Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O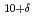 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopyIdeta, Shinichiro*; Johnston, S.*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Mori, Michiyasu; Anzai, Hiroaki*; Ino, Akihiro*; Arita, Masashi*; Namatame, Hirofumi*; Taniguchi, Masaki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.217004_1 - 217004_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sakai, Takuro; Iikura, Hiroshi; Yamada, Naoto*; Sato, Takahiro*; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Uchida, Masaya*
QST-M-8; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2016, P. 140, 2018/03
Iijima, Shizuka; Uchida, Naoki; Taguchi, Katsuya; Washiya, Tadahiro
JAEA-Review 2015-018, 39 Pages, 2015/11
There is a possibility that the fuel assemblies stored in the spent fuel pool (SFP) at Fukushima Daiichi NPS (or Nuclear Power Station) are not only exposed to seawater and concrete fragments, but also damaged by fallen rubbles. We checked the reprocessing experiences of leak fuels at Tokai Reprocessing Plant and overseas reprocessing facilities, and the storage conditions and the checked and inspected results of the fuel stored in the SFP at Fukushima Daiichi NPS, after that, we listed up the technological problems with reprocessing damaged nuclear fuels and selected elements of the research for the purpose of drawing indicators to make a judgmental decision of the possibility of damaged nuclear fuels reprocessing. And we drew the indicators to make a judgmental decision on the possibility of reprocessing based on the results of the examination and the study about elements of the research.
Abe, Hiroshi; Shimomura, Takuya; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Shimada, Yukihiro*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Yuta*; Nishimura, Akihiko; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
A short pulse laser (the nanosecond and femtosecond) was applied to hydrogen absorbing alloys surface layer, and a surface modification experiment was put into effective to aim at improvement of hydrogen adsorption functionally. It was investigated about correlation between an initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of hydrogen alloys and a laser irradiation in this research. The laser irradiation condition was done with pulse width 100 fsec and energy 0.2 - 3.4 mJ/pulse. It blazed down on hydrogen absorbing alloys (LaNi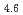 Al
Al ) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
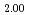
Kato, Masato; Uchida, Teppei; Matsumoto, Taku; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 451(1-3), p.78 - 81, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Linear thermal expansion of PuO was measured by dilatometry in an oxygen partial pressure-controlled atmosphere. The measured data of PuO
was measured by dilatometry in an oxygen partial pressure-controlled atmosphere. The measured data of PuO slightly increased with deviation
slightly increased with deviation  . The linear thermal expansion of PuO
. The linear thermal expansion of PuO was determined as a function of temperature and O/M ratio, and the equation for the thermal expansion coefficient was derived. Heat capacity of PuO
was determined as a function of temperature and O/M ratio, and the equation for the thermal expansion coefficient was derived. Heat capacity of PuO was evaluated using this equation. The effect of O/M ratio on heat capacity was small. In addition to the vibration and dilatational terms, it is important to analyze the Schottky term in evaluating heat capacity of PuO
was evaluated using this equation. The effect of O/M ratio on heat capacity was small. In addition to the vibration and dilatational terms, it is important to analyze the Schottky term in evaluating heat capacity of PuO .
.
Kikuchi, Kenji*; Okada, Noriyuki*; Kato, Mikio*; Uchida, Hiroshi*; Saito, Shigeru
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 450(1-3), p.237 - 243, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Three-dimensional atom probe techniques were applied to the investigation on the oxide scale in 12Cr ferritic-martensitic steel, HCM12A. A duplex oxide scale was formed in lead bismuth eutectic at 450-500 C, during 5500 h. Samples were located 500-700 nm away from the boundary between magnetite and Fe-Cr spinel layers, while the total oxide layer thickness is 18
C, during 5500 h. Samples were located 500-700 nm away from the boundary between magnetite and Fe-Cr spinel layers, while the total oxide layer thickness is 18  m. It detected super enrichment of Cr with a size of ten nm roughly, as well as depletion of Fe and enrichment of O at the same site. Surrounding the Cr super enrichment area, enrichment of Si was newly noticed due to the scanned profile of detected atom counts. It is also confirmed that Pb and Bi concentration in the observed spinel region is almost null or less than 0.01 atomic percent, which is possible detecting lowest limit.
m. It detected super enrichment of Cr with a size of ten nm roughly, as well as depletion of Fe and enrichment of O at the same site. Surrounding the Cr super enrichment area, enrichment of Si was newly noticed due to the scanned profile of detected atom counts. It is also confirmed that Pb and Bi concentration in the observed spinel region is almost null or less than 0.01 atomic percent, which is possible detecting lowest limit.
