Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Koike, Yuko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; Nagai, Shinji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-046, 164 Pages, 2024/03
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories conducts environmental radiation monitoring around the reprocessing plant in accordance with the "Safety Regulations for Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Part IV: Environmental Monitoring". This report summarizes the results of environmental radiation monitoring conducted during the period from April 2022 to March 2023 and the results of dose calculations for the surrounding public due to the release of radioactive materials into the atmosphere and ocean. In the results of the above environmental radiation monitoring, many items were affected by radioactive materials emitted from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Company, Incorporated (changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016), which occurred in March 2011. Also included as appendices are an overview of the environmental monitoring plan, an overview of measurement methods, measurement results and their changes over time, meteorological statistics results, radioactive waste release status, and an evaluation of the data which deviated of the normal range.
Yomogida, Takumi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Yamada, Shinya*; Tatsuno, Hideyuki*; Noda, Hirofumi*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Takatori, Sayuri*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
Analyst, 149(10), p.2932 - 2941, 2024/03
In this study, we successfully applied a transition-edge sensor (TES) spectrometer as a detector for microbeam X-ray measurements from a synchrotron X-ray light source to determine uranium (U) distribution at the micro-scale and its chemical species in biotite obtained from the U mine. It is difficult to separate the fluorescent X-ray of the U L
 line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K
line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
 and Rb K
and Rb K were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
Harii, Kazuya*; Umeda, Maki; Arisawa, Hiroki*; Hioki, Tomosato*; Sato, Nana; Okayasu, Satoru; Ieda, Junichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(7), p.073701_1 - 073701_4, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sasaki, Michiya*; Furukawa, Kyoji*; Satoh, Daiki; Shimada, Kazumasa; Kudo, Shinichi*; Takagi, Shunji*; Takahara, Shogo; Kai, Michiaki*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 48(2), p.90 - 99, 2023/06
This paper reports on the calculation code that is the result of the activities of the "Task Group for Development of Cancer Risk Estimation Codes Associated with Radiation Exposure (FY2020-2021)" established by the Japan Health Physics Society. In order to promote research on the estimation of cancer risk associated with radiation exposure, the Task Group decided to disclose the source code, including the algorithm and parameters used in the calculations, and to release the code under a license that permits modification and redistribution of the code. The computational code was named SUMRAY and coded in two computer languages, that is R and Python. The code is capable of calculating the accumulated excess risk using Monte Carlo methods with a 95% confidence interval. The results of SUMRAY were compared with the results of the existing codes whose source code is not publicly available, under the same calculation conditions. From the results, it was found that they were in reasonable agreement within the confidence interval. It is expected that SUMRAY, an open-source software, will be used as a common basis for cancer risk estimation studies associated with radiation exposure.
Umeda, Maki; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Imai, Masaki; Sato, Nana; Saito, Eiji
Review of Scientific Instruments, 94(6), p.063906_1 - 063906_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nomoto, Yasunobu; Mizuta, Naoki; Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Okita, Shoichiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Tanaka, Masato; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
Mizuta, Naoki; Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Okita, Shoichiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Tanaka, Masato; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Noguchi, Hiroki; et al.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/05
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Futagawa, Kazuo; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-078, 164 Pages, 2023/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2021 to March 2022. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sato, Rina; Nakayama, Mariko*; Tsubokura, Masaharu*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 64(2), p.203 - 209, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.01(Biology)After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident, individual exposure doses to residents have been assessed by many municipalities, governments and research institutes. Various methods including measurements with personal dosimeters and simulations have been used for this evaluation depending on purposes, but the information of assessments and methods has not been systematically organized. A comprehensive review of the knowledge and experiences of individual exposure doses assessments accumulated so far and understanding the characteristics of the assessment methods will be very useful for radiation protection and risk communication, following to governmental policy planning. We reviewed the efforts made by the Japanese government and research institutes to assess radiation doses to residents after the FDNPS accident in Part1. On the other hand, each method of assessing individual exposure doses includes uncertainties and points to be considered for the appropriate assessment. These knowledge and experiences are important for the assessment implementation and applying the assessment results to the governmental policy planning, and are summarized in Part2 of this article.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.37(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Sato, Rina; Sanada, Yukihisa; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Nakayama, Mariko*
