hybrid technique was prepared for the corrosion test in boiling sulfuric acid to evaluate the corrosion characteristics of the container. There was no detaching of the surface with the weld part and the R processing. We proposed the calculation method of corrosion rate from the ions dissolved in the sulfuric acid solution after the corrosion test.
Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00377_1 - 19-00377_11, 2020/06
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen with high cost performance. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kurata, Masaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Sato, Daiki*; Murakami, Nozomu*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.206 - 216, 2019/09
After the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, research and development (R&D) program for establishing technical basis of accident-tolerant fuel (ATF) started from 2015 in Japan. Since then, both experimental and analytical studies necessary for designing a new light water reactor (LWR) core with ATF candidate materials are being conducted within the Japanese ATF R&D Consortium for implementing ATF to the existing LWRs, accompanying with various technological developments required. Until now, we have accumulated experimental data of the candidate materials by out-of-pile tests, developed fuel evaluation codes to apply to the ATF candidate materials, and evaluated fuel behavior simulating operational and accidental conditions by the developed codes. In this paper, the R&D progresses of the ATF candidate materials considered in Japan are reviewed based on the information available such as proceedings of international conference and academic papers, providing an overview of ATF program in Japan.
Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Sawada, Shinichi*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(35), p.19141 - 19152, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:49.6(Chemistry, Physical)Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/05
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen using heat from solar power. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment.
on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment.
Yagmur, A.*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Ioka, Ikuo; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Ono, Madoka*; Endo, Junichi*; Kashiwagi, Kimiaki*; Nakashima, Tetsuya*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 109(24), p.243902_1 - 243902_4, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.94(Physics, Applied)Thermoelectric devices based on the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) were irradiated with gamma ( ) rays with the total dose of around 3
) rays with the total dose of around 3 10
10 Gy in order to investigate the
Gy in order to investigate the  -radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni
-radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni Zn
Zn Fe
Fe O
O /Glass and Pt/Bi
/Glass and Pt/Bi Y
Y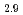 Fe
Fe O
O /Gd
/Gd Ga
Ga O
O SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the
SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the  -ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
-ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Katsuyama, Jinya; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(3), p.15-00619_1 - 15-00619_8, 2016/06
The IS process for hydrogen production has been developed by JAEA as application of a high-temperature gas cooled reactor. The IS process includes a severe corrosion environment which is made to boil and decompose concentrated sulfuric acid. The two-layer pipe consisted of the Fe-high Si alloy with boiling sulfuric acid-resistant and the carbon steel with the ductility was produced by centrifugal casting. The evaluation of characteristics was carried out. The Fe-high Si alloy lining showed enough corrosion resistance in boiling sulfuric acid. As evaluation of the Fe / Fe-high Si alloy interface, thermal cycle test was executed. There was no detachment of the interface though the cracks were generated in the vicinity of the interface. It is believed that the cracks parallel to the interface is attributed to the tensile stress during the thermal cyclic test using FEM analysis and the flake graphite precipitate. It was confirmed that the interface possessed the enough strength.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
The thermochemical water-splitting (IS process) for hydrogen production has been developed by JAEA as application of a high-temperature gas cooled reactor. The IS process includes a severe corrosion environment which is made to boil and decompose concentrated sulfuric acid. Two kinds of brittleness materials, SiC and Fe-high Si alloy, are reported as materials having enough corrosion resistance in this corrosion environment. The two-layer pipe consisted of the Fe-high Si alloy with boiling sulfuric acid-resistant and the carbon steel with the ductility was produced by centrifugal casting. The evaluation of characteristics was carried out. The Fe-high Si alloy lining showed enough corrosion resistance in boiling sulfuric acid. As evaluation of the Fe / Fe-high Si alloy interface, thermal cycle test (100 C-900
C-900 C) was executed. There was not the interface detachment and it was confirmed to have enough interfacial strength.
C) was executed. There was not the interface detachment and it was confirmed to have enough interfacial strength.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi*; Takizawa, Masayuki*; Ito, Takeshi*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(1), p.16 - 22, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)A multi-axis stress field is indispensable to quick and quantitative evaluation of stress corrosion cracking for constructional materials and weld joints of existing industrial plants. The applicability of multi-axis residual stress field into SCC tests was evaluated. The hard sphere ball was stuffed into small flat-plate of type 304SS. Numerical analysis was conducted in order to compare with the experimental results. The numerical analysis was comparatively in agreement with the experimental results. Parameters of the test were selected by numerical analysis to optimize the residual stress of specimen. SCC test in MgCl was performed using the specimen with optical residual stress condition. It is confirmed that the multi-axis residual stress field was useful in quick and quantitative SCC test by comparing the initiation of cracks with the distribution of residual stress obtained by numerical analysis.
was performed using the specimen with optical residual stress condition. It is confirmed that the multi-axis residual stress field was useful in quick and quantitative SCC test by comparing the initiation of cracks with the distribution of residual stress obtained by numerical analysis.