 -MOX system
-MOX systemUchida, Teppei; Hirooka, Shun; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Sato, Daisuke*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference; Nuclear Energy at a Crossroads (GLOBAL 2013) (CD-ROM), p.1549 - 1553, 2013/09
Abe, Hiroshi; Orimo, Satoshi; Kishimoto, Masahiko*; Aone, Shigeo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 307, p.218 - 220, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)We investigated the structure changes of a hydrogen storage alloy by ion irradiations, and its absorption property in order to obtain basic data and to elucidate relevant mechanisms of hydrogen absorption by the influence of the irradiation. In previous studies, the induction of vacancies in a hydrogen absorption alloy was found to be effective to increase in the hydrogen absorption rate. As well known, the rate of hydrogen absorption strongly depends upon the surface state of a hydrogen storage alloy because the dissociation of hydrogen molecules or water molecules needs electron change with the surface in the H gas or electrochemical reaction process. In this study, ion irradiations were made at a room temperature using the laser driven proton beam method, at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The beam treatment has several unique properties such as short pulse duration, high peak current, low transverse emittance, and wide energy range from KeV to MeV. The irradiation was used to modify the alloy surface using this equipment. From obtained results, the initial hydrogen absorption rate was found improved by the laser driven proton beam rather more effectively than a mono-energetic proton beam. Discussion is made on the correlation among proton irradiation (laser driven proton or mono-energetic proton) and the initial hydrogen absorption rate of the alloy. We argue about the usefulness of an energy spread beam.
gas or electrochemical reaction process. In this study, ion irradiations were made at a room temperature using the laser driven proton beam method, at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The beam treatment has several unique properties such as short pulse duration, high peak current, low transverse emittance, and wide energy range from KeV to MeV. The irradiation was used to modify the alloy surface using this equipment. From obtained results, the initial hydrogen absorption rate was found improved by the laser driven proton beam rather more effectively than a mono-energetic proton beam. Discussion is made on the correlation among proton irradiation (laser driven proton or mono-energetic proton) and the initial hydrogen absorption rate of the alloy. We argue about the usefulness of an energy spread beam.
Longhurst, G. R.*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Dorn, C.*; Folkman, S. L.*; Fronk, T. H.*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Tranter, T. N.*; Rohe, R.*; Uchida, Munenori*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 176(3), p.430 - 441, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)Beryllium has important roles in nuclear facilities such as fission reactors and fusion reactors. Its neutron multiplication capability and low atomic weight make it very useful as a reflector in fission reactors. In both applications, the beryllium and the impurities in it become activated by neutrons transmutating to radionuclides, some of which are long-lived and difficult to dispose of. Also, gas production, notably helium and tritium, results in swelling, embrittlement, and cracking, which means that the beryllium must be replaced periodically, especially in fission reactors where dimensional tolerances must be maintained. It has long been known that neutron activation of inherent iron and cobalt in the beryllium results in significant  Co activity. In 2001, it was discovered that activation of naturally occurring contaminants in the beryllium creates sufficient
Co activity. In 2001, it was discovered that activation of naturally occurring contaminants in the beryllium creates sufficient  C and
C and  Nb to render the irradiated beryllium "Greater-Than-Class-C" for disposal in US radioactive waste facilities. In this paper we review the extent of the disposal issue, processes that have been investigated or considered for improving the disposability of irradiated beryllium, and approaches for recycling.
Nb to render the irradiated beryllium "Greater-Than-Class-C" for disposal in US radioactive waste facilities. In this paper we review the extent of the disposal issue, processes that have been investigated or considered for improving the disposability of irradiated beryllium, and approaches for recycling.
Mounce, A. M.*; Oh, S.*; Mukhopadhyay, S.*; Halperin, W. P.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kuhns, P. L.*; Fujita, Kazuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Uchida, Shinichi*
Nature Physics, 7(2), p.125 - 128, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.32It has been predicted that superconducting vortices should be electrically charged and that this effect is particularly enhanced for high-temperature superconductors. Hall effect and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments suggest the existence of charge accumulation in the vortex core, but the effects are small and the interpretation controversial. Here we show that the Abrikosov vortex lattice, characteristic of the mixed state of superconductors, will become unstable at a sufficiently high magnetic field if there is charge trapped on the vortex core. Our NMR measurements of the magnetic fields generated by vortices in Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O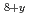 single crystals provide evidence for an electrostatically driven vortex lattice reconstruction with the magnitude of charge on each vortex pancake of
single crystals provide evidence for an electrostatically driven vortex lattice reconstruction with the magnitude of charge on each vortex pancake of 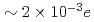 , depending on doping, in line with theoretical estimates.
