Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Be produced by the strongest solar proton event during the holocene
Be produced by the strongest solar proton event during the holoceneSpiegl, T. C.*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Langematz, U.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Chhin, R.*; Noda, Satoshi*; Miyake, Fusa*; Kusano, Kanya*; Schaar, K.*; Kunze, M.*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 127(13), p.e2021JD035658_1 - e2021JD035658_21, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.31(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)The abundance of cosmogenic isotopes in natural archives carries important information about the complex pathways from their source in the upper atmosphere to their deposition via atmospheric transport processes. Here, we use a new modelling framework to (a) estimate the  Be production yield for the 774 CE/775 event, (b) evaluate the performance of our model framework by comparing the model results to four ice core records and (c) investigate the atmospheric pathways with a state-of-the-art climate model in detail. The results give new constraints regarding the seasonal timing of the event, underpin the role of the background conditions in the stratosphere, and highlight regional variations in the cosmogenic surface flux.
Be production yield for the 774 CE/775 event, (b) evaluate the performance of our model framework by comparing the model results to four ice core records and (c) investigate the atmospheric pathways with a state-of-the-art climate model in detail. The results give new constraints regarding the seasonal timing of the event, underpin the role of the background conditions in the stratosphere, and highlight regional variations in the cosmogenic surface flux.
 -Mg alloys based on peak asymmetry analysis
-Mg alloys based on peak asymmetry analysisEgusa, Daisuke*; Manabe, Ryo*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Sato, Shigeo*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Today Communications (Internet), 31, p.103344_1 - 103344_6, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:66.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ishii, Mamoru*; Shiota, Daiko*; Tao, Chihiro*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Ishii, Takako*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Koga, Kiyokazu*; Kubo, Yuki*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.108_1 - 108_20, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.39(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We surveyed the relationship between the scale of space weather events and their occurrence rate in Japan and we discussed the social impact of these phenomena during the Project for Solar-Terrestrial Environment Prediction (PSTEP). The information was compiled for domestic users of space weather forecasts for appropriate preparedness against space weather disasters. This paper gives a comprehensive summary of the survey, focusing on the fields of electricity, satellite operations, communication and broadcasting, satellite positioning usage, aviation, human space activity, and daily life on the Earth's surface, using the cutting-edge knowledge of space weather. Quantitative estimations of the economic impact of space weather events on electricity and aviation are also given.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.19(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Tomota, Yo*; Ojima, Mayumi*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.*; Sato, Shigeo*; Ung r, T.*
r, T.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 743, p.32 - 39, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:80.65(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) observation of dislocation evolution in ferritic and austenitic stainless steels under tensile deformation by using neutron diffraction
observation of dislocation evolution in ferritic and austenitic stainless steels under tensile deformation by using neutron diffractionSato, Shigeo*; Kuroda, Asumi*; Sato, Kozue*; Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Harjo, S.; Tomota, Yo*; Saito, Yoichi*; Todoroki, Hidekazu*; Onuki, Yusuke*; Suzuki, Shigeru*
Tetsu To Hagane, 104(4), p.201 - 207, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:44.29(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Tomota, Yo*; Sato, Shigeo*; Uchida, M.*; Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Materials Science Forum, 905, p.25 - 30, 2017/08
Tomota, Yo*; Sato, Shigeo*; Harjo, S.
