Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Takanori; Suzuki, Koji*; Miyo, Tatsuya*; Ito, Takayoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1059, p.168956_1 - 168956_9, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Radial collimators (RC) with a 0.5 mm gauge size (GS) were specially designed for high-pressure neutron diffraction experiments and their performance and efficacy were investigated. The RCs with nominal GS of 0.75 mm, 1.5 mm, and 3.0 mm effectively exhibited GS of 0.50 mm, 1.07 mm, and 2.78 mm, respectively. The transmissions of all three RCs were almost equivalent. The assessment using a P-E press and a DAC revealed that the anvil scattering was considerably minimized and the sample-to-anvil signal ratio reached values of 0.5 and 2.0 for the PE press and DAC, respectively, when using the 0.5 mm-GS RCs. These results indicate that the 0.5mm-GS RCs have been fabricated as intended and exhibit efficacy for the high-pressure-neutron diffraction experiments, specifically those exceeding 30 GPa. Among those ever manufactured for neutron scattering experiments, the RCs display the smallest GS.
Nakajima, Taro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Oike, Hiroshi*; Kagawa, Fumitaka*; Kikkawa, Akiko*; Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Tokura, Yoshinori*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(1), p.014424_1 - 014424_5, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:34.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the phase-transition kinetics of magnetic skyrmion lattice (SkL) in MnSi by means of stroboscopic small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Temporal evolutions of SANS patterns were measured with time resolution of 13 ms while sweeping temperature as fast as 50 Ks . It turned out that the paramagnetic-to-SkL transition immediately occurs upon traversing the equilibrium phase boundary on the rapid cooling, whereas the SkL-to-conical transition can be kinetically avoided to realize the low-temperature metastable SkL with a long-range magnetic order. The formation of the metastable SkL was found to be strongly dependent not only on cooling rate, but also on magnetic eld and trajectory in the H-T phase diagram.
. It turned out that the paramagnetic-to-SkL transition immediately occurs upon traversing the equilibrium phase boundary on the rapid cooling, whereas the SkL-to-conical transition can be kinetically avoided to realize the low-temperature metastable SkL with a long-range magnetic order. The formation of the metastable SkL was found to be strongly dependent not only on cooling rate, but also on magnetic eld and trajectory in the H-T phase diagram.
Kawasaki, Takuro; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.*; Aizawa, Kazuya
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51(3), p.630 - 634, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.97(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ojima, Mayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Ito, Takayoshi*; Gong, W.; Vogel, S. C.*; Inoue, Junya*; Tomota, Yo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51(3), p.746 - 760, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:90.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Suzuki, Jiro*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1021(1), p.012015_1 - 012015_5, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:80.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)An event recording method for data acquisition for neutron scattering and its analysis provides a lot of benefits for the measurement of time-resolved and time transient phenomena. Almost all instruments installed in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC have adopted this method since the first beam came and have achieved good results. On the other hand, our treatment of event recorded data leaves room for improvements and developments to achieve more effective utilization. This paper introduces one of the applications of the event recording method to achieve the pseudo real-time data treatment in MLF in a simple way.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
Nakatani, Takeshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Moriyama, Kentaro*
Proceedings of 11th New Opportunities for Better User Group Software (NOBUGS 2016) (Internet), p.76 - 79, 2016/10
The public beamlines in MLF, J-PARC carry out many kinds of measurements and produce huge experimental data by users. It is important to be user-friendly and automated control software for efficient measurements. We have developed the MLF standard instrument control software framework "IROHA2". IROHA2 consists of the device control server to control and monitor each device, the instrument management server to authenticate a user, manage a measurement and configure an instrument setup, the sequence management server to do an automatic measurement and the integrate control server to unify instrument control and monitoring. Because each software component of IROHA2 has a web interface, we are able to use its all functions under multi-platform environment via a web browser. IROHA2 is also connected to and cooperated with several other systems which are the experimental status system, the MLF integrated authentication system and the MLF business database.
Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Uozumi, Yuki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Takayoshi*; Kubota, Masato; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Sheoran, G.*; Mitkova, M.*
Physica Status Solidi (A), 213(7), p.1894 - 1903, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:34.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Suzuki, Jiro*; Nakatani, Takeshi
JAEA-Testing 2016-001, 91 Pages, 2016/06
Manyo Library is a software framework for developing analysis software of neutron scattering data produced at MLF, J-PARC. This software framework is required to work on many instruments in MLF and to include base functions applied to various scientific purposes at beam lines. This framework mainly consists of data containers, which enable to store 1, 2 and 3 dimensional axes data for neutron scattering. Data containers have many functions to calculate four arithmetic operations with errors distribution between containers, to store the meta-data about measurements and to read or write text file. Since Manyo Library is built in C++ language, we' ve introduced the technology to call C++ function from Python environment into the framework. As results, we have already developed a lot of software for data reduction, analysis and visualization, which are utilized widely in beam lines at MLF. This document is the manual for the beginner to touch this framework.
Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Uozumi, Yuki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Takayoshi*; Kubota, Masato; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ailavajhala, M.*; Wolf, K.*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031023_1 - 031023_6, 2015/09
We report recent results of time-resolved neutron reflectivity measurements for silver photo-diffusion into Ge S
S (x=0.20, 0.33, 0.40) films performed on BL17 (SHARAKU). It is well known that silver diffuses into Ge-chalcogenide layer by visible light exposure with a distinct diffusion front, where the silver concentration abruptly drops off. Using an event recording system at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, neutron reflectivity profiles were collected with a time-resolution of 30 seconds in the shortest case. It was found from the measurements that a relatively stable Ag-rich phase in the reaction layer is firstly formed, and then, slower diffusion occurs at the interface between Ag-rich and Ag-poor layers. Fourier transform analysis showed that the position of the interface is essentially fixed. This result is in contrast to the previously reported model of silver diffusion that postulates a mechanism involving progression of the diffusion front. The results of the measurements on Ag/Ge-Se films performed on the INTER instrument at ISIS are also reported.
(x=0.20, 0.33, 0.40) films performed on BL17 (SHARAKU). It is well known that silver diffuses into Ge-chalcogenide layer by visible light exposure with a distinct diffusion front, where the silver concentration abruptly drops off. Using an event recording system at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, neutron reflectivity profiles were collected with a time-resolution of 30 seconds in the shortest case. It was found from the measurements that a relatively stable Ag-rich phase in the reaction layer is firstly formed, and then, slower diffusion occurs at the interface between Ag-rich and Ag-poor layers. Fourier transform analysis showed that the position of the interface is essentially fixed. This result is in contrast to the previously reported model of silver diffusion that postulates a mechanism involving progression of the diffusion front. The results of the measurements on Ag/Ge-Se films performed on the INTER instrument at ISIS are also reported.
 Sn strand at cryogenic temperature
Sn strand at cryogenic temperatureHarjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Ito, Takayoshi*; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Aizawa, Kazuya
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031001_1 - 031001_5, 2015/09
Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi*; Morii, Yukio*; Gong, W.; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Tomota, Yo; Lutterotti, L.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031022_1 - 031022_6, 2015/09
Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Uozumi, Yuki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Takayoshi*; Kubota, Masato; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ailavajhala, M.*; Latif, M. R.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 619(1), p.012046_1 - 012046_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:95.66(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We report the results of time-resolved neutron reflectivity measurements of Ag/a- Ge S
S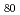 /Si and a- Ge
/Si and a- Ge Se
Se /Ag/ Si films taken while the films are exposed to visible light. Silver diffuses into an amorphous (a-) chalcogenide layer while visible light illuminates Ag/a-chalcogenide films. Neutron reflectometry is a suitable technique probing time evolution of the multi-layer structure without damaging the sample by the probe beam itself. It was found from the measurements of Ag/a-Ge
/Ag/ Si films taken while the films are exposed to visible light. Silver diffuses into an amorphous (a-) chalcogenide layer while visible light illuminates Ag/a-chalcogenide films. Neutron reflectometry is a suitable technique probing time evolution of the multi-layer structure without damaging the sample by the probe beam itself. It was found from the measurements of Ag/a-Ge S
S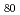 /Si films that a relatively stable Ag-rich phase in the reaction layer is first formed, and then, slower diffusion occurs at the interface between Ag-rich and Ag-poor layers. This result is in contrast to the previously reported model of silver diffusion that suggests a mechanism involving progression of the diffusion front. From the measurements of a-Ge
/Si films that a relatively stable Ag-rich phase in the reaction layer is first formed, and then, slower diffusion occurs at the interface between Ag-rich and Ag-poor layers. This result is in contrast to the previously reported model of silver diffusion that suggests a mechanism involving progression of the diffusion front. From the measurements of a-Ge Se
Se /Ag/ Si films, we found enormous changes in the neutron reflectivity profile, including loss of total reflection region, with continuous illumination even after forming one homogeneous layer, which was about 60 min after starting illumination. At this stage, clear off-specular scattering was observed by a linear detector and a surface roughness was observed with naked eyes.
/Ag/ Si films, we found enormous changes in the neutron reflectivity profile, including loss of total reflection region, with continuous illumination even after forming one homogeneous layer, which was about 60 min after starting illumination. At this stage, clear off-specular scattering was observed by a linear detector and a surface roughness was observed with naked eyes.
 S
S (
( =0.2 and 0.4) films using neutron reflectometry
=0.2 and 0.4) films using neutron reflectometrySakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Uozumi, Yuki; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Takayoshi*; Kubota, Masato; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ailavajhala, M.*; Latif, R.*; et al.