JAEA-Review 2022-055, 42 Pages, 2023/01
The evacuation order zones established after the accident at the Tokyo Electric Power Company's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station have been reorganized according to the decrease in ambient dose equivalent rates and the decontamination progress. It has been decided to decontaminate the difficult-to-return zones and lift the evacuation order depending on the evacuee's intention of returning to the areas over the course of the 2020s. In order to consider the future of individual exposure dose assessment for residents for lifting of the evacuation orders, the methods and characteristics of the assessment that have been conducted after the accident using personal dosimeter measurements and simulations were systematically reviewed. This report summarized the results of the review.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sato, Rina; Nakayama, Mariko*; Tsubokura, Masaharu*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 64(1), p.2 - 10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Biology)The evacuation orderareas established due to the accident at the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' (TEPCO) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) have been reorganized according to the decrease in ambient dose rates and the decontamination progress. The Japanese government decided to decontaminate the difficult-to-return areas and lift the evacuation order by 2030. This radiation protection strategy can be optimized by examining emergency exposure situations to date and the existing exposure after the accident. This article reviews the methods that can determine the individual radiation doses of residents who should return to their homes when the evacuation order is lifted in the specific reconstruction reproduction base area and the difficult-to-return areas outside this base area and summarizes the points to be considered when implementing these methods. In Part 1 of this article, we review the efforts made by the Japanese government and research institutes to assess radiation doses to residents after the FDNPP accident.
Shibata, Taiju; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Kubo, Shinji; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 398, p.111964_1 - 111964_4, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been promoting the research and development (R&D) of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). R&D on reactor technologies is carried out by using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). The HTTR was resumed without significant reinforcements in 2021. On January 2022, a safety demonstration test under the OECD/NEA LOFC project was carried out. JAEA is promoting R&D on a carbon-free hydrogen production by thermochemical water splitting Iodine-Sulfur process (IS process). JAEA conducts design study for various HTGR systems toward commercialization. A new test program about demonstration of hydrogen production by the HTTR was launched. Steam methane reforming hydrogen production system was selected for the first demonstration by 2030.
Entani, Shiro*; Sato, Shinichiro*; Honda, Mitsunori; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Oshima, Takeshi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110369_1 - 110369_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:29.26(Chemistry, Physical)Ni silicide synthesis by Ni ion beam irradiation into Si attracts attention due to its advantages including the ability of formation of local structures, the controllability of ion beams, the formability of silicide without heat treatment and the high reproducibility of the resulting specimen. In this work, we investigate the local atomic structure of Si implanted with 3.0 MeV Ni ions. Analysis of Ni K-edge fluorescent-yield extended X-ray absorption fine structure reveals that Ni atoms have mixed structure of metallic-like face-centered cubic Ni and NiSi
ions. Analysis of Ni K-edge fluorescent-yield extended X-ray absorption fine structure reveals that Ni atoms have mixed structure of metallic-like face-centered cubic Ni and NiSi phases at the initial stage of the irradiation and the formation of NiSi
phases at the initial stage of the irradiation and the formation of NiSi promotes significantly with the ion fluence above 10
promotes significantly with the ion fluence above 10  ions cm
ions cm . With consideration of the agreement between the ion fluence threshold for the structural transition and the critical Si-amorphization fluence, it is concluded that the amorphization of Si plays an important role in the synthesis of the NiSi
. With consideration of the agreement between the ion fluence threshold for the structural transition and the critical Si-amorphization fluence, it is concluded that the amorphization of Si plays an important role in the synthesis of the NiSi phase in Ni
phase in Ni -irradiated Si.
