Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakada, Akira; Nakano, Masanao; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Futagawa, Kazuo; Yamada, Ryohei; Uchiyama, Rei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-062, 163 Pages, 2022/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2020 to March 2021. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Matsubara, Natsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-069, 163 Pages, 2021/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2019 to March 2020. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Mukai, Kazuo; Arai, Masanobu; Ito, Kazuhiro; Okawachi, Yasushi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 56(9), p.554 - 560, 2014/09
, 56(9), p.554 - 560, 2014/09
no abstracts in English
Ito, Kazuhiro; Tanabe, Hiromi; Kaneko, Yoshihisa; Kagota, Eiichi; Takahashi, Yasuo
Proceedings of 2013 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2013) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2013/04
The Monju is equipped with two types of hydrogen-meters to detect water leakage in steam generators. Since they are so highly-sensitive as to detect minor water leak from a steam generator tube, they sometimes detect hydrogen concentration increases at plant operational condition changes such as start-up without any water leak. No water leak was experienced during one year operation of the Startup Test up to 40% in 1995, although hydrogen concentration sometimes increased at plant operational condition changes. The H behavior of Monju IHTS during the previous Startup Test was examined and the following knowledge was obtained: The in-sodium H behaves in parallel with the IHTS sodium temperature. In-cover-gas H behavior is more complicated and sensitive to plant operational condition changes such as plant load changes than the in-sodium one. Both types of H-meters underwent a certain degree of zero level drift during one year operation.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Fukumoto, Kenichi*; Narui, Minoru*; Matsui, Hideki*; Ito, Kazuhiro; Yano, Yasuhide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(2), p.171 - 178, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to perform irradiation experiments under liquid metal environment in a nuclear reactor, an irradiation technique with sodium bonding irradiation capsules has been developed and a series of neutron irradiation experiments with sodium bonding irradiation capsule were performed in Joyo. The design and fabrication of sodium bonding capsule, sodium filling into capsules, capsule loading to Joyo, irradiation experiments, dismantling for irradiated capsule, removing the irradiated specimens from sodium filled capsules, and sodium cleaning the irradiated specimens were established through this study. Using the Joyo irradiation with the sodium bonding capsules where irradiation temperature was distributed uniformly, the irradiation creep experiment for highly purified V-4Cr-4Ti alloys, NIFS-Heat was carried out and the knowledge about the irradiation creep behavior of the alloys was obtained.
Ito, Kazuhiro; Omura, Akiko; Hoshiya, Taiji; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings P.29-32, p.29 - 32, 2004/10
The Joyo MK-III rated power operation was started in 2003 to do various irradiation test more efficiently. Promotion of the outside use is being advanced. As the part and consideration is being advanced about formation of irradiation equipment of low flux neutron field near the space. By this report, this, JOYO as a low neutron irradiation field is introduced.
; Saikawa, Takuya*; Masui, Tomohiko*; Arima, Toshihiro*
JNC TN9410 2001-014, 26 Pages, 2001/03
The experimental fast reactor "JOYO" served as the MK-II irradiation test bed core for testing fuel and material for FBR development for 18 years from 1982 to 2000. "JOYO" has no fuel failure since the initial criticality. Impurity concentrations of fission products data were accumulated in the primary argon gas and primary sodium during the MK-II core operation in order to obtain background value. 352 samples of primaly argon gas and the online gamma-ray monitor determined the fission products concentration data in the primary argon gas. In order to demonstrate the performance of the cold trap pre-filter, the cold trap pre-filter function confirmation tests were carried out in 1995 during 10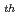 annual inspection. The
annual inspection. The  Cs concentration data in the primary sodium were determined by 10 samples of primary sodium. The in core tag gas release tests were carried out during 29th cycle to 31st cycle. The online gamma-ray monitor determined the activation tag gas concentration data in the primary argon gas These fission products concentration data, the cold trap pre-filter function confirmation tests data and in core tag gas release tests data were compiled, which were recorded on CD-ROM for user convenience.
Cs concentration data in the primary sodium were determined by 10 samples of primary sodium. The in core tag gas release tests were carried out during 29th cycle to 31st cycle. The online gamma-ray monitor determined the activation tag gas concentration data in the primary argon gas These fission products concentration data, the cold trap pre-filter function confirmation tests data and in core tag gas release tests data were compiled, which were recorded on CD-ROM for user convenience.