Canadian Journal of Physics, 92(7/8), p.654 - 658, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.3(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report our recent results of neutron reflectivity measurements for Ag/a-Ge  S
S (x=0.2, 0.4) films under light illumination. The neutron reflectivity measurements have been performed on a polarized neutron reflectometer (BL17, SHARAKU) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Japan. By using the time-of flight instrument with intensive pulsed neutrons produced by 300kW proton beams, time evolution of the neutron reflectivity under a light illumination has been revealed, with at least 2-min time resolution. From the detailed analysis, it was found for Ag 50nm/Ge
(x=0.2, 0.4) films under light illumination. The neutron reflectivity measurements have been performed on a polarized neutron reflectometer (BL17, SHARAKU) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Japan. By using the time-of flight instrument with intensive pulsed neutrons produced by 300kW proton beams, time evolution of the neutron reflectivity under a light illumination has been revealed, with at least 2-min time resolution. From the detailed analysis, it was found for Ag 50nm/Ge  S
S  150nm films under a light illumination from the Ag layer side that there are two types of diffusion processes: a fast change observed in the first 10 min after illumination using a xenon lamp, which is then followed by a slow change observed after a 1 hour of additional light exposure. The result indicates that there is a comparatively stable (metastable) state in the Ag-doped Ge
150nm films under a light illumination from the Ag layer side that there are two types of diffusion processes: a fast change observed in the first 10 min after illumination using a xenon lamp, which is then followed by a slow change observed after a 1 hour of additional light exposure. The result indicates that there is a comparatively stable (metastable) state in the Ag-doped Ge  S
S  layer in terms of Ag composition, and the next silver diffusion process occurs by affecting the Ag-doped Ge
layer in terms of Ag composition, and the next silver diffusion process occurs by affecting the Ag-doped Ge  S
S  layer / interface. This coincides with the Ge
layer / interface. This coincides with the Ge  S
S  results of Wagner et al. obtained for Ag/As-S films. These results are also in accord with the results reported by some of us by modeling of the Ag transport in Ge-Se glass showing the presence of slow and fast moving Ag ions. Our result demonstrated that the idea of a two-step reaction process can be applied to Ge-chalcogenide system. We also discuss illumination-side dependence and Ge-composition dependence of reaction process.
results of Wagner et al. obtained for Ag/As-S films. These results are also in accord with the results reported by some of us by modeling of the Ag transport in Ge-Se glass showing the presence of slow and fast moving Ag ions. Our result demonstrated that the idea of a two-step reaction process can be applied to Ge-chalcogenide system. We also discuss illumination-side dependence and Ge-composition dependence of reaction process.
Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Abe, Jun*; Gong, W.; Ito, Takayoshi*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Iwahashi, Takaaki
Materials Science Forum, 777, p.12 - 18, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Harjo, S.; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Abe, Jun; Gong, W.; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; Ito, Takayoshi*; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Machiya, Shutaro*; Osamura, Kozo*
Materials Science Forum, 777, p.84 - 91, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Kubota, Masato; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Chinese Journal of Physics, 50(2), p.161 - 170, 2012/04
 Sn cable-in-conduit conductors
Sn cable-in-conduit conductorsHemmi, Tsutomu; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi; Matsui, Kunihiro; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nakajima, Hideo; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Hiroshi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 21(3), p.2028 - 2031, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:49.97(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Residual strain in conductors is caused by the difference in the coefficient of expansion between Nb Sn strands and the jacket over a temperature range of 5 - 923 K. The superconducting properties of strands vary significantly, depending on the strain. It is important to clarify the residual strain as part of the evaluation of superconducting performance. However, the residual strain of strands in the conductor has not been measured so far because of their complicated configuration and their location in a jacket. The engineering materials diffractometer "Takumi" in J-PARC can measure residual strain with a relative accuracy of around 0.02%, using neutron diffraction. In this study, the Takumi was applied to the measurement of residual strain in strands for the ITER TF conductor. Results indicate that the residual strain of strands in the conductor can be determined, thereby clarifying the mechanism of residual strain and its relationship to superconducting performance.
Sn strands and the jacket over a temperature range of 5 - 923 K. The superconducting properties of strands vary significantly, depending on the strain. It is important to clarify the residual strain as part of the evaluation of superconducting performance. However, the residual strain of strands in the conductor has not been measured so far because of their complicated configuration and their location in a jacket. The engineering materials diffractometer "Takumi" in J-PARC can measure residual strain with a relative accuracy of around 0.02%, using neutron diffraction. In this study, the Takumi was applied to the measurement of residual strain in strands for the ITER TF conductor. Results indicate that the residual strain of strands in the conductor can be determined, thereby clarifying the mechanism of residual strain and its relationship to superconducting performance.
Ito, Takayoshi; Harjo, S.; Osamura, Kozo*; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Awaji, Satoshi*; Machiya, Shutaro*; Oguro, Hidetoshi*; Nishijima, Gen*; Takahashi, Koki*; Matsui, Kunihiro; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 681, p.209 - 214, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionXu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi; Li, J.*; Tomota, Yo*
Zairyo To Purosesu (CD-ROM), 24, p.547 - 549, 2011/03