, depending on doping, in line with theoretical estimates.
 Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O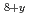
Mounce, A. M.*; Oh, S.*; Mukhopadhyay, S.*; Halperin, W. P.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kuhns, P. L.*; Fujita, Kazuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Uchida, Shinichi*
Physical Review Letters, 106(5), p.057003_1 - 057003_4, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Competition with magnetism is at the heart of high-temperature superconductivity, most intensely felt near a vortex core. To investigate vortex magnetism we have developed a spatially resolved probe based upon NMR spin-lattice-relaxation spectroscopy. With this approach we have found a spin-density wave associated with the vortex core in Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O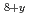 , similar to checkerboard patterns in the local density of electronic states reported from scanning tunneling microscope experiments. We have determined both the spin-modulation amplitude and decay length from the vortex core in fields up to
, similar to checkerboard patterns in the local density of electronic states reported from scanning tunneling microscope experiments. We have determined both the spin-modulation amplitude and decay length from the vortex core in fields up to  = 30 T.
= 30 T.
Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Saegusa, Jun; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Uchita, Yoshiaki; Yoshizawa, Michio
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.166 - 169, 2011/02
For the reliable dose evaluation in high intensity proton accelerator facilities such as J-PARC, high energy neutron calibration fields above 20 MeV to evaluate energy response of both the monitors and the dosimeters used there, are required. Therefore, development of three neutron calibration fields of 45, 60 and 75 MeV has been in progress at TIARA of JAEA-Takasaki. Evaluation of the neutron fluence and establishment of the monitoring technique are important for the development of the calibration fields. Here, results of the fluence evaluation in the absolute measurement by using proton recoil counter telescope with high detection efficiency, a transmission type neutron fluence monitor newly developed to monitor neutron beam directly and its performance will be reported.
Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Saegusa, Jun; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Uchida, Yoshiaki*; Yoshizawa, Michio; Harano, Hideki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 158, 2011/01
no abstracts in English
Shiine, Yasuharu*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Furuta, Yusuke*; Kanamitsu, Kaoru*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Nakao, Ryota*; Uchida, Satoshi*
Microelectronic Engineering, 87(5-8), p.835 - 838, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.49(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Uchida, Masahiro; Hama, Katsuhiro; Matsui, Hiroya; Takeuchi, Shinji; Amano, Kenji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mizuno, Takashi
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM '09/DECOM '09) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2009/10
Kondo, Yoshikazu; Uchida, Naoki; Terunuma, Hirotaka; Tanaka, Kosuke; Oyama, Koichi; Katsurai, Kiyomichi; Washiya, Tadahiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.277 - 280, 2009/09
The composition of sludge in the dissolver after dissolution of PWR and ATR fuels at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) was analyzed. As a result the presence of zirconium molybdate was confirmed by the analysis of X-ray diffraction (XRD). To clarify the formation behavior of the precipitates of zirconium molybdate, investigated the dependence of HNO concentration on the precipitation with Mo and Zr solution. To evaluate the adhesion on the metal surface (stainless steel and Ti metal), the deposition amounts of the precipitates of zirconium molybdate on the metal were also examined. In addition, it reports on the comparative result of executing a chemical dissolution of the precipitates by using the solutions of NaOH, C
concentration on the precipitation with Mo and Zr solution. To evaluate the adhesion on the metal surface (stainless steel and Ti metal), the deposition amounts of the precipitates of zirconium molybdate on the metal were also examined. In addition, it reports on the comparative result of executing a chemical dissolution of the precipitates by using the solutions of NaOH, C H
H O
O -HNO
-HNO and H
and H O
O -HNO
-HNO .
.
Takeuchi, Shinji; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-017, 29 Pages, 2009/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at the MIU project is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following 2009 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation Plan, (2) Construction Plan, (3) Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-002, 88 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2007 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site and the Shobasama Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-001, 110 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2006 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-073, 99 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2005 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.