Iguchi, Tetsuo; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Ogita, Toshiyuki*; Nose, Shoichi; Harano, Hideki; Ito, Kazuhiro
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (9), p.79 - 88, 2000/12
None
Iguchi, Tetsuo; Watanabe, Kenichi*; *; Nose, Shoichi; Harano, Hideki;
JNC TY9400 2000-019, 34 Pages, 2000/05
None
Harano, Hideki; Nose, Shoichi;
JNC TN9400 2000-076, 34 Pages, 2000/05
lmmediate detection of fuel failure and subsequent precise identification of failed fuel assembiies are extremely important and indispensable for fast reactors from the viewpoint of their safety and reliability as well as the improvement of plant availability. ln order to develop the failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) technology, laser resonance ionization spectrometry (RIMS) has been proposed to be applied to the trace analysis of krypton and xenon contained in cover gas, Various promising features have been reported including the results which suggest the feasibility of the method to the on-power real-time monitoring, through the fundamental study using the RIMS device at the nuclear engineering research laboratory (NERL) of the university of Tokyo. Based on the information obtained above, we are developing a new laser FFDL system using RIMS which is planned to be introduced onto the fast experimental reactor JOY0. By the use of the system at the JOY0, isotope analysis can be performed with high sensitivity for not only radioactive but also stable elements in fission product (FP) and tag gas in the cover gas. This permits the improvement of irradiation technology and the immediate identification of failed fuel assemblies. For instance, it is possible to identify burst samples in the breach test of fuel cladding materials during irradiation. From the isotopic composition of the FP nuclides, the burnup of failed fuel can be estimated which allows the preliminary focusing in the FFDL. ln this paper, we review the fundamental study using the RIMS device at NERL and report the basic design of the laser FFDL system for the JOY0.
; ; Saikawa, Takuya*; Sukegawa, Kazuya*
JNC TN9410 2000-008, 66 Pages, 2000/03
The experimental fast reactor "JOYO" served as the MK-II irradiation bed core for testing fuel and material for FBR development for 15 years from 1982 to 1997. During the MK-II operation, impurities concentrations in the sodium and the argon gas were determined by 67 samples of primary sodium, 81 samples of secondary sodium, 75 samples of primary argon gas, 89 samples of secondary argon gas (the overflow tank) and 89 samples of secondary argon gas (the dump tank). The sodium and the argon gas purity control data were accumulated from in thirty-one duty operations, thirteen special test operations and eight annual inspections. These purity control results and related plant data were compiled into database, which were recorded on CD-ROM for user convenience. Purity control data include concentration of oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine, iron, nickel and chromium in sodium, concentration of oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane and helium in argon gas with the reactor condition.
Harano, Hideki; Nose, Shoichi; Ito, Kazuhiro
RIS2000 FINAL PROGRA, 0 Pages, 2000/00
None
; ; ; ; Yasu, Tetsunori; Morimoto, Makoto;
PNC TN9410 95-243, 48 Pages, 1995/09
The Register on Machinery and Tools is used for recording, summarizing, and accumulating the career of operation and maintenance, the operation experiences, and the results of research and development. It has been provided in order to secure equipment maintenance, safety control, and stable plant operation. Arrange and improvement of the Register on Machinery and tools is indispensable for preparing the technical reports (ex. "JOYO" Operation and Maintenance Experience Compile (JOMEC)), and for Job transfer from the person who was in charged of the system. This report summarizes the register from 1992 to 1994, related to the primary sodium purification system, the primary sodium sampling system, the gas chromatography monitor of primary cover gas, the primary argon gas sampling system, the sodium fill and drain system, the primary argon gas system, and the compressed air supply system. The conspicuous contents are as follows; (1)The electromagnetic pump (EMP) in the primary sodium purification system has been impossible to be started several times, because the purification line was blockaded. The EMP was coming back into operation successfully by changing over of the lines, etc. The blockade line was melted by temperature increasing of the flowing sodium at restored EMP. (2)The outlet valve of the primary sodium sampling system did not operate because of broken stem pin. It was repaired. (3)There were movement inferiority of the fore side valve of the dehumidified tower in the compressed air supply system, and damage of control air piping, etc. We successfully kept continuous operation by replacing the damage parts. After that, the fore side valve control unit was renewed in order to cope with superannuating of dehumidified control system. (4)The other systems had been favorably operated without particular trouble.
