Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd using cadmium chloride
using cadmium chlorideHayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.503 - 510, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)The formation of MPd (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu -type GdPd
-type GdPd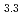 (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) and NpPd
0.0001 nm) and NpPd (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi
0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi -type NpPd
-type NpPd . Chlorination of the MPd
. Chlorination of the MPd (M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl
(M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl formation.
formation.
 He cryostat and a closed-cycle
He cryostat and a closed-cycle  He gas handling system installed in a SQUID magnetometer without continuous-cooling functionality
He gas handling system installed in a SQUID magnetometer without continuous-cooling functionalityShimamura, Kazutoshi*; Wajima, Hiroki*; Makino, Hayato*; Abe, Satoshi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Sato, Yoshiaki*; Kawae, Tatsuya*; Yoshida, Yasuo*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 61(5), p.056502_1 - 056502_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.38(Physics, Applied) -iron investigated using in situ high-voltage electron microscopy
-iron investigated using in situ high-voltage electron microscopyAbe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
Philosophical Magazine, 102(12), p.1173 - 1193, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We measured the growth rate of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters in electron-irradiated  -iron at 275-320 K using in situ high-voltage electron microscopy. To improve the statistical accuracy of the measurement, we used photographic films and video data. This enabled analysis of a considerable amount of data by extracting several SIA clusters and tracking their size growth using image processing techniques. By fitting the temperature-dependent cluster growth rate to the Arrhenius relations derived using rate theory analysis, we obtained vacancy migration energy of
-iron at 275-320 K using in situ high-voltage electron microscopy. To improve the statistical accuracy of the measurement, we used photographic films and video data. This enabled analysis of a considerable amount of data by extracting several SIA clusters and tracking their size growth using image processing techniques. By fitting the temperature-dependent cluster growth rate to the Arrhenius relations derived using rate theory analysis, we obtained vacancy migration energy of 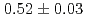 eV. In addition, the effects of impurities leading to decrease in the cluster growth rate were briefly discussed.
eV. In addition, the effects of impurities leading to decrease in the cluster growth rate were briefly discussed.
Sato, Yuki*; Abe, Yosuke; Okubo, Kenji*; Tanioka, Takashi*
Philosophical Magazine, 102(12), p.1152 - 1172, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using in situ observation with high-voltage electron microscope, one-dimensional (1D) migration of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters under electron irradiation at 300 K was surveyed for copper materials of five nominal purities and TEM specimens prepared with three methods. In standard (STD) specimens that were prepared through cold rolling and annealing in the vacuum, formation and 1D migration of SIA clusters did not depend much on the nominal purity. In non-annealed (NA) specimens, prepared from high purity materials through mechanical processing and electropolishing, defect structure was coarser than in STD specimens. Results of bulk annealing (BA) specimens showed that annealing of as-received block material had minor effects. Above results were discussed based on the hypothesis that impurity atoms existing in as-received materials and those induced by annealing act as traps for SIA clusters.
 -iron estimated by in situ observation of interstitial clusters at low temperatures using high-voltage electron microscopy
-iron estimated by in situ observation of interstitial clusters at low temperatures using high-voltage electron microscopyAbe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
Philosophical Magazine, 101(14), p.1619 - 1631, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Modeling cluster dynamics or rate theory to describe the microstructural evolution of irradiated materials requires a precise knowledge of the migration energy of a self-interstitial atom (SIA), a product of energetic particle radiation. We measured the evolution of the number density of SIA clusters in electron-irradiated  -iron at low temperatures (110-320 K) by in situ observation using high-voltage electron microscopy. We identified temperature-dependent physical quantities, including (1) the peak density of SIA clusters and (2) the critical defect-free zone thickness in a thin foil specimen, associated with interstitial mobility. By fitting these quantities to the Arrhenius relations derived by rate theory analysis, we obtained estimated interstitial migration energy values of
-iron at low temperatures (110-320 K) by in situ observation using high-voltage electron microscopy. We identified temperature-dependent physical quantities, including (1) the peak density of SIA clusters and (2) the critical defect-free zone thickness in a thin foil specimen, associated with interstitial mobility. By fitting these quantities to the Arrhenius relations derived by rate theory analysis, we obtained estimated interstitial migration energy values of 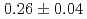 and
and 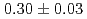 eV for (1) and (2), respectively.
eV for (1) and (2), respectively.