Kubo, Shinji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ioka, Ikuo; Onuki, Kaoru; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38(16), p.6577 - 6585, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:52.08(Chemistry, Physical)Very harsh environments exist in the iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production. Structural materials for sulfuric acid vaporizers and concentrators are exposed to high-temperature corrosive environments. Immersion tests were carried out to evaluate the corrosion resistance of ceramics and to evaluate corrosion-resistant metals exposed to environments of aqueous sulfuric acids at temperatures of 320, 380, and 460 C, and pressure of 2 MPa. The aqueous sulfuric acid concentrations for the temperatures were 75, 85, and 95 wt%, respectively. Ceramic specimens of silicon carbides (SiC), silicon impregnated silicon carbides (Si-SiC), and silicon nitrides (Si
C, and pressure of 2 MPa. The aqueous sulfuric acid concentrations for the temperatures were 75, 85, and 95 wt%, respectively. Ceramic specimens of silicon carbides (SiC), silicon impregnated silicon carbides (Si-SiC), and silicon nitrides (Si N
N ) showed excellent corrosion resistance from weight loss measurements after exposure to 75, 85, and 95 wt% sulfuric acid. High-silicon irons with silicon content of 20 wt% showed a fair measure of corrosion resistance. However, evidence of crack formation was detected via microscopy. Silicon enriched steels severely suffered from uniform corrosion with a corrosion rate in 95 wt% sulfuric acid of approximately 1 gm
) showed excellent corrosion resistance from weight loss measurements after exposure to 75, 85, and 95 wt% sulfuric acid. High-silicon irons with silicon content of 20 wt% showed a fair measure of corrosion resistance. However, evidence of crack formation was detected via microscopy. Silicon enriched steels severely suffered from uniform corrosion with a corrosion rate in 95 wt% sulfuric acid of approximately 1 gm h
h . Among the tested materials, the ceramics SiC, Si-SiC, and Si
. Among the tested materials, the ceramics SiC, Si-SiC, and Si N
N were found to be suitable candidates for structural materials in direct contact with the considered environments.
were found to be suitable candidates for structural materials in direct contact with the considered environments.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems (SMINS-2), p.391 - 400, 2012/12
Optimization of composition for high Cr-W-Si Ni base alloy has been studied to apply to a nitric acid with high oxidation-reduction potential of advanced reprocessing plants. The corrosion resistance of the Ni base alloy is superior to that of conventional stainless steels. In addition, The Ni base alloy has an excellent resistance of weld crack and ability of plastic deformation caused by extra high purity (EHP) refining technology. However, the Ni base alloy has a technical limitation in hot working and welding for practical use. Several Ni base EHP alloys with different content of Si and W were manufactured to choose an optimum composition range without losing corrosion resistance. High strain rate tensile tests at high temperature, corrosion tests and weldability tests were carried out to examine the optimum composition range of Ni base EHP alloy.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems (SMINS-2), p.273 - 279, 2012/12
Ioka, Ikuo; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Usami, Koji; Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.887 - 891, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-25Cr-35Ni EHP alloy was developed with conducting the countermeasure for IASCC. It is composed to adjust major elements, to remove harmful impurities and so on. The specimens were irradiated at 553 K for 25000h using JRR-3. The fluence was estimated to be 1.5 10
10 n/m
n/m . Type 304SS was also irradiated as a comparison material. SSRT test was conducted in oxygenated water at 561 K in 7.7 MPa. The fracture mode of EHP alloy was ductile. IGSCC was not observed in the fracture surface. On the other hand, the fraction of IGSCC on the fracture surface of type 304 was about 70%. Microstructural evolution of EHP and type 304 after irradiation was examined by TEM. The defects induced by irradiation mostly consisted of black dots and frank loops in both specimens. No void was also observed in grain and grain boundary of both specimens. There was a little difference in microstructure after irradiation. It is believed that EHP alloy is superior to type 304 in irradiation.
. Type 304SS was also irradiated as a comparison material. SSRT test was conducted in oxygenated water at 561 K in 7.7 MPa. The fracture mode of EHP alloy was ductile. IGSCC was not observed in the fracture surface. On the other hand, the fraction of IGSCC on the fracture surface of type 304 was about 70%. Microstructural evolution of EHP and type 304 after irradiation was examined by TEM. The defects induced by irradiation mostly consisted of black dots and frank loops in both specimens. No void was also observed in grain and grain boundary of both specimens. There was a little difference in microstructure after irradiation. It is believed that EHP alloy is superior to type 304 in irradiation.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nagae, Masahiro*; Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2011/10
The Thermochemical water-splitting cycle IS process constitutes severe environments to the materials of construction because of the corrosive chemicals. This paper discusses corrosion resistance of novel metallic materials in high temperature sulfuric and hydriodic acid. As for the sulfuric acid environment, corrosion resistances of MoN, Mo-Ta-N, and Mo-Cr-N alloys were examined. The experiments were performed for the duration of 5 hour in 90wt% sulfuric acid at 300 C. Although no material showed satisfactory corrosion resistance (ca. 1.5 mm/y in the case of MoN), the addition of Ta or Cr was found to be effective to improve the corrosion resistance. As for the hydriodic acid environment, corrosion resistance of Nb-W alloy was examined by immersing the test pieces for up to 100 hours in the test solutions of 200
C. Although no material showed satisfactory corrosion resistance (ca. 1.5 mm/y in the case of MoN), the addition of Ta or Cr was found to be effective to improve the corrosion resistance. As for the hydriodic acid environment, corrosion resistance of Nb-W alloy was examined by immersing the test pieces for up to 100 hours in the test solutions of 200 C. It was observed that the corrosion rates lowered with the progress of immersion time and reached to a stable value of lower than 0.1 mm/y.