Chatani, Keiji; ; Ito, Chikara; Setyadi*; ;
PNC TN9410 94-032, 76 Pages, 1993/12
Deposition density and gamma dose rate of the radioactive corrosion product(CP) have been measured along the primary sodium loop in Experimental Fast Reactor "JOYO" during every annual inspection in order to make clear the CP behavior and to verify the CP behavior analysis code "PSYCHE". As a result of the previous seven CP measurements, it is made clear that major CP nuclides deposited in the primary sodium loops are  Mn on the cold leg (CL) piping (from the outlet of the Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX) to the inlet of the reactor vessel (R/V)) and
Mn on the cold leg (CL) piping (from the outlet of the Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX) to the inlet of the reactor vessel (R/V)) and  Co on the hot leg (HL) piping (from the outlet of the R/V to the inlet of the IHX), and so on. In this study the CP behavior has been evaluated by using the measurement results during the 10th annual inspection. The results of this study are summarized as follows: (1)The distribution of the measured CP deposition density and gamma dose rate show the same tendency observed previously and no unusual phenomenon is observed. (2)The buildup of
Co on the hot leg (HL) piping (from the outlet of the R/V to the inlet of the IHX), and so on. In this study the CP behavior has been evaluated by using the measurement results during the 10th annual inspection. The results of this study are summarized as follows: (1)The distribution of the measured CP deposition density and gamma dose rate show the same tendency observed previously and no unusual phenomenon is observed. (2)The buildup of  Mn and
Mn and  Co is seemed to reach saturation because the average CP deposition density and the averaged dose rate is the same value as measured in the 9th annual inspection. (a)Deposition density of
Co is seemed to reach saturation because the average CP deposition density and the averaged dose rate is the same value as measured in the 9th annual inspection. (a)Deposition density of  Mn is 30kBq/cm
Mn is 30kBq/cm for HL piping, 60 kBq/cm
for HL piping, 60 kBq/cm at CL(1) piping (from the outlet of the IHX to the inlet of the pump) and 130 kBq/cm
at CL(1) piping (from the outlet of the IHX to the inlet of the pump) and 130 kBq/cm at CL(2) piping (from the outlet of the pump to the inlet of the R/V). Deposition density of
at CL(2) piping (from the outlet of the pump to the inlet of the R/V). Deposition density of  Co is 9 kBq/cm
Co is 9 kBq/cm at HL piping, 3kBq/cm
at HL piping, 3kBq/cm at CL(1) piping and 9 kBq/cm
at CL(1) piping and 9 kBq/cm at CL(2) piping. (b)Dose rate is 0.5mSV/h at HL piping, 0.6mSV/h at CL(1) piping and 1 mSV/h at CL(2) piping. (3)As a comparison between "PSYCHE" calculation(C) and measurement(E), C/E ratio is 0.9 to 1.5 for CP deposition density, and 1.6 for dose rate. The agreement between calculation and measurement is fairly good.
at CL(2) piping. (b)Dose rate is 0.5mSV/h at HL piping, 0.6mSV/h at CL(1) piping and 1 mSV/h at CL(2) piping. (3)As a comparison between "PSYCHE" calculation(C) and measurement(E), C/E ratio is 0.9 to 1.5 for CP deposition density, and 1.6 for dose rate. The agreement between calculation and measurement is fairly good.
Isozaki, Kazunori; ; Ito, Hideaki; ; Chatani, Keiji; ;
PNC TN9520 93-006, 198 Pages, 1992/11
None
; Chatani, Keiji; ; ; ;
PNC TN9410 92-345, 166 Pages, 1992/10
An evaluation about the radioactive corrosion product (CP) behaviour in sodium cooling systems of a fast reactor is presented in this report, based on the obtained measurement results in the operating experience of JOYO. The objective of this work is to update the calculational model for predicting the release and deposition behaviour of CP in primary sodium cooling systems of a fast reactor. The evaluation results are as follows; (1)The main radionuclides of CPs transported to the out-of-reactor primary sodium loop are  Mn and
Mn and  Co, and
Co, and  Mn is the most dominant. On the other hand,
Mn is the most dominant. On the other hand,  Co is the most dominant nuclide found in the liquid waste from spent fuel cleaning, which is produced by removal of activated CP deposits from surfaces of core sub-assemblies in sodium cleaning. (2)The deposition rate of
Co is the most dominant nuclide found in the liquid waste from spent fuel cleaning, which is produced by removal of activated CP deposits from surfaces of core sub-assemblies in sodium cleaning. (2)The deposition rate of  Mn onto the hot-leg (HL) piping walls corresponds fairly with the saturation of radioactivity induced in core materials by activation, on the other hand, that onto the cold-leg (CL) piping walls has been being accelerated. The deposition rate of
Mn onto the hot-leg (HL) piping walls corresponds fairly with the saturation of radioactivity induced in core materials by activation, on the other hand, that onto the cold-leg (CL) piping walls has been being accelerated. The deposition rate of  Co, due to the dependency of activation and release in a core, is strongly affected by the re-fuelling pattern and the oxygen concentration in sodium, and suggests the detouching process of deposits from wall surfaces. (3)Although
Co, due to the dependency of activation and release in a core, is strongly affected by the re-fuelling pattern and the oxygen concentration in sodium, and suggests the detouching process of deposits from wall surfaces. (3)Although  Mn was transported and deposited preferentially in the HL of the primary cooling system in an early stage, the transport and deposition in the CL regions has overcomed that in the HL along operating time.