Tetsu To Hagane, 103(2), p.73 - 85, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:62.95(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Onuki, Yusuke*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Sato, Shigeo*; Xu, P. G.; Ishigaki, Toru*; Saito, Yoichi*; Todoroki, Hidekazu*; Hayashi, Makoto*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(5), p.1579 - 1584, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:88.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Shigeo*; Onuki, Yusuke*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi*; Tashiro, Hitoshi*; Todoroki, Hidekazu*; Suzuki, Shigeru*
Kinzoku, 86(8), p.654 - 660, 2016/08
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Yamada, Rui*; Tsubaki, Shinki*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Sato, Shigeo*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Machida, Akihiko; Saida, Junji*
Metals, 6(1), p.12_1 - 12_11, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Elastic deformation behaviors of as-cast and annealed eutectic and hypoeutectic Zr-Cu-Al bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) were investigated on a basis of different strain-scales determined by X-ray scattering and the strain gauge. The microscopic strains determined by Direct-space method (DSM) and Q-space method (QSM) were compared with the macroscopic strain measured by the strain gauge, and the difference in the deformation mechanism between eutectic and hypoeutectic Zr-Cu-Al BMGs was investigated by their correlation. The eutectic Zr Cu
Cu Al
Al BMG obtains more homogeneous microstructure by free-volume annihilation after annealing, improving a resistance to deformation but degrading ductility because of a decrease in the volume fraction of WBRs (Weakly-Bonded Regions) with relatively high mobility. On the other hand, the as-cast hypoeutectic Zr
BMG obtains more homogeneous microstructure by free-volume annihilation after annealing, improving a resistance to deformation but degrading ductility because of a decrease in the volume fraction of WBRs (Weakly-Bonded Regions) with relatively high mobility. On the other hand, the as-cast hypoeutectic Zr Cu
Cu Al
Al BMG originally has homogeneous microstructure, but loses its structural and elastic homogeneities because of nanocluster formation after annealing. Such structural changes after annealing might develop unique mechanical properties showing no degradations of ductility and toughness for the structural-relaxed hypoeutectic BMGs.
BMG originally has homogeneous microstructure, but loses its structural and elastic homogeneities because of nanocluster formation after annealing. Such structural changes after annealing might develop unique mechanical properties showing no degradations of ductility and toughness for the structural-relaxed hypoeutectic BMGs.
Sato, Shigeo*; Shobu, Takahisa; Sato, Kozue*; Ogawa, Hiromi*; Wagatsuma, Kazuaki*; Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Tashiro, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Shigeru*
ISIJ International, 55(7), p.1432 - 1438, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:53.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To characterize the distribution and anisotropy of dislocations in cold-drawn pearlitic steel wires, X-ray diffraction line-profile analysis was performed using synchrotron radiation micro-beams. The plastic shear strain was generally more severe near the surface than the center of the wire, whereas the dislocation density distribution was almost constant from the center to the surface. On the other hand, the dislocation rearrangement, which evolves the dislocation cell structure, progressed closer to the surface. It was also revealed that a difference between the hardness in axial and transverse wire directions could be explained by anisotropic dislocation density. Line-profile analysis based on diffraction data at elevated temperatures was performed. Whereas the cementite recovery progressed at a constant rate, the ferrite phase recovery rate was temperature-dependent, suggesting that the ferrite phase recovery was less related to that of the cementite phase.
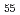 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing ZrC particles by synchrotron X-ray diffraction
bulk metallic glass containing ZrC particles by synchrotron X-ray diffractionSuzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Katsuyama, Jinya; Kato, Hidemi*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Sato, Shigeo*
Scripta Materialia, 66(10), p.801 - 804, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:37.98(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Compressive deformation mechanism of a Zr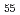 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing 10vol.%ZrC (ZrC-BMG) was evaluated by measuring the residual strains in the compressive deformed samples using the synchrotron X-ray diffraction and also evaluating the localized deformation behavior around the ZrC particles by the finite element analysis. Phase stress shared by the metallic glass matrix was increased before macroscopic yielding due to local plastic deformation around the ZrC particles. After macroscopic yielding, the phase stress shared by the ZrC phase was drastically increased, and finally the ZrC-BMG was fractured by breaking the ZrC particles reaching its fracture strength.
bulk metallic glass containing 10vol.%ZrC (ZrC-BMG) was evaluated by measuring the residual strains in the compressive deformed samples using the synchrotron X-ray diffraction and also evaluating the localized deformation behavior around the ZrC particles by the finite element analysis. Phase stress shared by the metallic glass matrix was increased before macroscopic yielding due to local plastic deformation around the ZrC particles. After macroscopic yielding, the phase stress shared by the ZrC phase was drastically increased, and finally the ZrC-BMG was fractured by breaking the ZrC particles reaching its fracture strength.
