Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tanaka, Taku*; Komatsu, Masabumi*; Gonze, M.-A.*; Sakashita, Wataru*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Nishina, Kazuya*; Ota, Masakazu; Ohashi, Shinta*; Calmon, P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106721_1 - 106721_10, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.59(Environmental Sciences)This study was aimed at analysing performance of models for radiocesium migration mainly in evergreen coniferous forest in Fukushima, by inter-comparison between models of several research teams. The exercise included two scenarios of countermeasures against the contamination, namely removal of soil surface litter and forest renewal, and a specific konara oak forest scenario in addition to the evergreen forest scenario. All the models reproduced trend of time evolution of radiocesium inventories and concentrations in each of the components in forest such as leaf and organic soil layer. However, the variations between models enlarged in long-term predictions over 50 years after the fallout, meaning continuous field monitoring and model verification/validation is necessary.
 Cs and
Cs and  Cs radioactivity measurements
Cs radioactivity measurementsMalins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Takahashi, Junko*; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 226, p.106456_1 - 106456_12, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.21(Environmental Sciences)Kubota, Tomohiro; Kuroda, Hisao*; Watanabe, Mirai*; Takahashi, Akiko*; Nakazato, Ryoji*; Tarui, Mika*; Matsumoto, Shunichi*; Nakagawa, Keita*; Numata, Yasuko*; Ouchi, Takao*; et al.
Atmospheric Environment, 243, p.117856_1 - 117856_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.82(Environmental Sciences)The dry and wet depositions of atmospheric ammonia (NH ) is one of the important pathways of nitrogen loads to aquatic ecosystems. Crop and livestock agriculture, one of the largest emitters of NH
) is one of the important pathways of nitrogen loads to aquatic ecosystems. Crop and livestock agriculture, one of the largest emitters of NH in Asian countries, are known to cause high spatial and seasonal variation of NH
in Asian countries, are known to cause high spatial and seasonal variation of NH and influence the surrounding lake basin areas via its dry and wet deposition. However, the spatial characteristics of the NH
and influence the surrounding lake basin areas via its dry and wet deposition. However, the spatial characteristics of the NH concentration in basin scale are not completely understood for regulation in NH
concentration in basin scale are not completely understood for regulation in NH emission. Here we aim to clarify dominant factors of spatial and seasonal variations of the NH
emission. Here we aim to clarify dominant factors of spatial and seasonal variations of the NH concentration in a eutrophic lake basin surrounded by agricultural areas in Japan. Passive sampling over various land use categories in the basin was conducted at 36 sites in total from October 2018 to January 2020. Interestingly, the observed NH
concentration in a eutrophic lake basin surrounded by agricultural areas in Japan. Passive sampling over various land use categories in the basin was conducted at 36 sites in total from October 2018 to January 2020. Interestingly, the observed NH concentration near the livestock houses were higher in winter than summer, which was inconsistent with knowledge of seasonal changes of current NH
concentration near the livestock houses were higher in winter than summer, which was inconsistent with knowledge of seasonal changes of current NH emission inventory based on temperature-driven volatilization process. Comparing monthly NH
emission inventory based on temperature-driven volatilization process. Comparing monthly NH concentrations with various meteorological factors, we suggested the importance of seasonal advection of NH
concentrations with various meteorological factors, we suggested the importance of seasonal advection of NH from high emission sources to which has been rarely paid attention by the previous past studies. As for this, should be considered for lake ecosystem management since deposition of NH
from high emission sources to which has been rarely paid attention by the previous past studies. As for this, should be considered for lake ecosystem management since deposition of NH is known to be closely related to the ecological processes such as phytoplankton blooming.
is known to be closely related to the ecological processes such as phytoplankton blooming.
Malins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Malins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
We analyzed changes in ambient dose equivalent rates (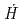 *(10)) between 2011 and 2017 in forests in Fukushima Prefecture. PHITS was used to calculate the effects of changes in the distribution of
*(10)) between 2011 and 2017 in forests in Fukushima Prefecture. PHITS was used to calculate the effects of changes in the distribution of 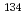 Cs and
Cs and 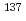 Cs within forests on
Cs within forests on 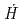 *(10). The transfer of radiocesium from the crowns of evergreen coniferous trees to the forest floor appeared to cause slower decreases in
*(10). The transfer of radiocesium from the crowns of evergreen coniferous trees to the forest floor appeared to cause slower decreases in 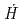 *(10) at 1 m height in early years than expected by the rate of
*(10) at 1 m height in early years than expected by the rate of 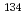 Cs and
Cs and 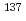 Cs decay.
Cs decay.
Malins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Katata, Genki*; Kubota, Tomohiro; Kuroda, Hisao*; Watanabe, Mirai*; Takahashi, Akiko*; Nakazato, Ryoji*; Tarui, Mika*; Matsumoto, Shunichi*; Nakagawa, Keita*; Numata, Yasuko*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tanaka, Taku*; Komatsu, Masabumi*; Gonze, M.-A.*; Sakashita, Wataru*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Nishina, Kazuya*; Ota, Masakazu; Ohashi, Shinta*; Calmon, P.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We applied modelling approaches to evaluate the past and future dynamics of  Cs in forests. In the model inter-comparison exercise using Fukushima data, six models with diverse model structures, processes, parameters and numerical approaches joined this exercise and the performance and uncertainties of the state-of-the-art models were explored. The inter-comparison revealed that, after appropriate calibration, the models reproduced the observed data reliably and the ranges of calculated trajectories were narrow in the early phase after the fallout. However, the envelope of the calculated model end points enlarged in long-term simulations over 50 years after the fallout. The model-inter comparison exercise emphasizes the importance of decadal data for various forest types and repetitive verification/validation processes using holistic, long-term data to improve the models and to update the forecasting capacity of the models.
Cs in forests. In the model inter-comparison exercise using Fukushima data, six models with diverse model structures, processes, parameters and numerical approaches joined this exercise and the performance and uncertainties of the state-of-the-art models were explored. The inter-comparison revealed that, after appropriate calibration, the models reproduced the observed data reliably and the ranges of calculated trajectories were narrow in the early phase after the fallout. However, the envelope of the calculated model end points enlarged in long-term simulations over 50 years after the fallout. The model-inter comparison exercise emphasizes the importance of decadal data for various forest types and repetitive verification/validation processes using holistic, long-term data to improve the models and to update the forecasting capacity of the models.