Mn was transported and deposited preferentially in the HL of the primary cooling system in an early stage, the transport and deposition in the CL regions has overcomed that in the HL along operating time.  Co was transported and deposited preferentially in the HL and the similar distribution pattern has been maintained thoroughout the operating periods. (4)The solution - precipitation model for CP behaviour in flowing sodium system was verified via the sensitivity test of model parameters and optimizing them on the above mentioned results, giving the measured to caluculated values of 1.36 or 1.03 for
Co was transported and deposited preferentially in the HL and the similar distribution pattern has been maintained thoroughout the operating periods. (4)The solution - precipitation model for CP behaviour in flowing sodium system was verified via the sensitivity test of model parameters and optimizing them on the above mentioned results, giving the measured to caluculated values of 1.36 or 1.03 for  Mn or
Mn or  Co buildup, and 1.61 ...
Co buildup, and 1.61 ...
; Chatani, Keiji; ; ;
PNC TN9410 92-224, 81 Pages, 1992/07
The radioactive corrosion product (CP) deposition density and gamma dose rate have been measured along the primary sodium circuits in Experimental Fast Reactor "JOYO" during every annual inspection and the CP behavior analysis code "PSYCHE" has been verified with measurement data in order to contribute the reduction of exposure dose of plant personal. The deposition density is measured by using a pure germanium detector system and determined by multiplying count rates by conversion factor. Gamma dose rate is measured with CaSO thermoluminescence dosimeters (TLD). This report presents measurement results during the 9th annual inspection and the evaluation results for all data measured so far. The results on this study are summarized as follows: (1)Major CP nuclides deposited along the primary sodium circuits are
thermoluminescence dosimeters (TLD). This report presents measurement results during the 9th annual inspection and the evaluation results for all data measured so far. The results on this study are summarized as follows: (1)Major CP nuclides deposited along the primary sodium circuits are  Mn and
Mn and  Co.
Co.  Mn is most dominant isotopes. Amounts of deposited
Mn is most dominant isotopes. Amounts of deposited  Mn is about twenty times as much as those of
Mn is about twenty times as much as those of  Co. (2)
Co. (2) Mn is deposited mainly on the cold leg pipings between the outlet of the intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) and the inlet of the reactor vessel.
Mn is deposited mainly on the cold leg pipings between the outlet of the intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) and the inlet of the reactor vessel.  Co is deposited mainly on the hot leg pipings between the outlet of the reactor vessel and the inlet of IHX. (3)The buildup of
Co is deposited mainly on the hot leg pipings between the outlet of the reactor vessel and the inlet of IHX. (3)The buildup of  Mn is saturated at 4
Mn is saturated at 4 4.5 EFPY. The averaged dose rate of the pipings is saturated at about 1.5mSV/h. The dose rates of IHX and primary sodium pump are about 1.5 mSv/h and 2.1 mSv/h, respectively. The dose rate distributions around IHX and primary sodium pump show the peaks at the stagnant part of the flow and at the turbulence part. (4)Calculation by "PSYCHE" and measurement are compared. Calculation-to-measurement ratio is 1.2 for the CP deposition density and 1.5 for the dose rate. It can be said that the features of the CP behavior in the primary circuit of "JOYO" is made clear. The more effort will be required for the evaluation of CP behavior for subassemblies such as outer reflectors, clearness of ...
4.5 EFPY. The averaged dose rate of the pipings is saturated at about 1.5mSV/h. The dose rates of IHX and primary sodium pump are about 1.5 mSv/h and 2.1 mSv/h, respectively. The dose rate distributions around IHX and primary sodium pump show the peaks at the stagnant part of the flow and at the turbulence part. (4)Calculation by "PSYCHE" and measurement are compared. Calculation-to-measurement ratio is 1.2 for the CP deposition density and 1.5 for the dose rate. It can be said that the features of the CP behavior in the primary circuit of "JOYO" is made clear. The more effort will be required for the evaluation of CP behavior for subassemblies such as outer reflectors, clearness of ...
Morimoto, Makoto; Okubo, Toshiyuki; ; ; ; ;
PNC TN9410 91-334, 64 Pages, 1991/10
An failed fuel detection and location system (FFDL) using a sipping method is adopted as the FFDL of Joyo. FFDL has not operated since the first falled fuel simulated (FFDL-I) test in April, 1985 because Joyo has not yet experienced any operation with breached fuels. Therefore, the operational test (II) of FFDL was carried out on July 12 19, 1991 for a preparation of the FFDL-II test which is scheduled in 1992. Main results from the test are as follows ; (1)The adequacy of the functions and operating procedure of FFDL was reaffirmed and the operating experience was gained. (2)Radioactivity measurement was conducted by FFDL for six subassemblies and their integrity was confirmed.
19, 1991 for a preparation of the FFDL-II test which is scheduled in 1992. Main results from the test are as follows ; (1)The adequacy of the functions and operating procedure of FFDL was reaffirmed and the operating experience was gained. (2)Radioactivity measurement was conducted by FFDL for six subassemblies and their integrity was confirmed.