Sakurai, Eiko*; Yanai, Kazuhiko*; Ishii, Keizo*; Fujiki, Kota*; Hiraishi, Shingo*; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Okamura, Nobuyuki*; Yokoyama, Akihito; Kada, Wataru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 84, 2012/01
Harada, Satoshi*; Ehara, Shigeru*; Ishii, Keizo*; Sato, Takahiro; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 89, 2012/01
Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Keizo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Arakawa, Kazuo; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.113 - 116, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new detection apparatus for both low energy X-rays and back-scattered protons of MeV energy and its measurement system were developed. The detection apparatus consists of a multi-element detector, pre-amplifiers with active reset system and so on. The detector elements are arranged in the shape of a pentagonal pyramid and fully cover the sample. On each one detection side, 9 detector elements are arranged. The entire detection system consists thus of 45 detector elements. The micro-beam irradiates the sample through the center of the pentagonal pyramid and X-rays emitted from the sample are detected in close to  geometry. This novel detection setup has about 10 times the sensitivity of a conventional Micro-PIXE camera. The counting rate of back-scattered protons per detection element is small despite lack of a passive absorber. It appears possible that X-rays from the very small quantity of elements could also be detected. The advantage over a conventional Micro-PIXE camera includes simultaneous detection of back-scattered protons from N, C and O.
geometry. This novel detection setup has about 10 times the sensitivity of a conventional Micro-PIXE camera. The counting rate of back-scattered protons per detection element is small despite lack of a passive absorber. It appears possible that X-rays from the very small quantity of elements could also be detected. The advantage over a conventional Micro-PIXE camera includes simultaneous detection of back-scattered protons from N, C and O.
Harada, Satoshi*; Tamakawa, Yoshiharu*; Ishii, Keizo*; Tanaka, Akira*; Sato, Takahiro; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Arakawa, Kazuo; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 189(1-4), p.437 - 442, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)To study the interactions between the induction of radiation-induced apoptosis and trace elements kinetics, human leukemia cells were irradiated in vitro by  Co
Co  rays, after which the cells were evaluated for the detection of apoptosis and trace element imaging was carried out. The frequency of apoptosis was obtained by microscopic assay using TUNEL staining. The trace element distribution in the cell was determined by micro-PIXE. In the early phase of apoptosis, the maximum level of Fe accumulation was observed in the cell stroma. In the mid to end phase, Fe accumulation was diminished, and instead, Ca accumulation increased and Zn decreased in the nucleus. There appear to be two steps for the development of apoptosis: (1) the signaling from cell stroma to nucleus by Fe or an Fe-containing enzyme; and (2) the degeneration of the nucleus by Ca-dependent enzyme, and release of Zn from digested nucleus. Those strong accumulations may be new markers for apoptosis.
rays, after which the cells were evaluated for the detection of apoptosis and trace element imaging was carried out. The frequency of apoptosis was obtained by microscopic assay using TUNEL staining. The trace element distribution in the cell was determined by micro-PIXE. In the early phase of apoptosis, the maximum level of Fe accumulation was observed in the cell stroma. In the mid to end phase, Fe accumulation was diminished, and instead, Ca accumulation increased and Zn decreased in the nucleus. There appear to be two steps for the development of apoptosis: (1) the signaling from cell stroma to nucleus by Fe or an Fe-containing enzyme; and (2) the degeneration of the nucleus by Ca-dependent enzyme, and release of Zn from digested nucleus. Those strong accumulations may be new markers for apoptosis.
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sato, Takahiro*; Ishii, Keizo*; Sugimoto, Asuka*; Matsuyama, Shigeo*
International Journal of PIXE, 9(3&4), p.217 - 225, 1999/11
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Sato, Shigeo*
no journal, ,
Residual stress measurements using neutron and X-ray diffractions are applicable to crystalline materials whereas the strain measurement in amorphous materials had been difficult. Recently, Q-space method, which can evaluate the strain from peak shift of 1st halo peak measured by synchrotron X-ray, and Direct space method, which can evaluate the strain from changes in local structures obtained by the radial distribution function, have been reported by Poulsed et al. In this study, the evaluation of tensile deformation in Zr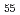 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu metallic glass using Q-space method was discussed by using neutron diffraction.
metallic glass using Q-space method was discussed by using neutron diffraction.
Sakurai, Eiko*; Yanai, Kazuhiko*; Ishii, Keizo*; Oyama, Ryohei*; Sakamaki, Manabu*; Yamanaka, Kentaro*; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English