C. It was observed that the corrosion rates lowered with the progress of immersion time and reached to a stable value of lower than 0.1 mm/y.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/10
An Extra high purity Nb-W alloy (Nb-W EHP) that is superior to current Zr for cracking in severer environment is developed for reprocessing plants. Nb-W EHP has a technical limitation in weldability for practical use. To choose an optimum composition range of W, Nb-W EHP with different content of W were manufactured. Weld joint specimens were prepared by TIG welding. Tensile, corrosion and Charpy impact tests were carried out to examine the effect of W on chemical and mechanical properties of Nb-W EHP. There was little effect of W on corrosion rate of weld joint of Nb-W EHP. The increase in W improves ultimate tensile strength of Nb-W EHP. A ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) of Nb-W EHP increased with an increase in W. The increase in DBTT is a problem as a structural material. Moreover, DBTT of the weld joint was high about 150K in comparison with the base metal. It is necessary to adjust W content to 8wt% or less in Nb-W EHP from the obtained results.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1298, p.61 - 66, 2011/04
The irradiation behaviour in two different precipitation hardening types of Ni-base alloys with the ultra high purity grade (EHP), namely, the  ' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe
' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe or Ni
or Ni ) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni
) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni , 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP(
, 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP( ') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along
') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along  planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP(
planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP( '), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP(
'), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP( '), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
'), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2010/05
An Extra High Purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP alloy) was developed with conducting the new multiple refined melting in order to suppress the harmful impurities less than 100 ppm. EHP alloy has great intergranular corrosion resistance. It is considered that intergranular corrosion becomes initiation of SCC. So, we try to apply EHP alloy to weld overlay materials to prevent from SCC. EHP alloy was melted by the new multiple refined method. The conventional weld metals were also prepared as comparisons. Specimens were machined from the welded metal of each material. Intergranular corrosion tests were performed in boiling 8 kmol/m HNO
HNO solutions containing 1 kg/m
solutions containing 1 kg/m Cr(VI) ions. The intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals was severer than those of EHP alloys. Crevice Beam bending tests to evaluate susceptibility of SCC were carried out in high temperature water of 561 K with saturated oxygen for 1000 h. Cracks and intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals were much more than those of EHP alloys. It was confirmed that EHP alloy had excellent SCC resistance in comparison with conventional materials when EHP alloy was used as a weld metal.
Cr(VI) ions. The intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals was severer than those of EHP alloys. Crevice Beam bending tests to evaluate susceptibility of SCC were carried out in high temperature water of 561 K with saturated oxygen for 1000 h. Cracks and intergranular corrosion of conventional weld metals were much more than those of EHP alloys. It was confirmed that EHP alloy had excellent SCC resistance in comparison with conventional materials when EHP alloy was used as a weld metal.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Materia, 49(3), p.122 - 124, 2010/03
In reprocessing plants, it is known that the corrosion environment for structural materials is extremely severe to be used boiling nitric acid with oxidized ions related to fission products (FP). Ultra low carbon stainless steels (SUS304ULC) were developed from the experience of corrosion troubles in foreign plants and the operation of domestic plant. In an advanced reprocessing plant, it is predicted that the corrosion environment will be more severe because of the advanced spent fuels which contain much FP than an existing spent fuel. Therefore, it is necessary to develop the new stainless steel with excellent corrosion resistance in comparison with SUS304ULC. We developed an extra high purity stainless steel (EHP alloy) having superior corrosion resistance in the strong acid environment for the advanced reprocessing plant. In the production process of EHP alloy, the practical use was taken into consideration. This report introduces the present conditions of EHP alloy.
Ioka, Ikuo; Suzuki, Jun; Motooka, Takafumi; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 4(1), p.105 - 112, 2010/02
An intergranular corrosion is an important degradation mechanism of austenitic stainless steels for use in a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant. The intergranular corrosion is caused by the segregation of impurities to grain boundaries. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP) was developed with conducting the new multiple refined melting to suppress the impurities less than 100ppm. The intergranular corrosion behavior of EHP alloys added various impurities was examined in boiling nitric acid solution with highly oxidizing ions. A multi regression analysis was performed using the obtained data. The degree of influence of the impurities on intergranular corrosion was shown from the analysis. The influence on corrosion rate became small in order of B, P, Si, C, S and Mn. There is little effect of Mn on corrosion rate of EHP-SSs in case of 10000appm or less.