Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
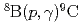 reaction rate through direct nuclear reaction theories
reaction rate through direct nuclear reaction theoriesFukui, Tokuro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Minomo, Kosho*; Yahiro, Masanobu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 14, p.020513_1 - 020513_3, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Astronomy & Astrophysics)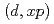 reactions on nuclei from
reactions on nuclei from  Be to
Be to  U at 100 MeV
U at 100 MeVYe, T.*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yahiro, Masanobu*
Physical Review C, 84(5), p.054606_1 - 054606_8, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:77.11(Physics, Nuclear)Inclusive proton emission from deuteron-induced reactions on various nuclear targets at an incident energy of 100 MeV are analyzed using the CDCC theory for elastic breakup process and the Glauber model for neutron stripping process. Moreover, the phenomenological moving source model is used to estimate evaporation and pre-equilibrium components in inclusive 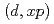 spectra. The calculation reproduces fairly well a prominent bump in experimental
spectra. The calculation reproduces fairly well a prominent bump in experimental 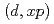 spectra for light and medium nuclei at forward angles of less than 20
spectra for light and medium nuclei at forward angles of less than 20 , whereas the calculation underestimates the bump component as target atomic number increases. The underestimation is likely to be attributed to the fact that the eikonal approximation used in the Glauber model becomes worse due to strong Coulomb interaction. It is shown that the Glauber model calculation for neutron stripping process leads to improvement of this discrepancy by substituting the eikonal phase shift for the quantum phase shift.
, whereas the calculation underestimates the bump component as target atomic number increases. The underestimation is likely to be attributed to the fact that the eikonal approximation used in the Glauber model becomes worse due to strong Coulomb interaction. It is shown that the Glauber model calculation for neutron stripping process leads to improvement of this discrepancy by substituting the eikonal phase shift for the quantum phase shift.
Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Matsumoto, Takuma*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Minomo, Kosho*; Egami, Tomoaki*; Iseri, Yasunori*; Kono, Michio*; Chiba, Satoshi; Bertulani, C. A.*; Shimizu, Yoshifumi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 312, p.082008_1 - 082008_10, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:47.57(Physics, Nuclear)Recent studies on breakup reactions with the continuum-discretized coupled channels method are reviewed. The topics covered are: four-body breakup processes for  He induced reaction, dynamical relativistic effects on coulomb breakup, microscopic description of projectile breakup processes, description of ternary processes (new triple-
He induced reaction, dynamical relativistic effects on coulomb breakup, microscopic description of projectile breakup processes, description of ternary processes (new triple- reaction rate) and new approach to inclusive breakup processes.
reaction rate) and new approach to inclusive breakup processes.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Yahiro, Masanobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Minomo, Kosho*; Chiba, Satoshi
Physical Review C, 83(5), p.054617_1 - 054617_11, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.81(Physics, Nuclear)The continuum-discretized coupled-channels method (CDCC) for exclusive reactions and the eikonal reaction theory (ERT) as an extension of CDCC to inclusive reactions are applied to deuteron induced reactions. The CDCC result reproduces experimental data on the reaction cross section for 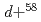 Ni scattering at 200 MeV/nucleon and ERT does data on the neutron-stripping cross section for inclusive
Ni scattering at 200 MeV/nucleon and ERT does data on the neutron-stripping cross section for inclusive  Li
Li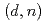 reaction at 40 MeV. For deuteron induced reactions at 200 MeV/nucleon, target-dependence of the reaction, elastic-breakup, nucleon-stripping, nucleon-removal, complete- and incomplete-fusion cross sections is clearly explained by simple formulae. Accuracy of the Glauber model is also investigated.
reaction at 40 MeV. For deuteron induced reactions at 200 MeV/nucleon, target-dependence of the reaction, elastic-breakup, nucleon-stripping, nucleon-removal, complete- and incomplete-fusion cross sections is clearly explained by simple formulae. Accuracy of the Glauber model is also investigated.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
Progress of Theoretical Physics, 122(5), p.1291 - 1300, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:77.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose a new method for evaluating incomplete and complete fusion cross sections separately using the Continuum-Discretized Coupled-Channels method. This method is applied to analysis of the deuteron induced reaction on a  Li target up to 50 MeV of the deuteron incident energy. Effects of deuteron breakup on this reaction are explicitly taken into account. Results of the method are compared with those of the Glauber model, and the difference between the two is discussed. It is found that the energy dependence of the incomplete fusion cross sections obtained by the present calculation is almost the same as that obtained by the Glauber model, while for the complete fusion cross section, the two models give markedly different energy dependence.