 -iron
-ironAbe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Onuki, Somei*
Philosophical Magazine, 100(1), p.110 - 125, 2020/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We derive analytical models associated with the experimentally revealed one-dimensional (1D) migration mechanisms to examine the decreasing behavior of the cluster number density. The model calculation indicates that the detrapping of the stationary SIA clusters causes the surface annihilation of the liberated SIA clusters, leading to the decrease in their number density. The decreasing behavior is in closer accordance with the experimental data when setting the impurity concentration in the same order as the estimation from the previous in situ HVEM experiment. This result suggests that the trapping and detrapping of the SIA clusters are the possible underlying processes for the decreasing behavior.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
NEA/NSC/R(2017)3, p.427 - 432, 2017/11
Transmutation of long-lived radioactive nuclides including minor actinides (MA: Np, Am, Cm) has been studied in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Pb-Bi cooled sub-critical accelerator-driven system (ADS) is regarded as one of the powerful tools for transmutation of MA under the double strata fuel cycle concept. Uranium-free MA-Pu nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate for MA transmutation. Reprocessing of spent ADS fuel and reusing MA recovered from the spent ADS fuels is necessary to improve the transmutation ratio. A pyrochemical process has been proposed as the first candidate for reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel for MA transmutation, because this technique has some advantages over aqueous process, such as the resistance to radiation damage, which is an important issue for the fuels containing large amounts of highly radioactive MA, and feasibility for recovering expensive N-15 in the spent fuels to be reused. This paper overviews the current status of the technology development, including our recent study. Development of the anode suitable for electro-refining of nitride fuels and that of the apparatus for renitridation of the metals recovered in Cd cathode for 100g-Cd scale cold tests are main topics. Evaluation of the batch sizes of each process, which is necessary for estimating the scale of the engineering-apparatus, with considering the decay heat of MA and FP, will also be introduced.
Sato, Yuki*; Abe, Yosuke; Abe, Hiroaki*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Kano, Sho*; Onuki, Somei*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
Philosophical Magazine, 96(21), p.2219 - 2242, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:51.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed in situ observation of one-dimensional (1D) migration of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters in iron under electron irradiation at 110-300 K using high-voltage electron microscopy. Most 1D migration was stepwise positional changes of SIA clusters at irregular time intervals at all temperatures. The frequency of 1D migration did not depend on the irradiation temperature. It was directly proportional to the damage rate, suggesting that 1D migration was induced by electron irradiation. In contrast, the 1D migration distance depended on the temperature: distribution of the distance ranged over 100 nm above 250 K, decreased steeply between 250 and 150 K and was less than 20 nm below 150 K. The distance was independent of the damage rate at all temperatures. Next, we examined fluctuation in the interaction energy between an SIA cluster and vacancies of random distribution at concentrations 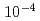 -
-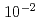 , using molecular statics simulations. The fluctuation was found to trap SIA clusters of 4 nm diameter at vacancy concentrations higher than
, using molecular statics simulations. The fluctuation was found to trap SIA clusters of 4 nm diameter at vacancy concentrations higher than 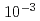 . We proposed that 1D migration was interrupted by impurity atoms at temperatures higher than 250 K, and by vacancies accumulated at high concentration under electron irradiation at low temperatures where vacancies are not thermally mobile.
. We proposed that 1D migration was interrupted by impurity atoms at temperatures higher than 250 K, and by vacancies accumulated at high concentration under electron irradiation at low temperatures where vacancies are not thermally mobile.
 and (U,Zr)O
and (U,Zr)O solid solution using MoCl
solid solution using MoCl
Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Takano, Masahide; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1253 - 1258, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to explore the applicability of the chlorination by MoCl as a potential pretreatment technique for waste treatment of fuel debris by pyrochemical methods, chlorination experiments of UO
as a potential pretreatment technique for waste treatment of fuel debris by pyrochemical methods, chlorination experiments of UO and (U
and (U Zr
Zr )O
)O simulated fuel debris were carried out in two steps: the first one is a chlorination reaction by homogeneous heating, the second one is a volatilization of molybdenum by-product by heating under temperature gradient condition. Most of UO
simulated fuel debris were carried out in two steps: the first one is a chlorination reaction by homogeneous heating, the second one is a volatilization of molybdenum by-product by heating under temperature gradient condition. Most of UO and (U
and (U Zr
Zr )O
)O powder were converted to UCl
powder were converted to UCl or UCl
or UCl and ZrCl
and ZrCl mixture at 573 K, respectively. In the case of (U
mixture at 573 K, respectively. In the case of (U Zr
Zr )O
)O sintered particle, most of sample was converted to the chlorides because the products evaporated and be separated from sample surface at 773 K, while only the surface of the sample disk was converted to the chlorides at 573 and 673 K. Most of molybdenum by-product and ZrCl
sintered particle, most of sample was converted to the chlorides because the products evaporated and be separated from sample surface at 773 K, while only the surface of the sample disk was converted to the chlorides at 573 and 673 K. Most of molybdenum by-product and ZrCl were separated from UCl
were separated from UCl by volatilization at 573 K.