-irradiated Si.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
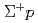 elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/c
elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/cNanamura, Takuya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Naruki, Megumi; Sato, Susumu; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(9), p.093D01_1 - 093D01_35, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:71.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sr analysis of environmental samples by ion-laser interaction mass spectrometry
Sr analysis of environmental samples by ion-laser interaction mass spectrometryHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Marchhart, O.*; Priller, A.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakaguchi, Aya*
Analytical Methods, 14(28), p.2732 - 2738, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.32(Chemistry, Analytical)The sensitive  Sr analysis with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was developed for the advances of environmental radiology. One advantage of AMS is the ability to analyze various environmental samples with
Sr analysis with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was developed for the advances of environmental radiology. One advantage of AMS is the ability to analyze various environmental samples with  Sr/
Sr/ Sr atomic ratios of 10
Sr atomic ratios of 10 in a simple chemical separation. Three different IAEA samples with known
in a simple chemical separation. Three different IAEA samples with known  Sr concentrations (moss-soil, animal bone, Syrian soil: 1 g each) were analyzed to assess the validity of the chemical separation and the AMS measurement. The
Sr concentrations (moss-soil, animal bone, Syrian soil: 1 g each) were analyzed to assess the validity of the chemical separation and the AMS measurement. The  Sr measurements were conducted on the AMS system combined with the Ion Laser InterAction MasSpectrometry (ILIAMS) setup at the University of Vienna, which has excellent isobaric separation performance. The isobaric interference of
Sr measurements were conducted on the AMS system combined with the Ion Laser InterAction MasSpectrometry (ILIAMS) setup at the University of Vienna, which has excellent isobaric separation performance. The isobaric interference of  Zr in the
Zr in the  Sr AMS was first removed by chemical separation. The separation factor of Zr in two-step column chromatography with Sr resin and anion exchange resin was 10
Sr AMS was first removed by chemical separation. The separation factor of Zr in two-step column chromatography with Sr resin and anion exchange resin was 10 . The
. The  Zr remaining in the sample was removed by ILIAMS effectively. This simple chemical separation achieved a limit of detection
Zr remaining in the sample was removed by ILIAMS effectively. This simple chemical separation achieved a limit of detection  0.1 mBq in the
0.1 mBq in the  Sr AMS, which is lower than typical
Sr AMS, which is lower than typical  -ray detection. The agreement between AMS measurements and nominal values for the
-ray detection. The agreement between AMS measurements and nominal values for the  Sr concentrations of IAEA samples indicated that the new highly-sensitive
Sr concentrations of IAEA samples indicated that the new highly-sensitive  Sr analysis in the environmental samples with AMS is reliable even for high matrix samples of soil and bone.
Sr analysis in the environmental samples with AMS is reliable even for high matrix samples of soil and bone.
Furuta, Takuya; Koba, Yusuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Ishikawa, Akihisa*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(14), p.145002_1 - 145002_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.25(Engineering, Biomedical)Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. The Monte Carlo simulation is a good candidate for the tool to assess secondary cancer risk, including the contributions of secondary particles produced by nuclear reactions. We therefore developed a new dose reconstruction system implementing PHITS as the engine. In this system, the PHITS input is automatically created from the DICOM data sets recorded in the treatment planning. The developed system was validated by comparing to experimental dose distribution in water and treatment plan on an anthropomorphic phantom. This system will be used for retrospective studies using the patient data in National Institute for Quantum and Science and Technology.
Murase, Kiyoka*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Nishiyama, Takanori*; Nishimura, Koji*; Hashimoto, Taishi*; Tanaka, Yoshimasa*; Kadokura, Akira*; Tomikawa, Yoshihiro*; Tsutsumi, Masaki*; Ogawa, Yasunobu*; et al.
Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (Internet), 12, p.18_1 - 18_16, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.65(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We identified two energetic electron precipitation (EEP) events during the growth phase of moderate substorms and estimated the mesospheric ionization rate for an EEP event for which the most comprehensive dataset from ground-based and space-born instruments was available. The mesospheric ionization signature reached below 70 km altitude and continued for ~15 min until the substorm onset, as observed by the PANSY radar and imaging riometer at Syowa Station in the Antarctic region. We also used energetic electron flux observed by the Arase and POES 15 satellites as the input for the air-shower simulation code PHITS to quantitatively estimate the mesospheric ionization rate. Combining the cutting-edge observations and simulations, we shed new light on the space weather impact of the EEP events during geomagnetically quiet times, which is important to understand the possible link between the space environment and climate.
 -iron
-ironHirayama, Shintaro*; Sato, Koichi*; Kato, Daiji*; Iwakiri, Hirotomo*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Watanabe, Yoshiyuki*; Nozawa, Takashi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101179_1 - 101179_9, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:66.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English