Li target up to 50 MeV of the deuteron incident energy. Effects of deuteron breakup on this reaction are explicitly taken into account. Results of the method are compared with those of the Glauber model, and the difference between the two is discussed. It is found that the energy dependence of the incomplete fusion cross sections obtained by the present calculation is almost the same as that obtained by the Glauber model, while for the complete fusion cross section, the two models give markedly different energy dependence.
 He +
He +  C scattering
C scatteringMatsumoto, Takuma*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Iseri, Yasunori*; Kamimura, Masayasu*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
Physical Review C, 70(6), p.061601_1 - 061601_5, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:154 Percentile:98.31(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
The incomplete or complete fusion reaction, in which a part or the whole of a projectile, respectively, is absorbed by a target, proceeds through a compound process. There is a long history of the study of the compound reaction. However, the incomplete fusion process is not sufficiently well understood. Recently, the study of neutron-rich nuclei has been studied, and the understanding of the incomplete fusion process in the reaction involving unstable nuclei is required. Since breakup of a weakly bound nucleus, such as deuteron, takes place easily in the reaction, the model taking into account the breakup process is required for the analysis. We applied the Continuum-Discretized Coupled-Channels (CDCC) method to the analysis in order to understand the reaction mechanism of incomplete fusion. In the present paper, we show results of each fusion cross section in the deuteron induced reaction on  Li target, and discuss the importance of the incomplete fusion process.
Li target, and discuss the importance of the incomplete fusion process.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
The incomplete fusion reaction, in which a part of a projectile is absorbed by a target, proceeds through a compound process. There is a long history of the study of the fusion reaction. However, the incomplete fusion process is not sufficiently well understood. The process contributes significantly in the reaction involving weakly bound nuclei, and the understanding of the reaction mechanism is required. Since a weakly bound nucleus, such as deuteron, breaks up easily in the reaction, the model taking into account the breakup process is required for the analysis. We extended the Continuum-Discretized Coupled-Channels (CDCC) method, and applied to the analysis of incomplete fusion reaction. In the present paper, we show calculated results of incomplete fusion cross section in the deuteron induced reaction on  Li target, and discuss the importance of the process.
Li target, and discuss the importance of the process.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
Deuteron induced reactions on Li targets are candidate reactions for the neutron source in the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) program. However, the theoretical model calculation of the 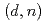 reaction cross sections underestimates the experimental data. The incomplete fusion process, in which a part of a projectile is absorbed by a target, may contribute significantly in the reaction, and the understanding of the reaction mechanism is required. Since a weakly bound nucleus, such as deuteron, breaks up easily in the reaction, the model taking into account the breakup process is required for the analysis. We extended the Continuum-Discretized Coupled-Channels (CDCC) method, and applied to the analysis of incomplete fusion reaction. In the present paper, we show results of incomplete fusion cross section in the deuteron induced reaction on
reaction cross sections underestimates the experimental data. The incomplete fusion process, in which a part of a projectile is absorbed by a target, may contribute significantly in the reaction, and the understanding of the reaction mechanism is required. Since a weakly bound nucleus, such as deuteron, breaks up easily in the reaction, the model taking into account the breakup process is required for the analysis. We extended the Continuum-Discretized Coupled-Channels (CDCC) method, and applied to the analysis of incomplete fusion reaction. In the present paper, we show results of incomplete fusion cross section in the deuteron induced reaction on  Li target, and discuss the importance of the process.
Li target, and discuss the importance of the process.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
The breakup effect on the fusion reaction is an interesting subject, and the understanding of the mechanism plays an important role in studying weakly-bound nuclei. The breakup process leads to two fusion reactions: complete fusion and incomplete fusion. The incomplete fusion process with emitting a neutron in deuteron induced reactions attracts nuclear engineers, because nuclear data of (d, n) on various targets are required for studies on nuclear applications. We propose a new approach for evaluating incomplete and complete fusion cross sections using CDCC. We apply this method to deuteron induced reactions at energies above the Coulomb barrier. Results of the method are compared with those of the Glauber model, which reproduces experimental data of  Li(d, n) at 40 MeV added by the elastic breakup cross section obtained by CDCC. We discuss the difference between the two models, and confirm the validity of approximations used in the Glauber model.
Li(d, n) at 40 MeV added by the elastic breakup cross section obtained by CDCC. We discuss the difference between the two models, and confirm the validity of approximations used in the Glauber model.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 and
and 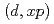 reactions for energies up to 100 MeV
reactions for energies up to 100 MeVYe, T.*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Ye, T.*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukui, Tokuro; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; Kikuchi, Yuma*; Matsumoto, Takuma*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Suhara, Tadahiro*; Taniguchi, Yasutaka*; Yahiro, Masanobu*
no journal, ,