by volatilization at 573 K.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki
NEA/NSC/R(2015)2 (Internet), p.360 - 367, 2015/06
Uranium-free nitride fuel was chosen as the first candidate for transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven system (ADS) under the double strata fuel cycle concept by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The advantages of nitride fuel are good thermal properties and large mutual solubility among actinide elements. A pyrochemical process is proposed as the first candidate for the reprocessing of the spent nitride fuel, because this technique has some advantages over aqueous process, such as the resistance to radiation damage, which is an important issue for the fuels containing large amounts of highly radioactive MA. This paper overviews the recent progress and future R&D plan of the study on the nitride fuel cycle technology in JAEA.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
Science China; Chemistry, 57(11), p.1427 - 1431, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:5.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nitride fuels have several advantages, such as high thermal conductivity and high metal density like metallic fuels, and high melting point and isotropic crystal structure like oxide fuels. Since the late 1990s, the partitioning and transmutation of minor actinides (MA) has been studied to decrease the long term radio-toxicity of high level waste and mitigate the burden on the final disposal. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been proposing dedicated transmutation cycle using the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) with the nitride fuels containing MA. We have been developing the nitride fuel cycle including pyrochemical process. Our focus is on electrolysis of nitride fuels and refabrication of nitride fuel from the recovered actinides because other processes are similar to the technology for the metal fuel treatment and have been studied elsewhere. In this paper, we summarized our activity on developments of the pyrochemical treatment of the spent nitride fuels.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Iwai, Takashi; Nishihara, Kenji; Arai, Yasuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/12
R&D on the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) by the accelerator-driven system (ADS) using nitride fuels is underway at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In regard to reprocessing technology, pyrochemical process has several advantages in case of treating spent fuel with large decay heat and fast neutron emission, and recovering highly enriched N-15. In the pyrochemical reprocessing, plutonium (Pu) and MA are dissolved in LiCl-KCl eutectic melts and selectively recovered into liquid cadmium (Cd) cathode by molten salt electrorefining. The recovered Pu and MA are converted to nitrides by the nitridation-distillation combined method, in which the Cd alloys containing Pu and MA are heated in nitrogen gas stream. The authors have investigated its elemental technologies such as electrorefining and renitridation. On the other hand, development of the process flow diagram with the material balance sheet of the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nitride fuel for ADS is in progress. This paper summarized recent progress of the study which aims to prove the technological applicability of pyrochemical process to the nitride fuel cycle for transmutation of MA.
Shibuta, Yasushi*; Unoura, Seiji*; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki*; Suzuki, Toshio*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 414(2), p.114 - 119, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The uranium dendrite growth on cathode during pyroprocessing of uranium is investigated using a novel phase-field model, in which electrodeposition of uranium and zirconium from molten-salt is taken into account. The threshold concentration of zirconium in molten salt demarcating the dendritic and planar growth is then estimated as a function of the current density. Moreover, growth process of both the dendritic and planar electrodeposits has been demonstrated by way of varying the mobility of the phase field, which consists of the effect of attachment kinetics and diffusion.
Arai, Yasuo; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Iwai, Takashi; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Takumi; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Iwai, Takashi; Akabori, Mitsuo; Arai, Yasuo; Minato, Kazuo
no journal, ,
Recent progress of research on pyrochemical process for nitride fuel cycle in JAEA is summarized. The electrochemical behaviors in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt of burnup-simulated UN containing representative solid fission product elements (Mo, Pd, Nd) and actinide nitrides containing inert matrix materials such as (U,Zr)N, (Pu,Zr)N, UN+TiN and PuN+TiN were clarified for the first time. The behavior of Am on the electrolysis of AmN in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt and that on nitride formation of Am recovered in the liquid Cd cathode were investigated.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Iwai, Takashi; Nishihara, Kenji; Arai, Yasuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Takumi; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Kurata, Masaki; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -iron
-ironAbe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Tsuru, Tomohito; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Onuki, Somei*
no journal, ,
One-dimensional (1D) migration behavior of self-interstitial atom (SIA) loops was studied for specimens of  -iron with different purities under electron irradiation using the HVEM at Hokkaido University. As increasing temperature, saturated loop number densities decreased and 1D jump distances became longer, indicating that the total concentration of trapping sites for SIA loops decreases at higher temperatures. According to the developed rate theory model, it was shown that the dependence of the irradiation intensity on the loop number density tends to be weaker with lowering the impurity concentration at room temperature.
-iron with different purities under electron irradiation using the HVEM at Hokkaido University. As increasing temperature, saturated loop number densities decreased and 1D jump distances became longer, indicating that the total concentration of trapping sites for SIA loops decreases at higher temperatures. According to the developed rate theory model, it was shown that the dependence of the irradiation intensity on the loop number density tends to be weaker with lowering the impurity concentration at room temperature.
Kishita, Shiori*; Abe, Hiroaki*; Abe Tomonori*; Kunii, Daichi*; Udagawa, Yutaka; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Sato, Yuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English